Lennox XP14 User manual
Other Lennox Heat Pump manuals

Lennox
Lennox HP21 Installation and operation manual

Lennox
Lennox HPXA12 SERIES Installation and operation manual

Lennox
Lennox HS29-211 Installation and operation manual

Lennox
Lennox Value 10ACB Series User manual

Lennox
Lennox 123B-600 User manual

Lennox
Lennox Elite SPB H4 Series User manual

Lennox
Lennox Magic-Pak PWC182 User manual
Lennox
Lennox 12CHP060 User manual

Lennox
Lennox ML18XC2 Series User manual
Lennox
Lennox HPXA12 SERIES User manual

Lennox
Lennox Signature XP19-024 User manual

Lennox
Lennox Merit Series13HPD Units User manual

Lennox
Lennox 13HPX User manual

Lennox
Lennox XP16 User manual

Lennox
Lennox Merit 14HPX-018 User manual
Lennox
Lennox Merit Series User manual

Lennox
Lennox ML14XC1 Series Manual

Lennox
Lennox Elite XP16-024-230 User manual

Lennox
Lennox ML16XP1 Series Installation and operation manual

Lennox
Lennox 16HPX Series Installation and operation manual
Popular Heat Pump manuals by other brands

Mitsubishi Electric
Mitsubishi Electric PUZ-SWM60VAA Service manual

Dimplex
Dimplex LI 16I-TUR Installation and operating instruction

Carrier
Carrier WSHP Open v3 Integration guide

TGM
TGM CTV14CN018A Technical manual

Carrier
Carrier 38MGQ Series installation instructions

Kokido
Kokido K2O K880BX/EU Owner's manual & installation guide

Viessmann
Viessmann VITOCAL 300-G PRO Type BW 2150 Installation and service instructions
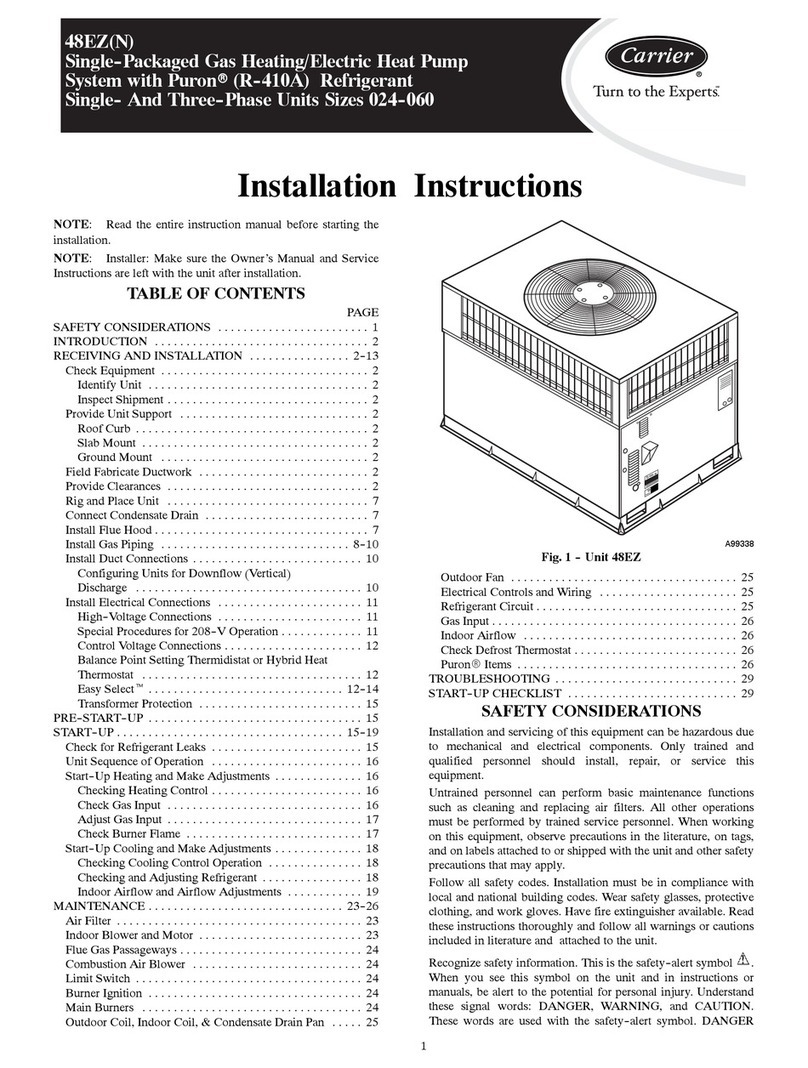
Carrier
Carrier 48EZN installation instructions

Viessmann
Viessmann KWT Vitocal 350-G Pro Series Installation and service instructions for contractors

Ariston
Ariston NIMBUS user manual
Weishaupt
Weishaupt WWP L 7 Installation and operating instruction
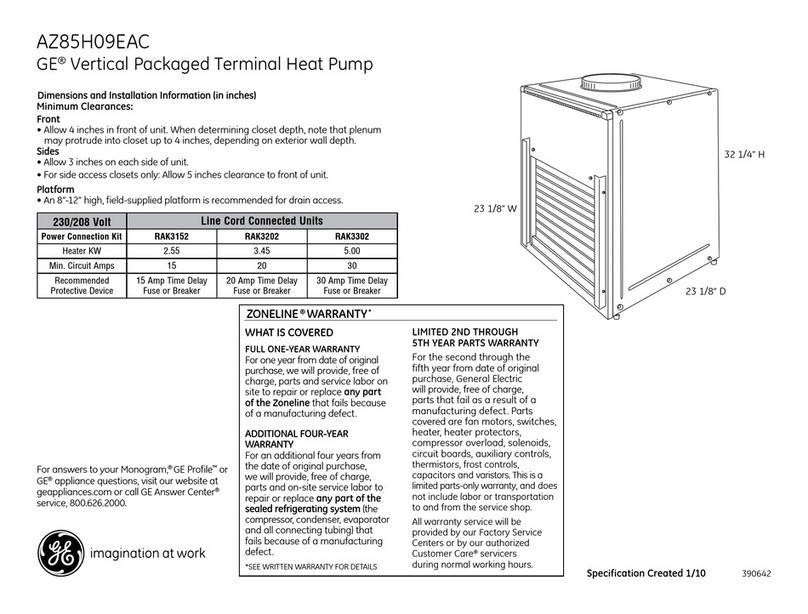
GE
GE Zoneline AZ85H09EAC datasheet