MITS Janus Time Engine
Page 2 of 39
Copyright© Instrumentation Technology Systems 2020 20200929
TABLE OF CONTENTS
CHANGE HISTORY ................................................................................................................................................... 4
1.0 GENERAL DESCRIPTION ............................................................................................................................ 5
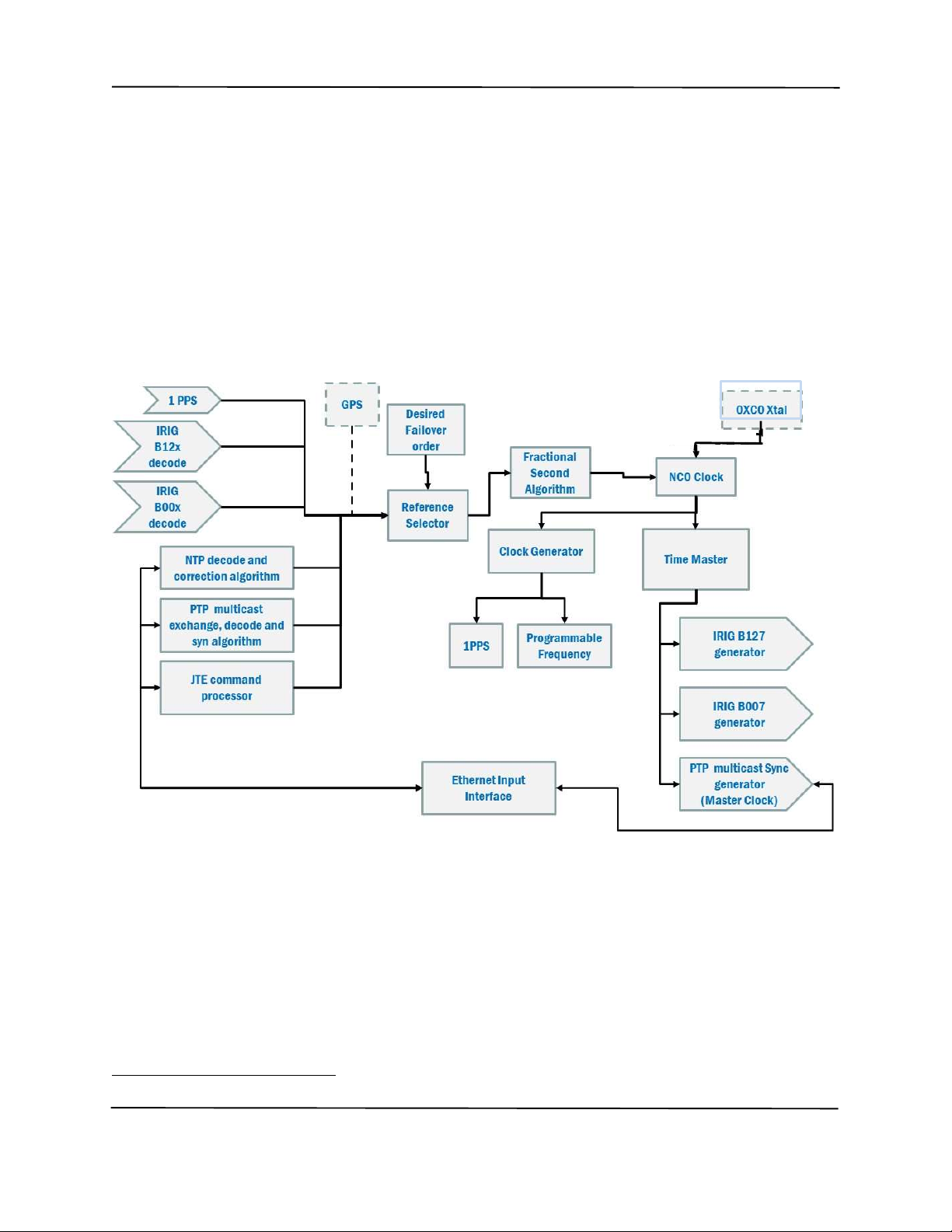
1.1 JANUS TIME ENGINE MASTER CONTROLLER (JTEMC) ................................................................................................. 5
1.1.1 Time Master .................................................................................................................................... 5
1.1.2 IRIG B Inputs .................................................................................................................................. 7
1.1.3 1PPS Inputs ..................................................................................................................................... 7
1.1.4 GPS Time Reference ....................................................................................................................... 8
1.1.5 PTPV2 Master Clock Function ....................................................................................................... 8
1.1.6 Time of Day Clock .......................................................................................................................... 9
1.1.7 Time Zone Offset ............................................................................................................................ 9
1.1.8 Ethernet ........................................................................................................................................... 9
1.1.9 Settings Flash ................................................................................................................................ 10
1.1.10 I/O Interface .................................................................................................................................. 10
1.2 PHOTO-SONICS INTERFACE (PSI/O) ...................................................................................................................... 11
1.2.1 Time code and frequency output ports .......................................................................................... 11
1.3 IRIG B TIME CODE GENERATOR ............................................................................................................................. 12
1.3.1 An IRIG B127 output buffer ......................................................................................................... 12
1.3.2 An IRIG B007 output buffer ......................................................................................................... 12
1.4 PROGRAMMABLE FREQUENCY GENERATORS ............................................................................................................ 12
1.4.1 Clock A ......................................................................................................................................... 12
1.4.2 Clock B ......................................................................................................................................... 12
2.0 NETWORK TIME SYNCRHONIZATION...................................................................................................... 12
2.1 NTP DECODE/CORRECTION ................................................................................................................................. 13
2.2 PTP SYNCHRONIZER ALGORITHM .......................................................................................................................... 13
3.0 WEBSERVER ........................................................................................................................................... 13
3.1 HOME PAGE ...................................................................................................................................................... 14
3.1.1 Time frame .................................................................................................................................... 14
3.2 ADMIN PAGE ..................................................................................................................................................... 15
3.2.1 Session Control frame ................................................................................................................... 15
3.3 CHANGE LOGIN PAGE .......................................................................................................................................... 16
3.4 INPUTS PAGE ..................................................................................................................................................... 16
3.4.1 Priority frame ................................................................................................................................ 16
3.4.2 TCP/IP Frame ............................................................................................................................... 17
3.4.3 Network Time Reference .............................................................................................................. 18
3.4.4 IRIG Reference ............................................................................................................................. 18