Operation Manual – VLAN
H3C S5500-SI Series Ethernet Switches Table of Contents
i
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 VLAN Configuration ....................................................................................................1-1
1.1 VLAN Overview..................................................................................................................1-1
1.1.1 Introduction to VLAN...............................................................................................1-1
1.1.2 VLAN Classification.................................................................................................1-2
1.2 Basic VLAN Configuration................................................................................................. 1-2
1.3 Basic VLAN Interface Configuration..................................................................................1-2
1.4 Port-Based VLAN Configuration........................................................................................1-3
1.4.1 Introduction of Port-Based VLAN............................................................................1-3
1.4.2 Configuring an Access Port-Based VLAN...............................................................1-5
1.4.3 Configuring a Trunk Port-Based VLAN...................................................................1-6
1.4.4 Configuring a Hybrid Port-Based VLAN..................................................................1-7
1.5 Displaying VLAN Configuration .........................................................................................1-8
1.6 VLAN Configuration Example............................................................................................1-9
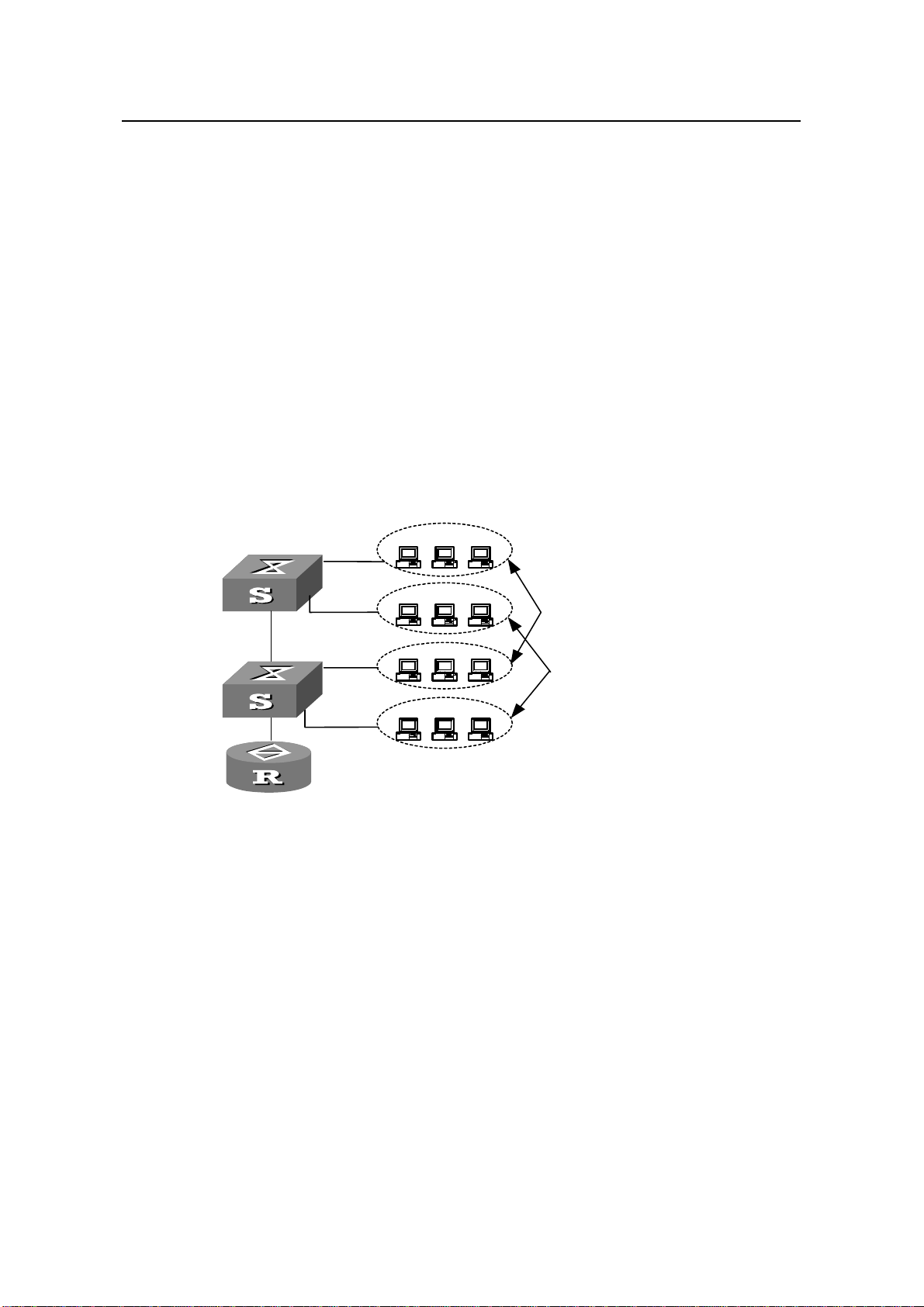
1.6.1 Network Requirements............................................................................................1-9
1.6.2 Network Diagram.....................................................................................................1-9
1.6.3 Configuration Procedure.........................................................................................1-9
Chapter 2 Voice VLAN Configuration.......................................................................................... 2-1
2.1 Voice VLAN Overview .......................................................................................................2-1
2.1.1 Automatic and Manual Voice VLAN Modes............................................................2-1
2.1.2 Security and Ordinary Voice VLAN Modes............................................................. 2-4
2.2 Voice VLAN Configuration................................................................................................. 2-4
2.2.1 Configuration Prerequisites.....................................................................................2-4
2.2.2 Configuring Voice VLAN in Automatic Mode ..........................................................2-5
2.2.3 Configuring Voice VLAN in Manual Mode...............................................................2-6
2.3 Displaying Voice VLAN...................................................................................................... 2-7
2.4 Voice VLAN Configuration Example..................................................................................2-7
2.4.1 Voice VLAN Configuration Example (Automatic Mode)..........................................2-7
2.4.2 Voice VLAN Configuration Example (Manual Mode)..............................................2-9
Chapter 3 GVRP Configuration....................................................................................................3-1
3.1 Introduction to GARP......................................................................................................... 3-1
3.1.1 Introduction to GARP..............................................................................................3-1
3.1.2 Introduction to GVRP..............................................................................................3-3
3.1.3 Protocols and Standards......................................................................................... 3-4
3.2 Configuring GVRP.............................................................................................................3-4
3.2.1 Configuring GVRP...................................................................................................3-4
3.2.2 Setting GARP Timer................................................................................................3-5
3.3 Displaying and Maintaining GARP/GVRP.........................................................................3-6