Inorea PI150 Series User manual

2 / 18
1.Foreword
Thank you for choosing Powtran PI150 series fundamental form frequency inverter.
The diagrams of these operating instructions are used for convenience of explanation and may be slightly
different from the product due to product upgrades. Please refer to the actual product.
Please take this manual to the end user and keep it for future maintenance use.
If you have any questions, please get in touch with our company or our agent in time, we will offer
dedicated service to you.
2.Instructions on nameplate
Model designation:
POWTRAN Inverter
PI 150 2R2 G 3
Rated output capacity
2R2:2.2kW
004:4kW
Series code
PI150 series Input Voltage Level
1:Single-phase 220V
2:Three-phase 220V
3:Three-phase 380V
4:Three-phase 480V
Standard load
Output configuration
0: Without brake unit as standard (Omitted)
Z: With brake unit (Optional)
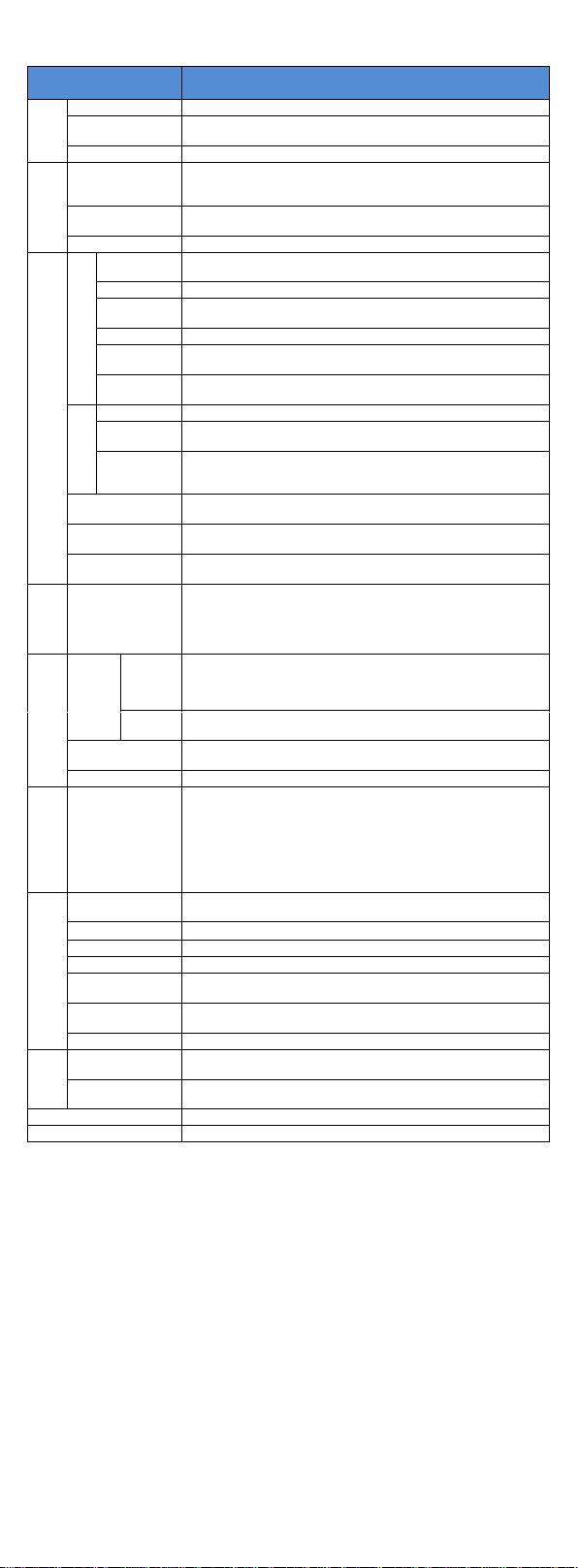
3.Dimension
E
L
W
d
HB
A
0.75~5.5kW G3 support rail mounting
1) Outline dimension drawing and installation dimension of single phase 220 VAC
Model
Output power
(kW)
Dimension
(mm)
Installation
(mm)
Guide rail
installation
position (mm)
Weight
(kg)
L
W
H
A
B
d
E
PI150 0R4G1(Z)
0.4
138
72
123.5
127
61
5
62
1.1
PI150 0R7G1(Z)
0.75
PI150 1R5G1(Z)
1.5
PI150 2R2G1(Z)
2.2
185
72
134
175
45
5
82
1.3
2) Dimensions and installation size of three-phase 220VAC
Model
Output power
(kW)
Dimension
(mm)
Installation
(mm)
Guide rail
installation
position (mm)
Weight
(kg)
L
W
H
A
B
d
E
PI150 0R4G2(Z)
0.4
138
72
123.5
127
61
5
62
1.1
PI150 0R7G2(Z)
0.75
PI150 1R5G2(Z)
1.5
PI150 2R2G2(Z)
2.2
185
72
134
175
45
5
82
1.3
3) Dimensions and installation size of three-phase 380VAC
4)
Model
Output power
(kW)
Dimension
(mm)
Installation
(mm)
Guide rail
installation
position (mm)
Weight
(kg)
L
W
H
A
B
d
E
PI150 0R7G3(Z)
0.75
138
72
123.5
127
61
5
62
1.1
PI150 1R5G3(Z)
1.5
PI150 2R2G3(Z)
2.2
PI150 004G3(Z)
4
185
72
134
175
45
5
82
1.3
PI150 5R5G3(Z)
5.5
5) Dimensions and installation size of three-phase 480VAC
Model
Output power
(kW)
Dimension
(mm)
Installation
(mm)
Guide rail
installation
position (mm)
Weight
(kg)
L
W
H
A
B
d
E
PI150 0R7G4(Z)
0.75
138
72
123.5
127
61
5
62
1.1
PI150 1R5G4(Z)
1.5

3 / 18
PI150 2R2G4(Z)
2.2
PI150 004G4(Z)
4
185
72
134
175
45
5
82
1.3
PI150 5R5G4(Z)
5.5
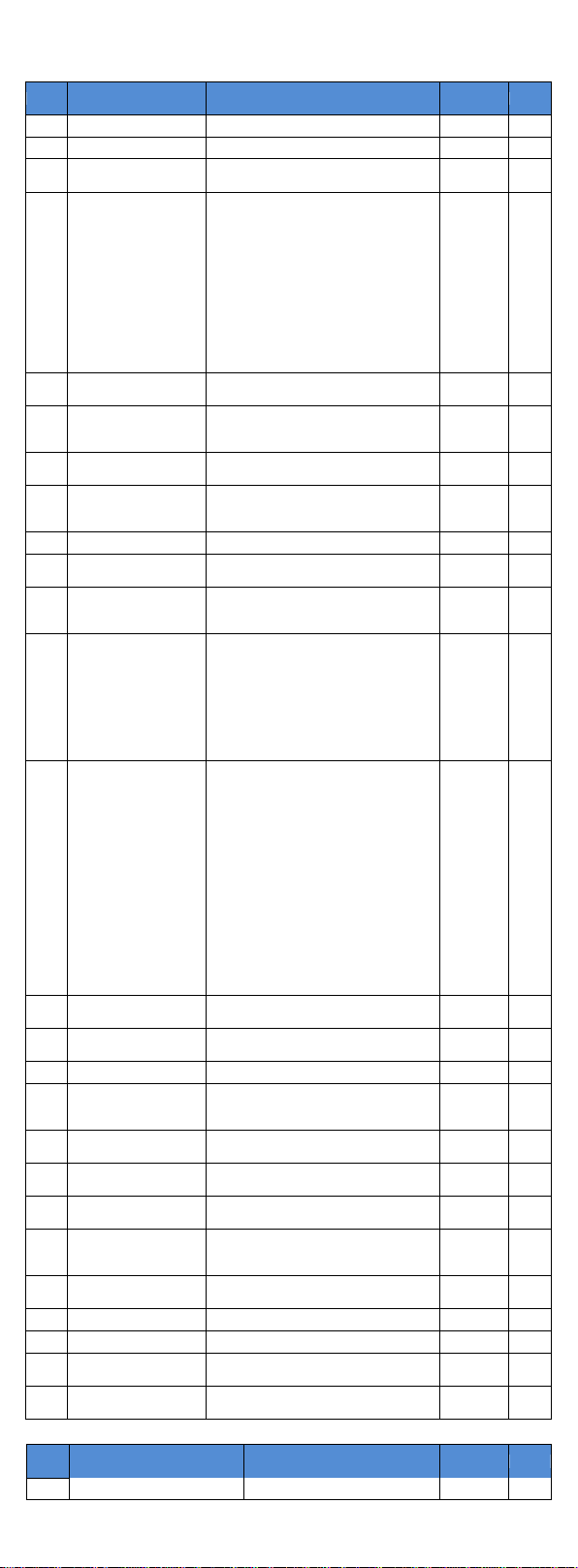
4.Operation keyboard introduction
Figure 4-1:Operation panel display
4.1 Keyboard indicator
Indicator light
Name
Status
light
RUN
Running indicator light
* ON: The inverter is working
* OFF: The inverter stops
FWD/REV
Forward/reverse running light
* ON: In forward status
* OFF: In reversal status
Hz
Frequency indicator
A
Current indicator
4.2 Operation panel button description
Sign
Name
Function
Parameter
setting/esc key
* Enter into the modified status of main menu;
* Esc from functional parameter modification;
* Esc submenu or functional menu to status menu
Shift Key
*Choose displayed parameter circularly under running or stop
interface; choose parameter’s modified position when modify
parameter
Increasing key
* Parameter or function number increasing
Decreasing key
* Parameter or function number decreasing
Running key
* For starting running in the mode of keyboard control status
Stop/Reset key
* For stopping running in the running status; for resetting the
operation in fault alarm status. The function of the key is subject to
F6.00
Enter key
* Step by step into the menu screen, set parameters to confirm.
Quick
multi-function
key
* This key function is determined by the function code F6.21
5.Standard specifications
Items
Specifications
Power Input
Rated voltage
AC 1PH 220V(-15%)~240V(+10%)
AC 3PH 220V(-15%)~240V(+10%)
AC 3PH 380V(-15%)~440V(+10%)
AC 3PH 480V(-10%)~480V(+10%)
Input frequency
50Hz/60Hz
Allowing fluctuations
Voltage continued
volatility:±10%
Less than 3% of voltage unbalance rate
3%;
Input frequency fluctuation:±5%;
Distortion satisfy IEC61800-2 standard
Control system
Control system
High performance vector control inverter based on DSP
Control method
V/F control, vector control W/O PG
Automatic torque
boost function
Realize low frequency (1Hz) and large output torque control under the V/F
control mode.
Acceleration/decelerati
on control
Straight or S-curve mode. Four times available and time range is
0.0~6500.0s.
V/F curve mode
Linear, square root/m-th power, custom V/F curve
Over load capability
G type:Rated current 150% - 1 minute, rated current 180% - 2 seconds
Maximum frequency
1. Vector control:0~300Hz; 2. V/F control:0~3200Hz
Carrier frequency
0.5~16kHz; automatically adjust carrier frequency according to the load
characteristics.
Input frequency
resolution
Digital setting:0.01Hz minimum analog:Maximum frequency*0.025%.
Start torque
G type: 0.5Hz/150% (Vector control W/O PG)
Speed range
1:100 (Vector control W/O PG)
Steady-speed precision
Vector control W/O PG: ≤± 0.5% (Rated synchronous speed)
Torque response
≤ 40ms (Vector control W/O PG)
Torque boost
Automatic torque boost; manual torque boost(0.1%~30.0%)
DC braking
The built-in PID adjusts the braking current to ensure sufficient braking
torque without over-flow.DC braking frequency: 0.0Hz to max. frequency,
braking time:0.0~100.0 seconds, braking current value: 0.0%~100.0%
Jogging control
Jog frequency range: 0.00Hz to max. frequency; jog Ac/deceleration time:
0.0~6500.0s.
4 / 18
Items
Specifications
Built-in PID
Easy to realize closed-loop control system for the process control.
Automatic voltage
regulation(AVR)
Automatically maintain a constant output voltage when the voltage of
electricity grid changes.
Speed tracking method
Automatically track current motor speed when the inverter starts
Personalization
function
Self-inspection of
peripherals after
power-on
After powering on, peripheral equipment will perform safety testing, such as
ground, short circuit, etc.
Quick current limiting
The current limiting algorithm is used to reduce the inverter over current
probability, and improve whole unit anti-interference capability.
Timing control
Timing control function: Time setting range(0m~6500m)
Running
Input Signal
DI Input
terminal
5 digital input terminals
AI1 analog input
1 analog AI1 input terminal, select 0~10V or 0~20mA input
Multi-speed
At most 16-speed can be set(Run by using the multi-function terminals or
program)
Emergency stop
Interrupt controller output
Fault reset
When the protection function is active, you can automatically or manually
reset the fault condition.
PID feedback
signal
Including DC(0~10V), DC(0~20mA)
Output Signal
Output terminal
1 way relay output terminal; 1 way DA1 analog output terminal
Relay output
There are 40 kinds of signals to choose from each way. Contact capacity of
the relay: Normally open contact 5A/AC 250V; 5A/DC 30V
DA1 analog
output
1 way analog output, you can select 16 kinds of signals such as frequency,
current, voltage, etc. The output signal range can be set arbitrarily within
0~10V/0~20mA.
Running command
channel
Three channels: Operation panel, control terminals and serial communication
port. They can be switched through a variety of ways.
Frequency source
Total 7 frequency sources: Digital, analog voltage, multi-speed, and serial
port.
Run function
Limit frequency, jump frequency, frequency compensation, auto-tuning, PID
control
Protection
function
Inverter protection
Overvoltage protection, undervoltage protection, overcurrent protection,
overload protection, overheat protection, overcurrent stall protection,
overvoltage stall protection, losting-phase protection (Optional),
communication error, PID feedback signal abnormalities, and short circuit to
ground protection.
Display
LED
display
keyboard
Running
information
Monitoring objects including: Running frequency, set frequency, bus voltage,
output voltage, output current, output power, output torque, input terminal
status, output terminal status, analogAI1 value , motor Actual running
speed ,PID set value percentage, PID feedback value percentage.
Error
information
At most save three error message, and the time, type, voltage, current,
frequency and work status can be queried when the failure is occurred.
Key lock and function
selection
Lock part or all of keys, define the function scope of some keys to prevent
misuse.
IGBT temperature
Display current IGBT temperature inside the inverter.
Communication
RS485
Built-in 485
Environment
Environment
temperature
-10~40℃(The environment temperature in 40~50 ℃, please derating use)
Storage temperature
-20~65 ℃
Environment humidity
Less than 90% R.H, no condensation.
Vibration
Below 5.9m/s²(= 0.6g)
Application sites
Indoor where no sunlight or corrosive, explosive gas and water vapor, dust,
flammable gas, oil mist, water vapor, drip or salt, etc.
Altitude
Use below 1000m without derating, 1% for each 100m increasing above
1000m, the highest altitude is 3000m
Protection level
IP20
Product
standard
Product adopts safety
standards.
IEC61800-5-1:
Product adopts EMC
standards.
IEC61800-3:
Cooling method
Forced air cooling
Installation method
Rail mounting, wall mounting

5 / 18
6.Wiring diagram
Notes in main circuit wiring
(1).Wiring specifications, please implement wiring in accordance with electrical regulations;
(2).Do not connect AC to the output of frequency converter (U, V, W), otherwise the frequency inverter
will be damaged;
(3).Power supply wiring, please try to use isolation line and pipeline, and the isolation line or pipeline ends
grounded;
(4).Frequency inverter grounding wire can not be grounded together with welding machine, high-power
motor or high current load, please grounding alone;
(5).Grounding please grounding correctly,grounding resistor less than 10Ω.
Notes in wiring control circuit
(1).Please separate the control signal line from the main circuit line and other power lines;
(2).To prevent misoperation caused by interference, use twisted or double shielded wires,specification
0.5~2mm²;
(3).Make sure the permissible conditions of each terminal, such as power supply, maximum permissible
current, etc;
(4).The terminal wiring requirements, correct selection of accessories, such as: Voltmeter, input power
supply, etc;
(5).After completing the wiring, please check it correctly and make sure that it is correct before powering
it on.
7. Parameter list
In PI150 series frequency inverters ,some parameters are "manufacturer reserved", and their serial numbers
are not listed in the function parameter table,which leads to the discontinuity of some parameter serial numbers
in the table. For the parameters not introduced in the manual, please do not attempt to modify them to avoid
causing errors.
7.1. d0 group Monitoring function group
Code
Parameter name
Functional Description
Factory
setting
d0.00
Running frequency
Inverter theoretical operating frequency
0.01Hz
d0.01
Set frequency
Actual set frequency
0.01Hz
d0.02
DC bus voltage
Detected value for DC bus voltage
0.1V
d0.03
Output voltage
Actual output voltage
1V
d0.04
Output current
Effective value for Actual motor current
0.01A
d0.05
Output power
Calculated value for motor output power
0.1kW
d0.06
Output torque
Motor output torque percentage
0.1%
d0.07
DI input status
DI input status
-
d0.08
DO output status
DO output status
-
d0.09
AI1 voltage
AI1 input voltage value
0.01V
d0.12
Count value
Actual pulse count value in counting function
-
d0.13
Length value
Actual length in fixed length function -
-
d0.14
Actual operating speed
Motor actual running speed
-
d0.15
PID setting
Reference value percentage when PID runs
%
d0.16
PID feedback
Feedback value percentage when PID runs
%
d0.17
PLC stage
PLC Stage display when PLC runs
-
d0.19
Feedback speed
Inverter actual output frequency
0.01Hz
d0.20
Remaining run time
Remaining run time display, it is for timing run
control
0.1Min
d0.22
Current power-on time
Total time of current inverter power-on
1Min
d0.23
Current run time
Total time of current inverter run
0.1Min
d0.25
Communication set value
Frequency, torque or other command values set by
communication port
0.01%
d0.27
Master frequency setting display
Frequency set by F0.03 master frequency setting
source
0.01Hz
d0.28
Auxiliary frequency setting display
Frequency set by F0.04 auxiliary frequency
setting source
0.01Hz
d0.35
Inverter status
Display the running and standby etc status
information
-
d0.36
Inverter type
1:G type: Suitable for constant torque load
-
d0.37
AI1 voltage before correction
Input voltage value before linear correction of AI1
0.01V
6 / 18
7.2. F0 group Basic Functional Parameter Group
Code
Parameter name
Setting range
Factory
setting
Change
F0.00
Motor control mode
0:Vector control without PG ; 2:V/F control
2
★
F0.01
Keyboard set frequency
0.00Hz~F0.19(Maximum frequency)
50.00Hz
☆
F0.02
Frequency command
resolution
1: 0.1Hz
2: 0.01Hz
2
★
F0.03
Frequency source master
setting
0:Keyboard set frequency(F0.01 ,UP/DOWN
can be modified, power-down without
memory)
1: Keyboard set
frequency(F0.01 ,UP/DOWNcan be modified,
power-down with memory);
2:Analog AI1 setting;
4:Panel potentiometer setting(External keyboard
use);
6:Multi-speed operation setting ;
7:Simple PLC program setting;
8:PID control setting;
9:Remote communications setting
1
★
F0.04
Frequency source auxiliary
setting
Same as F0.03 setting
0
★
F0.05
Reference object selection
for frequency source
auxiliary setting
0. Relative to maximum frequency;
1. Relative to master frequency source 1
2. Relative to master frequency source 2
0
☆
F0.06
Frequency source auxiliary
setting range
0%~150%
100%
☆
F0.07
Frequency superimposed
selection
Units digit: Frequency source selection;
Tens digit: Arithmetic relationship of master
and auxiliary for frequency soruce
00
☆
F0.08
Auxiliary offset frequency
0.00Hz~F0.19 (Maximum frequency)
0.00Hz
☆
F0.09
Shut down memory
selection
0: W/O memory;
1:With memory
1
☆
F0.10
Frequency command
UP/DOWN reference
when running
0: Running frequency ;
1: Set frequency
0
★
F0.11
Command source selection
0. Keyboard control (LED off);
1.Terminal block control (LED on)
2. Communications command control (LED
flashes)
3. Keyboard control+ Communications
command control
4.Keyboard control+ Communications
command
control+ Terminal block control
0
☆
F0.12
Binding frequency source
for command source
Units digit: Keyboard command binding
frequency source selection
0:Not binded;
1: Keyboard set frequency;
2:AI1 setting;
4:Panel potentiometer setting (External
keyboard)
6:Multi-speed setting;
7:Simple PLC setting;
8:PID setting;
9:Communications reference
Tens digit: Terminal command binding
frequency source selection (0~9, same as units
digit)
Hundreds digit: Communication command
binding frequency source selection (0~9, same as
units digit)
000
☆
F0.13
Acceleration time1
0.0s~6500s
Depends on
models
☆
F0.14
Deceleration time1
0.0s~6500s
Depends on
models
☆
F0.15
Ac/Deceleration time unit
0:1s; 1:0.1s; 2:0.01s
1
★
F0.16
Ac/deceleration time
reference frequency
0:F0.19(Maximum frequency) 1:Set
frequency;
2:100Hz
0
★
F0.17
Carrier frequency
adjustment
0:NO ;
1: YES
0
☆
F0.18
Carrier Frequency
0.5kHz~16.0kHz
Depends on
models
☆
F0.19
Maximum output
frequency
50.00Hz~320.00Hz
50.00Hz
★
F0.20
Upper limit frequency
source
0:F0.21setting; 1:Analog AI1
setting;
5: Communications reference
0
★
F0.21
Upper limit frequency
F0.23 (Lower limit frequency)~F0.19
(Maximum frequency)
50.00Hz
☆
F0.22
Upper limit frequency offset
0.00Hz~F0.19(Maximum frequency)
0.00Hz
☆
F0.23
Lower limit frequency
0.00Hz~F0.21(Upper limit frequency )
0.00Hz
☆
F0.24
Running direction
0: Same direction; 1: Opposite
direction
0
☆
F0.26
AIAnalog accuracy
0: 0.01Hz; 1: 0.05Hz;
2: 0.1Hz; 3: 0.5Hz
1
☆
7.3. F1 group Input terminals
Code
Parameter name
Setting range
Factory
setting
Change
F1.00
DI1 terminal function selection
0~51
1
★

7 / 18
F1.01
DI2 terminal function selection
2
★
F1.02
DI3 terminal function selection
8
★
F1.03
DI4 terminal function selection
9
★
F1.04
DI5 terminal function selection
0
★
The functions of digital multi-functional input terminal DI1~DI5 can be set by parameter F1.00~F1.04.
The optional functions are shown in the following table:
Setting
value
Function
Description
0
No function
The terminal for not use can be set to "no function" to prevent
accidental operation.
1
Forward run (FWD)
External terminals are used to control the FWD run mode of inverter.
2
Reverse run (REV)
External terminals are used to control the REV run mode of inverter.
3
Three-wire operation
control
This terminal is used to determine the inverter's three-wire control
mode. For details, please refer to the instructions of function code
F1.10 ("terminal command mode).
4
Forward JOG(FJOG)
FJOG means Forward JOG running, RJOG means Reverse JOG
running. For Jog running frequency and Jog Ac/deceleration time,
please refer to the description of the function code F7.00, F7.01, F7.02.
5
Reverse JOG(RJOG)
Modify frequency increment/decrement command when the frequency
is referenced by external terminal. Adjust up/down the set frequency
when the digital setting is selected as the frequency source.
6
Terminal UP
7
Terminal DOWN
8
Free stop
The inverter output is blocked, at the time, the parking process of
motor is not controlled by the inverter. This way is same as the
principle of free stop described in F3.07.
9
Fault reset (RESET)
The function make use of terminal for fault reset. It has same
function with RESET key on the keyboard. This function can be
used to realize remote fault reset
10
Run pausing
The inverter slows down and stops,but all operating parameters are
memorized.Such as PLC parameters,wobbulate frequency
parameters, and PID parameters. This terminal signal disappears, the
inverter reverts to the previous state of running before parking
11
External fault normally
open input
When the signal is sent to the inverter, the inverter reports fault
Err.15, and performs troubleshooting according to fault protection
action (For details, please refer to the function code F8.17)
12
Multi-speed terminal 1
The setting of 16 stage speed or 16 kinds of other command can be
achieved through the 16 states of the four terminals.
13
Multi-speed terminal 2
14
Multi-speed terminal 3
15
Multi-speed terminal 4
16
Ac/deceleration time
selection terminal 1
The selection of 4 ac/deceleration times can be achieved through the
4 states of the two terminals.
17
Ac/deceleration time
selection terminal 2
18
Frequency source
switching
Used to switch between different frequency sources.
According to the setting of frequency source selection function code
(F0.07) , the terminal is used to switch between two frequency sources
19
UP/DOWN setting
(Terminal, keyboard)
When the frequency reference is the digital frequency, this terminal is
used to clear the changed frequency value by terminal UP/DOWN or
keyboard UP/DOWN, so that the reference frequency can recover to
the set value of F0.01
20
Run command switch
terminal 1
When the command source is set to the terminal control (F0.11 =1), the
terminal can be used to switch between terminal control and keyboard
control.
When the command source is set to the communication control(F0.11
= 2), the terminal can be used to switch between communication
control and keyboard control.
21
Ac/deceleration
prohibited
Ensure the inverter is free from external signals affect (Except for
shutdown command), maintain current output frequency.
22
PID pause
PID is temporarily disabled, the inverter maintains current output
frequency, no longer performs PID adjustment of frequency source.
23
PLC status reset
When PLC pauses and runs again, this terminal is used to reset the
inverter to the initial state of simple PLC.
24
Wobbulate pause
When the inverter outputs at center frequency. Wobbulate will pause
25
Counter input
Input terminal of the count pulse
26
Counter reset
Clear counter status
27
Length count input
Input terminal of the length count.
28
Length reset
Clear length
32
Immediately DC
braking
If the terminal is active, the inverter switches directly to DC braking
status
33
External fault normally
closed input
When the signal of external fault normally closed input is inputted into
the inverter, the inverter will report fault Err.15 and shutdown.
34
Frequency change
enable
If the function is set to be valid, when the frequency changes, the
inverter does not respond to frequency changes until the terminal state
is invalid.
35
PID action direction
as reverse
If the terminal is valid, PID action direction opposites to the direction
set by E2.03
36
External parking
terminal 1
Under keyboard control mode, the terminal can be used to stop the
inverter, same as STOPkey on the keyboard.
37
Control command
switch terminal 2
Used to switch between terminal control and communication control. If
the command source is selected as terminal control, the system will be
switched to the communication control mode when the terminal is
active; vice versa.
38
PID integral pause
When the terminal is active, the PID integral adjustment function is
paused, but the proportion and differential adjustments of PID are still
valid.
39
Switch between frequency
source master setting and
preset frequency
When the terminal is active, the frequency source Ais replaced by the
preset frequency (F0.01)
40
Switch between frequency
source auxiliary setting
and preset frequency
When the terminal is active, the frequency source B is replaced with
the preset frequency (F0.01)
43
PID parameter
switching
When DI terminal (E2.19 = 1) is used to switch PID parameters, if the
terminal is invalid, PID parameters use E2.13~E2.15; if the terminal is
valid, PID parameters use E2.16~E2.18
44
Custom fault 1
When custom fault 1 and custom fault 2 are active, the inverter
respectively alarms fault Err.27 and fault Err.28, and deals with them
according to the mode selected by the fault protection action F8.19.
45
Custom fault 2
47
Emergency parking
If the terminal is valid, the inverter will park at the fastest speed, and
the current maintains at the set upper limit during the parking process.
This function is used to meet the requirements that the inverter needs
to stop as soon as possible when the system is in a emergency state.
48
External parking terminal
In any control mode (Keyboard control, terminal control,
8 / 18
2
communication control), the terminal can be used to decelerate the
inverter until stop, at the time the deceleration time is fixed for
deceleration time 4.
49
Deceleration DC
braking
If the terminal is valid, firstly the inverter decelerates to the initial
frequency of stop DC braking, and then switches directly to DC
braking status.
50
Clear current running time
If the terminal is valid, the inverter's current running time is cleared
Table 1 Multi command functions description:Over 4 segments command terminal, can be combined
into 16 states, each state corresponds to the 16 instruction set value. As shown in Table 1 below:
K4
K3
K2
K1
Command Setting
Parameters
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
0-Stage speed setting 0X
E1.00
OFF
OFF
OFF
ON
1-Stage speed setting 1X
E1.01
OFF
OFF
ON
OFF
2-Stage speed setting 2X
E1.02
OFF
OFF
ON
ON
3-Stage speed setting 3X
E1.03
OFF
ON
OFF
OFF
4-Stage speed setting 4X
E1.04
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
5-Stage speed setting 5X
E1.05
OFF
ON
ON
OFF
6-Stage speed setting 6X
E1.06
OFF
ON
ON
ON
7-Stage speed setting 7X
E1.07
ON
OFF
OFF
OFF
8-Stage speed setting 8X
E1.08
ON
OFF
OFF
ON
9-Stage speed setting 9X
E1.09
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
10-Stage speed setting 10X
E1.10
ON
OFF
ON
ON
11-Stage speed setting 11X
E1.11
ON
ON
OFF
OFF
12-Stage speed setting 12X
E1.12
ON
ON
OFF
ON
13-Stage speed setting 13X
E1.13
ON
ON
ON
OFF
14-Stage speed setting 14X
E1.14
ON
ON
ON
ON
15 Stage speed setting 15X
E1.15
F1.10
Terminal command mode
0: Two-wire type 1 1; 1: Two-wire type 2 2;
2: Three-wire type 1; 3: Three-wire type 2
0
★
F1.11
TerminalUP/DOWN
0.001Hz/s~65.535Hz/s
1.000Hz/s
☆
F1.12
Minimum input for AIC1
0.00V~F1.14
0.30V
☆
F1.13
F1.12 corresponding setting
-100.0%~+100.0%
0.0%
☆
F1.14
Maximum input for AIC1
F1.12~+10.00V
10.00V
☆
F1.15
F1.14 corresponding setting
-100.0%~+100.0%
100.0%
☆
F1.25
AIinput setting selection
Units digit:AI1 AI1 Below the minimum
input setting selection
0: Corresponding to the minimum input set
1:0.0%;
000
☆
F1.30
DI filter time
0.000s~1.000s
0.010s
☆
F1.31
AI1 filter time
0.00s~10.00s
0.10s
☆
F1.35
DI terminal Mode slection 1
Units digit:DI1 :
0:High level active; 1: Low level active
Tens digit: DI2(Same as the units digit);
Hundreds digit:DI3(Same as the units digit)
Thousands digit:DI4 (Same as the units
digit));
Ten thousands digit:DI5(Same as the units
digit)
00000
★
F1.37
DI1 delay time
0.0s~3600.0s
0.0s
★
F1.38
DI2 delay time
0.0s~3600.0s
0.0s
★
F1.39
DI3 delay time
0.0s~3600.0s
0.0s
★
F1.40
Define the input terminal
repeat
0:Unrepeatable;
1:Repeatable
0
★
7.4. F2 group Out put terminal
Code
Parameter name
Setting range
Factory
setting
Change
F2.02
Relay output function selection (TA.TC)
0~40
2
☆
Relay output function description:
Setting
value
Functions
Description
0
No output
No output action
1
Inverter running
Inverter is in running state, the output frequency (Can be
zero),the output ON signal.
2
Fault output (Fault down )
When the drive fails and downtime, the output ON signal.
3
Frequency level detection FDT1
output
Please refer to the function code F7.23, F7.24's instructions.
4
Frequency arrival
Please refer to the description of function code F7.25.
5
Zero-speed running (No output
when shutdown)
Inverter operation and the output frequency is 0, output ON
signal. When the drive is shut down, the signal is OFF.
6
Motor overload pre-alarm
Before the motor overload protection, according to the
overload pre-alarm threshold value judgment, more than the
pre-alarm threshold value output ON signal. Motor overload
parameter settings refer to the function code F8.02~F8.04.
7
Inverter overload pre- alarm
Before the inverter overload occurs 10s, output ON signal.
Setup counter arrive.
8
Setup counter arrive
When the count reaches the set value of E0.08, output ON
signal. Specifies the count value reaches.
9
Specifies the count value
reaches
When the count reaches the set value of E0.09, output ON
signal. Counting Function Reference E0 group.
10
Length arrival
When the actual length of the detection of more than E0.05
set length, output ON signal.
11
PLC cycle is complete
After simple PLC completes one cycle, the output of a pulse
width of 250ms signal.
12
Total running time arrival
Inverter total running time of more than F7.21 F6.07 set
time,the output ON signal.
13
Limited in frequency
When the set frequency exceeds the upper limit frequency or
lower frequency, and output frequency is beyond the upper
limit frequency or lower limit frequency, output ON signal.
14
Torque limiting
Drive under the speed control mode, when the output torque
reaches the torque limit, the inverter is stall protection status,
while the output ON signal.
15
Ready to run
When the inverter main circuit and control circuit power
supply has stabilized, and the drive does not detect any fault
information, the drive is in an operational state, output ON

9 / 18
signal.
17
Upper frequency arrival
When the operating frequency reaches the upper
frequency,output ON signal.
18
The lower frequency arrival (No
output when shutdown)
When the operating frequency reaches the lower frequency,
output ON signal. The next stop status signal is OFF.
19
Under voltage state output
When the inverter is in an undervoltage condition, output ON
signal.
20
Communication setting
Refer to the communication protocol.
23
Zero-speed operation 2 (Shutdown
also output)
The inverter‟s output frequency is 0, output ON signal. The
signal is also ON when shutdown.
24
Cumulative power-on time arrival
When the inverter's accumulated power on time (F6.08) over
F7.20 the set time, the output ON signal.
25
Frequency level detection FDT2
output
Please refer to the function code F7.26, F7.27's instructions.
26
Frequency 1 reaches output
Please refer to the function code F7.28, F7.29's instructions.
27
Frequency 2 reaches output
Please refer to the function code F7.30, F7.31's instructions.
28
Current 1 reaches output
Please refer to the function code F7.36, F7.37's instructions.
29
Current 2 reaches output
Please refer to the function code F7.38, F7.39's instructions.
30
Timing reach output
When the timer function selection (F7.42) is valid, the drive
time to reach this run after the set time runs out, output ON
signal.
31
AI1 input overrun
When the value of analog input AI1 greater than F7.51 (AI1
input protection limit) or less than F7.50 (AI1 input
protection under), output ON signal.
33
Off load
When the inverter is off-load state, output ON signal.
34
Reverse operation
Inverter in reverse run, output ON signal
35
0 current state
Refer to the description of function code F7.32, F7.33.
36
Module temperature reaches
Inverter module heatsink temperature (F6.06) reach the set
module temperature reaches value (F7.40), output signal ON.
37
Software current limit
Please refer to the function code F7.34, F7.35's instructions.
38
The lower frequency arrival (Stop
and output)
When the operating frequency reaches the lower limit
frequency, output ON signal. In shutdown state of the signal
is also ON.
40
Current running time of arrival
When the inverter starts running time is longer than the time
set by F7.45, it outputs ON signal.
F2.07
DA1 output function selection
0~17
2
☆
Analog Output DA output range is 0V~10V, or 0mA~20mA, with the corresponding scaling function
relationship in the following table
Setting
value
Functions
Description
0
Running frequency
0~max. output frequency
1
Set frequency
0~max. output frequency
2
Output current
0~2 times the motor rated current
3
Output torque
0~2 times the motor rated toqure
4
Output power
0~2 times rated power
5
Output voltage
0~1.2 times inverter rated voltage
7
Anolog AI1
0V~10V(Or 0~20mA)
10
Lentgh value
0~max. setting length
11
The count value
0~max. count value
12
Coummunication set
0.0%~100.0%
13
Motor speed
0~max. output frequency correspondent speed
14
Output current
0.0A~100.0A(Inverter power≦55kW);
0.0A~1000.0A(Inverter power>55kW)
15
DC bus voltage
0.0V~1000.0V
17
Frequency source main set
0~max. output frequency
F2.11
Relay 1 output delay time
0.0s~3600.0s
0.0s
☆
F2.15
DO terminal active status selection
Units digit:Reserve
Tens digit:Relay 0:Positive;
1:Negtive
00000
☆
F2.16
DA1 zero bias coefficient
-100.0%~+100.0%
20.0%
☆
F2.17
DA1 gain
-10.00~+10.00
0.8
☆
7.5. F3 group Start and stop control group
Code
Parameter name
Setting range
Factory
setting
Change
F3.00
Start-up mode
0:Direct startup;
1:Speed tracking restart
2:Pre-excitation start (AC asynchronous
motor)
0
☆
F3.01
Speed tracking mode
3:Hard speed tracking mode
3
★
F3.02
Speed tracking speed
0~100
20
☆
F3.03
Start frequency
0.00Hz~10.00Hz
0.00Hz
☆
F3.04
Hold time for start frequency
0.0s~100.0s
0.0s
★
F3.05
DC pre-excitation current
0%~100%
0%
★
F3.06
DC pre-excitation time
0.0s~100.0s
0.0s
★
F3.07
Stop mode
0:Deceleration stop; 1: Free stop
0
☆
F3.08
DC start frequency
0.00Hz~F0.19(Max.frequency)
0.00Hz
☆
F3.09
DC waiting time
0.0s~100.0s
0.0s
☆
F3.10
Braking current
0%~100%
0%
☆
F3.11
Braking time
0.0s~100.0s
0.0s
☆
F3.12
Braking utilization rate
0%~100%
100%
☆
F3.13
Ac/deceleration mode
0:Linear acceleration and deceleration;
1:S curve acceleration and deceleration A
2:S curve acceleration and deceleration B
0
★
F3.14
Proportion of S curve start-section
0.0%~(100.0%.~F3.15)
30.0%
★
10 / 18
F3.15
Proportion of S curve end-section
0.0%~(100.0%.~F3.14)
30.0%
★
7.6. F4 group V/F control parameter group
Code
Parameter name
Setting range
Factory
setting
Change
F4.00
V/F curve setting
0: Linear V/F;
1: Multi-point V/F;
2: Square V/F;
3: 1.2th power V/F;
4: 1.4th power V/F;
6: 1.6th power V/F;
8: 1.8th power V/F;
10: V/F completely separate;
11: V/F half separate
0
★
F4.01
Torque boost
0.0% (Automatic torque boost)
0.1~30%
0.0%
★
F4.02
Torque boost cut-off frequency
0.00Hz~F0.19 (Max. Frequency)
15.00Hz
★
F4.03
Multi-point V/F frequency point 1
0.00Hz~F4.05
0.00Hz
★
F4.04
Multi-point V/F voltage point V1
0.0%~100.0%
0.0%
★
F4.05
Multi-point V/F frequency point 2
F4.03~F4.07
0.00Hz
★
F4.06
Multi-point V/F voltage point V2
0.0%~100.0%
0.0%
★
F4.07
Multi-point V/F frequency point 3
F4.05~b0.04 (Motor rated frequency)
0.00Hz
★
F4.08
Multi-point V/F voltage point V3
0.0%~100.0%
0.0%
★
F4.09
V/F slip compensation gain
0.0%~200.0%
0.0%
☆
F4.10
V/F overexcitation gain
0~200
80
☆
F4.11
V/F oscillation suppression gain
0~100
0
☆
F4.12
V/F separation voltage source
0~9
0
☆
F4.13
V/F separation voltage digital setting
0V~motor rated voltage
0V
☆
F4.14
V/F separation voltage rise time
0.0s~1000.0s
0.0s
☆
7.7. F5 group Vector control parameter group
Code
Parameter name
Setting range
Factory
setting
Change
F5.00
Proportion of speed loop G1
1 ~ 100
30
☆
F5.01
Speed loop integral T1
0.01s ~ 10.00s
0.50s
☆
F5.02
Switching frequency 1
0.00 ~ F5.05
5.00Hz
☆
F5.03
Proportion of speed loop G2
0 ~ 100
20
☆
F5.04
Speed loop integral T2
0.01s ~ 10.00s
1.00s
☆
F5.05
Switching frequency 2
F5.02 ~ F0.19(Max. frequency)
10.00Hz
☆
F5.06
Speed loop integral
0: Invalid; 1: Valid
0
☆
F5.07
Torque limit source under speed
control mode
0: Function code F5.08 set; 1:AI1
set;
5: Communication set
0
☆
F5.08
Torque upper limit digital setting
0.0% ~ 200.0%
150.0%
☆
F5.09
Vector control differential gain
50% ~ 200%
150%
☆
F5.10
Speed loop filtering time
0.000s ~ 0.100s
0.000s
☆
F5.11
Vector control overexcitation gain
0 ~ 200
64
☆
F5.12
Excitation regulator proportional gain
0 ~ 60000
2000
☆
F5.13
Excitation regulator integral gain
0 ~ 60000
1300
☆
F5.14
Torque regulator proportional gain
0 ~ 60000
2000
☆
F5.15
Torque regulator integral gain
0 ~ 60000
1300
☆
7.8. F6 group Keyboard and display
Code
Parameter name
Setting range
Factory
setting
Change
F6.00
STOP/RESET key functions
0:STOP/RESET key is enabled only
under keyboard operation mode
1:STOP/RESET key is enabled under any
operation mode
1
☆
F6.01
Running status display parameters 1
0x0000 ~ 0xFFFF
001F
☆
F6.02
Running status display parameters 2
0x0000 ~ 0xFFFF
0000
☆
F6.03
Stop status display parameters
0x0001 ~ 0xFFFF
0033
☆
F6.04
Load speed display coefficient
0.0001 ~ 6.5000
3.0000
☆
F6.05
Decimal places for load speed
display
0:0 decimal place; 2:2 decimal place
1:1 decimal place; 3:3 decimal place
1
☆
F6.06
Inverter module radiator
temperature
0.0℃~ 100.0℃
-
●
F6.07
Total running time
0h ~ 65535h
-
●
F6.08
Total power-on time
0h ~ 65535h
-
●
F6.09
Total power consumption
0 ~ 65535℃
-
●
F6.10
Product number
Inverter product number
-
●
F6.11
Software version
Software version of control board
-
●
F6.13
Communication read and write
data selection
Single digit: CRC mistake selection:
0: Reply verification error;
1: No reply on verification error;
Ten digit: Broadcast message screening
selection: 0-no screening; 1-screening
Hundred digit: Inverter fault information
Read selection: 0-read; 1-no read
011
☆

11 / 18
F6.17
Power correction coefficient
0.00 ~ 10.00
1.00
☆
F6.20
Keyboard lock selection
0:Only RUN and STOP keyps are valid;
2:Only RUN, STOP, UP, DOWN keys are
valid;
3:Only STOP key is valid
0
☆
F6.21
QUICK key Function Selection
0:No function;
1:Jog running;
2:Shit key;
3:Forward/reverse running switching;
4: Clear UP/DOWN setting;
5:Free stop;
6: Running command given in sequence
1
☆
7.9. F7 group Auxiliary function parameter group
Code
Parameter name
Setting range
Factory
setting
Change
F7.00
Jog running frequency
0.00Hz ~ F0.19 (Max. frequency)
6.00Hz
☆
F7.01
Jog acceleration time
0.0s ~ 6500.0s
5.0s
☆
F7.02
Jog deceleration time
0.0s ~ 6500.0s
5.0s
☆
F7.03
Jog priority
0:Invalid; 1:Valid
1
☆
F7.04
Jump frequency 1
0.00Hz ~ F0.19 (Max. frequency)
0.00Hz
☆
F7.05
Jump frequency 2
0.00Hz ~ F0.19 (Max. frequency)
0.00Hz
☆
F7.06
Jump frequency range
0.00Hz ~ F0.19 (Max. frequency)
0.00Hz
☆
F7.07
Jump frequency availability
0:Invalid; 1:Valid
0
☆
F7.08
Acceleration time 2
0.0s ~ 6500.0s
Depends on
models
☆
F7.09
Deceleration time 2
0.0s ~ 6500.0s
Depends on
models
☆
F7.10
Acceleration time 3
0.0s ~ 6500.0s
Depends on
models
☆
F7.11
Deceleration time 3
0.0s ~ 6500.0s
Depends on
models
☆
F7.12
Acceleration time 4
0.0s ~ 6500.0s
Depends on
models
☆
F7.13
Deceleration time 4
0.0s ~ 6500.0s
Depends on
models
☆
F7.14
Switching frequency point between
acceleration time 1 and acceleration
time 2
0.00Hz ~ F0.19 (Max. frequency)
0.00Hz
☆
F7.15
Switching frequency point between
deceleration time 1 and deceleration
time 2
0.00Hz ~ F0.19 (Max. frequency)
0.00Hz
☆
F7.16
Forward/reverse rotation dead-band
0.00s ~ 3600.0s
0.00s
☆
F7.17
Reverse rotation control
0:Allow; 1:Prohibit
0
☆
F7.18
Mode under lower limit frequency
0: Running at lower limit
frequency;
1: Stop; 2: Running at zero
speed
0
☆
F7.19
Droop control
0.00Hz ~ 10.00Hz
0.00Hz
☆
F7.20
Setting of power-on arrival time
0h ~ 36000h
0h
☆
F7.21
Setting of running arrival time
0h ~ 36000h
0h
☆
F7.22
Start protection selection
0:OFF; 1:ON
0
☆
F7.23
FDT1 detection value
0.00Hz ~ F0.19 (Max. frequency)
50.00Hz
☆
F7.24
FDT1 detection hysteresis value
0.0% ~ 100.0% (FDT1 level)
5.0%
☆
F7.25
Frequency reaches detection width
0.00 ~ 100% (Max. frequency)
0.0%
☆
F7.26
FDT2 detection value
0.00Hz ~ F0.19 (Max. frequency)
50.00Hz
☆
F7.27
FDT2 detection hysteresis value
0.0% ~ 100.0% (FDT2 level)
5.0%
☆
F7.28
Frequency detection value 1
0.00Hz ~ F0.19 (Max. frequency)
50.00Hz
☆
F7.29
Frequency detection width 1
0.0% ~ 100.0% (Max. frequency)
0.0%
☆
F7.30
Frequency detection value 2
0.00Hz ~ F0.19 (Max. frequency)
50.00Hz
☆
F7.31
Frequency detection width 2
0.0% ~ 100.0% (Max. frequency)
0.0%
☆
F7.32
0 current detection
0.0% ~ 300.0% (Motor rated
current)
5.0%
☆
F7.33
0 current delay
0.01s ~ 360.00s
0.10s
☆
F7.34
Current over-run value
0.0% (Not detected);
0.1% ~ 300.0% (Max. frequency)
200.0%
☆
F7.35
Current over-run time
0.00s ~ 360.00s
0.00s
☆
F7.36
Arrival current 1
0.0% ~ 300.0% (Motor rated
current)
100.0%
☆
F7.37
Current 1 width
0.0% ~ 300.0% (Motor rated
current)
0.0%
☆
F7.38
Arrival current 1
0.0% ~ 300.0% (Motor rated
current)
100.0%
☆
F7.39
Current 1 width
0.0% ~ 300.0% (Motor rated
current)
0.0%
☆
F7.40
Module temperature arrival
0℃~ 100℃
75℃
☆
F7.41
Cooling fan control
0: Fan run when inverter is
running;
1: Fan keep running
0
☆
F7.42
Timing function selection
0: Invalid; 1: Valid
0
★

12 / 18
F7.43
Timing run time selection
0: F7.44 set; 1:AI1 set;
Note: Analog input range
correspond to F7.44
0
★
F7.44
Timing run time
0.0Min ~ 6500.0Min
0.0Min
★
F7.45
Running time arrive
0.0Min ~ 6500.0Min
0.0Min
★
F7.46
Awaken frequency
Dormancy frequency
(F7.48)~maximum frequency
(F0.19)
0.00Hz
☆
F7.47
Awaken delay time
0.0s ~ 6500.0s
0.0s
☆
F7.48
Dormancy frequency
0.00Hz ~ awaken frequency
(F7.46)
0.00Hz
☆
F7.49
Dormancy delay time
0.0s ~ 6500.0s
0.0s
☆
F7.50
AI1 input voltage protection lower
limit
0.00V ~ F7.51
3.1V
☆
F7.51
AI1 input voltage protection upper
limit
F7.50 ~ 10.00V
6.8V
☆
7.10. F8 group Fault and protection parameter gruop
Code
Parameter name
Setting range
Factory
setting
Change
F8.00
Overcurrent stall gain
0~100
20
☆
F8.01
Lost speed stall protection current
100%~200%
-
☆
F8.02
Overload protection
0:Prohibit; 1:Allow
1
☆
F8.03
Motor overload protection gain
0.20~10.00
1.00
☆
F8.04
Motor overload pre-alarm coefficient
50%~100%
80%
☆
F8.05
Overvoltage stall gain
0(No overvoltage stall)~100
0
☆
F8.06
Overvoltage stall protection voltage /energy
consumption brake voltage
120%~150%(Three-phase)
130%
☆
F8.08
Output phase loss protection
0:Prohibit; 1:Allow
1
☆
F8.09
Short to ground protection
0:Invalid; 1:Valid
1
☆
F8.10
Number of automatic fault reset
0 ~ 32767
0
☆
F8.11
Fault DO action selection during automatic
fault
0:OFF ; 1:ON
0
☆
F8.12
Automatic fault reset
0.1s ~ 100.0s
1.0s
☆
F8.25
Abnormal reserve frequency
60.0% ~ 100.0%
100%
☆
F8.26
Momentary power cut action selection
0: Invalid; 1:
Deceleration;
2: Deceleration and stop
0
☆
F8.28
Recovery voltage judgment time of
momentary power cut
0.00s ~ 100.00s
0.50s
☆
F8.29
Judgment voltage of momentary power cut
50.0% ~ 100.0%(Standard bus
voltage)
80%
☆
7.11. F9 group Communication parameter group
Code
Parameter name
Setting range
Factory
setting
Change
F9.00
Baud rate
Unit:Modbus
2:1200BPS;
3:2400BPS;
4:4800BPS;
5:9600BPS;
6:19200BPS;
7:38400BPS;
8:57600BPS;
9:115200BPS
Tens digit: Reserved;
Hundreds digit : Reserved
Thousands digit:Reserved
6005
☆
F9.01
Data format
0:No parity (8-N-2);
1:Even parity (8-E-1)
2:Odd parity (8-O-1)
3:No parity (8-N-1)
0
☆
F9.02
This unit address
1 ~ 250 ,for broadcast address
1
☆
F9.03
Response delay
0ms ~ 20ms
2ms
☆
F9.04
Communication timeout time
0.0(Invalid ); 0.1 ~ 60.0s
0.0
☆
F9.05
Data transfer format selection
Units digit:Modbus
0: Non-standard Modbus protocol;
1:Stand Modbus protocol
Tens digit: Reserved
31
☆
F9.06
Communication read current resolution
0:0.01A ; 1:0.1A
0
☆
7.12. Fb group Control parameter optimization group
Code
Parameter name
Setting range
Factory
setting
Change
Fb.00
Fast current limiting manner
0:Disable; 1: Enable
1
☆
Fb.01
Undervoltage point setting
50.0% ~ 140.0%
100.0%
☆
Fb.02
Overvoltage point setting
200.0 ~ 2500.0V
-
★
Fb.03
Deadband compensation mode
selection
0: No compensation;
1:Compensation mode 1;
2: Compensation mode 2
1
☆
Fb.04
Current detection compensation
0 ~ 100
5
☆
Fb.05
Vector optimization without PG
mode selection
0: No compensation;
1:Compensation mode 1;
2: Compensation mode 2
1
★

13 / 18
Fb.06
Upper limiting frequency for
DPWM switching
0.00 ~ 15.00Hz
12.00Hz
☆
Fb.07
PWM modulation mode
0:Asynchronous; 1:Synchronous
0
☆
Fb.08
Random PWM depth
0:Invalid
1 ~10:PWM carrier frequency random
depth
0
☆
7.13. E0 group Wobbulate, fixed-length and counting group
Code
Parameter name
Setting range
Factory
setting
Change
E0.00
Swing setting manner
0:Relative to center frequency;
1: Relative to maximum Frequency
0
☆
E0.01
Wobbulate range
0.0% ~ 100.0%
0.0%
☆
E0.02
Sudden jump frequency range
0.0% ~ 50.0%
0.0%
☆
E0.03
Wobbulate cycle
0.1s ~ 3000.0s
10.0s
☆
E0.04
Triangle wave rise time coefficient
0.1% ~ 100.0%
50.0%
☆
E0.05
Set length
0m ~ 65535m
1000m
☆
E0.06
Actual length
0m ~ 65535m
0m
☆
E0.07
Pulse per meter
0.1 ~ 6553.5
100.0
☆
E0.08
Set count value
1 ~ 65535
1000
☆
E0.09
Specified count value
1 ~ 65535
1000
☆
7.14. E1 group Multi-speed, sample PLC parameter
Code
Parameter name
Setting range
Factory
setting
Change
E1.00
0 stage speed setting 0X
-100.0%~100.0%
0.0%
☆
E1.01
1 stage speed setting 1X
-100.0%~100.0%
0.0%
☆
E1.02
2 stage speed setting 2X
-100.0%~100.0%
0.0%
☆
E1.03
3 stage speed setting 3X
-100.0%~100.0%
0.0%
☆
E1.04
4 stage speed setting 4X
-100.0%~100.0%
0.0%
☆
E1.05
5 stage speed setting 5X
-100.0%~100.0%
0.0%
☆
E1.06
6 stage speed setting 6X
-100.0%~100.0%
0.0%
☆
E1.07
7 stage speed setting 7X
-100.0%~100.0%
0.0%
☆
E1.08
8 stage speed setting 8X
-100.0%~100.0%
0.0%
☆
E1.09
9 stage speed setting 9X
-100.0%~100.0%
0.0%
☆
E1.10
10 stage speed setting 10X
-100.0%~100.0%
0.0%
☆
E1.11
11 stage speed setting 11X
-100.0%~100.0%
0.0%
☆
E1.12
12 stage speed setting 12X
-100.0%~100.0%
0.0%
☆
E1.13
13 stage speed setting 13X
-100.0%~100.0%
0.0%
☆
E1.14
14 stage speed setting 14X
-100.0%~100.0%
0.0%
☆
E1.15
15 stage speed setting 15X
-100.0%~100.0%
0.0%
☆
E1.16
PLC Simple PLC running mode
0:Stop after single running;
1: Hold final value after single
2: Circulating
0
☆
E1.17
PLC memory selection
Units:power-down memory;
0:Power-down without memory;
1:Power-down memory;
Tens:stop with memory;;
0:Stop without memory; 1:Stop
memory
11
☆
E1.18
0 stage running time ~
0.0s(h) ~ 6500.0s(h)
0.0s(h)
☆
E1.19
0 stage ac/deceleration time selection
0:F0.13, F0.14; 1:F7.08,
F7.09;
2:F7.10, F7.11; 3:F7.12,
F7.13
0
☆
E1.20
1 stage running time T1
0.0s(h) ~ 6500.0s(h)
0.0s(h)
☆
E1.21
1 stage ac/deceleration time selection
Same to E1.19
0
☆
E1.22
2 stage running time T2
0.0s(h) ~ 6500.0s(h)
0.0s(h)
☆
E1.23
2 stage ac/deceleration time selection
Same to E1.19
0
☆
E1.24
3 stage running time T3
0.0s(h) ~ 6500.0s(h)
0.0s(h)
☆
E1.25
3 stage ac/deceleration time selection
Same to E1.19
0
☆
E1.26
4 stage running time T4
0.0s(h) ~ 6500.0s(h)
0.0s(h)
☆
E1.27
4 stage ac/deceleration time selection
Same to E1.19
0
☆
E1.28
5 stage running time T5
0.0s(h) ~ 6500.0s(h)
0.0s(h)
☆
E1.29
5 stage ac/deceleration time selection
Same to E1.19
0
☆
E1.30
6 stage running time T6
0.0s(h) ~ 6500.0s(h)
0.0s(h)
☆
E1.31
6 stage ac/deceleration time selection
Same to E1.19
0
☆
E1.32
7 stage running time T7
0.0s(h) ~ 6500.0s(h)
0.0s(h)
☆
E1.33
7 stage ac/deceleration time selection
Same to E1.19
0
☆
E1.34
8 stage running time T8
0.0s(h) ~ 6500.0s(h)
0.0s(h)
☆
E1.35
8 stage ac/deceleration time selection
Same to E1.19
0
☆
E1.36
9 stage running time T9
0.0s(h) ~ 6500.0s(h)
0.0s(h)
☆
E1.37
9 stage ac/deceleration time selection
Same to E1.19
0
☆
E1.38
10 stage running time T10
0.0s(h) ~ 6500.0s(h)
0.0s(h)
☆
14 / 18
E1.39
10 stage ac/deceleration time selection
Same to E1.19
0
☆
E1.40
11 stage running time T11
0.0s(h) ~ 6500.0s(h)
0.0s(h)
☆
E1.41
11 stage ac/deceleration time selection
Same to E1.19
0
☆
E1.42
12 stage running time T12
0.0s(h) ~ 6500.0s(h)
0.0s(h)
☆
E1.43
12 stage ac/deceleration time selection
Same to E1.19
0
☆
E1.44
13 stage running time T13
0.0s(h) ~ 6500.0s(h)
0.0s(h)
☆
E1.45
13 stage ac/deceleration time selection
Same to E1.19
0
☆
E1.46
14 stage running time T14
0.0s(h) ~ 6500.0s(h)
0.0s(h)
☆
E1.47
14 stage ac/deceleration time selection
Same to E1.19
0
☆
E1.48
15 stage running time T15
0.0s(h) ~ 6500.0s(h)
0.0s(h)
☆
E1.49
15 stage ac/deceleration time selection
Same to E1.19
0
☆
E1.50
Simple PLC run-time unit
0:S(s); 1:H(h)
0
☆
E1.51
Multi-stage command 0 reference
manner
0: Function code E1.00 reference
1: Analog AI1 reference;
5: PID control setting;
6:Keyboard set frequency (F0.01)
setting, UP/DOWN can be modified
0
☆
7.15. E2 group PID function parameter group
Code
Parameter name
Setting range
Factory
setting
Change
E2.00
PID setting source
0: E2.01 setting;
1: Analog AI1 reference
5: Communications reference;
6: Multi-stage command reference
0
☆
E2.01
PID keyboard reference
0.0% ~ 100.0%
50.0%
☆
E2.02
PID feedback source
0: Analog A1 given; 5: Communications
given;
0
☆
E2.03
PID action direction
0:Positive; 1:Negative
0
☆
E2.04
PID setting feedback range
0 ~ 65535
1000
☆
E2.05
PID inversion cutoff frequency
0.00 ~ F0.19(Maximum frequency)
0.00Hz
☆
E2.06
PID deviation limit
0.0% ~ 100.0%
2.0%
☆
E2.07
PID differential limiting
0.00% ~ 100.00%
0.10%
☆
E2.08
PID reference change time
0.00s ~ 650.00s
0.00s
☆
E2.09
PID feedback filter time
0.00s ~ 60.00s
0.00s
☆
E2.10
PID output filter time
0.00s ~ 60.00s
0.00s
☆
E2.11
PID feedback loss detection value
0.0%:Not judged feedback loss;
0.1% ~ 100.0%
0.0%
☆
E2.12
PID feedback loss detection time
0.0s to 20.0s
0.0s
☆
E2.13
Proportional gain KP1
0.0 to 200.0
80.0
☆
E2.14
Integration time Ti1
0.01s to 10.00s
0.50s
☆
E2.15
Differential time Td1
0.00s to 10.000s
0.000s
☆
E2.16
Proportional gain KP2
0.0 to 200.0
20.0
☆
E2.17
Integration time Ti2
0.01s to 10.00s
2.00s
☆
E2.18
Differential time Td2
0.00 to 10.000
0.000s
☆
E2.19
PID parameter switfching
conditions
0: No switching;
1: Switching via terminals
2: Automatically switching according to
deviation.
0
☆
E2.20
PID parameter switching
deviation 1
0.0% to E2.21
20.0%
☆
E2.21
PID parameter switching
deviation 2
E2.20 to 100.0%
80.0%
☆
E2.22
PID integral properties
Units digit: Integral separation
0: Invalid; 1: Valid
Tens digit: Whether stop integration when
output reaches limit
0: Continue; 1: Stop
00
☆
E2.23
PID initial value
0.0% to 100.0%
0.0%
☆
E2.24
PID initial value hold time
0.00s to 360.00s
0.00s
☆
E2.25
Maximum deviation of twice
outputs(Forward)
0.00% to 100.00%
1.00%
☆
E2.26
Maximum deviation of twice
outputs(Backward)
0.00% to 100.00%
1.00%
☆
E2.27
Computing status after PID stop
0: Stop without computing;
1: Stop with computing
1
☆
E2.29
PID automatic decrease
frequency selection
0:Invalid;
1:Valid
1
☆
E2.30
PID stop frequency
0.00Hz to maximum frequency(F0.19)
25
☆
E2.31
PID checking time
0s to 3600s
10
☆
E2.32
PID checking times
10 to 500
20
☆
7.16. b0 group Motor parameters
Code
Parameter name
Setting range
Factory
setting
Change
b0.00
Motor type selection
0: General asynchronous motor
1: Asynchronous inverter motor
0
★
b0.01
Rated power
0.1kW to 1000.0kW
Depends on
models
★
15 / 18
b0.02
Rated voltage
1V to 2000V
Depends on
models
★
b0.03
Rated current
0.01A to 655.35A(Inverter power ≦55kW);
0.1A to 6553.5A(Inverter rate> 55kW)
Depends on
models
★
b0.04
Rated frequency
0.01Hz to F0.19 (Maximum frequency)
Depends on
models
★
b0.05
Rated speed
1rpm to 36000rpm
Depends on
models
★
b0.06
Asynchronous motor
stator resistance
0.001Ω to 65.535Ω (Inverter power <= 55kW)
0.0001Ω to 6.5535Ω (Inverter power> 55kW)
Motor
parameters
★
b0.07
Asynchronous motor
rotor resistance
0.001Ω to 65.535Ω (Inverter power <= 55kW)
0.0001Ω to 6.5535Ω (Inverter power> 55kW)
Motor
parameters
★
b0.08
Asynchronous motor
leakage inductance
0.01mH to 655.35mH (inverter power <= 55kW)
0.001mH to 65.535mH (inverter power> 55kW)
Motor
parameters
★
b0.09
Asynchronous motor
mutual inductance
0.1mH to 6553.5mH (Inverter power <= 55kW)
0.01mH to 655.35mH (Inverter power> 55kW)
Motor
parameters
★
b0.10
Asynchronous motor
no-load current
0.01A to b0.03 (Inverter power <= 55kW)
0.1A to b0.03 (Inverter power> 55kW)
Motor
parameters
★
b0.27
Motor parameter auto
tunning
0: No operation
1: Asynchronous motor parameters still auto tuning
2: Asynchronous motor parameters comprehensive
auto tunning
0
★
7.17. y0 group Function code management
Code
Parameter name
Setting range
Factory
setting
Change
y0.00
Parameter initialization
0: No operation
1:Restore default parameter values, not including
motor parameters
2: Clear history
3: Restore default parameter values, including motor
parameters
4: Backup current user parameters
5: Restore from backup user parameters
0
★
y0.01
User password
0 to 65535
0
☆
y0.02
Function parameter
group display selection
Units digit: d group display selection
0: Not displays 1: Displays
Tens digit: E group display selection(The same
above)
Hundreds digit:b group display selection(The same
above)
Thousands digit:y group display selection(The same
above)
Tens thousands digit:L group display selection(The
same above)
11111
★
y0.03
Personality parameter
group display selection
Units digit:Reserved
Tens digit :User’s change parameter display selection
0:Not display 1:Display
00
☆
y0.04
Function code
modification properties
0: Modifiable
1: Not modifiable
0
☆
7.18. y1 group Fault query parameter group
Code
Parameter name
Setting range
Factory
setting
Change
y1.00
Type of the first fault
0: No fault
1: Inverter unit protection
2: Acceleration overcurrent
3: Deceleration overcurrent
4: Constant speed overcurrent
5: Acceleration overvoltage
6: Deceleration overvoltage
7: Constant speed overvoltage
8: Control power failure
9: Undervoltage
10: Inverter overload
11: Motor Overload
12: Input phase loss
13: Output phase loss
14: Module overheating
15: External fault
16: Communication abnormal
17: Contactor abnormal
18: Current detection abnormal
19: Motor self-learning
abnormal
20: Encoder/PG card abnormal
21: Parameter read and write
abnormal
22: Inverter hardware abnormal
23: Motor short to ground
24: Reserved
25: Reserved
26: Running time arrival
27: Custom fault 1
28: Custom fault 2
29; Power-on time arrival
30: Load drop
31: PID feedback loss when
running
40: Fast current limiting timeout
41: Switch motor when running
42: Too large speed deviation
43: Motor overspeed
45:Motor over-temperature
51:Initial position error
COF: communication failure
-
●
y1.01
Type of the second fault
-
●
y1.02
Type of the third(At last) fault
-
●
y1.03
Frequency of the third(At last) fault
-
-
●
y1.04
Current of the third(At last) fault
-
-
●
16 / 18
y1.05
Bus voltage of the third(At last) fault
-
-
●
y1.06
Input terminal status of the third(At last) fault
-
-
●
y1.07
Output terminal status of the third(At last)
fault
-
-
●
y1.08
Reserved
-
y1.09
Power-on time of the third(At last) fault
-
●
y1.10
Running time of the third(At last) fault
-
-
●
y1.13
Frequency of the second fault
-
●
y1.14
Current of the second fault
-
-
●
y1.15
Bus voltage of the second fault
-
-
●
y1.16
Input terminal status of the second fault
-
-
●
y1.17
Output terminal status of the second fault
-
-
●
y1.19
Power-on time of the second fault
-
●
y1.20
Running time of the second fault
-
-
●
y1.23
Frequency of the first fault
-
●
y1.24
Current of the first fault
-
-
●
y1.25
Bus voltage of the first fault
-
-
●
y1.26
Input terminal status of the first fault
-
-
●
y1.27
Output terminal status of the first fault
-
-
●
y1.29
Power-on time of the first fault
-
●
y1.30
Running time of the first fault
-
●
8. Fault alarm and countermeasures
PI150 can provide effective protection when the equipment performance is played fully. In case of
abnormal fault, the protection function will be invoked, the inverter will stop output, and the faulty relay
contact of the inverter will start, and the fault code will be displayed on the display panel of the inverter. Before
consulting the service department, user can perform self-check , analyze the fault cause and find out the
solution according to the instructions of this chapter. If the fault is caused by the reasons as described in the
dotted frame, please consult the agents of inverter or directly contact with our company.
No.
Fault
ID
Failure type
Possible causes
Solutions
1
Err.01
Inverter unit
protection
1.The short circuit of inverter
output happens
2.The wiring for the motor and the
inverter is too long
3.Module overheating
4.The internal wiring of inverter is
loose
5.The main control panel is
abnormal
6.The drive panel is abnormal.
7.The inverter module is abnormal
1.Eliminate peripheral faults
2.Additionally install the reactor or
the output filter
3.Check the air duct is blocked or
not and the fan is working normally
or not, and eliminate problems
4.Correctly plug all cables
5.Seek for technical support
2
Err.02
Acceleration
overcurrent
1.The acceleration time is too short
2.Manual torque boost or V/F curve
is not suitable
3.The voltage is low
4.The short-circuit or earthing of
inverter output happens
5.The control mode is vector and
without identification of parameters
6.The motor that is rotating is
started unexpectedly.
7.Suddenly increase the load in the
process of acceleration.
8.The type selection of inverter is
small
1.Increase acceleration time
2.Adjust manual torque boost or
V/F curve
3.Set the voltage to the normal range
4.Eliminate peripheral faults
5.Perform identification for the
motor parameters
6.Select Speed Tracking Start or
restart after stopping the motor.
7.Cancel the sudden load
8.Choose the inverter with large
power level
3
Err.03
Deceleration
overcurrent
1.The short-circuit or earthing of
inverter output happens
2.The control mode is vector and
without identification of parameters
3.The deceleration time is too short
4.The voltage is low
5.Suddenly increase the load in the
process of deceleration.
6.didn't install braking unit and
braking resistor
1.Eliminate peripheral faults
2.Perform identification for the
motor parameters
3.Increase the deceleration time
4.Set the voltage to the normal
range
5.Cancel the sudden load
6.Install braking unit and brake
resistor
4
Err.04
Constant speed
overcurrent
1.The short-circuit or earthing of
inverter output happens
2.The control mode is vector and
without identification of parameters
3.The voltage is low
4, Whether suddenly increase the
load when running
5.The type selection of inverter is
small
1.Eliminate peripheral faults
2.Perform identification for the
motor parameters
3.Set the voltage to the normal range
4.Cancel the sudden load
5.Choose the inverter with large
power level
5
Err.05
Acceleration
overvoltage
1.Didn't install braking unit and
braking resistor
2.The input voltage is high
3.There is external force to drag the
motor to run when accelerating.
4.The acceleration time is too short
1.Install braking unit and brake
resistor
2.Set the voltage to the normal range
3.Cancel the external force or
install braking resistor.
4.Increase acceleration time
6
Err.06
Deceleration
overvoltage
1.The input voltage is high
2.There is external force to drag the
motor to run when decelerating.
3.The deceleration time is too short
4.Didn't install braking unit and
braking resistor
1.Set the voltage to the normal range
2.Cancel the external force or
install braking resistor.
3.Increase the deceleration time
4.Install braking unit and brake
resistor
7
Err.07
Constant speed
overvoltage
1.There is external force to drag the
motor to run when running
2.The input voltage is high
1.Cancel the external force or install
braking resistor.
2.Set the voltage to the normal range
8
Err.08
Control power
failure
The range of input voltage is not
within the specification
Adjust the voltage to the range of
the requirements of specification
9
Err.09
Under voltage
fault
1.The momentary power cut
2.The inverter's input voltage is not
within the specification
3.The bus voltage is not normal
1.Reset fault
2.Adjust the voltage to the normal
range
3.Seek for technical support

17 / 18
4.The rectifier bridge and buffer
resistance are abnormal
5.The drive panel is abnormal.
6.The control panel is abnormal
10
Err.10
Inverter overload
1.The type selection of inverter is
small
2.Whether the load is too large or
the motor stall occurs
1.Choose the inverter with large
power level
2.Reduce the load and check the
motor and its mechanical conditions
11
Err.11
Motor Overload
1. Power grid voltage is too low
2.Whether the setting motor
protection parameters (F8.03) is
appropriate or not
3.Whether the load is too large or
the motor stall occurs
1.Check the power grid voltage
2.Correctly set this parameter.
3.Reduce the load and check the
motor and its mechanical
conditions
13
Err.13
Output phase loss
1.The lead wires from the inverter
to the motor is not normal
2.The inverter's three phase output
is unbalanced when the motor is
running
3.The drive panel is abnormal.
4.The module is abnormal
1.Eliminate peripheral faults
2.Check the motor's three-phase
winding is normal or not and
eliminate faults
3.Seek for technical support
14
Err.14
Module
overheating
1.The air duct is blocked
2.The fan is damaged
3.The ambient temperature is too
high
4.The module thermistor is
damaged
5.The inverter module is damaged
1.Clean up the air duct
2.Replace the fan
3.Decrease the ambient temperature
4.Replace the thermistor
5.Replace the inverter module
15
Err.15
External equipment
fault
Input external fault signal through
the multi-function terminal DI
Reset run
16
Err.16
Communication
fault
1.The communication cable is not
normal
2.The settings for communication
expansion card F9.07 are incorrect
3.The settings for communication
parameters F9 group are incorrect
4.The host computer is not working
properly
1.Check the communication cable
2.Correctly set the communications
expansion card type
3.Correctly set the communication
parameters
4.Check the wiring of host computer
17
Err.17
Contactor fault
1.Input phase loss
2.The drive plate and the contact
are not normal
1.Check and eliminate the existing
problems in the peripheral line
2.replace the drive, the power
board or contactor
18
Err.18
Current detection
fault
1.Check Hall device
2.The drive panel is abnormal.
1.Replace the drive panel
2.Replace hall device
19
Err.19
Motor parameter
auto tuning fault
1.The motor parameters was not set
according to the nameplate
2.The identification process of
parameter is timeout
1.Correctly set motor parameter
according to the nameplate
2.Check the lead wire from the
inverter to the motor
21
Err.21
EEPROM read
and write fault
EEPROM chip is damaged
Replace the main control panel
22
Err.22
Inverter hardware
fault
1.Overvoltage
2.Overcurrent
1.Eliminate overvoltage fault
2.Eliminate overcurrent fault
23
Err.23
Short-circuit to
ground fault
Motor short to ground
Replace the cable or motor
26
Err.26
Cumulative
running time
arrival fault
Cumulative running time arrival
fault
Clear history information by using
initialization function parameters
27
Err.27
Custom fault 1
Input custom fault 1 signal through
the multi-function terminal DI
Reset run
28
Err.28
Custom fault 2
Input custom fault 2 signal through
the multi-function terminal DI
Reset run
29
Err.29
Total power-on
time arrival fault
Total power-on time reaches the set
value
Clear history information by using
initialization function parameters
31
Err.31
PID feedback loss
when running
fault
PID feedback is less than the set
value of E2.11
Check PID feedback signal or set
E2.11 to an appropriate value
40
Err.40
Quick current
limiting fault
1.Whether the load is too large or
the motor stall occurs
2.The type selection of inverter is
small
1.Reduce the load and check the
motor and its mechanical conditions
2.Choose the inverter with large
power level
42
Err.42
Too large speed
deviation fault
1.The setting for Too Large Speed
Deviation parameters(F8.15, F8.16)
is unreasonable.
2.The setting for encoder
parameters is incorrect;
3.The parameter was not identified
1.Reasonably set the detection
parameters
2.Correctly set encoder parameters
3.Perform identification for the
motor parameters
51
Err.51
Initial position
error
The deviation between the motor
parameters and the actual
parameters is too large
Reconfirm the correct motor
parameters, focus on whether the
rated current is set to too small.
-
COF
Communication
failure
1.Keyboard interface control board
interface;
2.Keyboard or crystal connector;
3.Control board or keyboard
hardware damage;
4.Keyboard line is too long,
causing the interference.
1.Detection of keyboard interface,
control board interface is abnorma.
2.Detect keyboard, crystal joints
are abnormal.
3.Replace control board or keyboard.
4. Consult factory, seek help.

18 / 18
Figure:
Installation dimension drawing of PI150 keyboard:
Outline dimension drawing of keyboard
Dimension drawing of PI150 keyboard compartment:
Dimension drawing of keyboard compartment
PI150 English Manual V4.2
This manual suits for next models
18
Table of contents
Other Inorea Inverter manuals
Popular Inverter manuals by other brands

Siemens
Siemens micromaster 410 operating instructions

Solar Stik
Solar Stik 11-1000020 Operator and maintenance manual

Generac Power Systems
Generac Power Systems Guardian 5340 Specification sheet

Dometic
Dometic TEC 40D Operation installation manual

SolaX Power
SolaX Power X3-Retro Fit Series user manual

Lenze
Lenze i950 Series Mounting and switch-on instructions












