Operating Instructions BA 77 600..A00 // Last updated: 13/03/2020 // Page 2 of 33
Contents
1. General information .............................................................................................................................. 3
1.1 Introduction ............................................................................................................................................ 3
1.2 Standards and directives ....................................................................................................................... 3
1.3 Declaration of Incorporation (in accordance with Annex II, part 1, Section B of Machinery Directive
2006/42/EC)........................................................................................................................................... 3
1.4 Declaration of Conformity ...................................................................................................................... 4
1.5 Manufacturer's liability ........................................................................................................................... 4
1.6 Brake versions ....................................................................................................................................... 4
2. Product description............................................................................................................................... 5
2.1 Operating principle................................................................................................................................. 5
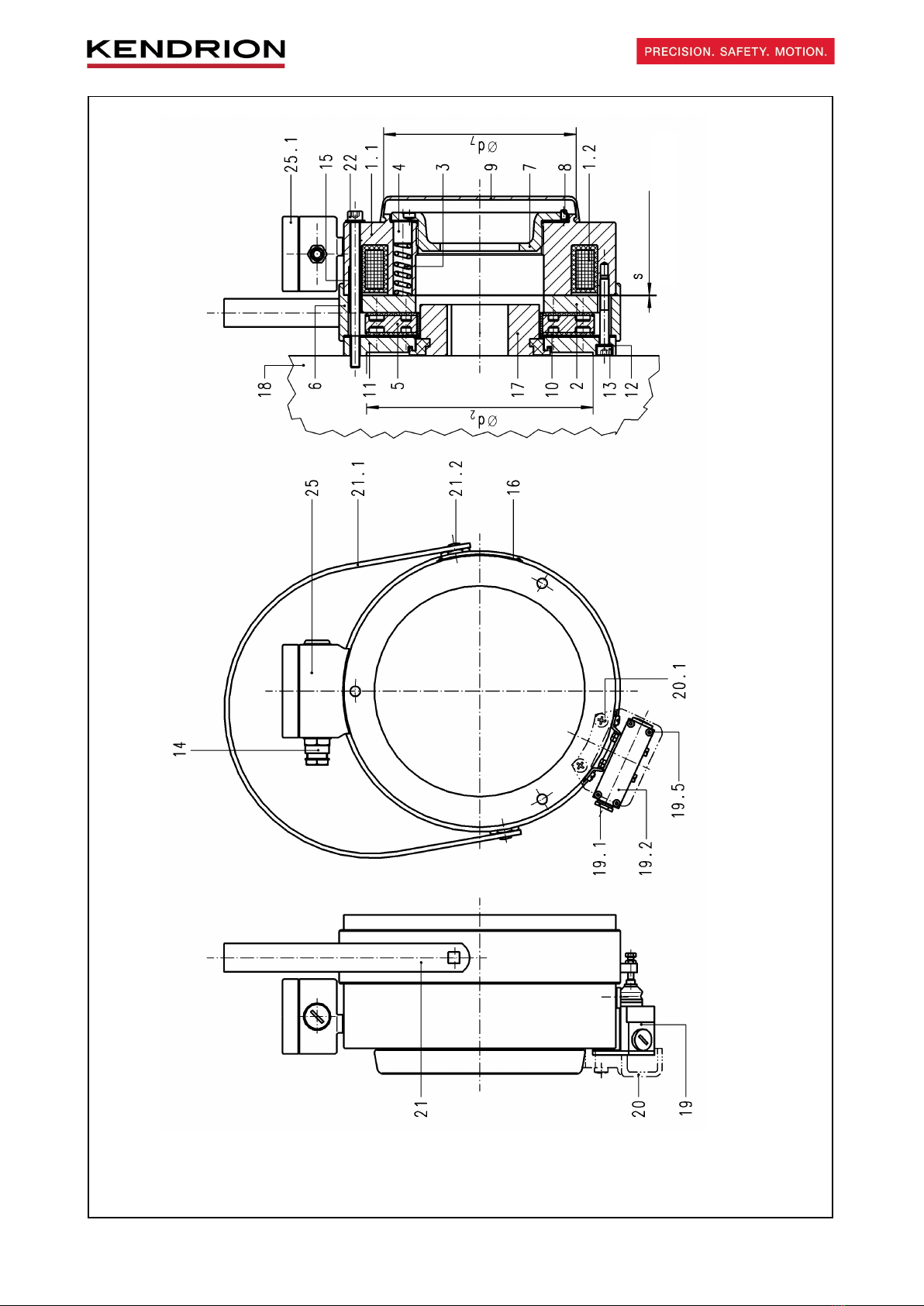
2.2 Design.................................................................................................................................................... 5
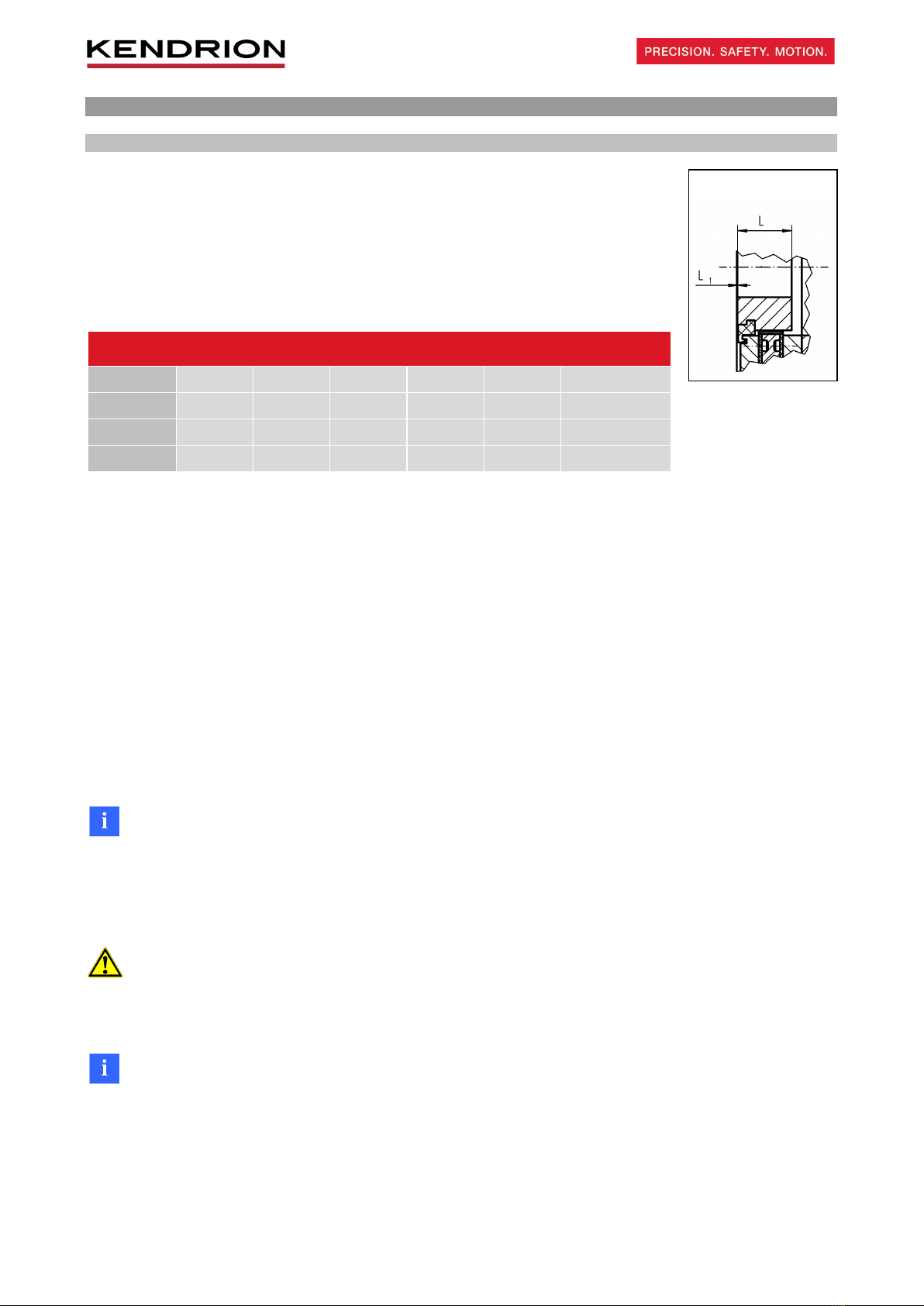
3. Installation.............................................................................................................................................. 8
3.1 Mechanical installation........................................................................................................................... 8
3.2 Installation of accessories...................................................................................................................... 9
3.3 Electrical connection and operation..................................................................................................... 10
3.3.1 DC power supply ............................................................................................................................. 11
3.3.2 AC power supply.............................................................................................................................. 11
3.3.3 Microswitch (19) connection ............................................................................................................ 13
3.4 Electromagnetic compatibility .............................................................................................................. 15
3.5 Set-up and start-up .............................................................................................................................. 18
3.5.1 Functional checks ............................................................................................................................ 18
3.5.2 Manual brake release ...................................................................................................................... 19
3.6 M2rated torque adjustments................................................................................................................ 19
4. Maintenance......................................................................................................................................... 20
4.1 Checks and service ............................................................................................................................. 20
4.2 Microswitch (19) adjustment (only applicable to brakes with microswitch (19)).................................. 21
4.3 Spare parts and accessories ............................................................................................................... 22
5. Condition at delivery........................................................................................................................... 22
6. Emissions............................................................................................................................................. 22
6.1 Noise.................................................................................................................................................... 22
6.2 Heat ..................................................................................................................................................... 23
7. Troubleshooting .................................................................................................................................. 23
8. Safety.................................................................................................................................................... 24
8.1 Intended use ........................................................................................................................................ 24
8.2 General safety information................................................................................................................... 24
8.2.1 Set-up .............................................................................................................................................. 25
8.2.2 Set-up and start-up .......................................................................................................................... 25
8.2.3 Installation........................................................................................................................................ 25
8.2.4 Operation ......................................................................................................................................... 25
8.2.5 Maintenance, repair and replacement ............................................................................................. 26
8.3 Warning symbols ................................................................................................................................. 26
9. Definitions ............................................................................................................................................ 27
10. Technical specifications..................................................................................................................... 29
11. Product number / type number / version number............................................................................ 32
12. Specialist repair shops ....................................................................................................................... 32
13. Revision history................................................................................................................................... 32
Document information:
Issued by: Kendrion (Villingen) GmbH Last updated: 13/03/2020
Replaces document: - Replaces the issue dated: 30/12/2009
Document type:translation of original German operating Document status: released
instructions BA 77 600..A00
Document title: BA 77 600..A00 Englisch