RH-42
Troubleshooting Instructions CCS Technical Documentation
Page 10 Nokia Corporation Confidential Issue 2 09/2003
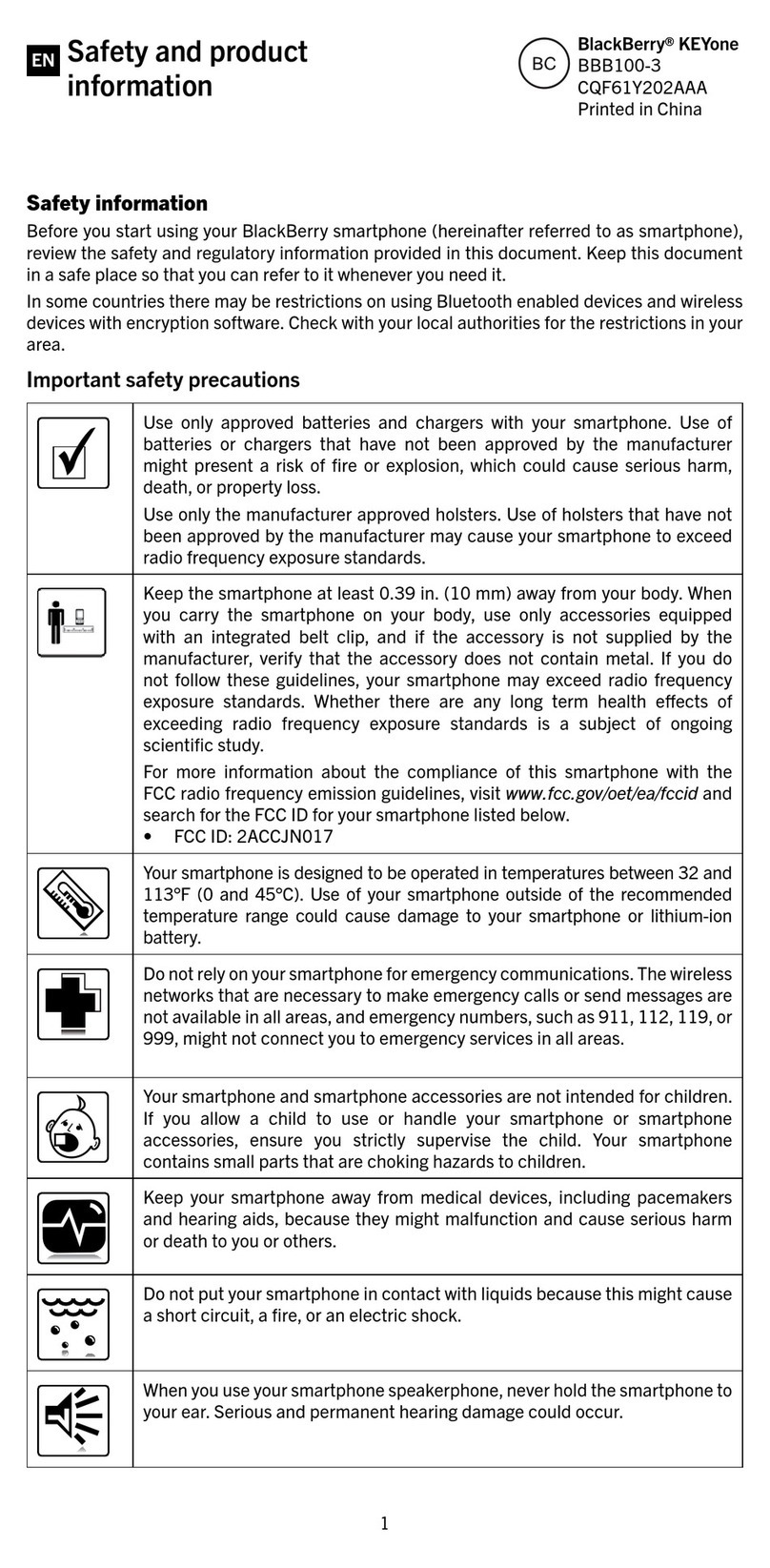
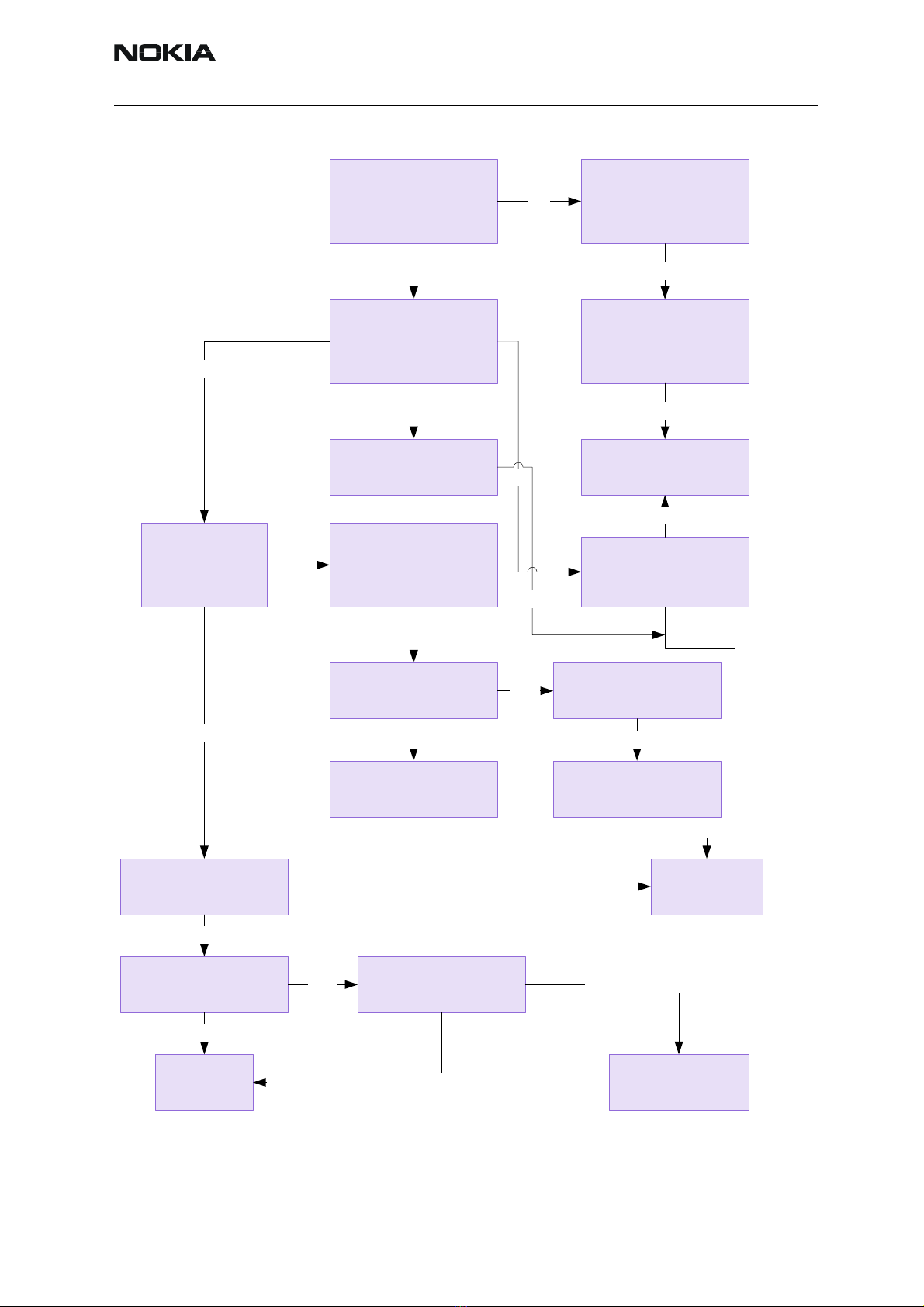
Flash Programming does not work
Flash programming procedure
1 The phone communicates with the prommer via the production test pattern,
using the following signals:
• FBUSTX(serial data to phone)
• FBUSRX(serial data from phone)
• MBUS(serial clock for FBUSRX)
• VPP(External flashing voltage for speed up flashing)
The BSI line is also used when initializing flashing (battery connector).
2 When the phone is powered (VBAT>3V), the MBUS and FBUSTX lines are pulled
up internally by the phone.
3 The prommer sends a command to the UEM, using FBUSRX, to enter the Flash-
mode. During the sending of this command, the prommer keeps the BSI line high
and MBUS is used as a serial clock.
4 When the Flash-mode command is acknowledged, UEM enters the Flash-mode
and releases reset (PURX) to MCU.
5 After reset is released, UPP checks if there is a request for the Bootstrap code
(that resides in the UPP ROM).
6 The request for Bootstrap is the MBUS pulled down by the prommer (if the boot-
strap is not requested, the bootstrap code jumps to FLASH SW).
7 If the Bootstrap code is requested, UPP enters the Flash-mode and sets FbusTX to
'0' as an acknowledgement to the prommer. This is an indication that UPP can
run, at least, the fixed Bootstrap code – although it is not able to run the FLASH
code. UPP then sends an UPP-ID to the prommer via the FBUSTX line.
8 After the prommer has received the UPP-ID, it sends a corresponding Secondary
Boot Code to the phone via FBUSRX. The Secondary Boot Code, when run in UPP,
requests UPP to send information to the prommer about the flash type and other
HW-related parameters about the device to be flashed.
9 Prommer then sends the Algorithm Code corresponding to the HW parameters,
and this algorithm, when run in UPP, takes over handling the MCUSW transfer to
Flash.
10 12 volts can be supplied to Vpp (by the prommer) to speed up flashing.