Page 2
Noisy Operation.
1. Starved suction: Check fluid supply, length of suction line, and
obstructions in pipe.
2. Bearings worn: Replace parts; check alignment, belt tension,
pressure at discharge port.
3. Broken flexible joint: Replace part; check pressure at discharge
port.
4. Insufficient mounting: Mount to firm base. Vibration-induced
noise can be reduced by using mount pads and hose on
suction and discharge ports.
Pump Overloads.
1. Excessive discharge pressure: Check discharge pressure for
maximum rating given in Table 1. Check for obstruction in
discharge pipe.
2. Excessive temperature.
3. Belt or coupling slip: Check pressure at discharge port.
4. Loose bond in stator: High temperature and caustics will cause
bond between rubber and tube to fail. Replace stator. Check
fluid temperature and pressure at discharge port.
5. Fluid viscosity too high: See chart below for recommended
maximum RPM.
Viscosity CP Limit RPM
1-1,000
1750
1,000-2,500
1200
2,500-5,000
600
5,000-10,000
300
10,000-20,000
175
20,000-50,000
80
Based on 60% min. volumetric efficiency. See PEC449 or consult
Moyno representative for exact values.
6. Motor connected incorrectly: Motor wired for 230 VAC,
connected to 115 VAC service.
Poor Performance.
1. Low pressure; worn stator: Replace stator: Check for
excessive abrasive material in fluid. Check for run dry
condition.
Mechanical Seal Leakage.
1. Leakage at startup: If leakage is slight, allow pump to run
several hours to let faces run in.
2. Persistent seal leakage: Faces may be cracked from freezing
or thermal shock. Replace seal.
Pump Will Not Prime.
1. Air leak on suction side: Check pipe connections. Suction lift
over 15 ft. will cause seal faces to open.
2. Defective mechanical seal: Inspect and repair as necessary.
MAINTENANCE
General. These pumps have been designed for a minimum of
maintenance. The pump is one of the easiest to work on in that
the main elements are very accessible and require few tools to
disassemble.
Bearing Lubrication. The prelubricated, fully sealed bearings do
not require additional lubrication.
PUMP DISASSEMBLY
WARNING: Before disassembling pump, disconnect power
source and thoroughly bleed pressure from
system. Failure to do so could result in electric
shock or serious bodily harm.
1. Disconnect power source.
2. Remove suction and discharge piping.
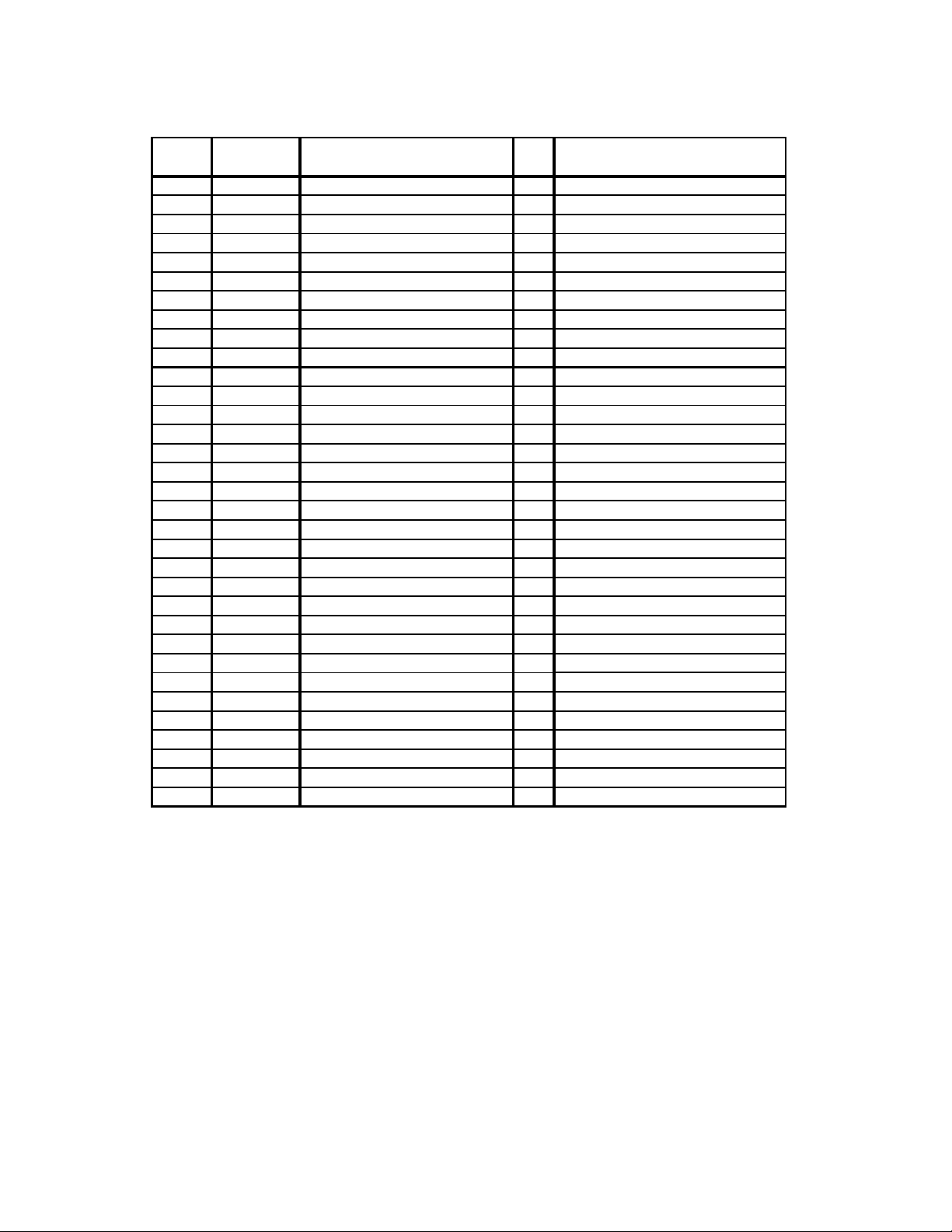
3. Discharge coupling (9) may be removed from stator (21) by
unscrewing in a counter-clockwise direction (RH thread).
4. Remove stator support clamp screw and remove top half of
stator support (38).
5. Stator (21) may be removed from suction housing (2) by
unscrewing in a counter-clockwise direction (RH thread). Use
strap wrench on stator to avoid crushing with a pipe wrench.
Pull stator (21) from rotor (22). To assist removal of stator, hold
drive shaft (26) from turning and turn stator clockwise when
facing suction housing after disengaging thread.
6. Remove screws (112) holding suction housing (2) to bearing
housing (1) or adapter (74). Remove suction housing and
suction housing gasket (83). Gaskets on cast iron models only.
Remove O-Ring (270) on other models.
7. The rotor (22) and flexible joint (24) may be removed using the
following procedure (do not bend joint more than 15 degrees).
a. Remove rotor (22) from flexible joint (24) by using a punch
to remove rotor shaft pin (46). Support joint while removing
pin.
b. Remove joint (24) from shaft (26) by using a punch to
remove shaft pin (46).
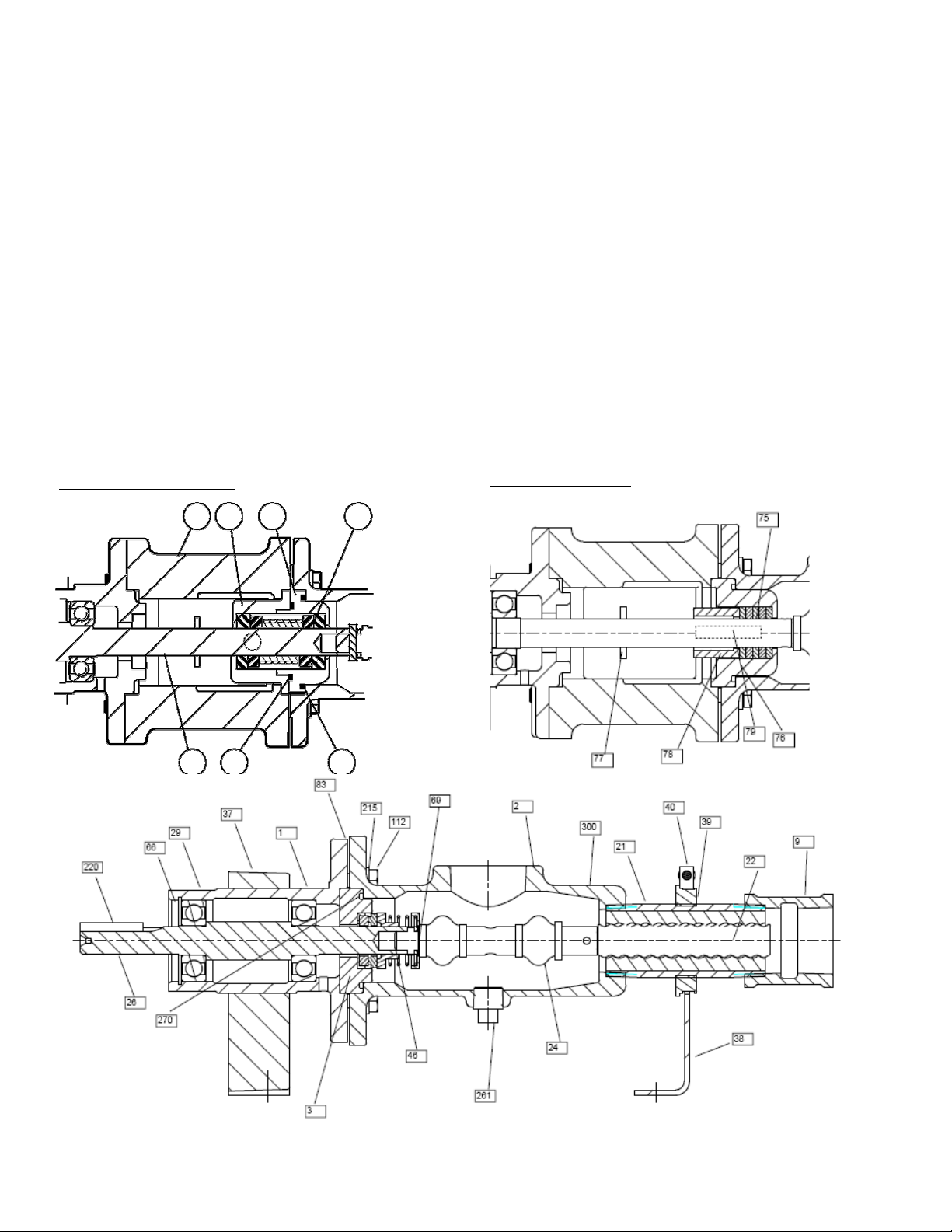
8. Single Mechanical Seal Models. Carefully slide mechanical
seal (69) off shaft (26). Carefully pry seal out of bearing
housing (1), or seal housing (3). Remove seal housing if pump
is a stainless model.
Double Mechanical Seal Models. Carefully slide seal housing
(71) from the drive shaft. Remove rotational part of mechanical
seal from the shaft. Carefully remove seal gland (73) from
adapter. Remove stationary seal faces if required.
If any parts of mechanical seal are worn out or broken, the
complete assembly should be replaced. Seal components are
matched parts and are not interchangeable.
Packing Models. Slide stuffing box assembly from the shaft.
Remove packing gland halves and replace packing.
9. The bearings (29) and shaft (26) assembly can be removed
from bearing housing (1) after snap ring (66) has been
removed. To remove the shaft assembly, lightly tap the shaft at
the flexible joint connection end using a block of wood to
protect the shaft. The bearings may be pressed off the shaft.
PUMP ASSEMBLY
1. Press bearings (29) on shaft (26), and locate slinger ring (77)
on the shaft near the radial bearing.
NOTE: When replacing bearings, always press on the inner race
when assembling to shaft, and on the outer race when
pressing bearings into the housings.
2. Press shaft assembly into bearing housing (1) securing with
snap ring (66).
3. On stainless steel models install seal housing (3) in bearing
housing with O-Ring (270) installed in the O-Ring groove.
On packing models install stuffing box assembly (stuffing box,
packing, and packing gland) on shaft with O-ring (270) installed
in the O-ring groove.