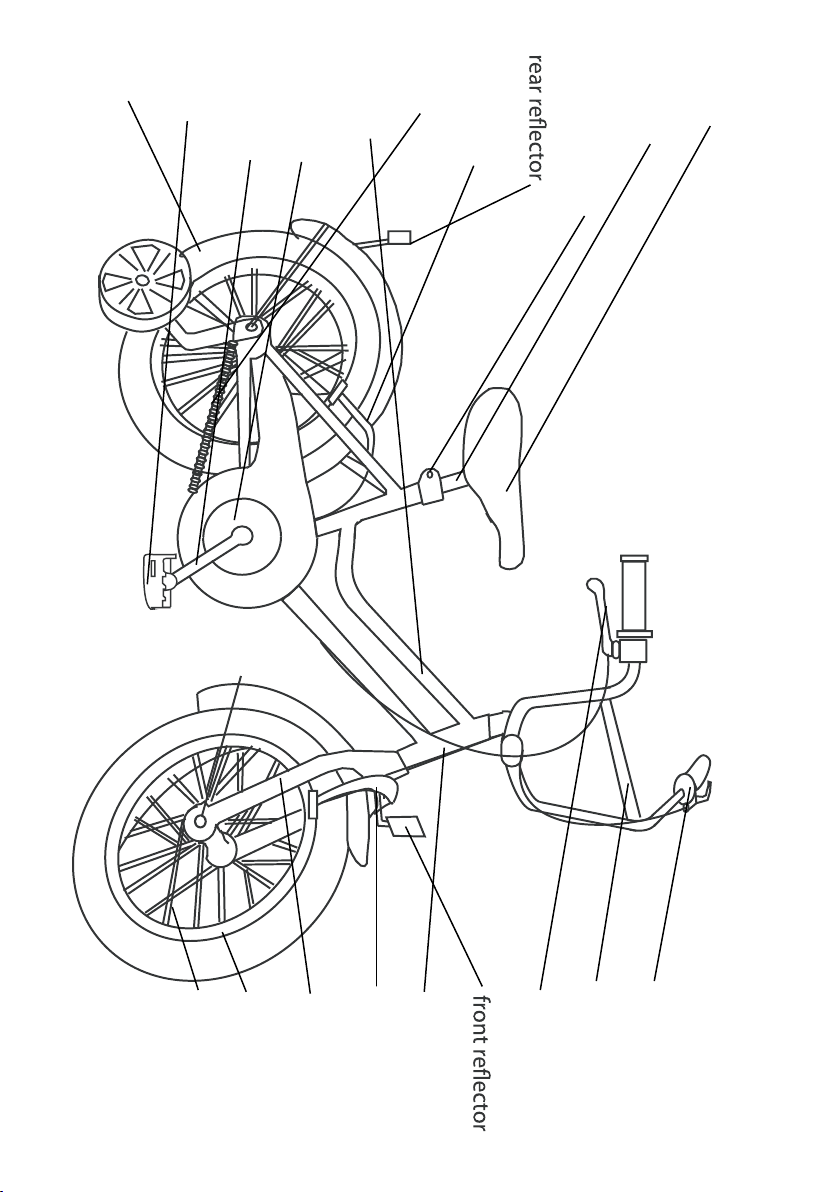
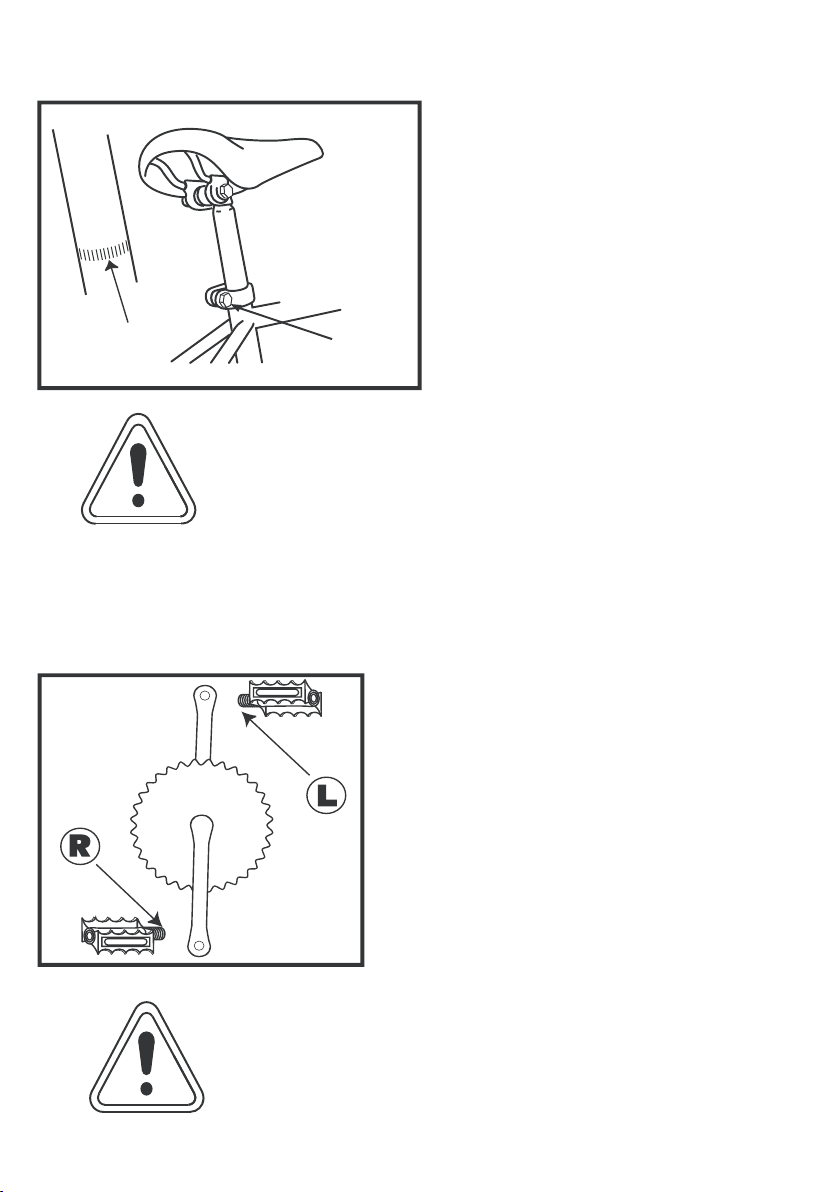
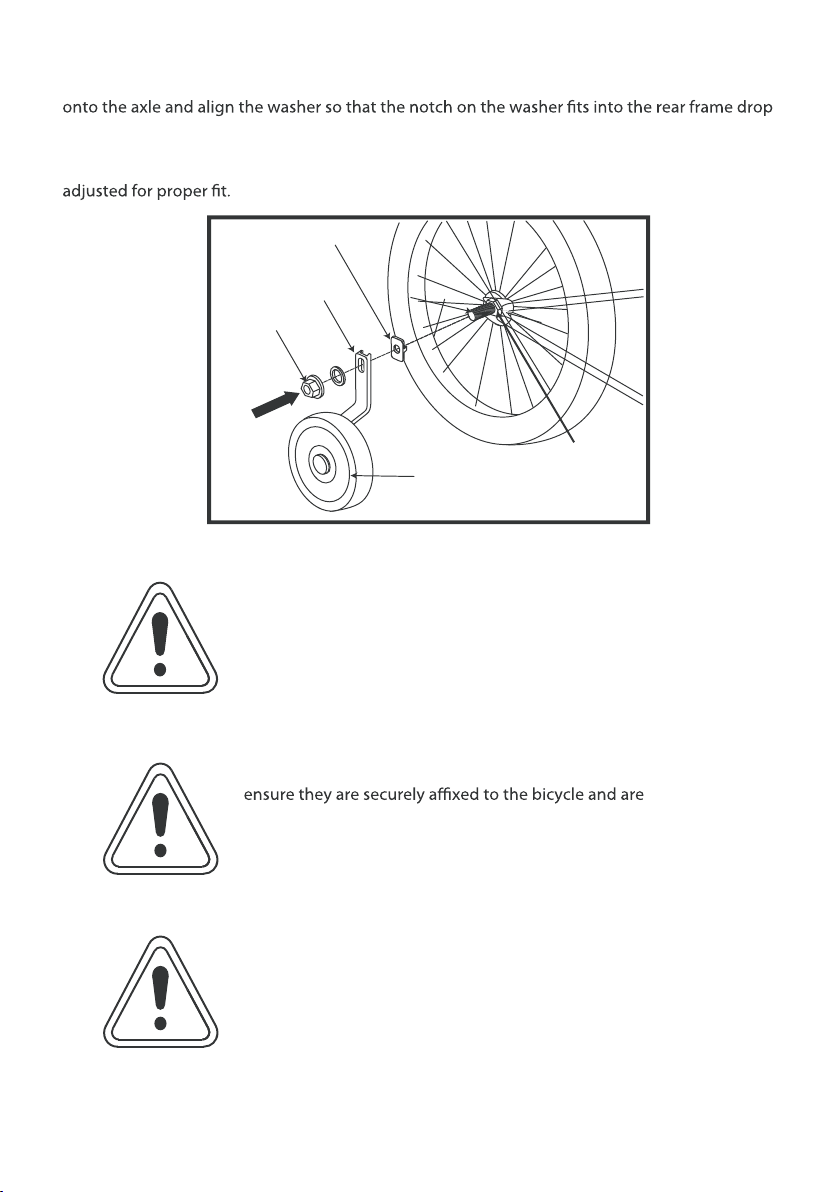
Please ensure you have read and fully understood the entirity of this
manual before assembling your child’s bicycle and allowing them to use it.
This is the WARNING symbol. It is used throughout this
manual to preceed safety instructions. Make sure you and
your child understand these instructions. Failure to do so
may result in your child losing control and falling. As any fall
has the potential to result in serious injury or death please pay
particular attention to these warnings. If you are unsure of any aspect of
these warnings you should consult a qualified bicycle technician before
using this product.
Congratulations on your purchase of this MooreLarge child’s bicycle.
Cycling is an excellent way for children to get some of the daily exercise
they need to keep healthy. It is also a fun way of teaching young children
valuable skills such as mobility, independence, balance, judgment and
self-confidence.
Once learned, these are skills that will last a lifetime
The most important part of fun cycling is to learn to do it safely.
IMPORTANT INFORMATION FOR PARENTS.
This manual has been written to help you maximise your child’s safety,
comfort and enjoyment whilst cycling. It is important that you and your
child understand the bike’s operations, limits and features to ensure
that your child enjoys safe cycling from the very first ride.
Rules for Children
To avoid accidents, teach children good riding skills with an emphasis on safety from an early age.
Children should be supervised by an adult.
1. Always wear a properly fitted helmet.
2. Do not play in driveways or the road.
3. Do not ride on busy streets.
4. Do not ride at night.
5. Be aware of other road vehicles behind and nearby.
6. Before entering a street: Stop, look right, left, and right again for traffic. If there's no traffic,
proceed into the roadway.
7. If riding downhill, be extra careful. Slow down using the brakes and maintain control of the steering.
8. Never take your hands off the handlebars, or your feet off the pedals when riding downhill.
The riding of small wheel diameter bicycles at excessive speeds can lead to instability and
is not recommended.Children should be made aware of all possible riding hazards and correct
riding behavior before they take to the streets. - Do not leave it up to trial and error.
-i-