6 of 136
2011-09-05 / 0110079-7
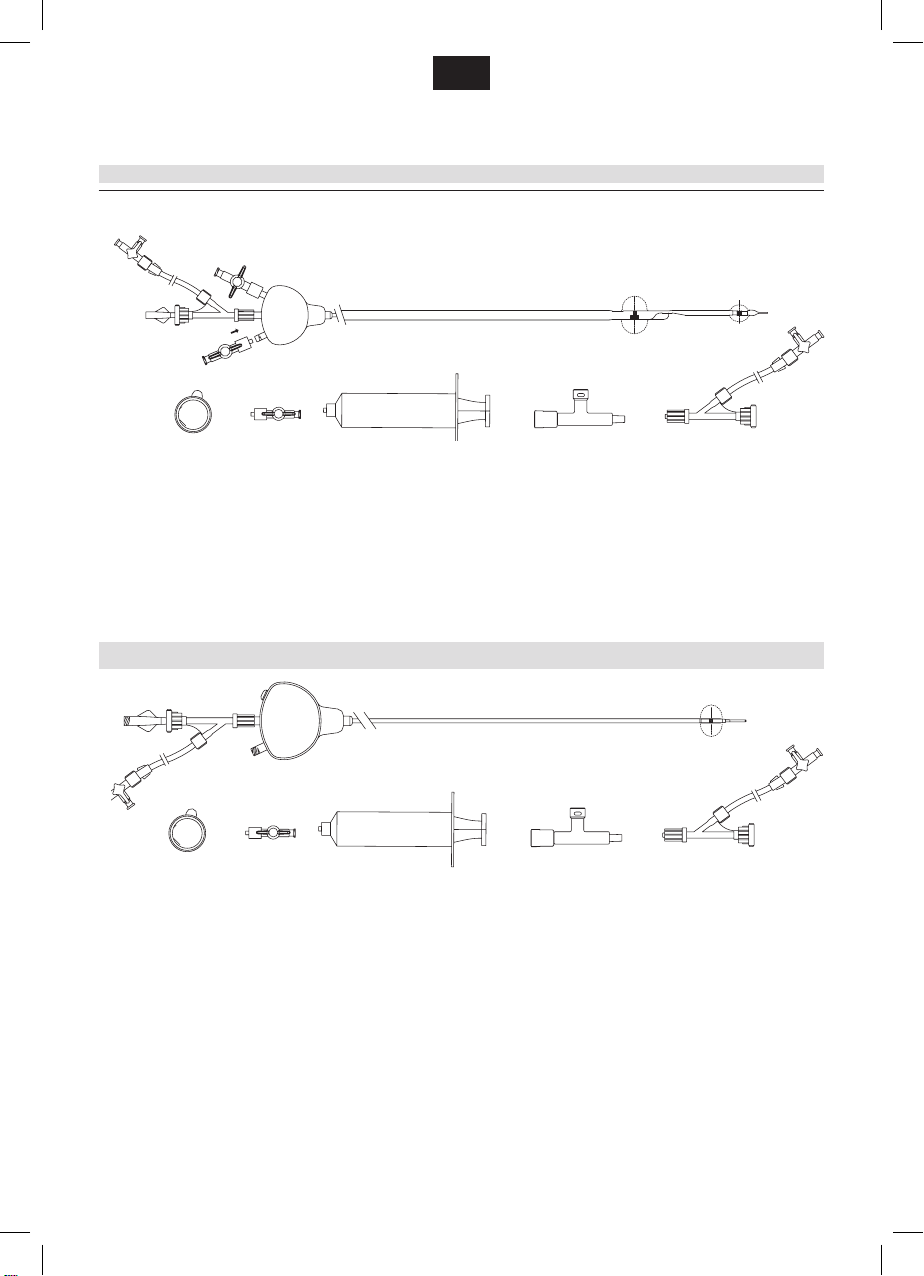
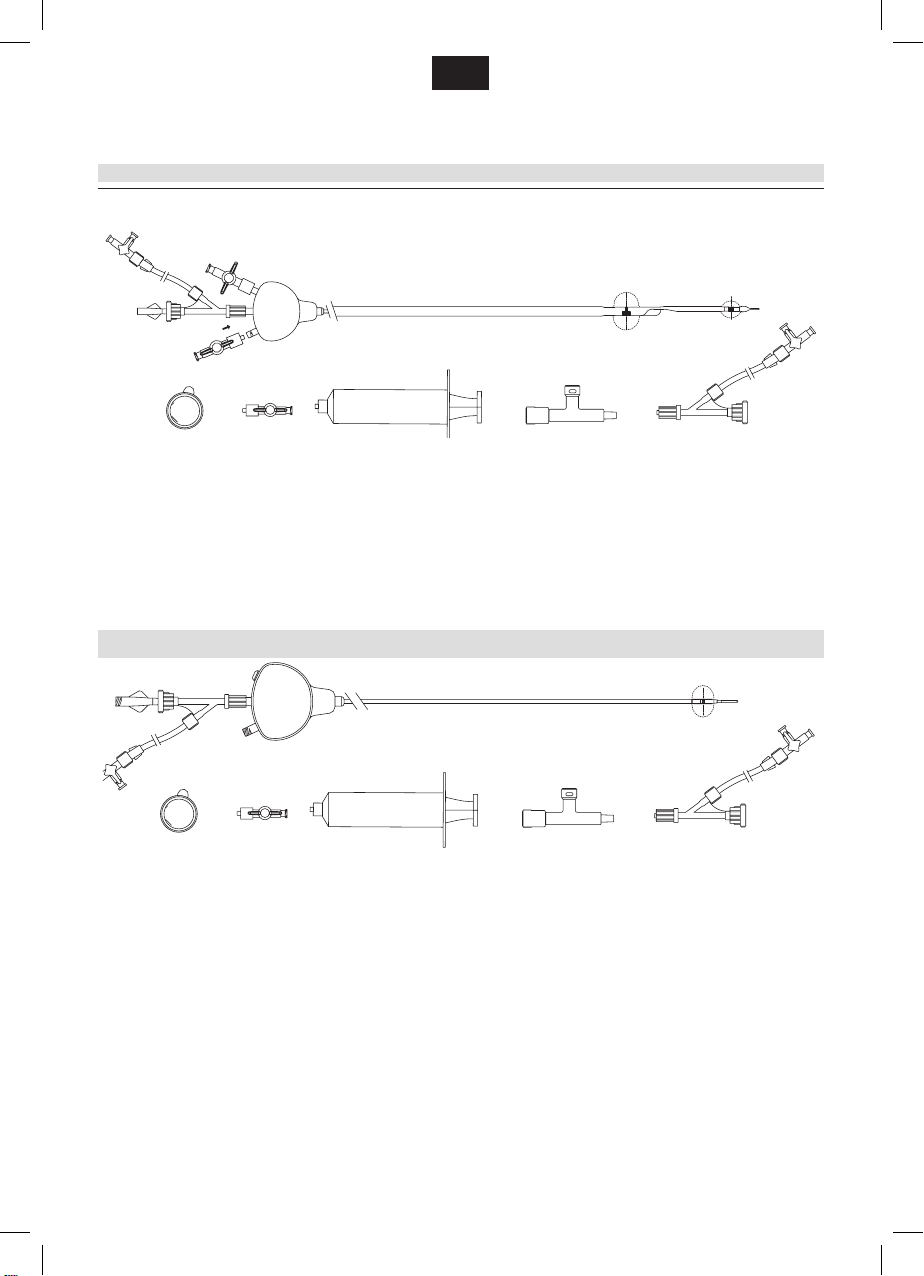
for Mo.Ma mono balloon
Mo.Ma Ultra Proximal Cerebral Protection Device consists of a two-
lumen shaft (one working channel and one ination-deation lumen)
integrating one compliant balloon and a handle, which is located at the
proximal end. The compliant balloon can be inated in the Common
Carotid Artery (CCA). This balloon can be inated up to 13 mm (CCA
balloon). A hollow mandrel is included in the packaging and is intended
to be inserted inside the Mo.Ma Ultra’s working channel to improve
trackability during device insertion over a 0.035” (0.89 mm) guidewire.
The system is compatible with 8F introducer sheath, its usable length
(distance measured from the handle to the tip of the catheter) is 900 mm
and its total length (distance measured from the hemostatic valve to the
tip of the catheter) is 1,050 mm (please refer to the device drawing at
the previous page).
The working channel is a 0.069” (1.76 mm) internal diameter fully
usable lumen, with a length of 1.050 mm (distance measured from the
hemostatic valve to the tip), which serves as guiding catheter and as
blood aspiration lumen.
One radiopaque marker for the CCA balloon allows correct and prompt
device positioning.
CONTENTS
One Mo.Ma Ultra Proximal Flow Blockage Cerebral Protection Device,
one hollow mandrel, one hemostatic valve with 3-way stopcock and
extension line, three 40 µm cell lters, one 30 cc syringe with x male
Luer for the purging procedure, one T-safety connector,
for Mo.Ma double balloon – two 1-way-stopcocks.
for Mo.Ma mono balloon – one 1-way-stopcock.
INDICATIONS FOR USE
Mo.MaTM Ultra Cerebral Protection Device is intended to be used
during Angioplasty and Stenting of lesions located in the ICA and/or
lesions involving the carotid bifurcation. This device allows protection
of the brain from cerebral embolism during the entire duration of the
intervention, thus preventing severe and disabling complications.
The system allows achieving cerebral protection before target lesion
crossing plus allowing debris removal by blood aspiration at any stage
during the procedure.
for Mo.Ma double balloon
Mo.Ma Ultra is indicated to be used in patients eligible for carotid
angioplasty and/or stenting with stenosis involving the ICA and / or the
Carotid Bifurcation and reference diameter of ECA from 3 to 6 mm and
reference diameter of CCA from 5 to 13 mm.
for Mo.Ma mono balloon
Mo.Ma Ultra is indicated to be used in patients eligible for carotid
angioplasty and/or stenting with occlusion of the ECA and stenosis
involving the ICA and / or the Carotid Bifurcation and reference diameter
of CCA from 5 to 13 mm.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Mo.Ma Ultra is contraindicated for use in patients showing one of the
following criteria
− Severe disease of the ipsilateral CCA
− Intracranial tumors, aneurysms or severe intracranial stenosis
distal to the target lesion
− Relevant acute neurological events occurring in the last 5 days
before scheduled intervention and diagnosed by neurological
assessment, TAC, Cranial MR
− Inability to respond to external questions and stimuli and to exert a
pressure with the contralateral hand
− Patient suffering from dementia
Procedure related
− Severe chronic renal failure (Creatinine values > 2,5 mg/dl)
− Contraindication for antiplatelets and/or anticoagulation therapy
− Allergy to contrast media
− Severe peripheral vascular disease preventing femoral access,
hemorrhagic or hyper-coagulable status and / or inability to obtain
hemostasis at the site of the femoral puncture
− Inability to accept a temporary pacemaker
WARNINGS
− This device is designed and intended for single use only. DO
NOT RESTERILIZE AND/OR REUSE. Reuse or resterilization
may create a risk of contamination of the device and/or cause
patient infection or cross-infection, including, but not limited to, the
transmission of infectious disease(s) from one patient to another.
Contamination of the device may lead to injury, illness or death of
the patient. Reuse or resterilization may compromise the structural
integrity of the device and/or lead to device failure which, in turn,
may result in patient injury, illness and death. INVATEC will not be
responsible for any direct, incidental or consequential damages
resulting from resterilization or reuse.
− Perform balloon purging as described in this Instruction for Use,
before inserting Mo.Ma Ultra inside the patient.
− Avoid the positioning of the Mo.Ma Ultra system without the hollow
mandrel.
− Exercise care during handling and avoid acute bends of the device
before and during balloon purging procedure.
− When inating the occlusive balloon(s), ination control must be
made by angiographic visual estimation of balloon cylindrical
shape deformation (not by pressure!).
− After inating the balloon(s) immediately perform angiographic
check of blood ow blockage as described in the present
Instruction for Use, and check patient’s clinical tolerance to
occlusion right after.
− Should patient intolerance to occlusion occur during the
procedure, immediately remove all debris performing syringe blood
aspirations and deate the proximal (CCA) balloon right after.
− Before deating the occlusion balloon(s) always verify that no
more debris are retrieved in the aspirated blood.
− Appropriate antiplatelet and/or anticoagulant therapy should be
administered to the patient, as determined by the physician in
accordance with standard protocols for carotid stenting. ACT
should be maintained > 250 sec through the intervention.
− ICA lesion must not be crossed by guidewires or any other
interventional catheters before the balloon(s) have been inated
and before having checked that blood ow has been effectively
blocked.
− When the catheter is exposed to the vascular system, it should be
manipulated while under high-quality uoroscopic observation.
− Do not place the occlusion balloon(s) into highly calcied vessel
segments of the carotid vessels.
− Do not manipulate the Mo.Ma Ultra system in inated state.
− If resistance occurs during manipulation do not force or continue.
The reason of resistance must rst be ascertained by uoroscopy,
road mapping or DSA before the device is moved backwards or
forwards.
− Use only a mixture of contrast medium and saline solution to
ll the balloon(s) (50/50 - 30/70). Never use air or any gaseous
medium or pure contrast dye to inate the balloon(s).
− Do not use with Lipiodol or Ethidiol contrast media, or other such
contrast media, which incorporate the components of these
agents.
− Do not expose the Mo.Ma Ultra system to organic solvents,
e.g. alcohol, acetone.
− Use the catheter by date specied on the package label.
PRECAUTIONS
− Only interventionalists who have sufcient experience should carry
out Carotid Artery Angioplasty aided by proximal ow blockage
cerebral protection devices. A thorough understanding of the
technical principles, clinical applications and risks associated with
carotid artery angioplasty is necessary before using this product.
− Allergic reactions to contrast medium should be identied before
PTA.
− The general technical requirements for catheter insertion must be
observed at all times. This includes purging the balloons, ushing
the components with sterile, isotonic saline solution prior to use
and the usual prophylactic, systemic heparinization.
− Catheter applications vary and the technique must be selected
0110079-7.indd 6 1.11.2011 23:03:43