Hisun Motors SECTOR 450 Manual

FOREWORD
Brief introduction to maintenance handbook of
HS450UTV
The handbook is edited by Technical Center of Chongqing Huansong Science And
Technology Industrial Co.,Ltd, and is supplied to dealers and technicians as document of
technique.Mainly, the handbook gives methods to check, maintain and repair utility terrain
vehicles (UTV), and supplies some relevant technique and performance data. Some
techniques and method inside may be used to check, maintain and repair other models of
UTV, although it is mainly for HS450UTV.
Please read the handbook through and fully understand it; otherwise, any improper
repairing and amounting would bring you problems, and accident may occur in your use.
Proper use and maintenance can guarantee UTV being driven safely, reduce its
malfunction, and help the vehicle remain its best performance.
The standards, performances and specifications mentioned in interpretation are
based on the sample in design, and they are subject to changes according to the
product’s improvement without prior notice.
First version ,April 2016
Published by Chongqing Huansong Science And Technology Industrial Co.,Ltd
Chongqing Huansong Science And Technology Industrial Co.,Ltd holds the copy right.
No publishing and reprinting without permission.

- 1 -
CONTENT
CHAPTER 1
GENERAL INFORMATION
GENERAL INFORMATION……………………………………………………………………1
WATNINGS, CAUTIONS AND NOTES……………………………………………………1
DESCRIPTION……………………………………………………………………………………2
IDENTIFICATION CODE……………………………………………………………………… 3
Frame No. ………………………………………………………………………………… 3
Engine No. ………………………………………………………………………………… 3
SAFETY ………………………………………………………………………………………… 4
Handing gasoline safely…………………………………………………………………… 4
Cleaning parts……………………………………………………………………………… 5
Warning labels……………………………………………………………………………… 5
SERIAL NUMBERS…………………………………………………………………………… 6
FASTENERS…………………………………………………………………………………… 6
Torque specifications ……………………………………………………………………… 6
Self-locking fasteners……………………………………………………………………… 6
Washers…………………………………………………………………………………… 6
Cotter pins…………………………………………………………………………………… 7
Snap rings and E-clips …………………………………………………………………… 7
SHOP SUPPLIES……………………………………………………………………………… 8
Lubricants and Fluids……………………………………………………………………… 8
Engine oils…………………………………………………………………………………… 8
Greases……………………………………………………………………………………… 8
Brake fluid………………………………………………………………………………… 9
Coolant…………………………………………………………………………………… 9
Cleaners, Degreasers and solvents …………………………………………………… 9
Gasket sealant…………………………………………………………………………… 9
Gasket remover ………………………………………………………………………… 10
Thread locking compound……………………………………………………………… 10
BASIC TOOLS ………………………………………………………………………………… 10
Screwdrivers……………………………………………………………………………… 11

- 2 -
Wrenches ………………………………………………………………………………… 11
Adjustable wrenches …………………………………………………………………… 12
Socket wrenches, ratchets and handles ……………………………………………… 12
Impact drivers …………………………………………………………………………… 13
Allen wrenches…………………………………………………………………………… 13
Torque wrenches………………………………………………………………………… 13
Torque adapters ………………………………………………………………………… 14
Pliers……………………………………………………………………………………… 15
Snap ring pliers…………………………………………………………………………… 15
Hammers ………………………………………………………………………………… 16
Ignition grounding tool…………………………………………………………………… 16
PRECISION MEASURING TOOLS ………………………………………………………… 16
Feeler gauge ……………………………………………………………………………… 17
Calipers…………………………………………………………………………………… 17
Micrometers……………………………………………………………………………… 18
Adjustment ……………………………………………………………………………… 18
Care ………………………………………………………………………………………19
Metric micrometer………………………………………………………………………… 19
Standard inch micrometer……………………………………………………………… 20
Telescoping and small bore gauges…………………………………………………… 21
Dial Indicator……………………………………………………………………………… 21
Compression gauge……………………………………………………………………… 22
Multimeter………………………………………………………………………………… 22
Cltp-on ammeter………………………………………………………………………… 22
Magneto puller………………………………………………………………………………23
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM FUNDAMENTALS……………………………………………… 23
Voltage …………………………………………………………………………………… 23
Resistance………………………………………………………………………………… 23
Amperage………………………………………………………………………………… 23
BASIC SERVICE METHODS……………………………………………………………… 24
Removing frozen fasteners……………………………………………………………… 25
Removing broken fasteners …………………………………………………………… 25
Repairing damaged threads …………………………………………………………… 26
Stud Removal/Installation ……………………………………………………………… 26

- 3 -
Removing hoses ………………………………………………………………………… 26
Bearings…………………………………………………………………………………… 27
Removal…………………………………………………………………………………… 27
Installation………………………………………………………………………………… 28
Interference fit …………………………………………………………………………… 28
Seal replacement………………………………………………………………………… 30
STORAGE……………………………………………………………………………………… 30
Storage area selection…………………………………………………………………… 30
Preparing the motorcycle for storage …………………………………………………… 30
Returning the UTV to service…………………………………………………… 31
TROVBLESHOOTING……………………………………………………………………… 31
ENGINE PRINCIPLES AND OPERATING REQUIREMENTS………………………… 32
STARTING THE ENGINE ………………………………………………………………… 32
Engine is cold …………………………………………………………………………… 33
Engine is warm…………………………………………………………………………… 33
Flooded engine……………………………………………………………………………33
ENGINE WILL NOT START ……………………………………………………………… 34
Identifying the problem ………………………………………………………………… 34
Spark test………………………………………………………………………………… 35
The starter cannot work repeatedly or can only work slowly………………… 36
POOR ENGINE PERFORMANCE………………………………………………………… 36
The engine starts slowly or difficultly…………………………………………… 36
Engine backfires, cuts out or misfires during acceleration…………………………… 36
The engine is not idling or cannot idle stably…………………………………………… 37
Poor fuel mileage………………………………………………………………………… 37
Engine will not idle or idles roughly …………………………………………………… 37
Low engine power ………………………………………………………………………… 37
Poor idle or low speed performance…………………………………………………… 39
Poor high speed performance ………………………………………………………… 39
FUEL SYSTEM……………………………………………………………………………… 39
Rich mixture……………………………………………………………………………… 40
Lean mixture……………………………………………………………………………… 40
ENGINE………………………………………………………………………………………… 40
Engine smoke……………………………………………………………………………… 40

- 4 -
Black smoke ……………………………………………………………………………… 40
Blue smoke………………………………………………………………………………… 40
White smoke or steam…………………………………………………………………… 41
Low engine compression ………………………………………………………………… 41
High engine compression ……………………………………………………………… 41
Engine overheating (cooling system) ………………………………………………… 41
Engine overheating (engine)…………………………………………………………… 42
The ignition advance angle is too large………………………………………………… 42
Detonation………………………………………………………………………………… 42
Power loss ……………………………………………………………………………… 42
engine noises……………………………………………………………………………… 43
ENGLNE LUBRICATION…………………………………………………………………… 43
HIGH OIL CONSUMPTION OR EXCESSIVE……………………………………………… 44
Exhaust smoke…………………………………………………………………………… 44
Low oil pressure ………………………………………………………………………… 44
High oil pressure ………………………………………………………………………… 44
No oil pressure…………………………………………………………………………… 44
Oil level too low…………………………………………………………………………… 44
Oil contamination………………………………………………………………………… 45
CYLINDER LEAK DOWN TEST…………………………………………………………… 45
ELECTRICAL TESTING…………………………………………………………………… 47
Preliminary checks and precautions …………………………………………………… 47
Intermittent problems…………………………………………………………………… 48
Electrical component replacement ……………………………………………………… 49
Test equipment …………………………………………………………………………… 49
Ammeter …………………………………………………………………………………… 49
Self-powered test light …………………………………………………………………… 49
Ohmmeter ………………………………………………………………………………… 49
Jumper wire……………………………………………………………………………… 50
TEST PROCEDURES………………………………………………………………………… 51
Voltage test……………………………………………………………………………… 51
Voltage drop test………………………………………………………………………… 51
Peak voltage test………………………………………………………………………… 52
Continuity test……………………………………………………………………………… 52

- 5 -
Testing for a short with a self-powered test light or ohmmeter……………………… 52
Testing for a short with a test light or voltmeter………………………………………… 53
BRAKE SYSTEM……………………………………………………………………………… 53
Soft or spongy brake lever or pedal…………………………………………………… 53
Brake drag………………………………………………………………………………… 54
Hard brake lever or pedal operation…………………………………………………… 54
Brake Grabs……………………………………………………………………………… 55
Brake squeal or chatter ………………………………………………………………… 55
Leaking brake caliper …………………………………………………………………… 55
Leaking master cylinder………………………………………………………………… 55
CHAPTER 2
SPECIFICATIONS
HOW TO USE CONVERSION TABLE OF UNIT…………………………………………… 57
How to use conversion table…………………………………………………………… 57
Definition of unit ………………………………………………………………………… 57
GEBERAR SPECIFICATIONS ……………………………………………………………… 58
ENGINE SPECIFICATIONS ………………………………………………………………… 61
CHASSIS SPECIFICATIONS………………………………………………………………… 67
ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS…………………………………………………………… 69
TIGHTENING TORQUES …………………………………………………………………… 71
Engine tightening torques………………………………………………………………… 71
Chassis tightening torques ……………………………………………………………… 74
GENERAL TIGHTENING TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS ………………………………… 76
LUBRICATION PIONTS AND LUBRICANT TYPES……………………………………… 77
Engine……………………………………………………………………………………… 77
Chassis……………………………………………………………………………………… 78
HYDROGRAPHIC CHART…………………………………………………………………… 79
LUBRICATION OIL WAY…………………………………………………………………… 80

- 6 -
CHAPTER 3
MAINTENCE AND ADJUSTMENT OF THE UTV
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULE……………………………………………………………… 81
ENGINE
Adjusting the valve clearance…………………………………………………………… 83
Checking the spark plug………………………………………………………………… 85
Checking the ignition timing……………………………………………………………… 86
Measuring the compression pressure………………………………………………… 87
Checking the engine oil level……………………………………………………………... 89
Changing the engine oil……………………………………………………………… 90
CHASSIS
Cleaning the air filter………………………………………………………………… 92
Checking the coolant level …………………………………………………………… 93
Changing the coolant…………………………………………………………………… 94
Checking the coolant temperature warning light …………………………………… 97
Checking the v-belt……………………………………………………………………… 98
Cleaning the spark arrester …………………………………………………………… 99
Adjusting the brake pedal……………………………………………………………… 99
Adjusting the parking brake……………………………………………………………… 100
Checking the brake fluid level ………………………………………………………… 101
Checking the front brake pads………………………………………………………… 101
Checking the rear brake pads………………………………………………………… 102
Checking the brake hoses and brake pipes ………………………………………… 102
Bleeding the hydraulic brake system ………………………………………………… 102
Adjusting the select lever shift rod …………………………………………………… 104
Adjusting the brake light switch……………………………………………………........104
Checking the final gear oil level…………………………………………………… 105
Changing the final gear oil…………………………………………………… 105
Checking the differential gear oil…………………………………………………… 106
Changing the differential gear oil……………………………………………………...... 106
Checking the constant velocity joint dust boots……………………………………… 108
Checking the steering system………………………………………………………… 108
Adjusting the toe-in …………………………………………………………………… 109
Adjusting the front and rear shock absorbers………………………………………… 110

- 7 -
Checking the tires ……………………………………………………………………… 112
Checking the wheels…………………………………………………………………… 114
Checking and lubricating the cables ………………………………………………… 114
ELECTRICAL
Checking and charging the battery…………………………………………………… 115
Checking the fuses …………………………………………………………………… 120
Adjusting the headlight beam………………………………………………………… 122
Changing the headlight bulbⅠ……………………………………………………… 122
Changing the tail/brake light bulb …………………………………………………… 123
CHAPTER 4
ENGINE
ENGINE NOTE……………………………………………………………………………… 124
ENGINE REMOVAL………………………………………………………………………… 125
CYLINDER HEAD AND CYLINDER HEAD COVER…………………………………… 128
ROCKER ARMS VALES AND CAMSHAFT……………………………………………… 131
VALVES AND VALVE SPRINGS…………………………………………………………… 135
CYLINDER AND PISTON………………………………………………………………… 140
ENGING COOLING FAN AND A.C. MAGNETO…………………………………144
BALANCER GEARS AND OIL PUMP GEARS…………………………………………149
PRIMARY AND SECONDARY SHEAVES…………………………………………………152
Primary and secondary sheaves…………………………………………………152
Primary sheaves………………………………………………………………………153
Secondary sheaves………………………………………………………………………154
CLUTCH………………………………………………………………………………………159
CRANKCASE…………………………………………………………………………………163
Starter motor and oil filter………………………………………………………………163
Crankcase…………………………………………………………………………………165
Crankcase bearings…………………………………………………………………166
CRANKCASE AND OIL PUMP……………………………………………………………170
Crankcase and oil pump……………………………………………………………170

- 8 -
Oil pump…………………………………………………………………………………171
TRANSMISSION………………………………………………………………………………174
Transmission……………………………………………………………………………174
Drive axle assembly……………………………………………………………………175
MIDDLE GEAR………………………………………………………………………………179
Middle drive shaft…………………………………………………………………………179
CHAPTER 5
CHASSIS
MALFUNCTION INSPECTION…………………………………………………………… 186
PANEL AND CARGO BED
Front panel…………………………………………………………………………………189
Side cover, Footrest part ………………………………………………………………193
Cargo rack………………………………………………………………………………197
Cargo bed……………………………………………………………………………… 200
Head shed frame………………………………………………………………………… 204
DIRECTION SYSTEM
Steering wheel part……………………………………………………………………… 206
Steering mechanism part……………………………………………………………… 209
BRAKE SYSTEM…………………………………………………………………………… 214
Disk brake components………………………………………………………… 215
WHEEL AND TYRE PARTS ……………………………………………………………… 233
Front wheels……………………………………………………………………………… 233
Rear wheels……………………………………………………………………………… 234
TRANSMISSION SYSTEM……………………………………………………………… 238
C.V axle, front axle……………………………………………………………………… 238
Front bridge……………………………………………………………………… 239
C.V axle, rear axle……………………………………………………………………… 248
Rear bridge…………………………………………………………………… 249
SHIFT OPERATING SYSTEM …………………………………………………………… 255
SUSPENSION……………………………………………………………………………… 260

- 9 -
Front swing arm……………………………………………………………………… 260
Front suspension……………………………………………………………………… 261
Rear suspension……………………………………………………………………… 266
COOLING SYSTEM………………………………………………………………………… 272
Water and oil radiator…………………………………………………………………… 272
SEAT ………………………………………………………………………………………… 277
FUEL TANK………………………………………………………………………………… 279
CHAPTER 6
ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM MALFUNCTION INSPECTION ……………………………… 282
ELECTRICAL………………………………………………………………………………… 283
ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS…………………………………………………………… 283
Checking the switch…………………………………………………………………… 285
Checking the switch continuity………………………………………………………… 286
Checking the bulbs and bulb sockets ……………………………………… 287
IGNITION SYSTEM…………………………………………………………………………287
Circuit diagram…………………………………………………………………………… 287
Troubleshooting……………………………………………………………………… 288
ELECTRIC STARTING SYSTEM…………………………………………………………291
Circuit diagram………………………………………………………………………… 291
Troubleshooting……………………………………………………………………… 292
STARTER MOTOR………………………………………………………………………… 295
CHARGING SYSTEM……………………………………………………………………… 295
Circuit diagram………………………………………………………………………… 295
Troubleshooting……………………………………………………………………… 296
LIGHTING SYSTEM………………………………………………………………………… 297
Circuit diagram………………………………………………………………………… 297
Troubleshooting……………………………………………………………………… 298
Checking the lighting system…………………………………………………… 299
SIGNALING SYSTEM……………………………………………………………………… 300
Circuit diagram………………………………………………………………………… 300

- 10 -
Troubleshooting……………………………………………………………………… 301
Checking the signal system……………………………………………………… 302
COOLING SYSTEM………………………………………………………………………… 308
Circuit diagram………………………………………………………………………… 308
Troubleshooting……………………………………………………………………… 309
2WD/4WDSELECTINGSYSTEM………………………………………………………… 311
Circuit diagram………………………………………………………………………… 311
Troubleshooting……………………………………………………………………… 312
CHAPTER 7
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
INTRODUCTION
Ems (engine management system) …………………………………………………… 313
Typical components of EMS………………………………………………………………313
Layout of EMS components………………………………………………………………314
COMPONENTS OF EMS
Electronic control unit …………………………………………………………………… 314
Multec 3.5 injectors ……………………………………………………………………… 315
Throttle body assembly(with stepper motor) …………………………………………319
Engine coolant temperature sensor ……………………………………………………321
Intake air pressure and temperature sensor …………………………………………321
Oxygen sensor ………………………………………………………………………… 322
Ignition coil……………………………………………………………………………… 322
Fuel pump module…………………………………………………………………………326
EMS FAULT DIAGNOSIS
EME fault diagnosis ………………………………………………………………………332
Fault code list………………………………………………………………………………332
CHAPTER 8
TROUBLESHOOTING
STARTING FAILURE/HARD STARTING………………………………………………… 334
Fuel system ………………………………………………………………………………334

- 11 -
Electrical system ………………………………………………………………………… 334
Compression system …………………………………………………………………… 335
POOR IDLE SPEED PERFORMANCE ………………………………………………… 335
Poor idle speed performance…………………………………………………………… 335
POOR MEDIUM AND HIGH-SPEED PERFORMANCE ……………………………… 336
Poor medium and high-speed performance………………………………………… 336
FAULTY GEAR SHIFTING………………………………………………………………… 336
Shift lever does not move ……………………………………………………………… 336
Jumps out of gear……………………………………………………………………… 336
ENGING OVERHEATING…………………………………………………………………… 337
Overheating……………………………………………………………………………… 337
FAULTY BRAKE…………………………………………………………………………… 337
Poor braking effect……………………………………………………………………… 337
SHOCK ABSORBER MALFUNCTION………………………………………………… 338
Loss of damping function……………………………………………………………… 338
UNSTABLE HANDLING…………………………………………………………………… 338
Unstable handling……………………………………………………………………… 338
LIGHTING SYSTEM………………………………………………………………………… 338
Head light is out of work………………………………………………………………… 338
Bulb burnt out…………………………………………………………………………… 339
Error display of meter…………………………………………………………………… 339
CHAPTER 9
WIRING DIAGRAM
WIRING DIAGRAM…………………………………………………………………… 340

GENERALINFORMATION
-1-
GENERAL INFORMATION
The text provides complete information on maintenance,tune-up repair and overhaul,Hundreds of
photographs and illustrations created during the complete disassembly of four wheel utility terrain
venires (UTV) guide the reader through every job,All procedures are in step-by-step format and
designed for the reader who may be working on the UTV for the first time.
WARNINGS, CAUTIONS AND NOTES
The terms WARNING, CAUTION and NOTE have specific meaning in this manual.
WARNING: emphasizes areas where injury or even death could result from negligence.
Mechanical damage may also occur. WARNINGS are to be taken seriously
CAUTION: emphasizes areas where equipment damage could result. Disregarding a
CAUTION could cause permanent mechanical damage. though injury is unlikely.
NOTE: provides additional information to make a step or procedure easier or clearer.
Disregarding a NOTE could cause inconvenience. but would not cause
equipment damage or injury.

GENERALINFORMATION
-2-
DESCRIPTION
1. Headlight Assy
2. Front Shock Absorber Assembly
Unit Qa(Gasbag Shock Absorber)
3. Second Water Tank
4. Steering Wheel Comp
5. Driver Seat
6. Driver Safety Belt
7. Rear Cargo
8. Rear Shock Absorber Assembly
Unit Q(Gasbag Shock Absorber)
9. Rear Position Lamp Assy
10. Rear Tire
11. Muffler Parts
12. Fuel Tank Switch Cap
13. Passenger Safety Belt
14. Passenger Seat
15. Gearshift Arm Assy
16. Passenger Handrail
17. Front Tire
18. Cooling Water Tank Component
19. WeldingAssembly, Front Bumper
20. Horn Switch
21. Light Switch
22. High/Low Beam Lights
23. Emergency Light
24. Turn The Lamp
25. Front Axle Differential
26. Combination Instrument
27. Parking Pedal
28. Welding Assembly Brake Pedal
29. Accelerator Pedal Welding Assy
30. DC-Socket
31. 4WD Button
32. Carrying Case
NOTE:
The vehicle you have purchased may
differ slightly from those in the figures of
this manual.
GENERALINFORMATION
-3-
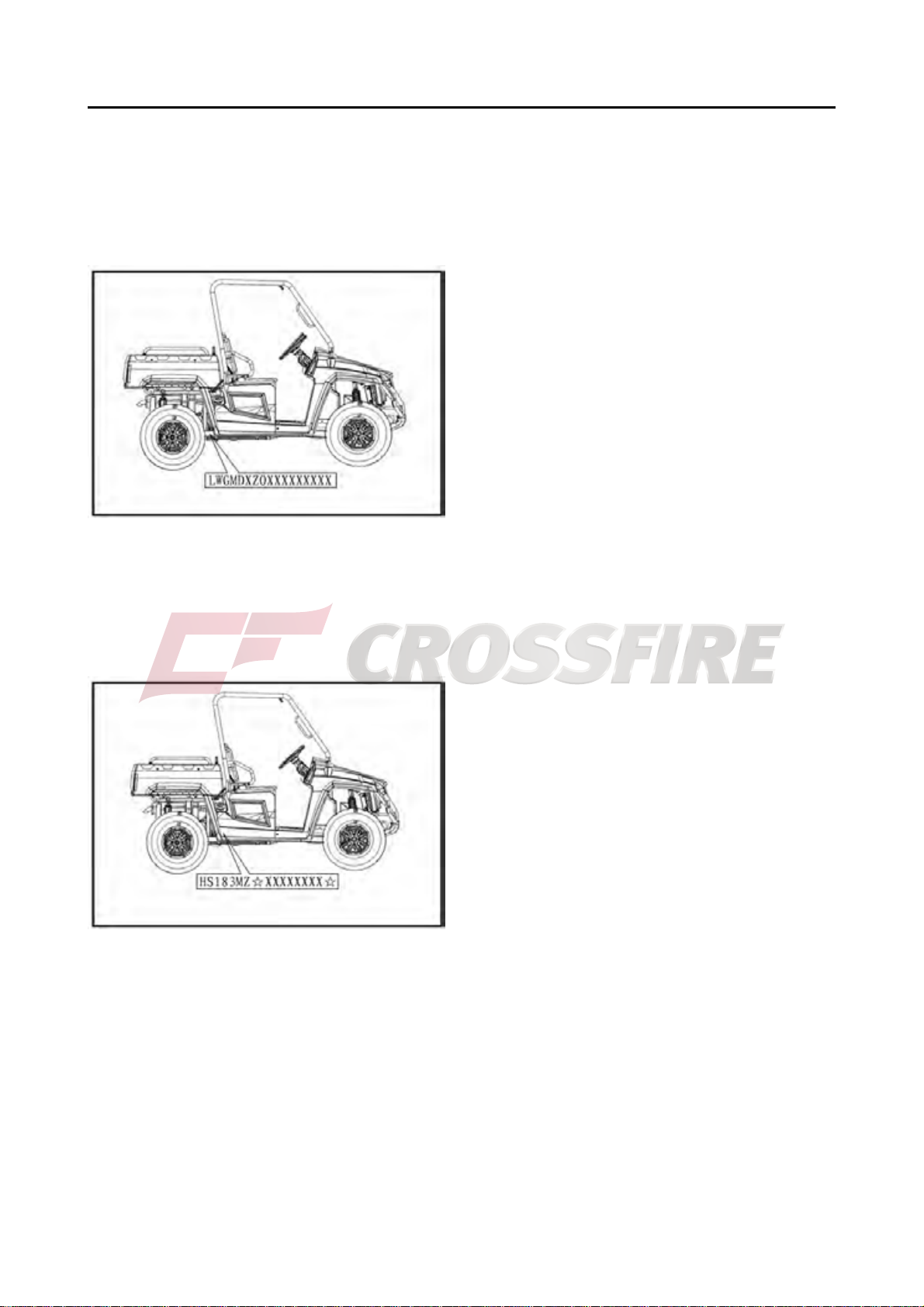
IDENTIFICATION CODE
Frame No.
Frame No. is carved on the right side of front
main frame
Engine No.
Engine NO. Is carved on the right side of the
engine, Figure.

GENERALINFORMATION
- 4 -
SAFETY
Professional mechanics can work for years and never sustain a serous injury or mishap. Follow
these guidelines and practice common sense to safely service the utility terrain venires
1. Do not operate the utility terrain venires in an enclosed area venires The exhaust gasses contain
carbon monoxide. an odorless, colorless and tasteless poisonous gas. Carbon monoxide levels
build quickly in small enclosed areas and can cause unconsciousness and death in a short time.
Make sure to properly ventilate the work area or operate the UTV side
2. Never use gasoline or any extremely flammable liquid to clean parts. Refer to cleaning parts and
handling Gasoline Safely in this section
3. Never smoke or use a torch in the vicinity of flammable liquids, such as gasoline or cleaning
solvent.
4. If welding or brazing on the UTV the fuel tank to a safe distance at least 50ft.(15m) away.
5. Use the correct type and size of tools to avoid damaging fasteners.
6. Keep tools clean and in good condition. Replace or repair worn or damaged equipment.
7. When loosening a tight fastener, be guided by what would happen if the tool slips.
8. When replacing fasteners, make sure the new fasteners are the same size and strength as the
original ones.
9. Keep the work area clean and organized.
10. Wear eye protection anytime the safety of the eyes is in question. This includes procedures that
involve drilling, grinding, hammering, compressed air and chemicals.
11. Wear the correct clothing for the job. Tie up or cover long hair so it does not get caught in moving
equipment.
12. Do not carry sharp tools in clothing pockets.
13. Always have an approved fire extinguisher available. Make sure it is rated for gasoline (Class B)
and electrical (Class C) fires.
14. Do not use compressed air to clean clothes, the UTV or the work area. Debris may be blown into
the eyes or skin. Never direct compressed air at anyone. Do not allow children to use or play with
any compressed air equipment.
15. When using compressed air to dry rotating parts, hold the part so it does not rotate. Do not allow
the force of the air to spin the part. The air jet is capable of rotating parts at extreme speed. The
part may disintegrate of become damaged, causing serious injury.
16. Do not inhale the dust created by brake pad and clutch wear. These particles may contain
asbestos. In addition, some types of insulating materials and gaskets may contain asbestos.
Inhaling asbestos particles is hazardous to one’s health.
17. Never work on the UTV while someone is working under it.
Handling Gasoline Safely
Gasoline is a volatile flammable liquid and is one of the most dangerous items in the shop.
Because gasoline is used so often, many people forget it is hazardous. Only use gasoline as fuel
for gasoline internal combustion engines. Keep in mind when working on the machine, gasoline is
always present in the fuel tank fuel line throttle. To avoid a disastrous accident when working
around the fuel system, carefully observe the following precautions:

GENERALINFORMATION
- 5 -
1. Never use gasoline to clean parts. Refer to Cleaning Parts in this section.
2. When working of the fuel system, work outside or in a well-ventilated area.
3. Do not add fuel to the fuel tank or service the fuel system while the UTV is near open flames,
sparks or where someone is smoking .Gasoline vapor is heavier than air, it collects in low areas
and is more easily ignited than liquid gasoline.
4. Allow the engine to cool completely before working on any fuel system component.
5. Do not store gasoline in glass containers. If the glass breaks, a serious explosion of fire may
occur.
6. Immediately wipe up spilled gasoline with rags. Store the rags in a metal container with a lid until
they can be properly disposed of, or place them outside in a safe place for the fuel to evaporate.
7. Do not pour water onto a gasoline fire. Water spreads the fire and makes it more difficult to put out.
Use a class B, BC or ABC fire extinguisher which are dedicated to extinguish the gasoline fire.
8. Always turn off the engine before refueling. Do not spill fuel onto the engine or exhaust system.
Do not overfill the fuel tank. Leave an air space at the top of the tank to allow room for the fuel to
expand due to temperature fluctuations.
Cleaning Parts
Cleaning parts is one of the more tedious and difficult service jobs performed in the home garage.
Many types of chemical cleaners and solvents are available for shop use. Most are poisonous and
extremely flammable. To prevent chemical exposure, vapor buildup, fire and serious injury, observe
each product warning label and note the following:
1. Read and observe the entire product label before using any chemical. Always know what type of
chemical is being used and whether it is poisonous and/or flammable.
2. Do not use more than one type of cleaning solvent at a time. If mixing chemicals is required,
measure the proper amounts according to the manufacturer.
3. Work in a well-ventilated area.
4. Wear chemical-resistant gloves.
5. Wear safety glasses.
6. Wear a vapor respirator if the instructions call for it.
7. Wash hands and arms thoroughly after cleaning parts.
8. Keep chemical products away from children and pets.
9. Thoroughly clean all oil, grease and cleaner residue from any part that must be heated.
10. Use a nylon brush when cleaning parts. Metal brushes may cause a spark.
11. When using a parts washer, only use the solvent recommended by the manufacturer. Make sure
the parts washer is equipped with a metal lid that will lower in case of fire.
Warning Labels
Most manufacturers attach information and warning labels to the UTV. These labels contain
instructions that are important to personal safety when operating, servicing, transporting and storing
the UTV. Refer to the owner’s manual for the description and location of labels. Order replacement
labels from the dealers or manufacturer if they are missing or damaged.

GENERALINFORMATION
- 6 -
SERIAL NUMBERS
Serial and identification numbers are stamped on various locations on the frame engine throttle
body. Record these numbers in the Quick Reference Data section in the front of the manual. Have
these numbers available when ordering parts.
FASTENERS
Proper fastener selection and installation is important to ensure the motorcycle operates as
designed and can be serviced efficiently. The choice of original equipment fasteners is not arrived at
by chance. Make sure replacement fasteners meet all the same requirements as the originals
Many screws. Bolts and studs are combined with nuts to secure particular components. to indicate
the size of a nut. Manufactures specify the internal diameter and the thread pitch
The measurement across two flats on a nut or bolt indicates the wrench size
WARNING
Do not install fasteners with a strength
classification lower than what was originally
installed by the manufacturer doing so may cause
equipment failure and or damage
Torque Specifications
The material used in the manufacturing of the UTV may be subjected to uneven stresses if the
fasteners of the various subassemblies are not installed and tightened correctly. Fasteners that are
improperly installed or work loose can cause extensive damage. it is essential to use an accurate
torque wrench as described in this chapter
Self-Locking Fasteners
Several types of bolts. Screws and nuts incorporate a system that creates interference between
the two fasteners. Interference is achieved in various ways. The most common types are the nylon
insert nut and a dry adhesive coating on the threads of a blot.
Self-locking fasteners offer greater holding strength than standard fasteners, which improves their
resistance to vibration.All self-locking fasteners cannot be reused. The materials used to from the lock
become distorted after the initial installation and removal. Discard and replace self-locking fasteners
after removing them. Do not replace self-locking fasteners with standard fasteners.
Washers
The two basic types of washers are flat washers and lock washers. Flat washers are simple discs
with a hole to fit a screw or bolt. Lock washers are used to prevent a fastener from working loose.
Washers can be used as spacers and seals. Or can help distribute fastener load and prevent the
fastener from damaging the component
As with fasteners. When replacing washers make sure the replacement washers are of the same
design and quality
GENERALINFORMATION
- 7 -
Cotter Pins
A cotter pin is a split metal pin inserted into a hole or slot to prevent a fastener from loosening. In
certain applications, such as the rear axle on an UTV or motorcycle, the fastener must be secured in
this way. For these applications.A cotter pin and castellated (slotted) nut is used.
To use a cotter pin, first make sure the diameter is correct for the hole in the fastener. Aster
correctly tightening the fastener and aligning the holes, insert the cotter pin through the hole and bend
the ends over the fastener, Unless instructed to do so, never loosen a tightened fastener to align the
holes. If the holes do not align. Tighten the fastener enough to achieve alignment
Cotter pins are available in various diameters and lengths. Measure the length from the bottom of
the head to the tip of the shortest pin
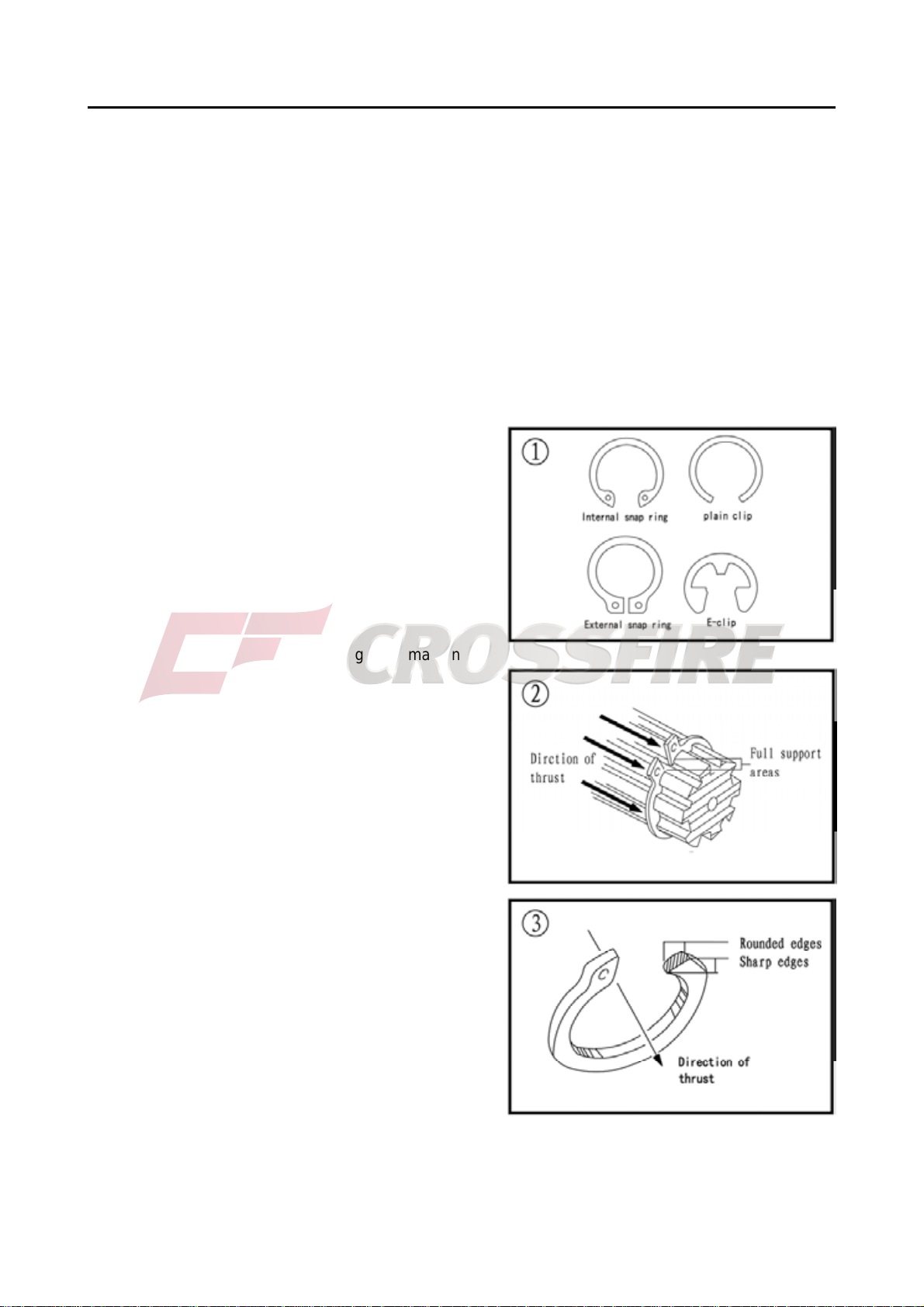
Snap Rings and E-clips
Snap rings (Figure 1) are circular-shaped metal
retaining clips. They secure parts in place on parts
such as shafts. External type snap rings are used to
retain items on shafts. Internal type snap rings secure
parts within housing bores. In some applications. in
addition to securing the component(s). snap rings of
varying thicknesses also determine endplay. These
are usually called selective snap rings.
The two basic types of snap rings are machined
and stamped snap rings. Machined snap rings (Figure
2) can be installed in either direction. Because both
faces have sharp edges. Stamped snap rings (Figure
3) are manufactured with a sharp and a round edge.
When installing a stamped snap ring in a thrust
application, install the sharp edge facing away from
the part producing the thrust.
E-clips are used when it is not practical to use a
snap ring. Remove E-clips with a flat blade
screwdriver by prying between the shaft and E-clip. To
install an E-clip. Center it over the shaft groove and
push or tap it into place
Observe the following when installing snap rings:
1. Remove and install snap rings with snap rings
pliers. Refer to Basic Tools in this chapter
2. In some applications. it may be necessary to
replace snap rings after removing them
3. Compress or expand snap rings only enough to
install them. If overly expanded. Lose their
retaining ability
4. After installing a snap ring. Make sure it seats completely
5. Wear eye protection when removing and installing snap rings

GENERALINFORMATION
- 8 -
SHOP SIPPLIES
Lubricants and Fluids
Periodic lubrication help ensure a long service life for any type of equipment. Using the correct
type of lubricant is as important as performing the lubrication service. Although in an emergency the
wrong type is better than not using one, The following section describes the types of lubricants most
often required. Make sure to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for lubricant types
Engine oils
Engine oil for four-stroke the UTV engine use is classified by two standards: the American
Petroleum Institute (API) service classification. The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) viscosity
rating Standard classification
The API and SAE information is on all oil container labels. Two letters indicate the API service
classification. The number or sequence of numbers and letter (10W-40SG for example) is the oil’s
viscosity rating. The API service classification and the SAE viscosity index are not indications of oil
quality.
The APL service classification standards, The first letter in the classification S indicates that the oil
is for gasoline engines. The second letter indicates the standard the oil satisfies .
The classifications are: MA (high friction applications) and MB( low frication applications).
NOTE
Refer to Engine Oil and Filter in
Chapter Three for further information
on API, SAE classifications.
Always use an oil with a classification recommended by the manufacturer, Using an oil with a
different classification can cause engine damage.
Viscosity is an indication of the oil’s thickness. Thin oils have a lower number while thick oil have a
higher number. Engine oils fall into the 5-to50-weight range for single-grade oils.
Most manufactures recommend multi-grade oil. These oils perform efficiently across a wide
range of operating conditions. Multi-grade oils are identified by a W after the first number, which
indicates the low-temperature viscosity.
Engine oils are most commonly mineral (petroleum) based, but synthetic and semi-synthetic types
are used more frequently. When selecting engine oil, follow the manufacturer’s recommendation for
type, classification and viscosity.
Greases
Grease is lubricating oil with thickening agents added to it. The National Lubricating Grease
Institute (NLGI) grades grease. Grades range from No.000 to No.6, with No.6 being the thickest.
Typical multipurpose grease is NLGI No.2. For specific applications, manufacturers may recommend
water-resistant type grease or one with an additive such as molybdenum disulfide (MoS2).
This manual suits for next models
1
Table of contents
Other Hisun Motors Utility Vehicle manuals
Popular Utility Vehicle manuals by other brands

Yamaha
Yamaha YTF1 Owner's/operator's manual

Toro
Toro TransPro 200 installation instructions

Polaris
Polaris RANGER 800 HD owner's manual

American Sportworks
American Sportworks 200 SERIES owner's manual

Ingersoll-Rand
Ingersoll-Rand Run-A-Bout owner's manual

Taylor-Dunn
Taylor-Dunn B0-248-TT Operation, t roubleshooting and replacement parts manual
















