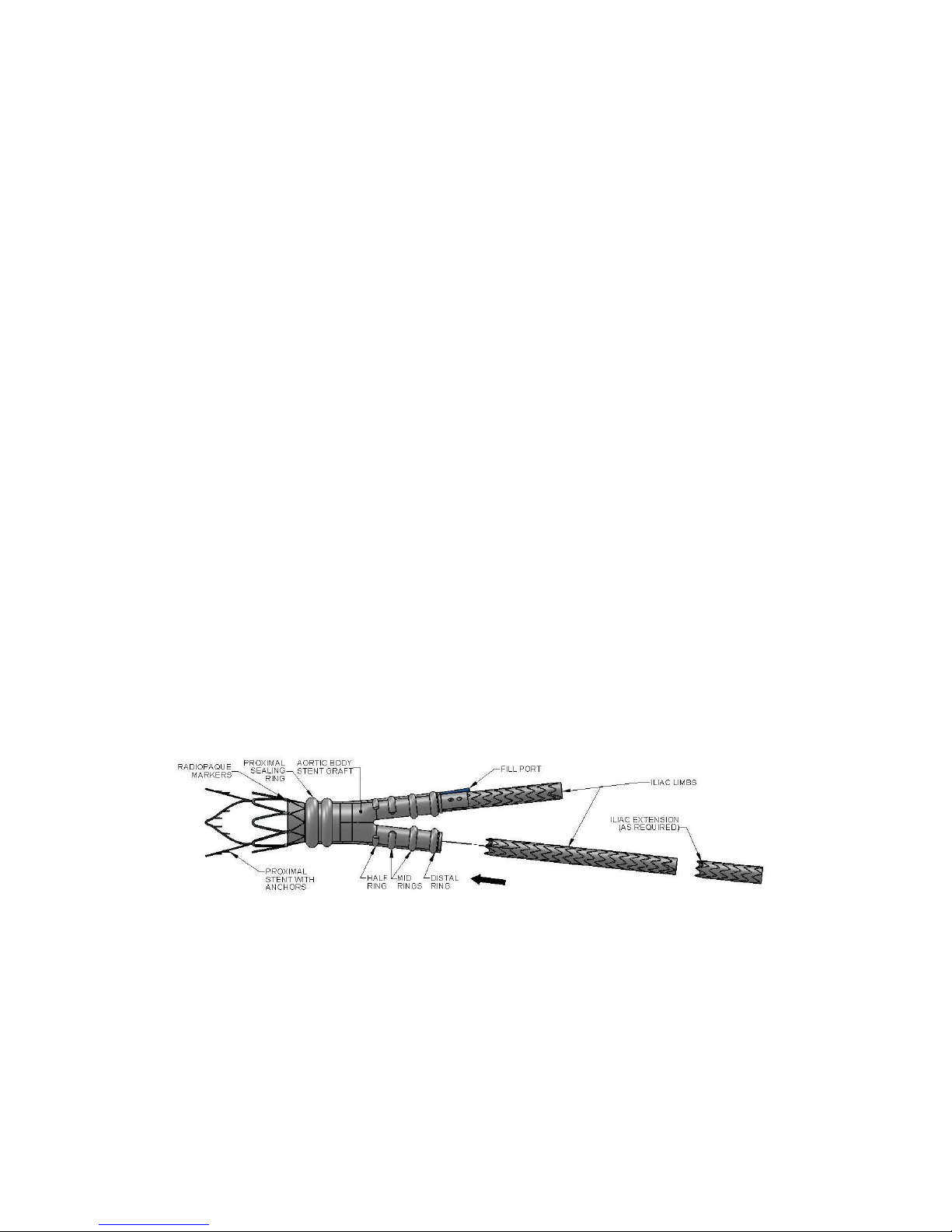
7
•Do not resterilize any components of the Ovation Abdominal Stent Graft
System.
•Systemic anticoagulation should be used during the implantation procedure
based on hospital and physician preferred protocol. If heparin is
contraindicated, an alternative anticoagulant should be considered.
•Do not bend or kink the Ovation Abdominal Stent Graft System because it
may damage the device and/or its components.
•Always use fluoroscopic guidance to advance the delivery system and to
monitor the implant procedure and the device deployment.
•Inaccurate placement or inadequate seal may result in increased risk of
leakage into the aneurysm.
•Do not continue advancing any portion of the delivery system if resistance is
felt during advancement of procedure accessories or of stent graft system.
Exercise particular care in areas of stenosis, intravascular thrombosis, or in
calcified or tortuous vessels.
•Unless medically indicated, do not deploy the stent graft components in a
location that will occlude arteries necessary to supply blood flow to organs or
extremities.
•Patients who experience hypersensitivity reactions during the procedure
should be managed in accordance with standard recommendations for
treatment of patients with radiocontrast agent allergies (e.g., antihistamines,
corticosteroids, adrenaline).
5. Adverse Events
5.1. Potential Adverse Events
Adverse events that may occur include but are not limited to:
•Acute and chronic renal failure, renal microembolism, renal insufficiency,
renal artery occlusion, contrast toxicity;
•Allergic reaction to x–ray dye, anti-platelet therapy, device materials;
•Anesthetic complications and subsequent attendant problems (aspiration);
•Aneurysm enlargement or rupture;
•Blood or bleeding events such as anemia, gastrointestinal bleeding,
retroperitoneal bleeding;
•Bowel events such as bowel ischemia, bowel necrosis, colon ischemia,
paralytic or adynamic ileuses, obstruction, fistulas;
•Cardiac events and subsequent attendant problems such as congestive
heart failure, volume overload, arrhythmias, myocardial infarction, chest
discomfort or angina, elevations in creatinine phosphokinase (CPK),
hypotension, hypertension;
•Cerebral events (local or systemic) and subsequent attendant problems
such as change in mental status, cerebrovascular accident (hemorrhagic or
embolic), reversible ischemic neurologic deficit, nerve injury, transient
ischemic attacks, paraplegia, paraparesis, paralysis;
•Death;
•Device events such as deployment or device malfunction, loss of stent graft
system component integrity, endograft occlusion, migration, or dislodgement,
endoleak;
•Embolic and thrombotic events such as deep vein thrombosis,
thromboembolism, microembolism, thrombophlebitis, phlebothrombosis, air
embolism;
•General discomfort related to the procedure;
•Generalized inflammatory response that may be associated with elevated
levels of systemic mediators of inflammation, elevated temperature;