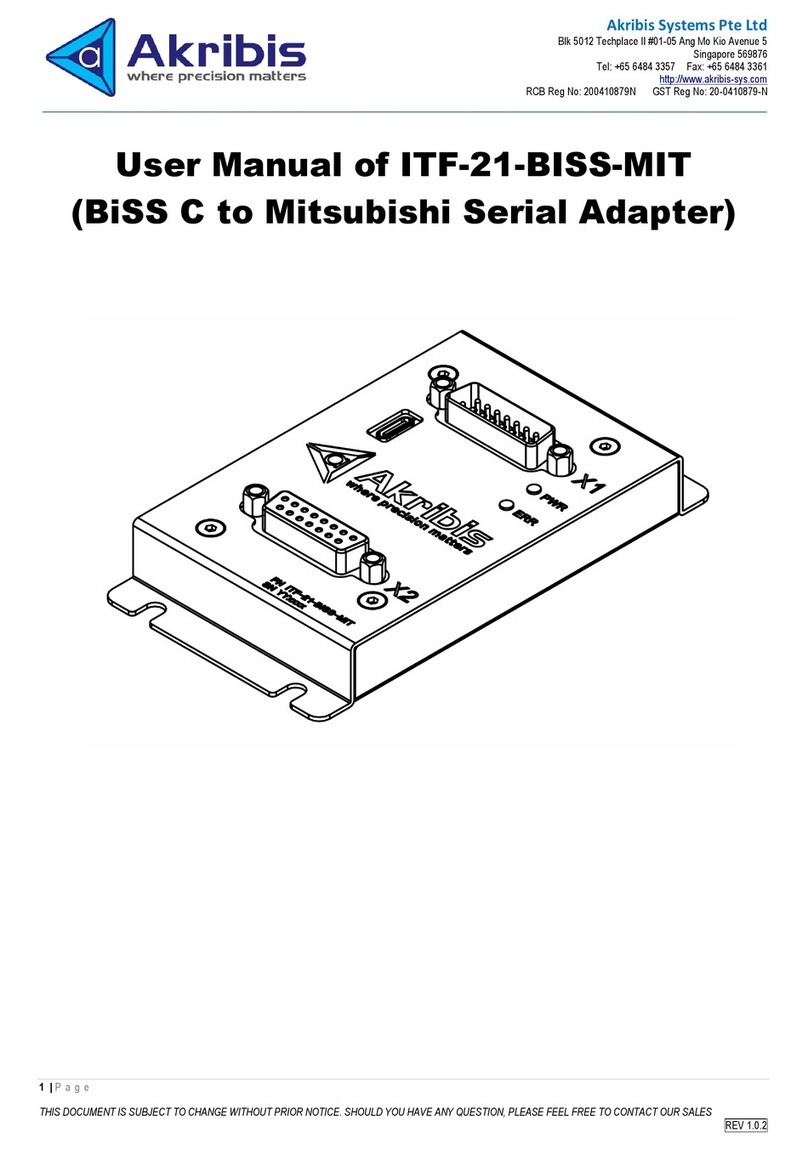
HighPoint RocketRAID 272x/271x – PCI-Express 2.0
RocketRAID 272x/271x Host Adapters
The RocketRAID 272x/271x host adapters are high-performance SAS RAID solutions, delivering reliability
to demanding data-intensive applications such as tiered storage environments, security and surveillance,
video editing, and digital content creation.
Support for both 6Gb/s SAS and SATA drives on the same controller maintains configuration optimization
for performance based on the characteristics of SAS and SATA drives available today.
HighPoint RAID Management HighPoint RAID Management software offers a user friendly interface to
create, manage and maintain your storage solutions. Email notification and remote are some of the
advance features that the RAID Management software has to offer.
1Features and Specifications
Host Adapter Architecture
•
PCI-Express x8 (Gen2)
•
Support up to 4/8 SAS/SATA drives
•
1 Internal Mini-SAS Connectors (SFF-8087) (RocketRAID 2710)
•
1 External Mini-SAS Connector(SFF-8808) (RocketRAID 2711)
•
2 Internal Mini-SAS Connectors (SFF-8087) (RocketRAID 2720)
•
1 External Mini-SAS Connector (SFF-8088) / 1 Internal Mini-SAS Connector (SFF-8087) (RocketRAID
2721)
•
2 External Mini-SAS Connectors (SFF-8088) (RocketRAID 2722)
•
Hot Swap and hot plug
•
Low Profile
•
RoHS complaint
Advanced RAID Features
•
Supports RAID 0, 1, 5, 6, 10,50 and JBOD
•
NCQ (Native Command Queuing)
•
Auto detect of unplug/plug SAS/SATA hard drive for RAID auto rebuild
•
Staggered drive spin up
•
HDD bad sector repair and remapping
•
Support Disk Scrubbing
•
BIOS Booting (INT13) to RAID array for better redundancy
•
64bit LBA for RAID arrays greater than 2TB single partition
•
S.M.A.R.T array monitoring for hard drive status and reliability
Array Monitors, Alerts and Indicators
•
Hard Drive LED Indicators (Activity and Failed) (except RocketRAID 2711/2722)
•
SMTP email notification for events and error reporting
•
Alarm/Buzzer alerts for drive/array failure
•
SAF-TE (I2C) and SGPIO enclosure management
RAID Management
•
Online Capacity Expansion (OCE) and Online RAID Level Migration (ORLM) for
Windows/Linux/FreeBSD
•
Quick and Background initialization for instant RAID access
•
API library for customization
•
CLI (Command Line Interface) for Linux and FreeBSD