COU-02/0ETH version 1.1 R&D Department 10
Ethernet controlled
change over unit
N.B.: The IP address can also be set by software (see
section 6). If this action is taken, the IP ADDRESS DIP
switches on the unit cease to be operative.
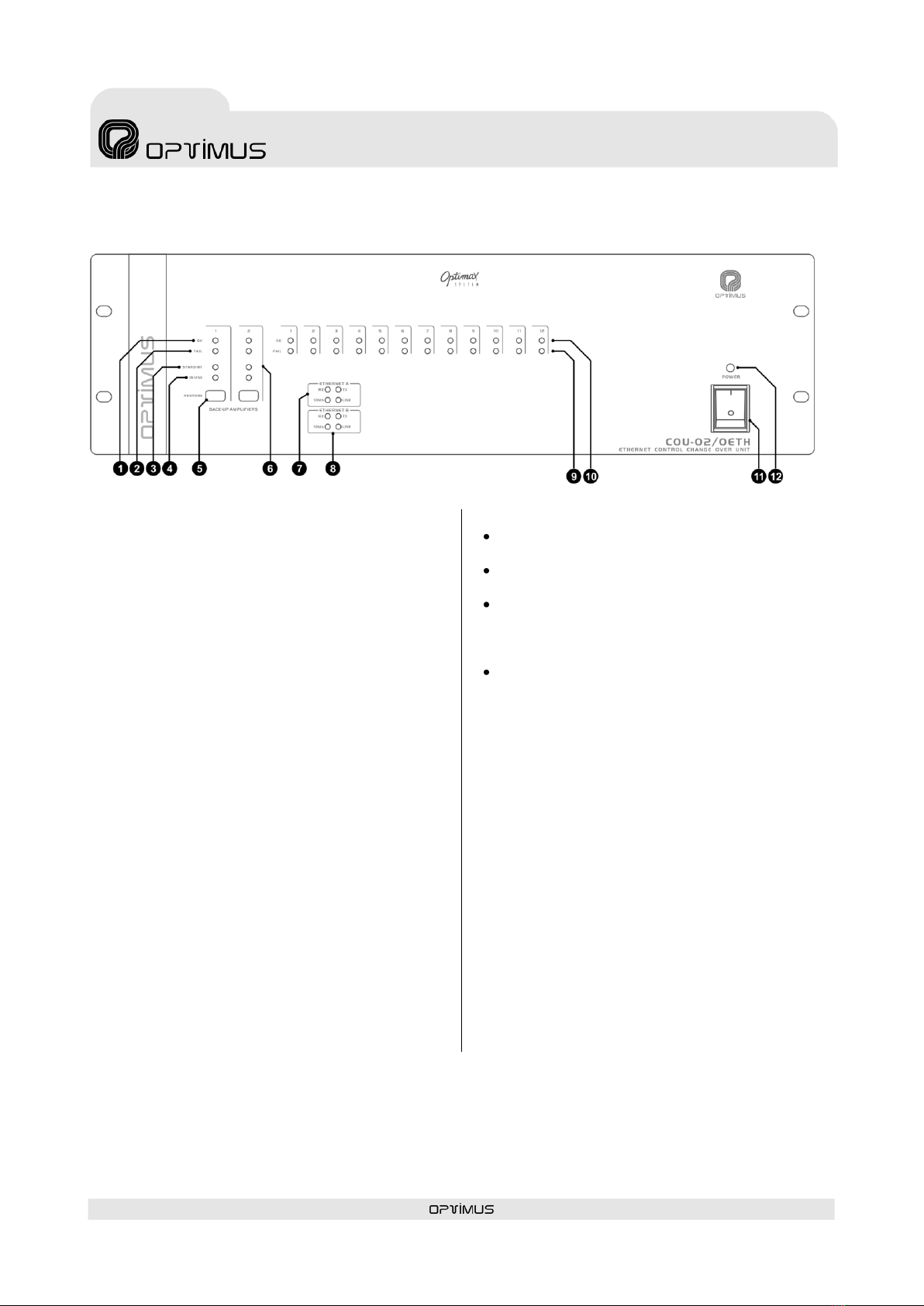
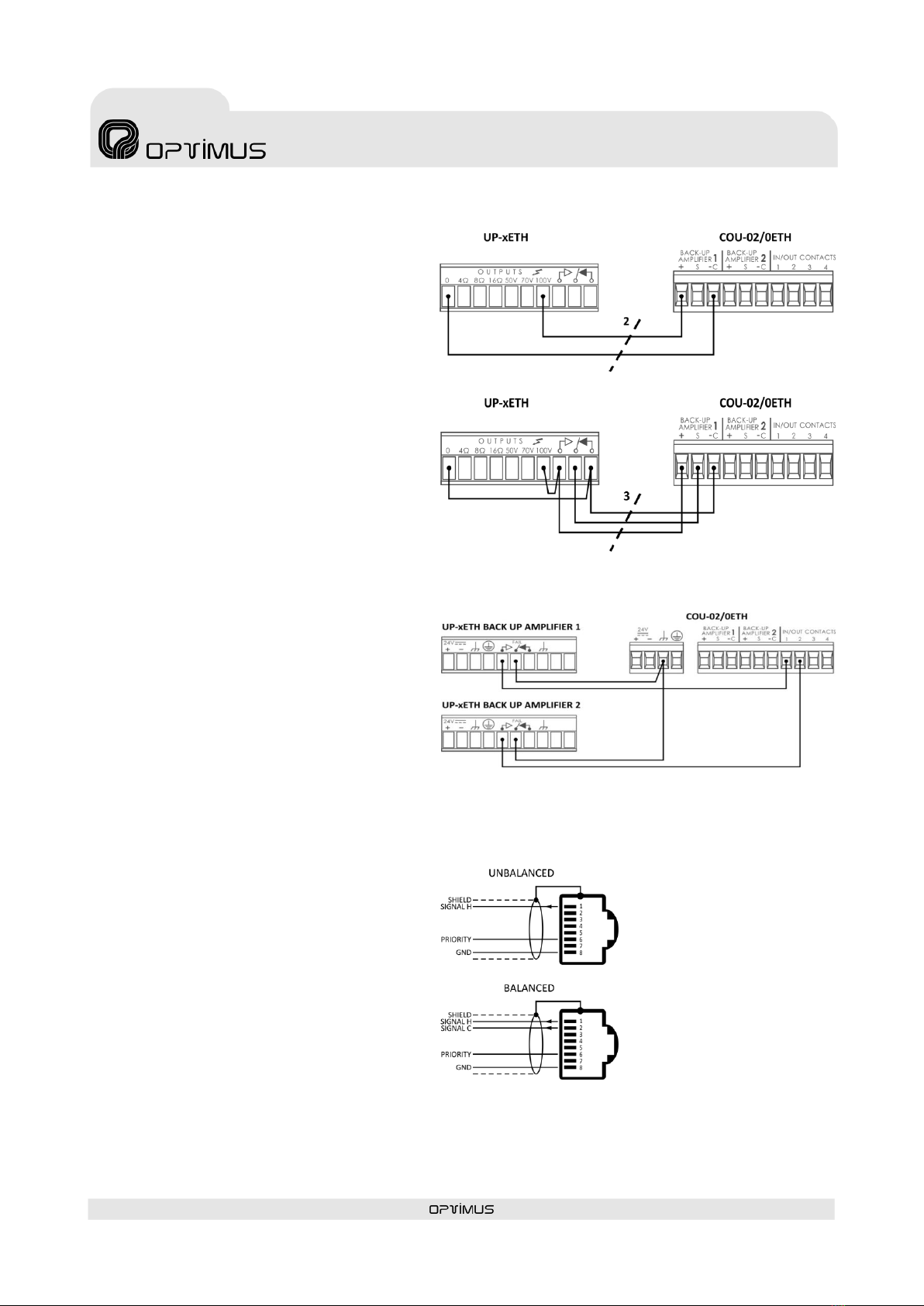
(10) OUTPUT 1 of Backup Amplifier 2
Audio output towards backup amplifier 2. An
RJ45 connector is used.
The signal present in this output is the signal of
INPUT 1 of the COU-02/ESETH card whose
amplifier is faulty and has switched to backup
amplifier 2.
Use Cat 5 STP cable for its connection (see Figure
5).
(11) OUTPUT 2 of Backup Amplifier 2
Audio output towards backup amplifier 2. RJ45
connector is used.
The signal present in this output is the signal of
INPUT 2 of the COU-02/ESETH card whose
amplifier is faulty and has switched to backup
amplifier 2.
Use Cat 5 STP cable for its connection (see Figure
5).
(12) ETHERNET A input 10 Mb, ACT and
LINK LED indicators
10 Mb: Indicates the speed of the ETHERNET
network connected to the ETHERNET A input. If
the LED is lit, it indicates a speed of 10 Mb. If it
is not lit, it indicates a network speed of 100 Mb.
ACT: ACTIVITY indicator. It lights when data is
being sent or received through the ETHERNET A
input.
LINK: When lit, it indicates the connection of the
ETHERNET A input with the HUB or SWITCH.
(13) ETHERNET B input 10 Mb, ACT and
LINK LED indicators
These serve the same purpose as the ETHERNET
A indicators, applied in this case to the
ETHERNET B input.
(14) ETHERNET A connector
RJ45 type connector. Used for connection to
the ETHERNET network. Use Cat 5 STP cable
for its connection.
(15) ETHERNET B connector
RJ45 type connector. Used, in a redundant
network, as a secondary connection to the
ETHERNET network. Use Cat 5 STP cable for
its connection.
If the ETH A connection fails, the amplifier
automatically switches to this B connection,
so that the PA system continues to operate.
(16) IP ADDRESS DIP switches
The IP address of the COU-02/0ETH is configured
through these 4 DIP switches. This address
identifies the equipment unit in the network, and
so each unit must have a unique IP address.
An IP address is represented by means of a 32-
bit binary number. The IP addresses are
expressed as decimal notation numbers: the 32
bits of the address are divided into four octets
(an octet is a group of 8 bits). In the amplifier,
each octet is represented by A0 to A7 for the first
octet, B0 to B7 for the second octet, C0 to C7 for
the third octet, and D0 to D7 for the fourth octet.
In an octet, each bit can have the value 0 (DIP
switch OFF) or 1 (DIP switch ON). In order to
obtain the decimal value of the octet, the decimal
values of each bit that is in the ON position must
be added up (from left to right: 1, 2, 4, 8, 16,
32, 64 and 128).
Figure 6 shows an example in which the IP
address 192.168.100.128 is configured.
Table I on the next page shows all the DIP switch
combinations from 0 to 255.
When the IP address of a unit is changed, it is
necessary to restart the unit by means of the
ON/OFF switch on the front.