Intel SBC 711 Quick user guide
Other Intel Computer Hardware manuals

Intel
Intel X3350 - Xeon 2.66 Ghz 12M L2 Cache 1333MHz FSB LGA775 Quad-Core... Guide

Intel
Intel RS2WC080 Installation manual

Intel
Intel 946GZ User manual

Intel
Intel BX80570E8200 - Core 2 Duo 2.66 GHz Processor Guide

Intel
Intel PD6730 Installation and operating instructions

Intel
Intel ICH10R User manual

Intel
Intel XL710-Q2 User manual

Intel
Intel SASWT4I Installation manual
Intel
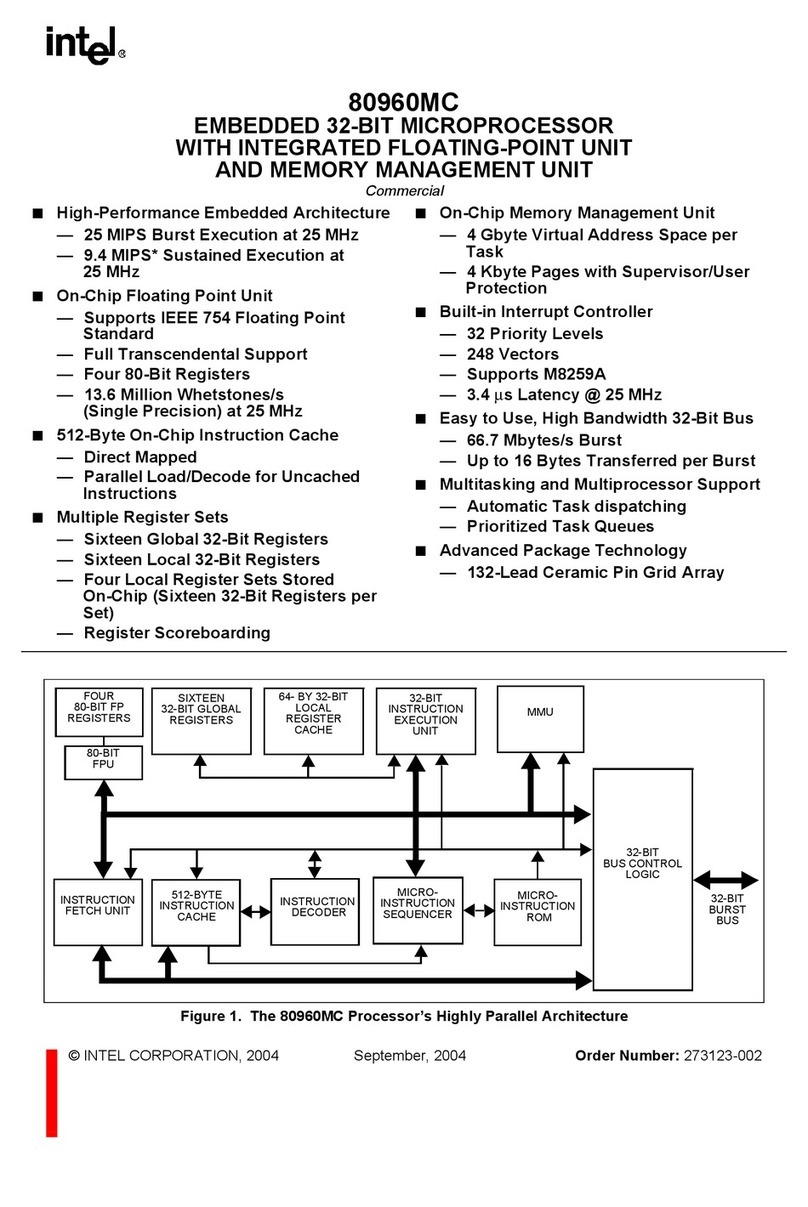
Intel 80960MC User manual

Intel
Intel DP43TF - CARACTERISTIQUES TECHNIQUES User manual

Intel
Intel BX80569Q9550 - Core 2 Quad 2.83 GHz... User manual

Intel
Intel QX9770 - Core 2 Extreme Quad-Core Processor Guide

Intel
Intel RS3FC044 User manual

Intel
Intel I7-900 DESKTOP PROCESSOR - VOLUME 1 User manual

Intel
Intel NUC Kit NUC11PAHi7 User manual

Intel
Intel Mobileye EyeCAN Kit User manual

Intel
Intel 855GME Guide

Intel
Intel E3300 User manual

Intel
Intel Core 2 Quad Q9400 Reference guide

Intel
Intel NUC11ATKPE User manual
Popular Computer Hardware manuals by other brands

EMC2
EMC2 VNX Series Hardware Information Guide

Panasonic
Panasonic DV0PM20105 Operation manual

Mitsubishi Electric
Mitsubishi Electric Q81BD-J61BT11 user manual

Gigabyte
Gigabyte B660M DS3H AX DDR4 user manual

Raidon
Raidon iT2300 Quick installation guide

National Instruments
National Instruments PXI-8186 user manual

ST
ST X-NUCLEO-SAFEA1B How to use

STEINWAY LYNGDORF
STEINWAY LYNGDORF SP-1 installation manual

Advantech
Advantech ASMB-935 Series user manual

Jupiter
Jupiter RAM PACK instructions
Measurement Computing
Measurement Computing CIO-EXP-RTD16 user manual

Matrox
Matrox DigiSuite DigiMix Installation & reference manual



















