6CP100/50-10
3-2
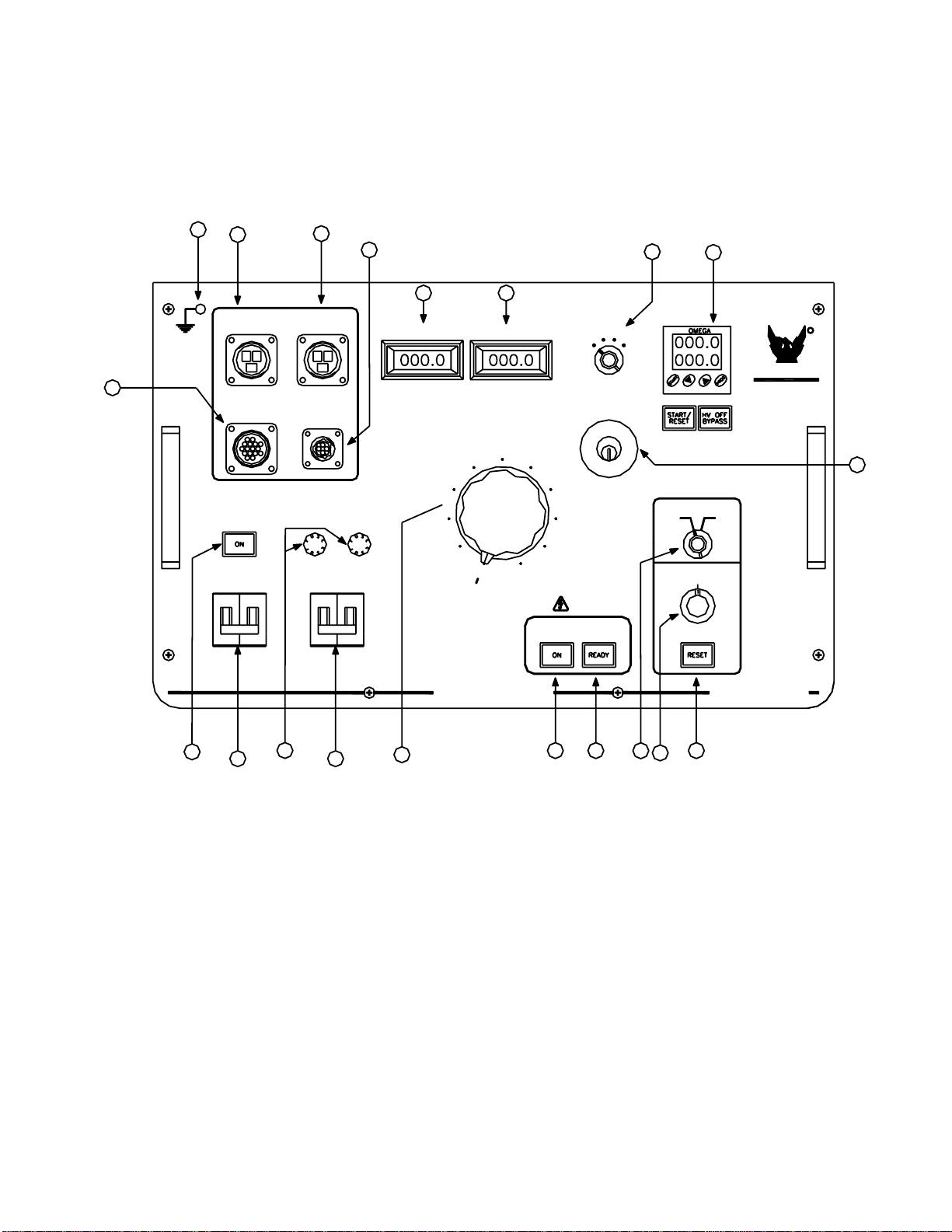
CONTROLS AND INDICATORS
Control Panel (Cont’d)
1. Reset
Will light when Overcurrent trip setting is exceeded. Push to reset. Lamp must be extinguished for
H.V. ON.
2. Emergency Off
Push down to stop test immediately. Button must be pulled up to activate High Voltage Output.
3. High Voltage On Switch and Indicator Lamp
Turns on H.V. when Ready indicator is illuminated.
4. High Voltage Off Switch and Indicator Lamp
Turns H.V. off, indicator shows when all conditions are met to turn H.V. ON. (External Interlock closed,
Reset Lamp off, Emergency Off Button pulled up, Voltage Control at Zero).
5. Voltage Control
Adjusts Output Voltage and must be set at zero to turn High Voltage on.
6. Currentmeter Range Selector
7. Output Currentmeter
8. Output Voltmeter
9. SX1 External Interlock
Provides for user connection of external interlock or auxiliary safety control device such as Emergency
Off Switch, Gate Switch, Footswitch, Dead man Switch, etc.
10. Output to Transformer
High Voltage Transformer power connection.
11. Main Input
Main input cable connects here.
12. Ground Terminal
13. TX1
Signal/ Metering cable between H.V. Unit and controls connects here.
14. Timer
Press START/RESET to start the timer after test voltage has been reached. Press START/RESET
again to reset timer to the original setting. Press HV OFF BYPASS to allow high voltage to remain on
after the timer has expired. Test time can be set using the buttons on the face of the timer.