03
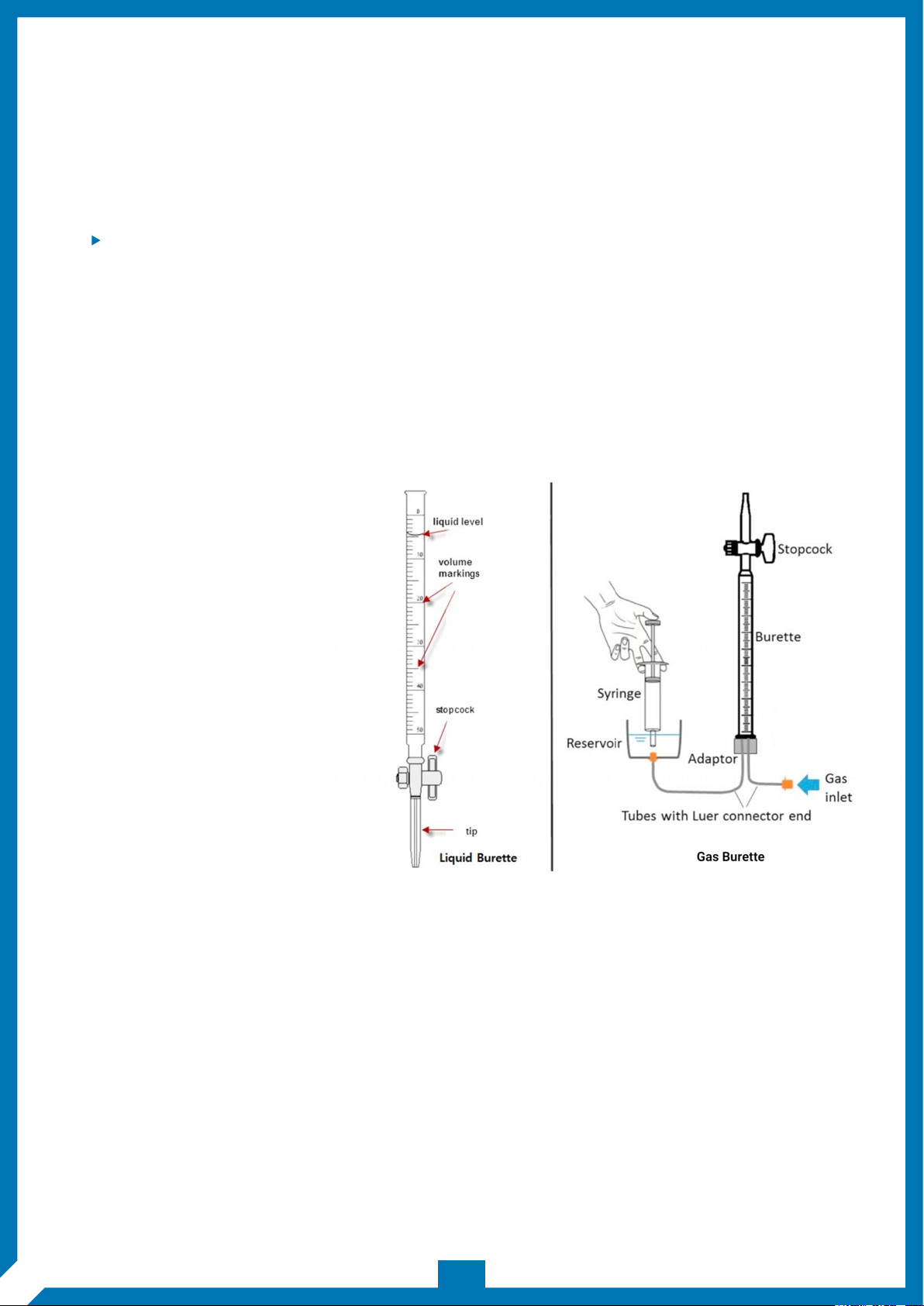
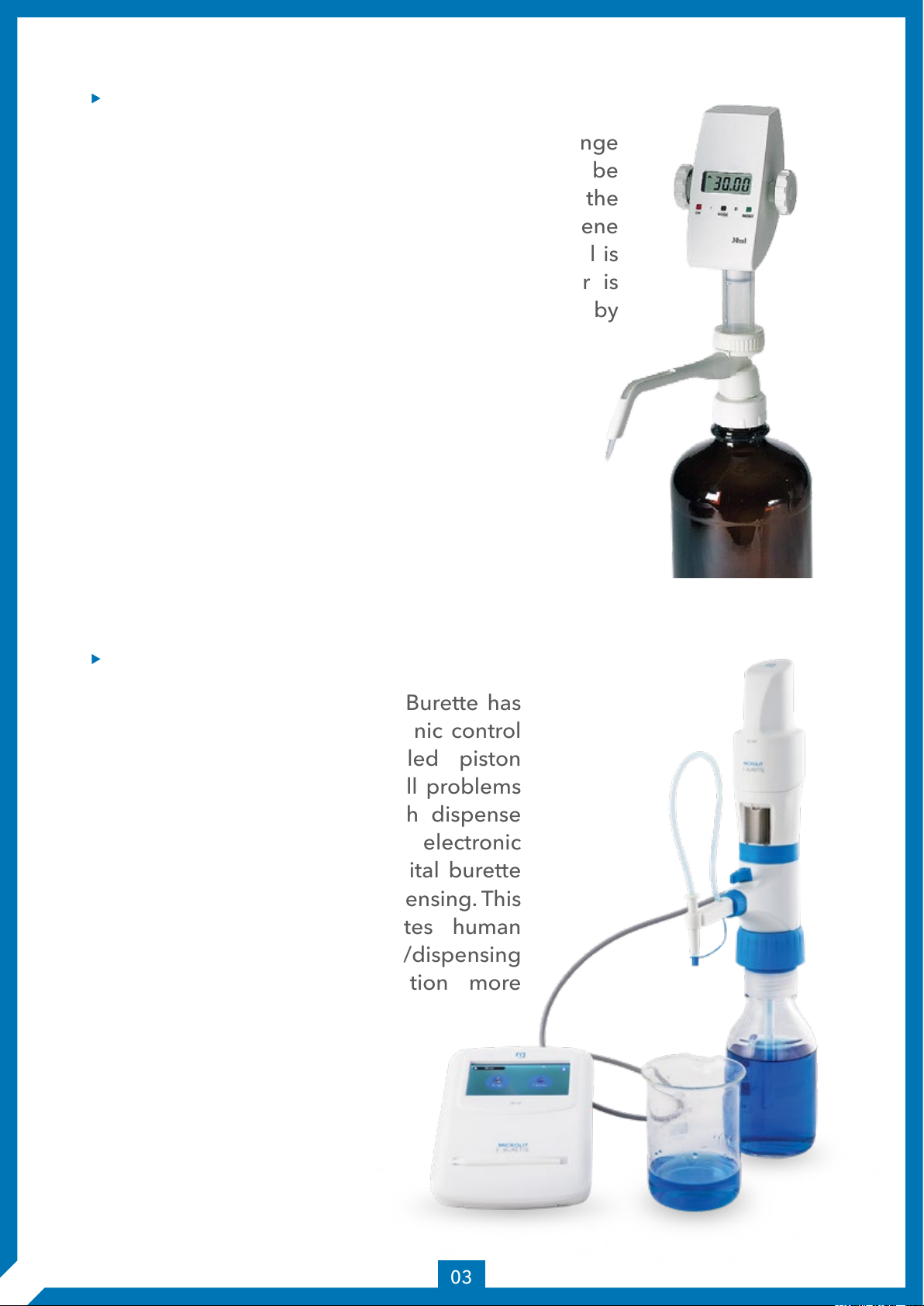
PISTON OR DIGITAL BURETTE:
A piston or digital burette is based on a syringe
design wherein the barrel and plunger can be
made of glass or plastic. For alkali solutions, the
barrel and plunger may be made of polyethylene
or another resistant plastic material. The barrel is
placed in a fixed position and the plunger is
moved incrementally by rotating the wheel by
hand or by means of a step motor.
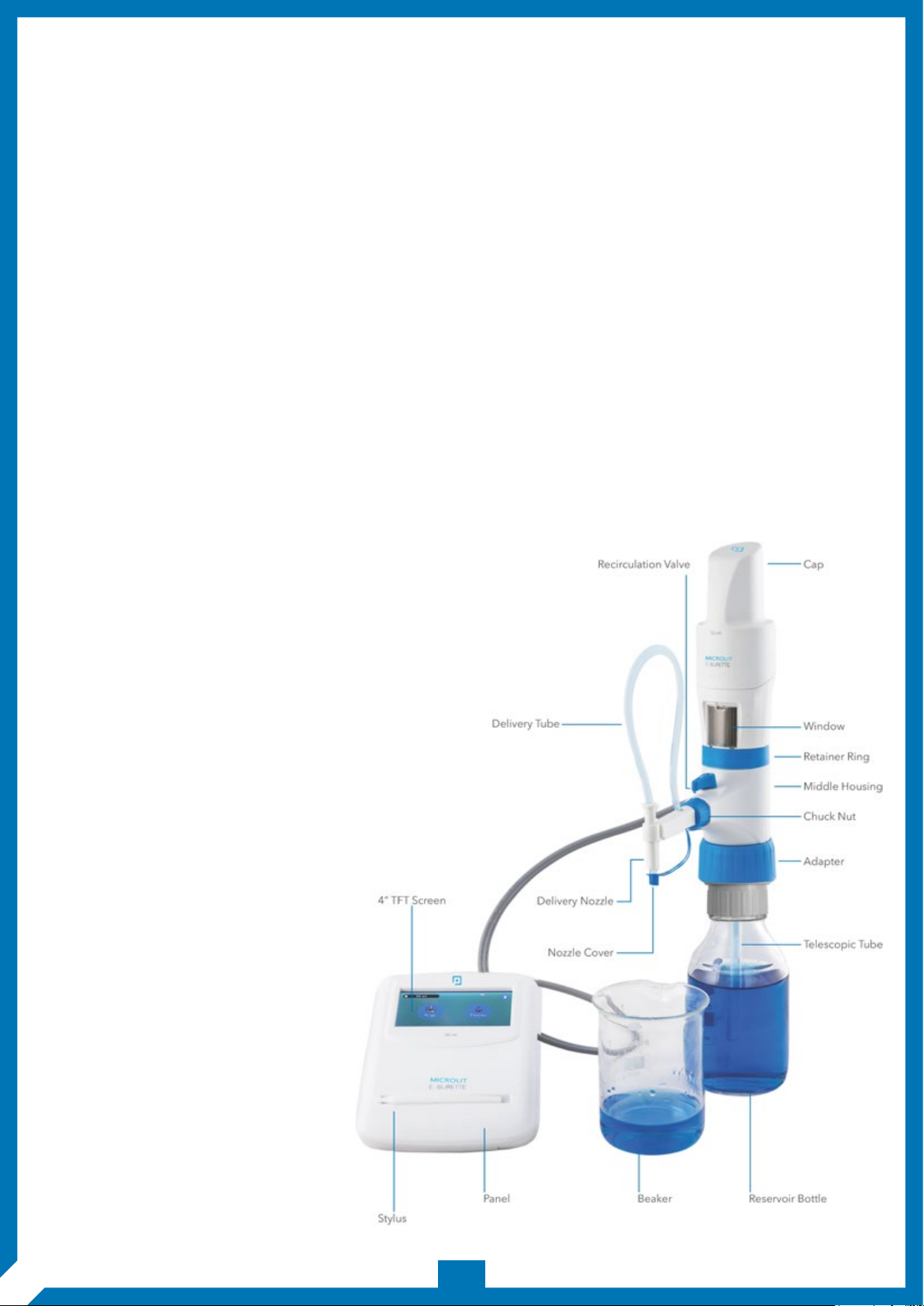
The Electronic Burette or E-Burette has
an electronic display, electronic control
panel and motor controlled piston
movements that eliminate all problems
of the digital burette which dispense
manually. The accuracy of electronic
burette is higher than a digital burette
due to motor controlled dispensing. This
motorized system eliminates human
errors in the titration/dispensing
process, making the titration more
precise.
The volume is shown on a digital
display given at the top of the
burette. A high-precision syringe can
be used to deliver a very precise
amount of liquid. A motorized digital
burette can be controlled by a
computer.
ELECTRONIC BURETTE