2
TABLE OF CONTENT
1TESTING....................................................................................................................... 4
1.1 Airflow measurements.........................................................................................................5
1.1.1Downflow (hotwire anemometer)...................................................................................................5
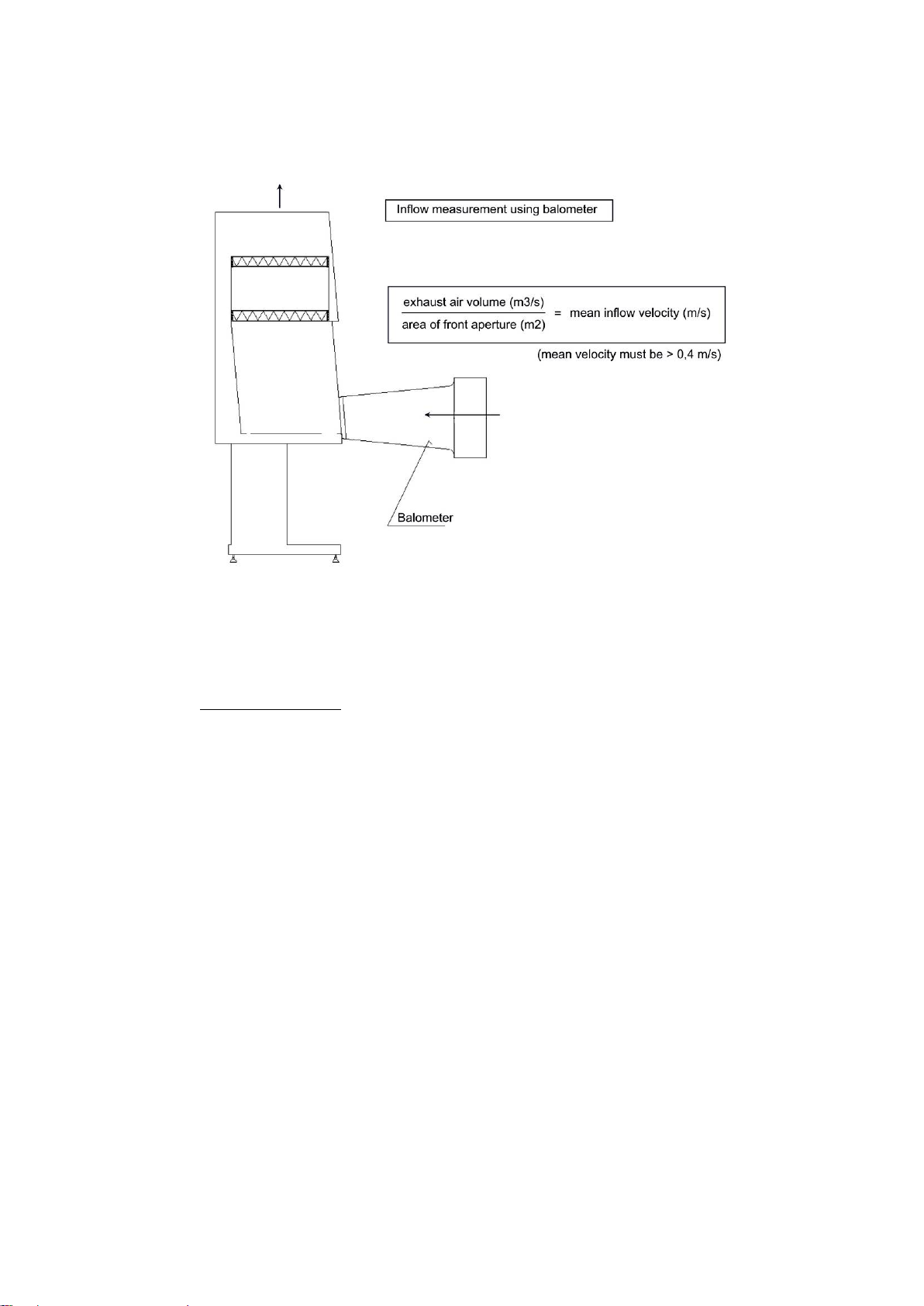
1.1.2 Inflow (using balometer).................................................................................................................7
1.1.3 Airflow visualization (smoke test) ...................................................................................................9
1.2 Aerosol challenge test of filters............................................................................................9
1.2.1 In general........................................................................................................................................9
1.2.2 SF, MF and CW-V cabinets:...........................................................................................................9
1.2.3 Exhaust filters...............................................................................................................................11
1.2.4 XL cabinets...................................................................................................................................12
1.2.5 DEF cabinets................................................................................................................................14
1.2.6 CW-V cabinets..............................................................................................................................17
1.2.7 Acceptance criterions:..................................................................................................................17
1.3 KI -Diskus test...................................................................................................................18
2MAINTENANCE.......................................................................................................... 19
2.1 Yearly Maintanance ..........................................................................................................20
2.2 H2O2Decontamination ......................................................................................................21
2.3 Replacing lights.................................................................................................................22
2.4 Changing filters.................................................................................................................23
2.4.1 In general......................................................................................................................................24
2.4.2 SF Cabinets..................................................................................................................................28
2.4.3 MF Cabinets .................................................................................................................................28
2.4.4 DEF Cabinet.................................................................................................................................30
2.4.5 XL cabinets...................................................................................................................................32
2.4.6 CW-V cabinets..............................................................................................................................35
2.4.7 After filter change .........................................................................................................................36
2.5 Changing main board........................................................................................................36
3MATERIALS ............................................................................................................... 37
4DISCHARGING THE CABINET.................................................................................. 37
5SOFTWARE UPDATE................................................................................................ 38
5.1 Update Core version.........................................................................................................38
5.2 Update Biocontro i.............................................................................................................38
5.3 Update Main version.........................................................................................................40
6TECHNICAL DATA..................................................................................................... 41
7SPARE PARTS LIST.................................................................................................. 46
8CIRCUIT DIAGRAMS ................................................................................................. 56
9SERVICE HISTORY.................................................................................................... 64
10 TROUBLE SHOOTING .............................................................................................. 65