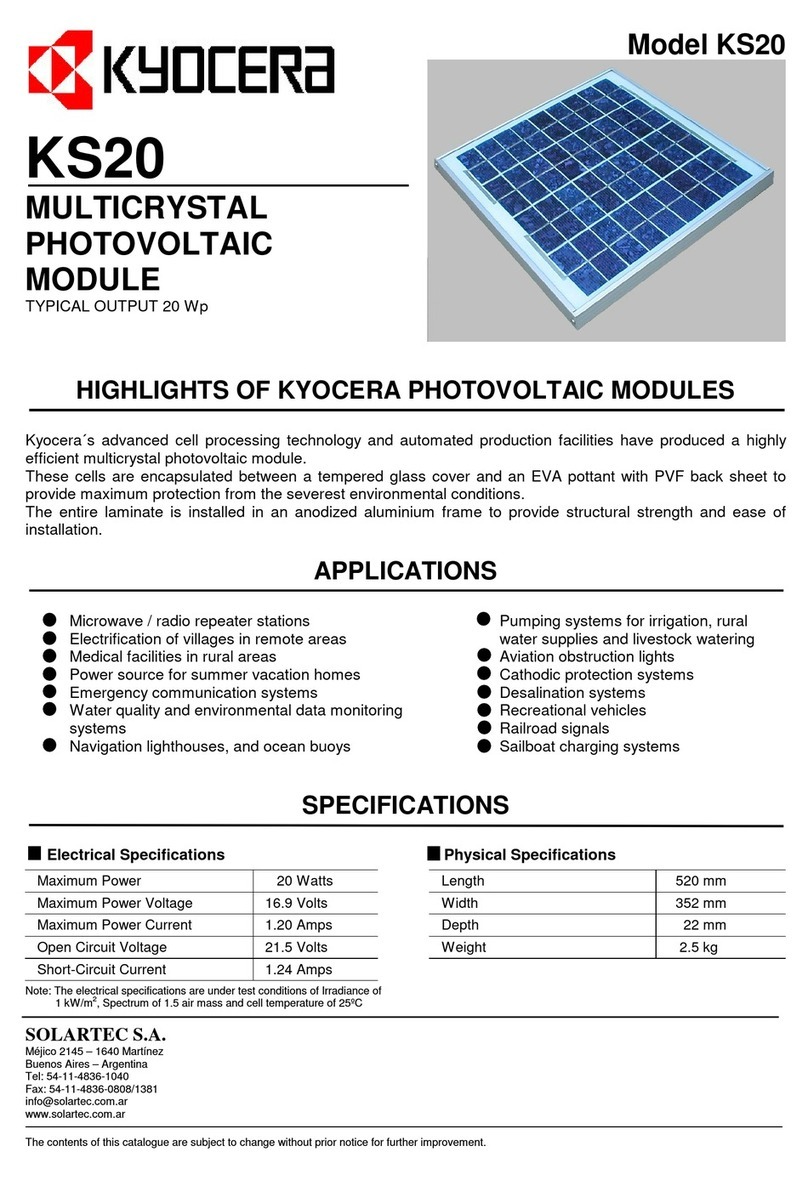
1) Series: MC4
Made by Multi Contact (www.multi-contact.com)
Pole Positive Negative
Model PV-KBT4/6Ⅱ-UR PV-KST4/6Ⅱ-UR
Symbol +-
Figure
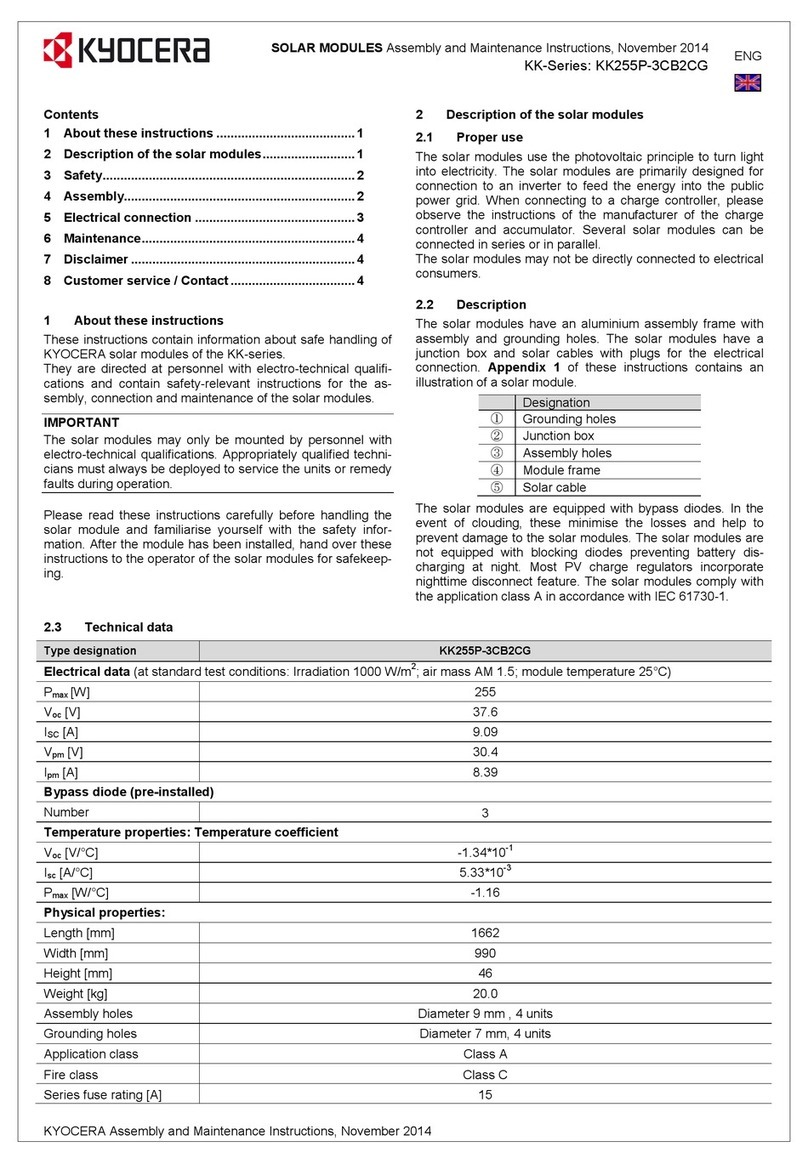
2) Series: MC4-EVO3
Made by Multi Contact (www.multi-contact.com)
Pole Positive Negative
Model PVMC4PLS-XX PVMC4PLS-XX
Symbol + -
Figure
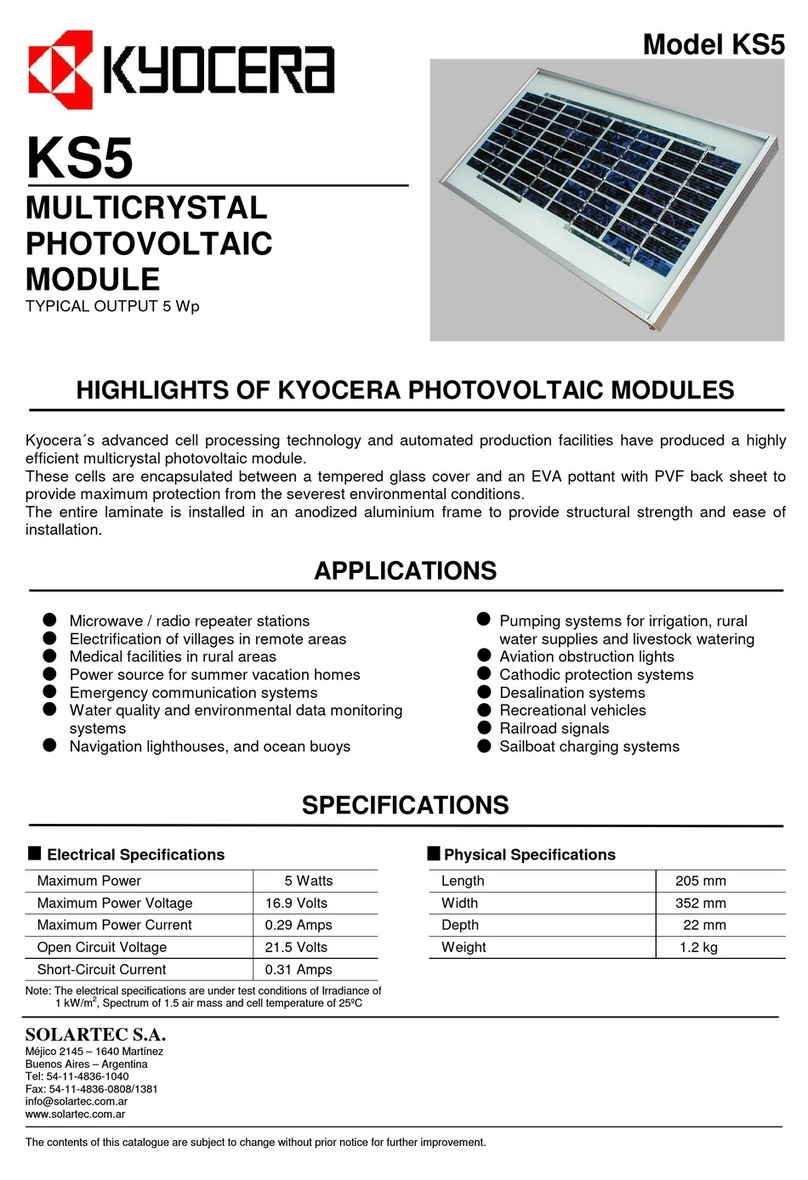
3) Series:H4 UTX
Made by Amphenol (www.amphenol.com)
Pole Positive Negative
Model H4 UTX H4 UTX
Symbol + -
Figure
NOTE: When making connections with the connectors,
make sure the array is disabled. DO NOT MAKE
CONNECTIONS WHILE UNDER LOAD.Module output
connections are marked “Do not disconnect under load”.
NOTE: MAXIMUM SYSTEM VOLTAGE IS 1000 VDC.
The PV module and most PV system components have a
maximum system voltage rating of 1000 volts DC. Some
grid-tie systems operate at or near this voltage rating. Like
other polycrystalline PV modules, the open-circuit voltage
of the PV modules increases as the ambient temperature
decreases. Maximum system voltage is computed as the
sum of the open-circuit voltage of the series-connected PV
modules for the lowest expected ambient temperature.
Refer to the National Electrical Code Article 690-7(A) for
determining the maximum number of the PV module that
can be placed
in series. Temperature coefficients, specific
to the module of use, can be used to provide the most
accurate prediction of module voltage under temperature
extremes.
NOTE: Limit the maximum number of series connection of
the PV module so that the system voltage is 1000V or less.
NOTE: Do not connect the modules in parallel without
maximum over current protection.
NOTE: The minimum radius that the cable can be bent for
the PV module is 1.14” (29mm).
NOTE: Under normal conditions, PV module is likely to
experience conditions that produce more current and/or
voltage than reported at standard test conditions. The
requirements of the National Electrical Code (NEC) in
Article 690 shall be followed to address these increased
outputs. In installations not under the requirements of the
NEC, the values of ISC and VOC marked on this module
should be multiplied by a factor of 1.25 when determining
component voltage ratings, conductor ampacities,
overcurrent device ratings, and size of controls connected
to the PV output.
8. GROUNDING
Before installation, consult the local codes and the
authorities having jurisdiction to determine the necessary
grounding requirements. When installing in the US market,
attach all PV module frames to an earth ground in
accordance with the National Electrical Code (NEC) Article
250. Proper grounding is achieved by connecting PV
module frames and all metallic structural members
contiguously to one another using a suitable grounding
conductor. The grounding conductor shall be of copper,
copper alloy or another material suitable for use as an
electrical conductor per NEC. The grounding conductor
must then make a connection to earth using a suitable earth
grounding electrode. Ensure positive electrical contact
through the anodizing on the module frame extrusion by
utilizing one of the following methods.
Attach the grounding conductor:
(1) to one of the .28” (7mm) diameter holes marked
“ground” using 1/4”(6mm) stainless steel bolt. Wrap
conductor around bolt. Tighten the screws with
adequate torque (62 in-lb: UL evaluation torque).
(2) to a ground lug (manufacturer:ILSCO, model:GBL-
4DBT). The lug is attached to one of the .28”(7mm)
diameter holes marked “ground”, using #10-32
stainless steel bolt with 40 in-lb torque.
(3) to a ground lug (manufacturer:ILSCO, model:GBL-
4DBT). The lug is attached to one of the .16”(4mm)
diameter holes marked “ground”, using #10-32
stainless steel tapping machine screw with 30 in-lb
torque. Screw length should be 1/2"(12.7mm) or less.
(4) to a wire bolt (manufacturer:Tyco, model:2058729-1)
using 3/8”(10mm) wire biding nut with 45 in-lb torque.
The bolt is attached to one of the .19”(4.7mm) diameter
holes marked “ground”, using #8-32 (4mm) mounting
washer nut with 25 in-lb torque.
NOTE: A stainless steel star washer or mounting washer
nut, having contact with anodized surface of the frame,
must be employed to break through the anodized layer of
the frame extrusion and electrically connect the grounding
conductor to the conducting aluminum frame material.
NOTE: As a general rule, avoid direct contact of copper or
copper alloy ground conductors with the aluminum frame to
prevent galvanic corrosion. All ground bond securing
hardware in contact with either the aluminum module frame
and/or copper or copper alloy ground conductors must be
stainless steel.
NOTE: Where common grounding hardware (nuts, bolts,
star washers, spring-ring lock washers, flat washers and
like that) is used to attach a listed grounding/bonding device,
the attachment must be made in conformance with the
grounding device manufacturer's instructions.
NOTE: Common hardware items such as nuts, bolts,
star-washers, lock washers and the like have not been
evaluated for electrical conductivity or for use as grounding
devices and should be used only for maintaining
mechanical connections and holding electrical grounding
devices in the proper position for electrical conductivity.
Such devices, where supplied with the module and
evaluated through the requirement in UL 1703, may be
used for grounding connections in accordance with the
instructions provided with the module.