2|ni.com |NI myDAQ User Guide
Making Signal Connections with NI myDAQ..........................................................................7
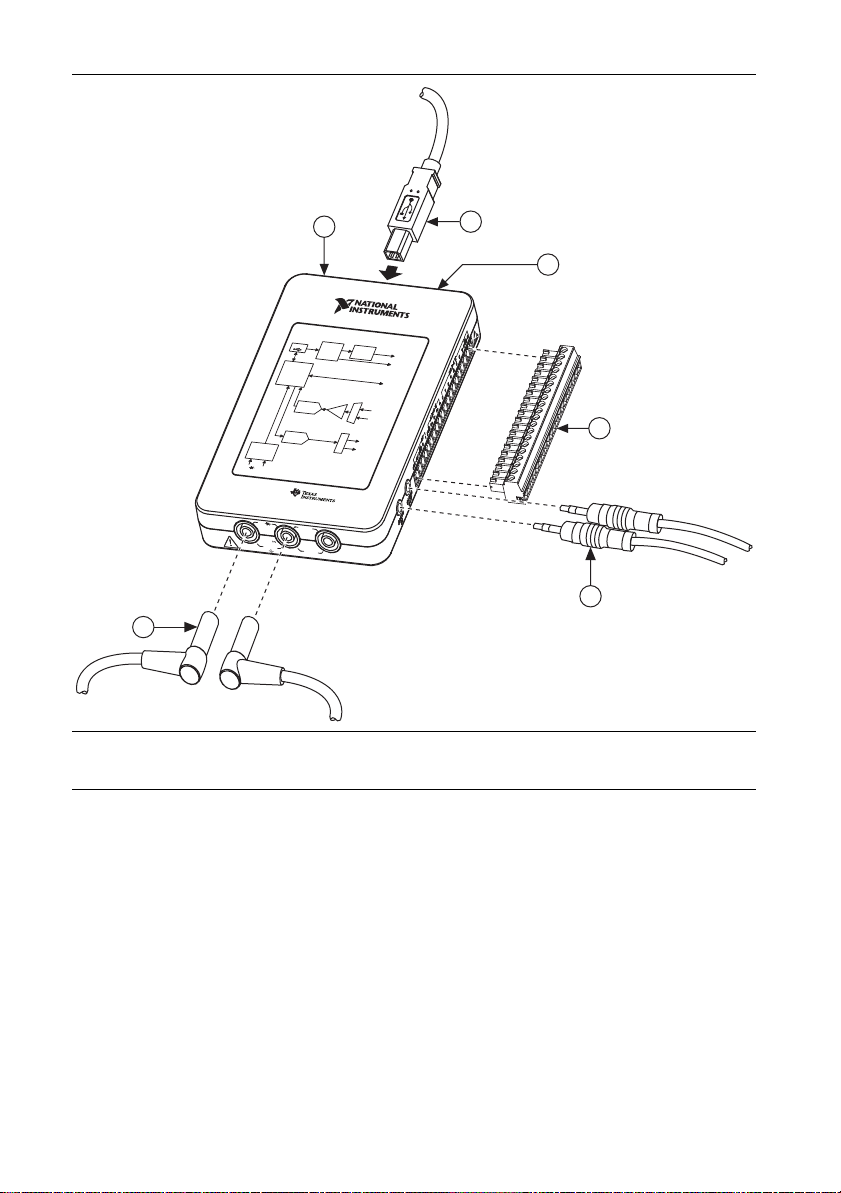
Setting up Your NI myDAQ Device.................................................................................7
Connecting Signals ...........................................................................................................9
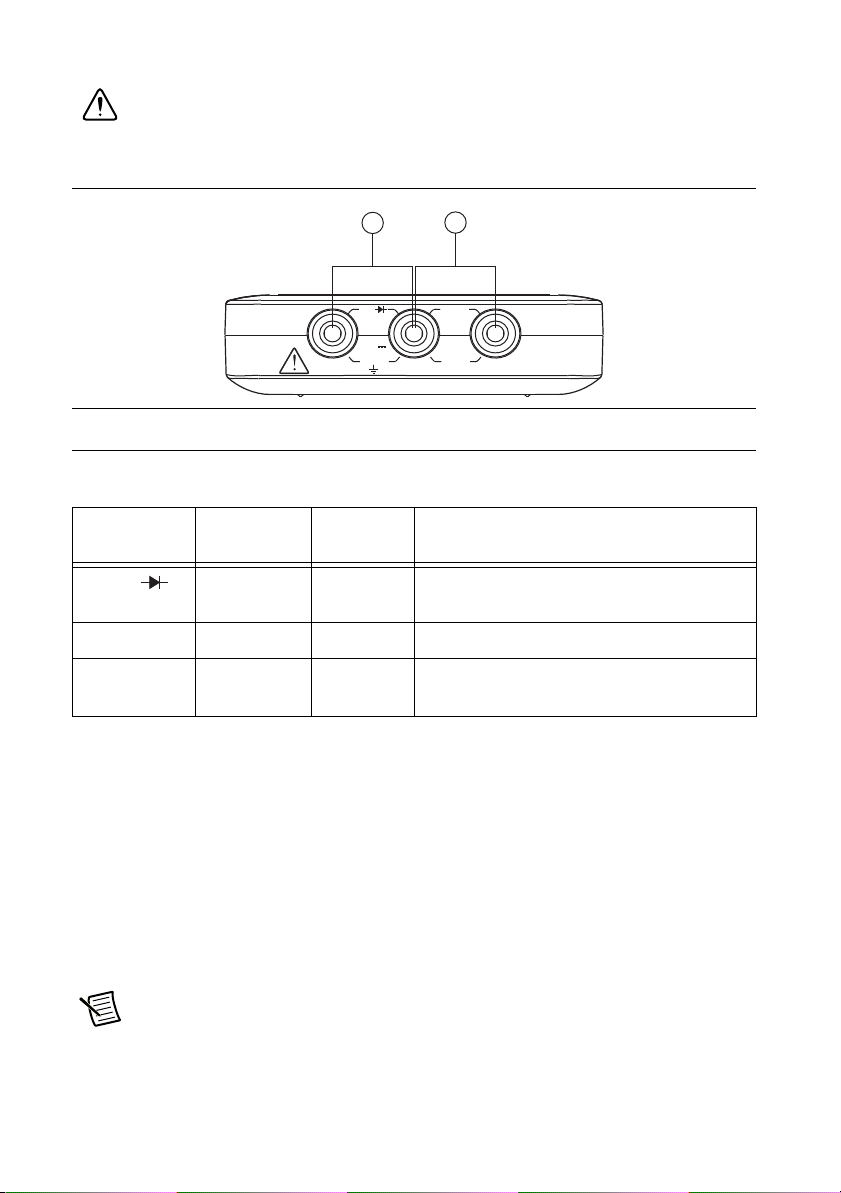
Connecting Analog Input Signals ..................................................................................... 10
NI myDAQ DMM Fuse Replacement .............................................................................. 13
Digital I/O (DIO) and Counters/Timers.................................................................................... 15
Using NI myDAQ with NI ELVISmx Software Instruments................................................... 16
NI ELVISmx Instrument Launcher ..................................................................................17
Digital Multimeter (DMM)............................................................................................... 18
Oscilloscope (Scope) ........................................................................................................ 19
Function Generator (FGEN) .............................................................................................20
Bode Analyzer .................................................................................................................. 21
Dynamic Signal Analyzer (DSA) ..................................................................................... 22
Arbitrary Waveform Generator (ARB)............................................................................. 23
Digital Reader ................................................................................................................... 24
Digital Writer.................................................................................................................... 25
Example: Measuring a Signal Using the NI ELVISmx Oscilloscope
with NI myDAQ ............................................................................................................ 26
Using NI myDAQ with LabVIEW ...........................................................................................27
NI ELVISmx Express VIs in LabVIEW...........................................................................27
Example: Measuring Signals Using the NI ELVISmx Oscilloscope Express VI
with NI myDAQ ............................................................................................................ 28
Using NI-DAQmx with NI myDAQ ................................................................................30
Example: Measuring Audio Pass-Through in LabVIEW with NI myDAQ .....................30
Texas Instruments Components in NI myDAQ........................................................................34
Resource Conflicts ....................................................................................................................35
Additional Resources ................................................................................................................ 37
Related Documentation..................................................................................................... 37
Other Resources ................................................................................................................ 38
Common Terms and Acronyms........................................................................................ 38
Warranty ...........................................................................................................................39
Worldwide Support and Services .....................................................................................39
Safety Information
Caution Do not operate the hardware in a manner not specified in this document
and in the user documentation. Misuse of the hardware can result in a hazard. You
can compromise the safety protection if the hardware is damaged in any way. If the
hardware is damaged, return it to National Instruments for repair.
Clean the hardware with a soft, nonmetallic brush. Make sure that the hardware is completely
dry and free from contaminants before returning it to service.