Inverter DC MIG Welder Manual www.gentt.ie
INSTALLATION
5.1 MIG Welding Set Up & Operation
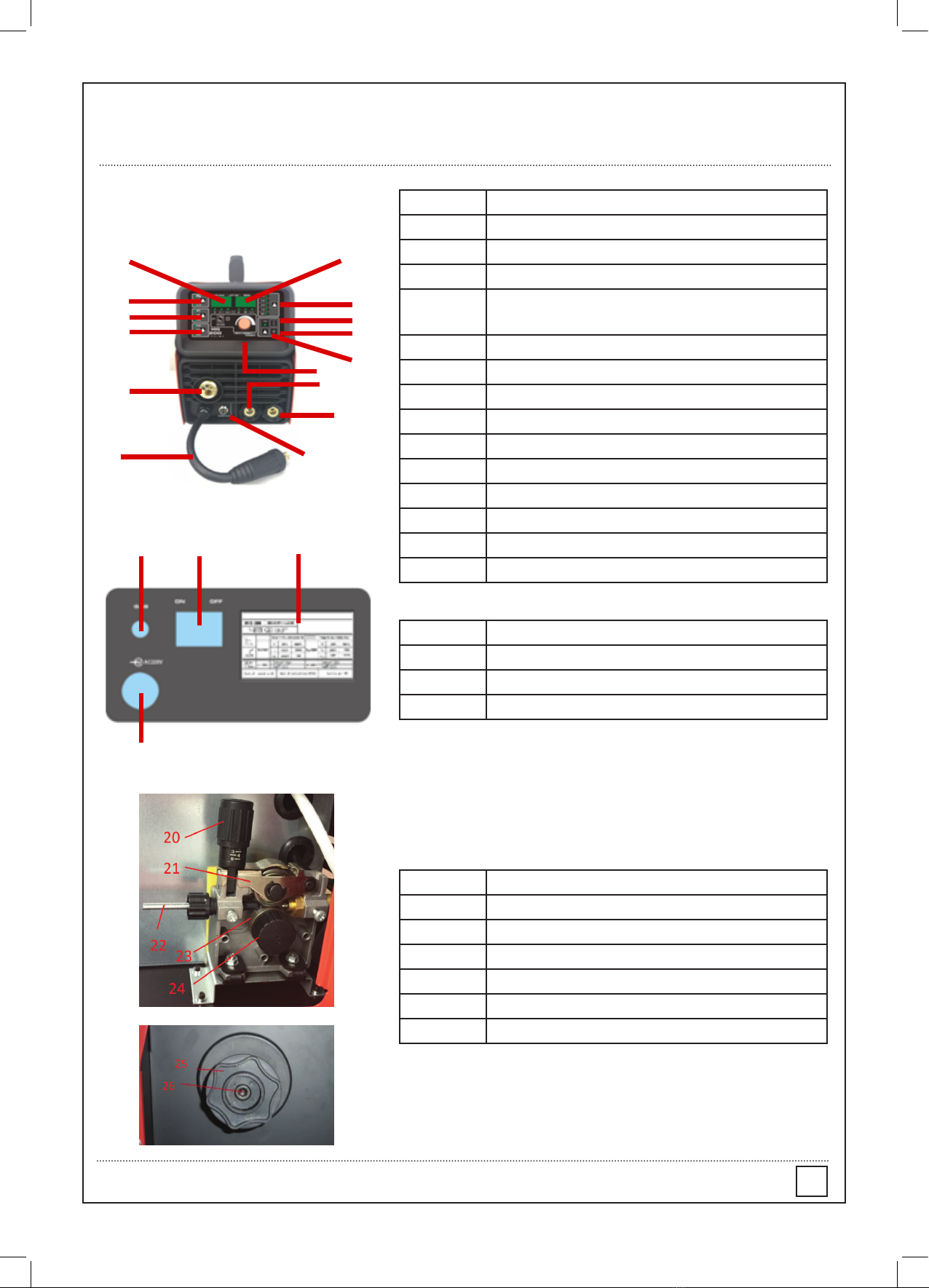
5.1.1 Fitting the spool
5.1.1.1 Open the cover door for the wire feed compartment. Remove the wire spool retainer (24) by
threading off anti clockwise.
5.1.1.2 Fit the 200mm diameter wire spool to the spool holder, ensuring the end of the wires exits towards the
wire feeder from the bottom of the spool. Ret the wire spool retainer (25) and tighten hand tight.
5.1.1.3 Set the spool brake tension by rotating the adjustment screw (26) using an Allen Key wrench. Clockwise
to increase brake tension, anti-clockwise to decrease brake tension. The spool brake tension should be set so
that the spool can rotate freely, but does not continue to rotate once the wire feed stops. This may need to be
adjusted as the wire is used up and the spool weight decreases.
5.1.2 Loading wire feeder
5.1.2.1 Release the wire feeder tension arm (21) by pivoting the wire feed tension adjuster (20) as pictured
below.
5.1.2.2 Check the wire drive roller (23) groove matches the selected MIG wire type and size. The drive roller will
have two different sized grooves; the size of the groove in use is stamped on the side of the drive roller. For ux
cored ‘soft’ wire, such as that used in gas less MIG welding, the drive roller groove has a serrated prot. For solid
‘hard’ MIG wire, the roller groove has a ‘v’ shaped prole.
5.1.2.3 The drive roller (23) is removed by threading the drive roller retainer(24) off in the anti-clockwise
direction. Once the correct drive roller prole is selected, re-t the drive roller.
5.1.2.4 Thread the MIG wire from the spool through the input guide tube (22), through the roller groove and into
the outlet guide tube.
5.1.2.5 Replace the tension arm (21) and the tension adjustment (20). Double check the wire has located
correctly in the drive roller groove.
5.1.2.6 Adjusting wire feed tension: this is accomplished by winding the knob on the wire tension adjustment
arm (20). Clockwise will increase tension, anti-clockwise will decrease tension. There is a numbered scale on
the tensioner to indicate the position. Ideal tension should be as little as possible, while maintaining a consistent
wire feed with no drive roller slippage. Check all other possible causes of slippage, such as; incorrect/ worn drive
roller, worn/ damaged torch consumables, blocked/ damaged torch feed liner, before increasing feed tension.
8