Netgate SG-5100 User manual

Product Manual
SG-5100
Netgate
Sep 21, 2018

Product ManualSG-5100
Thank you for your purchase of the pfSense® SG-5100 Firewall Appliance. This appliance provides a powerful,
reliable, cost-effective solution.
Quick Start Guide
The Quick Start Guide covers the first time connection procedures and will provide you with the information you need
to get your appliance up and running.
CONTENTS 1

CHAPTER
ONE
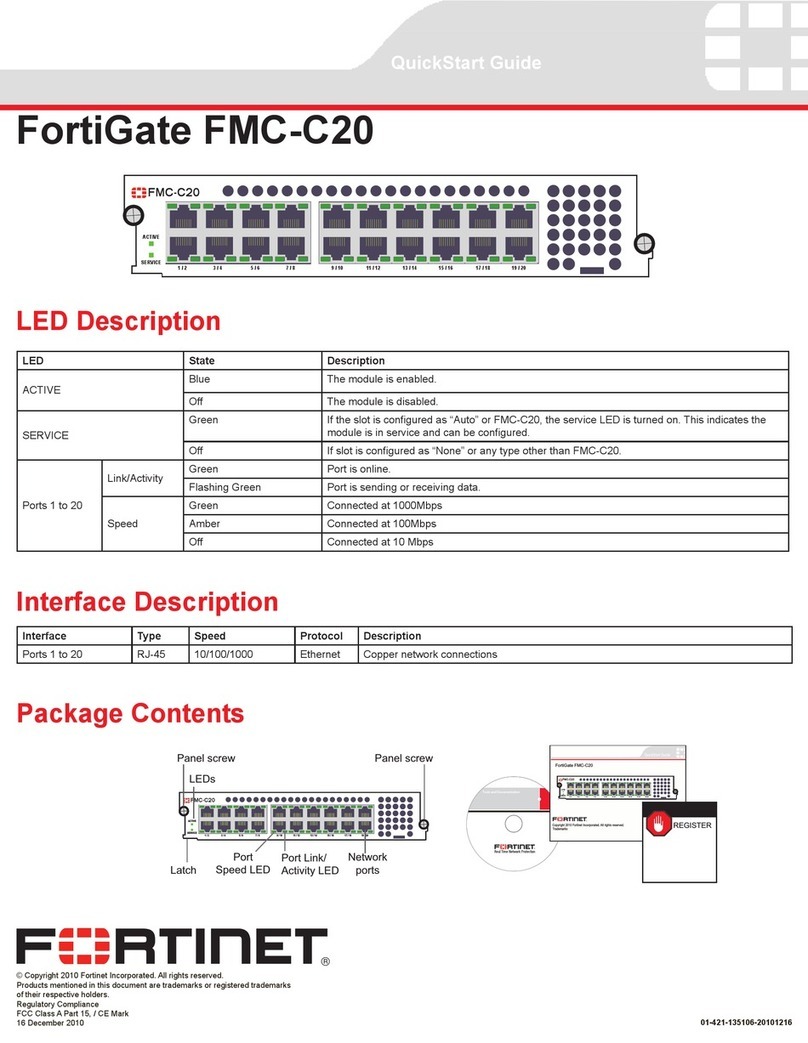
I/O PORTS
1.1 Rear Side
1.2 Ethernet Ports
Interface Name Port Name Port Type Port Speed
WAN IGB0 RJ-45 1 Gbps
LAN IGB1 RJ-45 1 Gbps
OPT1 IX0 RJ-45 1 Gbps
OPT2 IX1 RJ-45 1 Gbps
OPT3 IX2 RJ-45 1 Gbps
OPT4 IX3 RJ-45 1 Gbps
Note: All Ethernet ports of the pfSense appliance support auto-MDIX and are capable of utilizing either straight-
through or crossover ethernet cables.
2

Product ManualSG-5100
1.3 Other Ports and Indicators
• Console (Mini-USB)
• Status LEDs
• 2x USB 3.0
Status LED Description
Top LED Add-on storage activity (does not show eMMC activity)
Middle LED Activity
Bottom LED Power
1.4 Front Side
1. Receessed Reset Button
2. Power Button
3. Power (12VDC with threaded locking connector)
Center Pin Positive
1.3. Other Ports and Indicators 3

CHAPTER
TWO
GETTING STARTED
Tip: Before configuring the pfSense appliance it is best to activate it by following the instructions at https://www.
netgate.com/register/.
The basic firewall configuration begins with connecting the pfSense appliance to the Internet. Neither the modem nor
the pfSense appliance should be powered up at this time.
Establishing a connection to the Internet Service Provider (ISP) starts with connecting one end of an ethernet cable to
the WAN port (shown in the I/O Ports section) of the pfSense appliance.
Warning: The default LAN subnet on the firewall is 192.168.1.0/24. The same subnet cannot be used on
both WAN and LAN, so if the subnet on the WAN side of the firewall is also 192.168.1.0/24,disconnect the
WAN interface until the LAN interface has been renumbered to a different subnet.
The opposite end of the same ethernet cable should be inserted in to the LAN port of the ISP-supplied modem. The
modem provided by the ISP might have multiple LAN ports. If so, they are usually numbered. For the purpose of this
installation, please select port 1.
The next step is to connect the LAN port (shown in the I/O Ports section) of the pfSense appliance to the computer
which will be used to access the firewall console.
Connect one end of the second ethernet cable to the LAN port (shown in the I/O Ports section) of the pfSense appliance.
Connect the other end to the network connection on the computer. In order to access the web configurator, the PC
network interface must be set to use DHCP, or have a static IP set in the 192.168.1.x subnet with a subnet mask
of 255.255.255.0. Do not use 192.168.1.1, as this is the address of the firewall, and will cause an IP conflict.
2.1 Initial Setup
The next step is to power up the modem and the firewall. Plug in the power supply to the power port (shown in the I/O
Ports section).
Once the modem and pfSense appliance are powered up, the next step is to power up the computer.
Once the pfSense appliance is booted, the attached computer should receive a 192.168.1.x IP address via DHCP
from the pfSense appliance.
4

Product ManualSG-5100
2.2 Logging Into the Web Interface
Browse to https://192.168.1.1 to access the web interface. In some instances, the browser may respond with a message
indicating a problem with website security. Below is a typical example in Google Chrome. If this message or similar
message is encountered, it is safe to proceed.
At the login page enter the default pfSense password and username:
Username admin
Password pfsense
Click Login to continue
2.3 Wizard
Upon successful login, the following is displayed.
2.2. Logging Into the Web Interface 5

Product ManualSG-5100
2.4 Configuring Hostname, Domain Name and DNS Servers
2.5 Hostname
For Hostname, any desired name can be entered as it does not affect functionality of the firewall. Assigning a hostname
to the firewall will allow the GUI to be accessed by hostname as well as IP address.
For the purposes of this guide, use pfsense for the hostname. The default hostname, pfsense may be left un-
changed.
Once saved in the configuration, the GUI may be accessed by entering http://pfsense as well as http://192.168.1.1
2.6 Domain
If an existing DNS domain is in use within the local network (such as a Microsoft Active Directory domain), use that
domain here. This is the domain suffix assigned to DHCP clients, which should match the internal network.
For networks without any internal DNS domains, enter any desired domain name. The default localdomain is used
for the purposes of this tutorial.
2.7 DNS Servers
The DNS server fields can be left blank if the DNS Resolver is used in non- forwarding mode, which is the default
behavior. The settings may also be left blank if the WAN connection is using DHCP, PPTP or PPPoE types of Internet
2.4. Configuring Hostname, Domain Name and DNS Servers 6

Product ManualSG-5100
connections and the ISP automatically assigns DNS server IP addresses. When using a static IP on WAN, DNS server
IP addresses must be entered here for name resolution to function if the default DNS Resolver settings are not used.
DNS servers can be specified here even if they differ from the servers assigned by the ISP. Either enter the IP addresses
provided by the ISP, or consider using Google public DNS servers (8.8.8.8,8.8.4.4). Google DNS servers are
used for the purpose of this tutorial. Click Next after filling in the fields as appropriate.
2.8 Time Server Configuration
2.9 Time Server Synchronization
Setting time server synchronization is quite simple. We recommend using the default pfSense time server address,
which will randomly select an NTP server from a pool.
2.10 Setting Time Zone
Select an appropriate time zone for the location of the firewall. For purposes of this manual, the Timezone setting will
be set to America/Chicago for US Central time.
2.11 Configuring Wide Area Network (WAN) Type
The WAN interface type is the next to be configured. The IP address assigned to this section becomes the Public IP
address that this network will use to communicate with the Internet.
2.8. Time Server Configuration 7

Product ManualSG-5100
This depicts the four possible WAN interface types. Static, DHCP, PPPoE and PPTP. One must be selected from the
drop-down list.
Further information from the ISP is required to proceed when selecting Static,PPPoE and PPTP such as login name
and password or as with static addresses, an IP address, subnet mask and gateway address.
DHCP is the most common type of interface for home cable modems. One dynamic IP address is issued from the
ISP DHCP server and will become the public IP address of the network behind this firewall. This address will change
periodically at the discretion of the ISP. Select DHCP as shown and proceed to the next section.
2.12 MAC Address
If replacing an existing firewall, the WAN MAC address of the old firewall may be entered here, if it can be determined.
This can help avoid issues involved in switching out firewalls, such as ARP caches, ISPs locking to single MAC
addresses, etc.
If the MAC address of the old firewall cannot be located, the impact is most likely insignificant. Power cycle the ISP
router and modem and the new MAC address will usually be able to get online. For some ISPs, it may be necessary to
call them when switching devices, or an activation process may be required.
2.13 Configuring MTU and MSS
MTU or Maximum Transmission Unit determines the largest protocol data unit that can be passed onwards. A 1500-
byte packet is the largest packet size allowed by Ethernet at the network layer and for the most part, the Internet so
leaving this field blank allows the system to default to 1500-byte packets. PPPoE is slightly smaller at 1492-bytes.
Leave this blank for a basic configuration.
2.12. MAC Address 8

Product ManualSG-5100
2.14 Configuring DHCP Hostname
Some ISPs specifically require a DHCP Hostname entry. Unless the ISP requires the setting, leave it blank.
2.15 Configuring PPPoE and PPTP Interfaces
Information added in these sections is assigned by the ISP. Configure these settings as directed by the ISP
2.14. Configuring DHCP Hostname 9

Product ManualSG-5100
2.16 Block Private Networks and Bogons
When enabled, all private network traffic originating on the internet is blocked.
Private addresses are reserved for use on internal LANs and blocked from outside traffic so these address ranges may
be reused by all private networks.
The following inbound address Ranges are blocked by this firewall rule:
•10.0.0.1 to 10.255.255.255
•172.16.0.1 to 172.31.255.254
•192.168.0.1 to 192.168.255.254
•127.0.0.0/8
•100.64.0.0/10
•fc00::/7
Bogons are public IP addresses that have not yet been allocated, so they may typically also be safely blocked as they
should not be in active use.
Check Block RFC1918 Private Networks and Block Bogon Networks.
Click Next to continue.
2.16. Block Private Networks and Bogons 10

Product ManualSG-5100
2.17 Configuring LAN IP Address & Subnet Mask
A static IP address of 192.168.1.1 and a subnet mask (CIDR) of 24 was chosen for this installation. If there are
no plans to connect this network to any other network via VPN, the 192.168.1.x default is sufficient.
Click Next to continue.
Note: If a Virtual Private Network (VPN) is configured to remote locations, choose a private IP address range more
obscure than the very common 192.168.1.0/24. IP addresses within the 172.16.0.0/12 RFC1918 private
address block are the least frequently used. We recommend selecting a block of addresses between 172.16.x.x
and 172.31.x.x for least likelihood of having VPN connectivity difficulties. An example of a conflict would be If
the local LAN is set to 192.168.1.x and a remote user is connected to a wireless hotspot using 192.168.1.x
(very common), the remote client won’t be able to communicate across the VPN to the local network.
2.18 Change Administrator Password
Select a new Administrator Password and enter it twice, then click Next to continue.
2.17. Configuring LAN IP Address & Subnet Mask 11

Product ManualSG-5100
2.19 Save Changes
Click Reload to save configuration.
2.20 Basic Firewall Configured
To proceed to the webConfigurator, make the selection as highlighted. The Dashboard display will follow.
2.21 Backing Up and Restoring
At this point, basic LAN and WAN interface configuration is complete. Before proceeding, backup the firewall con-
figuration. From the menu at the top of the page, browse to Diagnostics > Backup/Restore.
2.19. Save Changes 12

Product ManualSG-5100
Click Download Configuration and save a copy of the firewall configuration.
This configuration can be restored from the same screen by choosing the backup file under Restore configuration.
2.21. Backing Up and Restoring 13

Product ManualSG-5100
2.22 Connecting to the Console
There are times when accessing the console is required. Perhaps GUI console access has been locked out, or the
password has been lost or forgotten.
See also:
Connecting to Console Port Connect to the console. Cable is required.
2.22. Connecting to the Console 14

CHAPTER
THREE
CONNECTING TO CONSOLE PORT
3.1 Simple Configuration
Below are the simple instructions for connecting to the console port with Microsoft Windows. If these steps do not
work for you or if you’re an operating system other than Windows, then please skip forward to Advanced Configura-
tion.
3.1.1 Serial Terminal Emulation Client
A serial terminal emulation program is required to access the pfSense appliance console through the serial interface.
Microsoft Windows no longer includes HyperTerminal in Versions 7 and up. PuTTY is free and can be downloaded
from:
http://www.chiark.greenend.org.uk/~sgtatham/putty/download.html
3.1.2 Configuring Serial Terminal Emulator
PuTTY must be configured to communicate with the pfSense appliance. In order to do so, you must first know what
COM Port your computer has assigned to your serial port. Even if you assigned your serial port to COM1 in the BIOS,
Windows may remap it to a different COM Port.
To determine this, you must open Windows Device Manager and view the COM port assignment:
15

Product ManualSG-5100
Note: The first time you connect your computer to the SG-5100, it may take up to 3 minutes for the driver to install.
It should install automatically for Windows 7 and above.
Open PuTTY and locate the Session display as shown below. For the Connection type, select Serial. Set Serial line
to the COM Port that is displayed in Windows Device Manager, COM3 for this example, and the Speed to 115200
bits per second, the speed of the BIOS in this case.
3.1. Simple Configuration 16

Product ManualSG-5100
Select Open and the console screen will be displayed.
3.2 Advanced Configuration
A Prolific PL2303 USB-to-UART bridge is used to provide access to the serial port that acts as a system console. This
is exposed via a USB Mini-b (5-pin) port on the front of the case. There are several steps required to access the system
console via this port.
3.2.1 Install the Driver
Install an appropriate PL2303 USB to UART Bridge VCP (virtual COM port) driver on the workstation used to connect
with the system if needed. There are drivers available for Windows, Mac OS X, and Linux available in the Download
Software section of the Prolific Website.
3.2. Advanced Configuration 17

Product ManualSG-5100
Note: Recent versions of FreeBSD and many Linux distributions include this driver and will not require manual
installation.
3.2.2 Connect a USB Cable
Next, locate an appropriate USB cable. The type of cable required for the serial console has a USB Mini-b (5-pin)
connector on one end and a regular USB (Type A) plug on the other end. These cables are commonly used with
smaller USB peripherals such as GPS units, cameras, and so on.
Attach the USB cable between a workstation and the system. Gently push the Mini-B plug end into the console port
on the system and connect the USB type A plug into an available USB port on the workstation.
Tip: Be certain to gently push in the Mini-B connector on the system side completely. With most cables there will
be a tangible “click”, “snap”, or similar indication when the cable is fully engaged.
3.2.3 Locate the Console Port Device
The appropriate device to attach the terminal program to each platform varies by platform and must be located before
attempting to connect to the console.
Windows
To locate the device name on Windows, open Device Manager and expand the section for Ports (COM & LPT).
Look for an entry with a title such as Prolific USB-to-Serial Comm Port. If there is a label in the name that contains
“COMX” where X is a decimal digit (e.g. COM1), that value is what would be used as the port in the terminal
program.
Mac OS X
The device associated with the system console is likely to show up as /dev/cu.usbserial.
Linux
The device associated with the system console is likely to show up as /dev/ttyUSB0. Look for messages about the
device attaching in the system log files or by running dmesg.
Note: If the device does not appear in /dev/, see the note above in the driver section about manually loading the Linux
driver and then try again.
3.2. Advanced Configuration 18
Other manuals for SG-5100
3
Table of contents
Other Netgate Firewall manuals
Popular Firewall manuals by other brands
ZyXEL Communications
ZyXEL Communications ZyWALL VPN2S quick start guide

McAfee
McAfee NS Series Product guide

SonicWALL
SonicWALL NSA 2400 Getting started guide

NETGEAR
NETGEAR ProSafe FVS318N Reference manual

Trend Micro
Trend Micro viruswall enforcer 1500i Installation and guide

Draytek
Draytek Vigor2850 Series user guide

Cigent Technology
Cigent Technology RECON SENTINEL user guide

Rohde & Schwarz
Rohde & Schwarz GP-E user manual

Stonesoft
Stonesoft StoneGate FW-5105 installation guide

Neoware
Neoware Neoware c50 - Thin Client user manual

Infoblox
Infoblox Infoblox-550 user guide

Fortinet
Fortinet FortiGate ASM-FX2 quick start guide