3
Table of Contents
1. General information ...................................................... Błąd! Nie zdefiniowano zakładki.
2. Description and purpose of the device .......................... Błąd! Nie zdefiniowano zakładki.
3. Fuel specification .......................................................... Błąd! Nie zdefiniowano zakładki.
4. Construction of the heater ............................................. Błąd! Nie zdefiniowano zakładki.
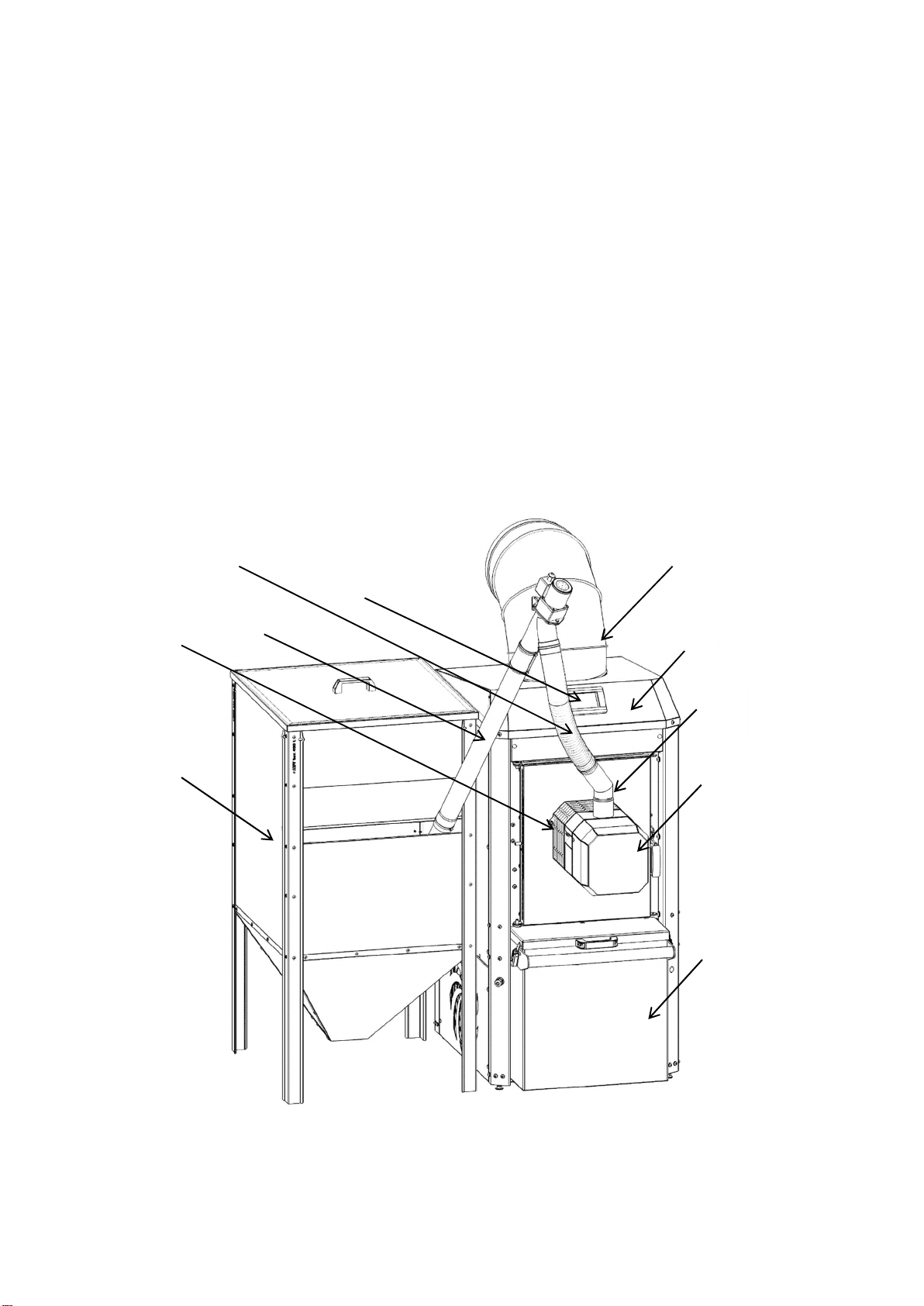
5. Components .................................................................. Błąd! Nie zdefiniowano zakładki.
6. Safety systems used in the heater ...................................................................................... 10
7. Transport ........................................................................................................................... 14
8. Assembly ........................................................................................................................... 15
8.1. The sequence of assembly works .......................... Błąd! Nie zdefiniowano zakładki.
9. Installation ..................................................................... Błąd! Nie zdefiniowano zakładki.
9.1. Connecting the heater to the electrical system .......................................................... 21
9.2. Connecting the heater to the chimney installation . Błąd! Nie zdefiniowano zakładki.
9.3. Verification of the ventilation system ................... Błąd! Nie zdefiniowano zakładki.
10. Running ..................................................................... Błąd! Nie zdefiniowano zakładki.
10.1. Preparing the device for the first start ................ Błąd! Nie zdefiniowano zakładki.
10.2. The first start of the burner. ................................................................................... 25
10.2.1. The sequence of works related to the first start-up ........ Błąd! Nie zdefiniowano
zakładki.
11. Exploitation ............................................................... Błąd! Nie zdefiniowano zakładki.
11.1. Safe operation conditions ................................... Błąd! Nie zdefiniowano zakładki.
11.2. Heater maintenance ............................................... Błąd! Nie zdefiniowano zakładki.
11.3. Wytyczne ogólne ............................................... Błąd! Nie zdefiniowano zakładki.
11.4. General guidelines ............................................. Błąd! Nie zdefiniowano zakładki.
11.5. Cleaning the combustion chamber ..................... Błąd! Nie zdefiniowano zakładki.
11.6. Cleaning the hatch .............................................. Błąd! Nie zdefiniowano zakładki.
11.7. Cleaning the ash pan .......................................... Błąd! Nie zdefiniowano zakładki.
12. Technical data ........................................................... Błąd! Nie zdefiniowano zakładki.
12.1. Models of heaters, overall dimensions ............... Błąd! Nie zdefiniowano zakładki.
12.2. Device identification .......................................... Błąd! Nie zdefiniowano zakładki.
12.3. Electrical diagram of the ecoTOUCH 920P regulator ....... Błąd! Nie zdefiniowano
zakładki.
12.4. Technical parameters of heaters ......................... Błąd! Nie zdefiniowano zakładki.
13. EC declaration of conformity ........................................................................................ 42
14. List of common faults ............................................... Błąd! Nie zdefiniowano zakładki.
15. Spare parts list ........................................................... Błąd! Nie zdefiniowano zakładki.
16. Terms of warranty ..................................................... Błąd! Nie zdefiniowano zakładki.
17. Attachments: .................................................................................................................. 53
17.1. Warranty - first run - a copy to be sent along with the GDPR consent clause ...... 53
17.2. Warranty - first start of the heater ...................... Błąd! Nie zdefiniowano zakładki.
17.3. Warranty - annual inspection ............................. Błąd! Nie zdefiniowano zakładki.
17.4. Warranty - two-year inspection.......................... Błąd! Nie zdefiniowano zakładki.
17.5. Repairs ............................................................... Błąd! Nie zdefiniowano zakładki.