Specifications
Wingspan: 46cm
Airframe Bare Weight: 31 grams
Flying Weight:
60 grams (With 750mah battery)
65 grams (With 950mah battery)
Max Flying Weight: 85 grams
Channels: 3 (aileron elevator throttle)
Suggested Receiver: 4Ch Micro
Suggested Motors:
Brushless AP03
Brushless D1103-8,200kv or 10,000kv
Included Components
* Airframe Parts Sheets (Depron)
* Airframe Bracing Parts (Balsa / Ply)
* Wing Rib Sheets (Paulwonia Wood)
* Carbon Struts / Supports
* Control Linkages + Pushrods
* Sandpaper Sheet
* Decal Stickers
Electronics Required
* Micro Receiver (< 2.5 gram)
* Two Micro Servos (5320 / 5330 Servos)
* Brushless Motor / Propeller
* Transmitter
* Battery (500 –950 Mah 1S)
* Battery Charger
Tools / Supplies Required
* Soldering Iron with Fine Tip
* 1.2mm Drill Bit
* Tweesers
* Sanding Block
* Hobby Knife
* Steel ruler (or plastic)
* White PVA Glue or Wood Glue
* UHU Por Expanded Polystyrene Glue (link)
* Blenderm Hinge Tape (Link)
* Modelling Tape (Product Link)
The new Mini Delta V2 is designed for stable long duration
flight at relatively slow speeds. While not being suitable for
aerobatics, this airframe excels in its stability and straight
tracking. Designed with micro FPV setups in mind, this
airframe features two component bays (top and bottom)
which give ample room for large batteries, multiple batteries
and FPV gear.
With a wingspan of just 46cm (18 inches), the Mini Delta is
suitable for outdoor flight in calm conditions with no wind or
indoor stadium flight in the hands of an experienced pilot.
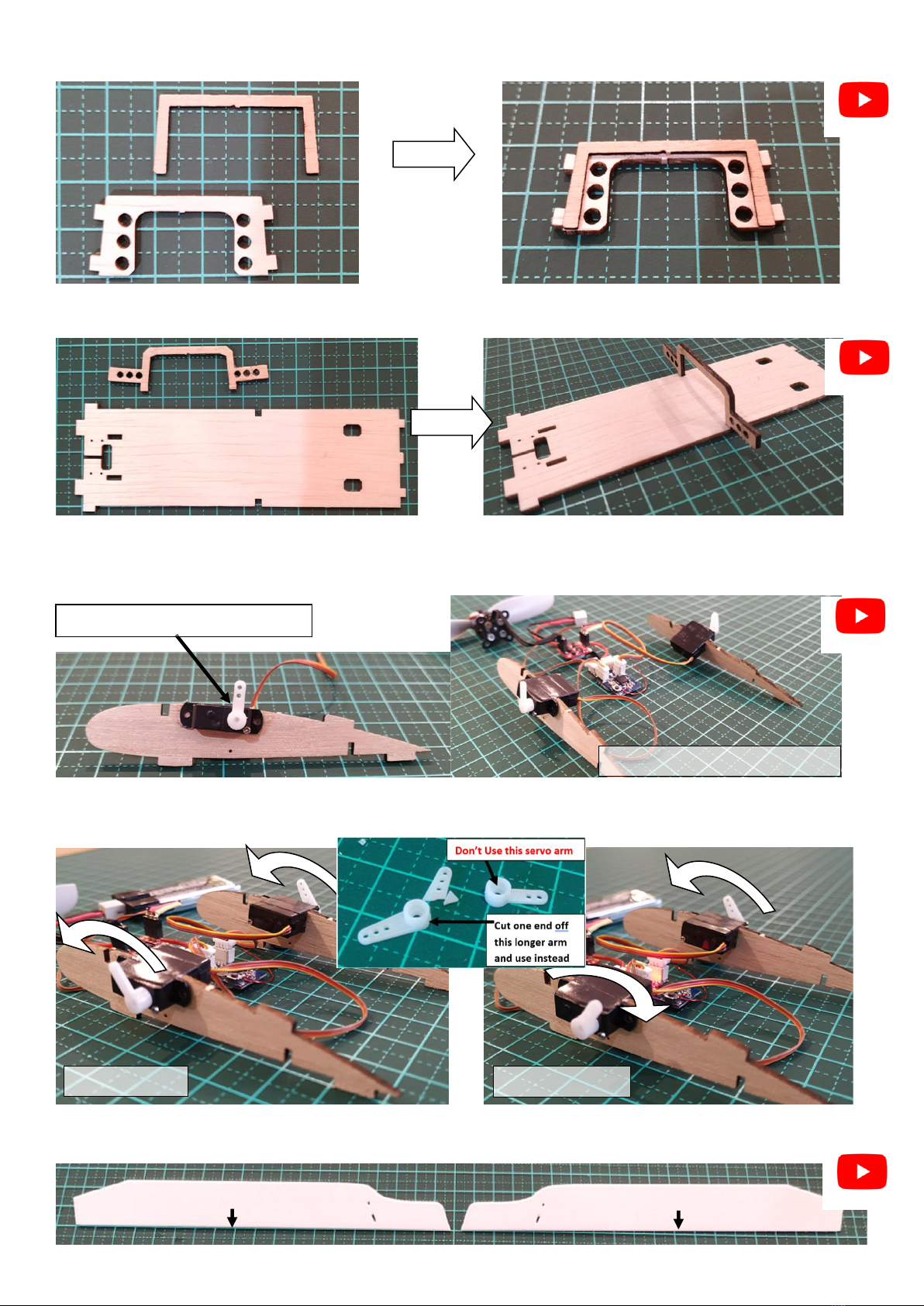
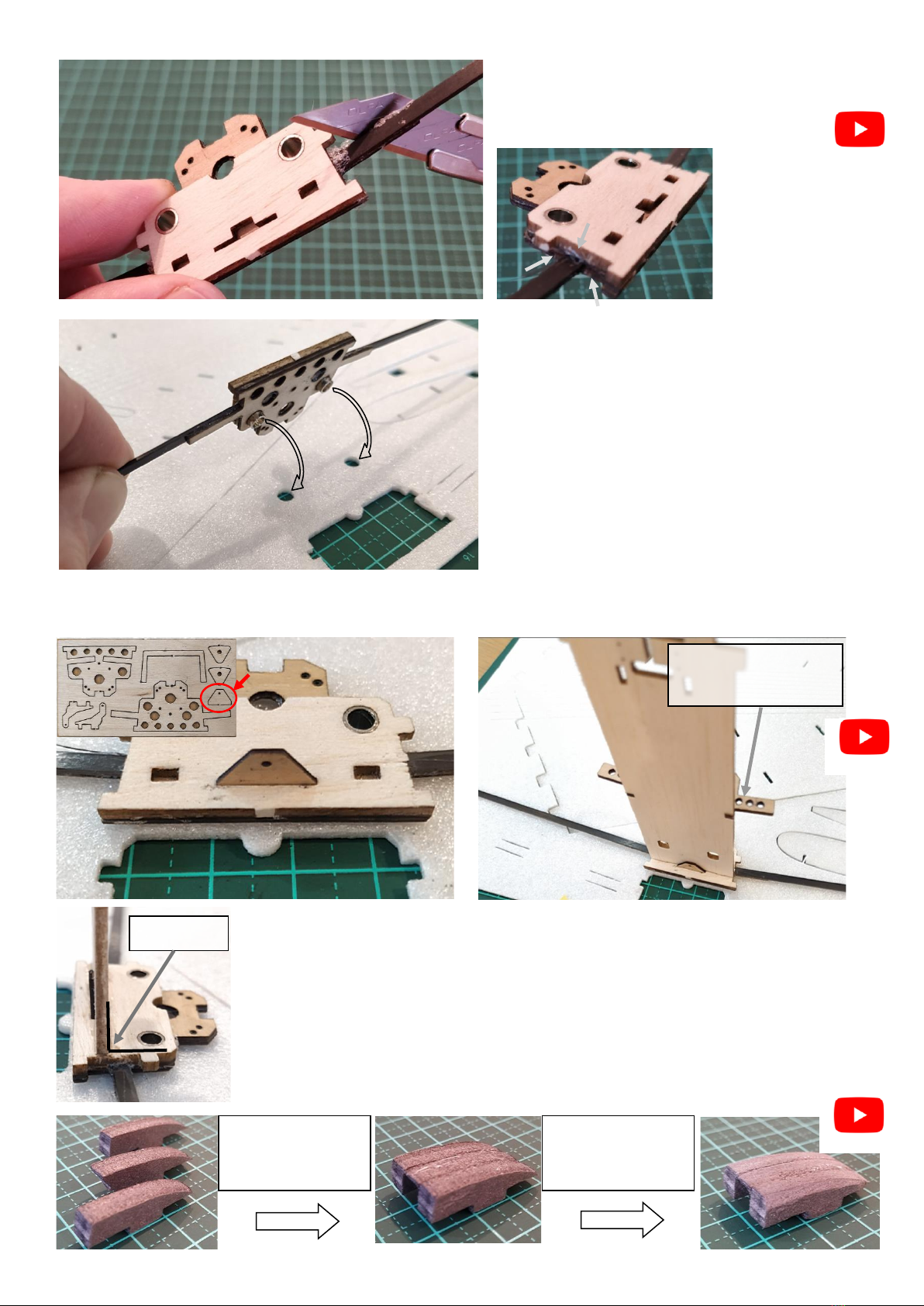
The two videos below cover the complete build process as
set out in this manual. At stages throughout this manual
there are links to the relevant position in the build videos.