3
PME−MP60DP
HBMA0623−6.1 en/de/fr
Contents Page
1 Introduction 4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2 How to connect to a PLC 5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.1 Configuring and assigning parameters 6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3 Installation 8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4 Connections 9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.1 Pin assignment 9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5 Operation via the keyboard 10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.1 Expanded menus 11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6 Setup for Profibus 12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
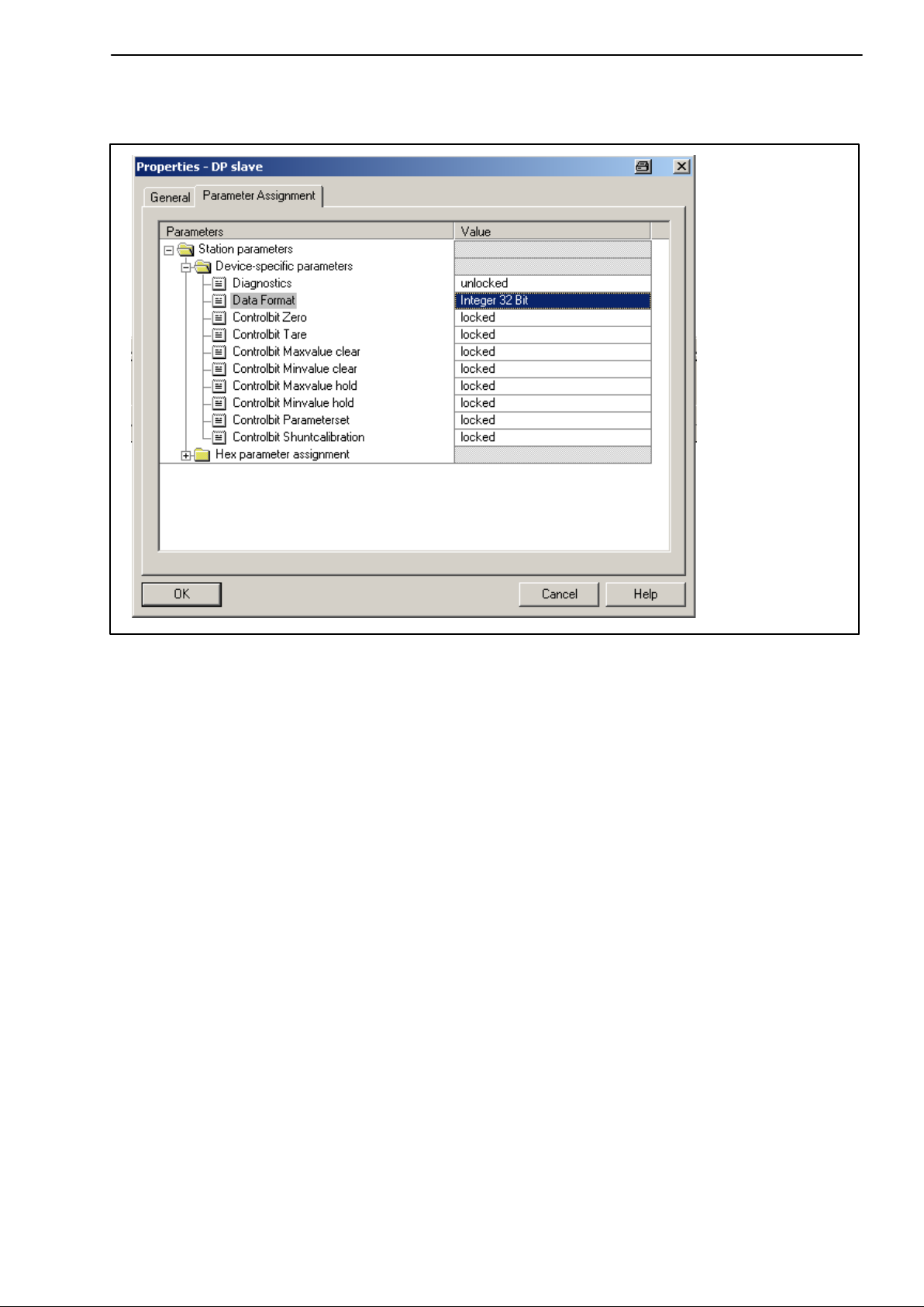
6.1 Parameter assignment 12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
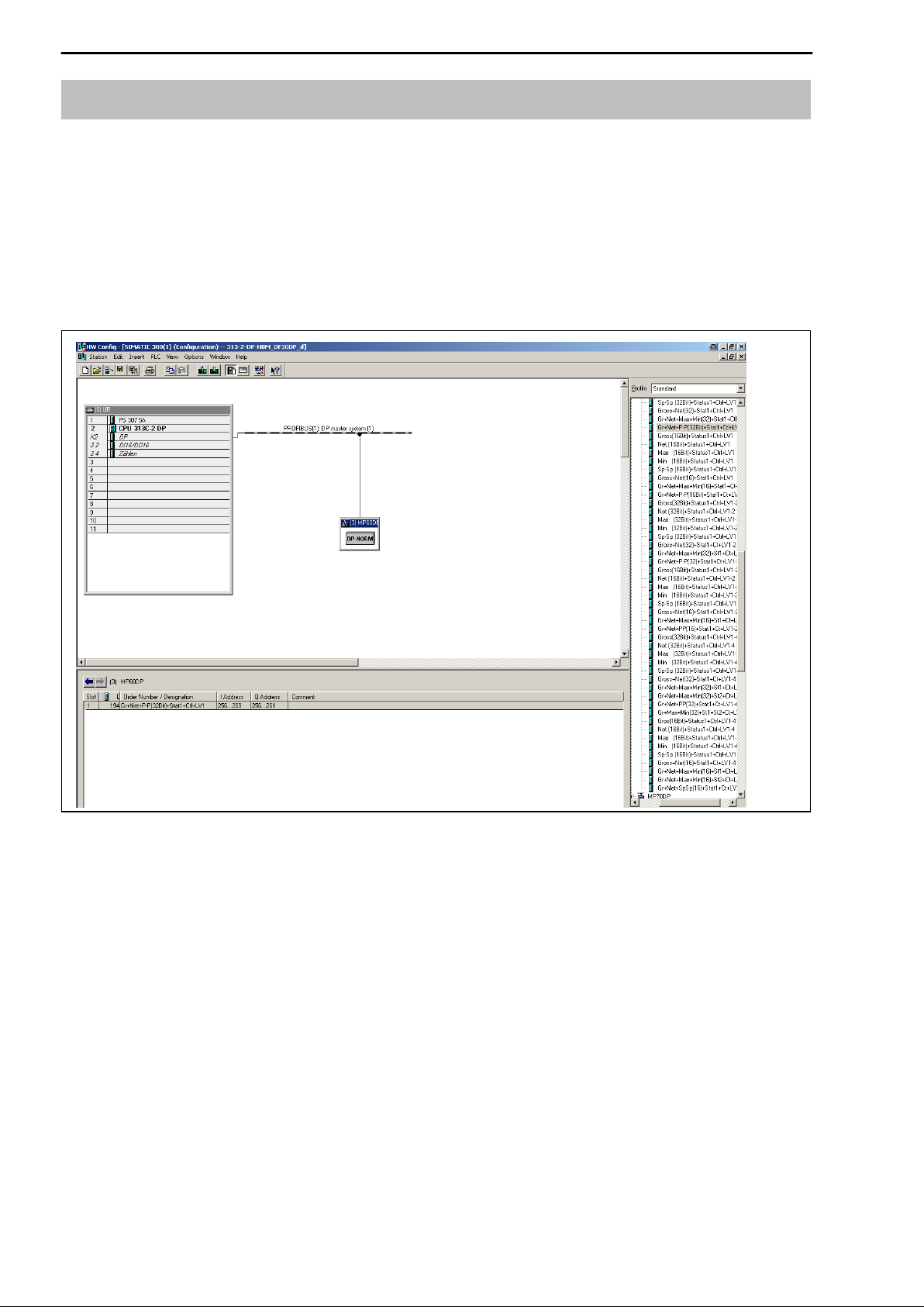
6.2 Configuration 14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6.2.1 Defining your own configuration combinations 15. . . . . . . . . . .
6.3 Cyclical data exchange 16. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6.3.1 Inputs (from MP55IBS to the PLC) 16. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6.3.2 Outputs (from the PLC to MP55IBS) 18. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6.4 Diagnosis 19. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .