Nos 05183NOS User manual

2005-2008 Chrysler 5.7 Hemi Kit Number 05183NOS
OWNER’S MANUAL
P/N 199R11456

2
CONGRATULATIONS on purchasing your NOS Nitrous Oxide Injection System! Your system is composed of the highest quality
components available.
NOTICE: The installation of Nitrous Oxide Systems, Inc. products signifies that you have read this document and have
agreed to the terms stated within.
It is the purchaser’s responsibility to follow all installation instruction guidelines and safety procedures supplied with the product as it is
received by the purchaser to determine the compatibility of the product with the vehicle or the device the purchaser intends to install the
product on.
Nitrous Oxide Systems Inc. assumes no responsibility for damages occurring from accident, misuse, abuse, improper installation,
improper operation, lack of reasonable care, or all previously stated reasons resulting from incompatibility with other manufacturers’
products.
Nitrous Oxide Systems Inc. assumes no responsibility or liability for damages incurred by the use of products manufactured or sold by
Nitrous Oxide Systems Inc. on vehicles used for competition or racing.
Nitrous Oxide Systems Inc. neither recommends nor condones the use of products manufactured or sold by Nitrous Oxide Systems Inc.
on vehicles, which may be driven on public roads or highways, and assumes no responsibility for damages incurred by such use.
NOS nitrous oxide is legal for use in most states when used in accordance with state and local traffic laws. NOS does not recommend
or condone the use of its products in illegal racing activities.
NOS has not pursued California Air Research Board (CARB) exemptions for its kits, hence, they are not legal for use on pollution-
controlled vehicles in California. A correctly installed NOS nitrous system should not alter the emission control performance of your
vehicle under standard EPA test cycle conditions.
HAZARDS DEFINED
This manual presents step-by-step instructions that describe the process of installing your NOS Nitrous Oxide Injection System. These
procedures provide a framework for the installation and operation of this kit. Parts are referenced by name and number to avoid
confusion. Within the instructions, you are advised of potential hazards, pitfalls, and problems to avoid. The following examples
explain the various hazard levels:
WARNING! Failure to comply with instructions may result in injury or death.
CAUTION! Failure to comply with instructions may result in damage to equipment.
NOTE: This information is important, needs to be emphasized, and is set apart from the rest of the text.
HINT: These special instructions provide a handy work tip.
NITROUS OXIDE INJECTION SYSTEM SAFETY TIPS
WARNINGS
IT IS NOT LEGAL TO ENGAGE NITROUS OXIDE INJECTION SYSTEMS ON PUBLIC ROADS OR HIGHWAYS.
NITROUS OXIDE INJECTION SYSTEMS ARE ONLY TO BE ENGAGED DURING SANCTIONED COMPETITION OR
RACING EVENTS.
Do not attempt to start the engine if the nitrous has been injected while the engine was not running. Disable the ignition and
fuel systems (consult owner’s manual) and turn the engine over with the throttle wide open for several revolutions before
attempting to start. Failure to do so can result in extreme engine damage.
Never permit oil, grease, or any other readily combustible substances to come in contact with cylinders, valves, solenoids,
hoses, and fittings. Oil and certain gases (such as oxygen and nitrous oxide) may combine to produce a highly flammable
condition.
Never interchange nitrous and fuel solenoids. Failure to follow these simple instructions can result in extreme engine
damage and/or personal injury.
Never drop or violently strike the bottle. Doing so may result in an explosive bottle failure.
Never change pressure settings of safety relief valve on the nitrous bottle valve. Increasing the safety relief valve pressure
settings may create an explosive bottle hazard.

3
Please note that the NOS bottle label has changed to a two-part assembly. The first label is already located on the bottle.
Upon filling your bottle with nitrous oxide, apply the (second) material information label in the area indicated in the picture to
the right.
NOTE: The material information decal is located in the same
plastic bag as the bottle.
WARNING! Once the nitrous bottle has been filled, it must be
shipped according to the applicable transportation and shipping
regulations!
Do not deface or remove any markings, which are used for
content identification.
Nitrous bottle valves should always be closed when the system
is not being used.
Notify the supplier of any condition that may have permitted any
foreign matter to enter the valve or bottle.
Keep the valves closed on all empty bottles to prevent
accidental contamination.
After storage, open the nitrous bottle valve for an instant to
clear the opening of any possible dust or dirt.
It is important that all threads on the valves and solenoids are properly mated. Never force connections that do not fit
properly.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
WHAT IS NITROUS OXIDE? ...................................................................................................... 4
DO’S AND DON’TS OF NITROUS OXIDE.................................................................................. 4
Chapter 1 Introduction to Your NOS Nitrous Oxide Kit......................................................... 4
1.1 General Information ...........................................................................................................4
1.2 System Requirements........................................................................................................5
1.3 Kit Components..................................................................................................................5
Chapter 2 Kit Installation.......................................................................................................... 7
2.1 Bottle Mounting Instructions............................................................................................... 7
2.2 Bottle Orientation ...............................................................................................................7
2.3 Bottle Installation................................................................................................................7
2.4 05183NOS Kit Plate Installation.........................................................................................8
2.5 05183NOS Solenoid Mounting........................................................................................... 8
2.6 Electrical System.............................................................................................................. 11
2.7 Preparing for Operation.................................................................................................... 13
2.7.1 Programming the Mini 2-Stage Progressive Controller .............................................. 14
Chapter 3 Tuning .................................................................................................................... 16
Chapter 4 Determining Optimum System Performance ...................................................... 16
Chapter 5 Alternate Sensor, Actuator, and Switch Components ....................................... 17
Chapter 6 Routine Maintenance ............................................................................................ 18
6.1 Nitrous Solenoid Filter...................................................................................................... 18
6.2 Nitrous Solenoid Plunger.................................................................................................. 18
6.2.1 General Information....................................................................................................18
6.2.2 Nitrous Solenoid Plunger Disassembly and Inspection............................................... 18
Appendix A Troubleshooting Guide...................................................................................... 20
Nitrous Oxide Accessories ..................................................................................................... 22

4
WHAT IS NITROUS OXIDE?
NITROUS OXIDE…
…Is a cryogenic gas composed of nitrogen and oxygen molecules
…Is 36% oxygen by weight
…Is non-flammable by itself
…Is stored as a compressed liquid
…Exists in two grades—U.S.P. and Nitrous Plus:
U.S.P. is medical grade nitrous oxide; its common use is dental and veterinary anesthesia. It is also commonly used as a
propellant in canned whipped cream. U.S.P. is not available to the public.
Nitrous Plus differs from U.S.P. in that it contains trace amounts of Sulphur dioxide added to prevent substance abuse. Nitrous
Plus is intended for automotive applications and is available for sale to the public.
In automotive applications, Nitrous Plus and fuel are injected into the engine’s intake manifold, producing the following results:
Lowers engine intake air temperature, producing a dense inlet charge.
Increases the oxygen content of the inlet charge (air is only 22 percent oxygen by weight).
Increases the rate at which combustion occurs in the engine’s cylinders.
DO’S AND DON’TS OF NITROUS OXIDE
Do’s
Read all instructions before attempting to install your NOS nitrous system.
Make sure your fuel delivery system is adequate for the nitrous jetting you have chosen. Inadequate fuel pressure or flow will
result in engine damage.
Use 14 gauge (minimum) wire when installing electrical system components.
Use high-quality connections at all electrical joints.
Use PTFE-based paste on pipe-style fittings.
Make sure your engine and related components (ignition, carburetor, and driveline) are in proper working condition.
Do not attempt to start the engine if the nitrous has been injected while the engine was not running. Disable the ignition
and fuel systems (consult owner’s manual) and turn the engine over with the throttle wide open for several revolutions
before attempting to start. Failure to do so can result in extreme engine damage.
Use your NOS nitrous system only at wide-open throttle and at engine speeds above 3000 RPM.
Install a proper engine to chassis ground. Failure to do so may result in an explosive failure of the main nitrous supply
line.
Use a high-quality fuel, as suggested in Chapter 3, Baseline Tuning Suggestions.
Don’ts
Engage your nitrous system with the engine off. Severe engine damage can occur.
Modify NOS nitrous systems (if you need a non-stock item, call NOS Technical Service for assistance)
Overtighten AN type fittings.
Use PTFE Tape on any pipe threads. Pieces of PTFE tape can break loose and become lodged in the nitrous or fuel solenoids or
solenoid filters. Debris lodged in a nitrous or fuel solenoid can cause catastrophic engine failure.
Use sealant of any kind on AN type fittings.
Allow nitrous pressure to exceed 1100 psi. Excessive pressure can cause swelling or in extreme cases failure of the nitrous
solenoid plunger. Solenoid plungers are designed so that pressure-induced failures will prevent the valve from operating. No
leakage should occur with this type of failure.
Inhale nitrous oxide. Death due to suffocation can occur.
Allow nitrous oxide to come in contact with skin. Severe frostbite can occur.
Use octane boosters that contain methanol. Fuel solenoid failure may occur, producing severe engine damage.
Chapter 1 Introduction to Your NOS Nitrous Oxide Kit
1.1 General Information
Kit Number 05183NOS was engineered to be a clean, simple installation on a Chrysler vehicle with a 2005-2008 Chrysler 5.7L HEMI.
Power output can be increased from 75 to 150 Rear Wheel Horse Power (RWHP) with the supplied jetting. The system can support up
to 250 RWHP with optional jetting, but be aware that an increase over 100 RWHP will require an upgrade to the OEM fuel system in the
form of larger injectors, increased capacity fuel pump or a dedicated, stand-alone fuel system.

5
1.2 System Requirements
When used correctly, Kit Number 05183NOS is designed to work with stock 5.7L Hemi internal engine and driveline components. The
four jet combinations in this kit generate approximately 75, 100, 125, or 150 RWHP gains. Colder spark plugs (no platinum, Iridium or
fine wire) are recommended. If the jetting is increased over 100 HP, it is necessary to upgrade the fuel delivery system to ensure safe
operation.
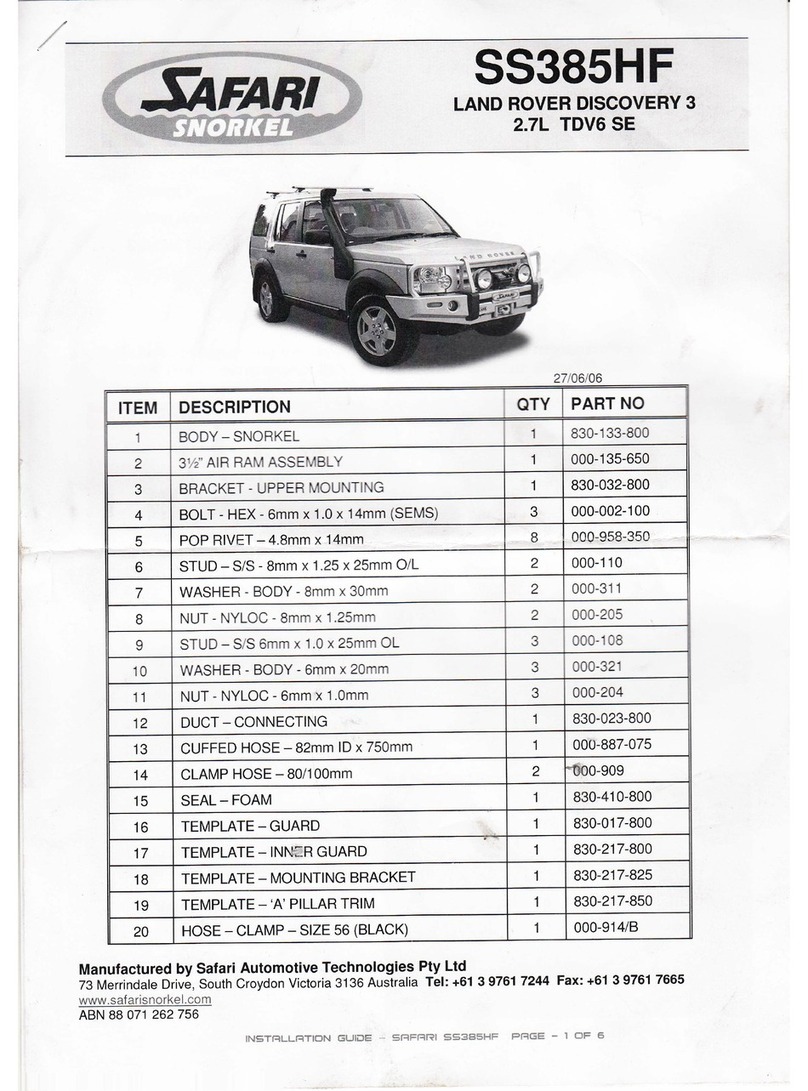
1.3 Kit Components
Before beginning the installation of your NOS kit, compare the components in your kit with those listed in Table 1.
Table 1 Kit Number 05183NOS Parts List
Item
Description
Quantity
NOS P/N
(1)
Bottle Nut Adapter
1
16230NOS
(2)
Bottle Valve Washer
1
16210NOS
(3)
10 lb. Bottle w/ racer safety
1
14745-TPINOS
(4)
Blow Down Tube
1
16160NOS
(5)
Bottle Mounting Bracket, Short
1
14126-SNOS
(6)
Bottle Mounting Bracket, Long
1
14127-SNOS
(7)
N2O Cheater Solenoid
1
18000NOS
(8)
Cheater Fuel Solenoid
1
18055NOS
(9)
Relay Wiring Harness
1
15604-SNOS
(10)
30 Amp Relay
1
15618NOS
(11)
6AN –1/4NPT Nitrous Filter (Blue)
1
15564NOS
(12)
4AN –1/8” NPT 90° Fuel Filter (Red)
1
15571NOS
(13)
3AN –1/8” NPT Adapter (Blue)
1
17952NOS
(14)
3AN –1/8” NPT Adapter (Red)
1
17953NOS
(15)
0.028” Flare Jet
1
13760-28NOS
(16)
0.030” Flare Jet
1
13760-30NOS
(17)
0.033” Flare Jet
1
13760-33NOS
(18)
0.037” Flare Jet
1
13760-37NOS
(19)
0.038” Flare Jet
1
13760-38NOS
(20)
0.040” Flare Jet
1
13760-40NOS
(21)
0.044” Flare Jet
1
13760-44NOS
(22)
0.050” Flare Jet
1
13760-50NOS
(23)
6AN 14 ft. Hose (Blue)
1
15475NOS
(24)
3/8 OE Fuel Line Adapter
1
17002NOS
(25)
MOPAR Nitrous Plate
1
40R944-1
(26)
Screws, Solenoid Mounting 10-32
2
16501-SNOS
(27)
Screws, Solenoid Mounting 8-32
2
16506-SNOS
(28)
Throttle Body Bolts M6-1 x 60mm
4
505R87
(29)
Throttle Body Bolts for Composite Manifold
4
5R2546
(30)
Solenoid Mounting Bracket
1
49R3405
(31)
Gauge Adapter (Blue)
1
16104NOS
(32)
Nitrous Gauge
1
15910NOS
(33)
Mini 2-Stage Progressive Nitrous Controller
1
15974NOS
(34)
Drive By Wire –Electrical Kit
1
85R9801
(35)
-4 AN 18” Fuel Supply Hose
1
15221NOS
(36)
-3 AN 12” Fuel Supply Hose
1
15031NOS
(37)
-3 AN 12” Nitrous Supply Hose
1
15030NOS
Rocker Switch
1
89R687
1/4” Ring Terminal –Red –18-20 AWG
1
1/4” Female Spade – Red –18-20 AWG
3
25 Amp Fuse ATC (large)
1
15 Amp Fuse ATM (mini)
1
Add-A-Fuse Tap for Mini ATM Fuses
1
Posi-Lock Splice Connector 22-20 AWG
4
5/16” Ring Terminal – Yellow –10-12 AWG
2
5/16” Ring Terminal – Red –18-20 AWG
1
Posi-Twist Connector 10-22 AWG
2
Wire –Red –20AWG
8ft
Wire –Black –20AWG
8ft
Table of contents
Other Nos Automobile Accessories manuals
Popular Automobile Accessories manuals by other brands

ULTIMATE SPEED
ULTIMATE SPEED 279746 Assembly and Safety Advice

SSV Works
SSV Works DF-F65 manual

ULTIMATE SPEED
ULTIMATE SPEED CARBON Assembly and Safety Advice
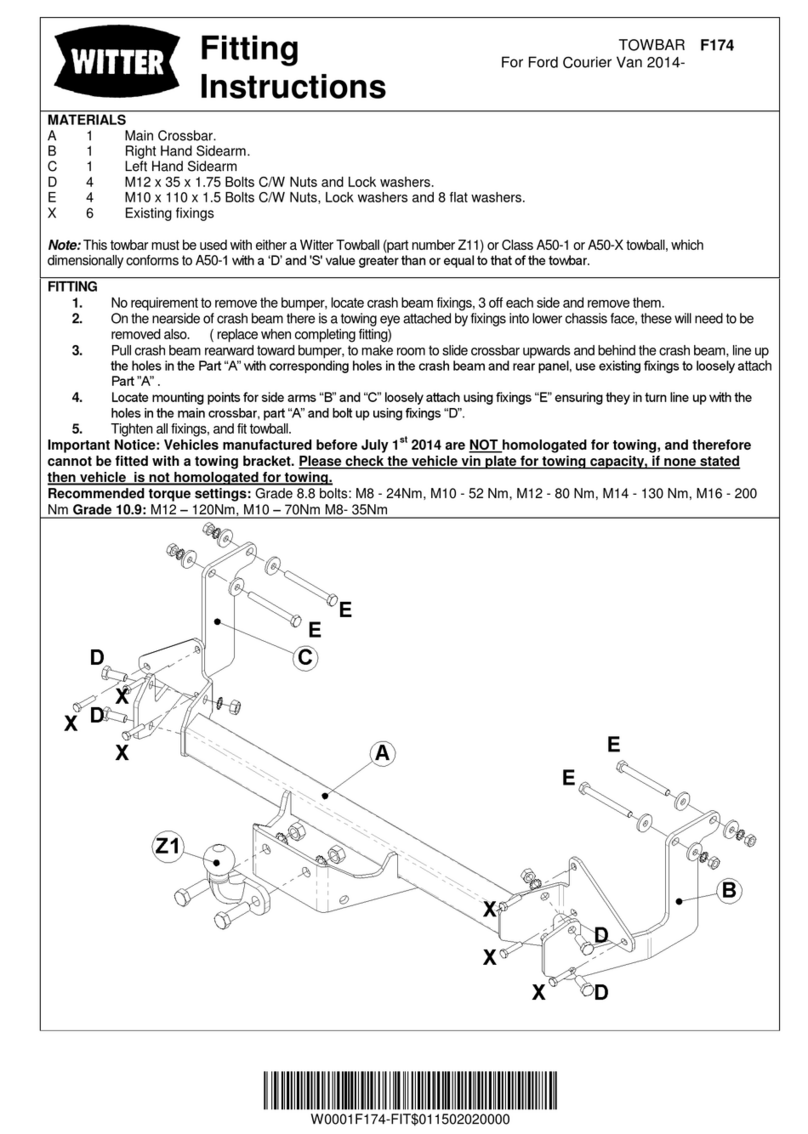
Witter
Witter F174 Fitting instructions

WeatherTech
WeatherTech No-Drill installation instructions

TAUBENREUTHER
TAUBENREUTHER 1-336050 Installation instruction