Pearl 4MWP Series User manual
















Table of contents
Other Pearl Water Pump manuals

Pearl
Pearl CSP User manual
Pearl
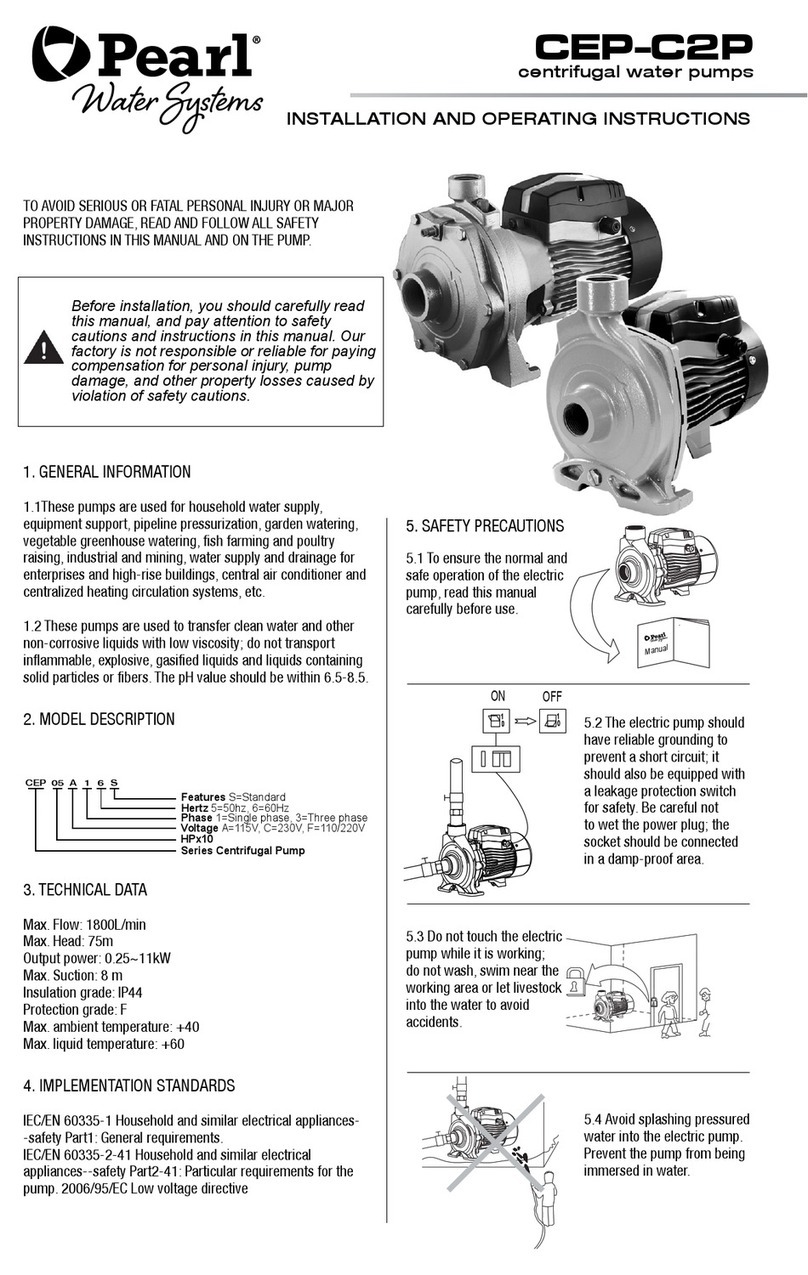
Pearl CEP-C2P User manual

Pearl
Pearl JCC Series User manual

Pearl
Pearl JACKY User manual

Pearl
Pearl JCCH Series User manual

Pearl
Pearl THOR 10 User manual

Pearl
Pearl CQPL Series User manual

Pearl
Pearl Iron Jet IRONJ 05 User manual

Pearl
Pearl CEP BIG User manual

Pearl
Pearl CEP-C2P User manual
Popular Water Pump manuals by other brands
Wilo
Wilo COR MHIE Series Installation and operating instructions

Tallas Pumps
Tallas Pumps P1 330W Instruction for installation and maintenance
wiwa
wiwa 300 Operation manual

Lowara
Lowara DOMO Quick start up guide

Dover
Dover Wilden Original Series Engineering, operation & maintenance

Henden
Henden HPHDB Installation & owner's manual

EINHELL
EINHELL GC-DP 3730 Original operating instructions

KNF
KNF OEM TRANSLATION OF ORIGINAL OPERATING AND INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS
Barnant Company
Barnant Company PK15 operating manual

XPOtool
XPOtool CGP Operation manual

Desmi
Desmi GP user manual

Pfeiffer Vacuum
Pfeiffer Vacuum HiPace 30 operating instructions