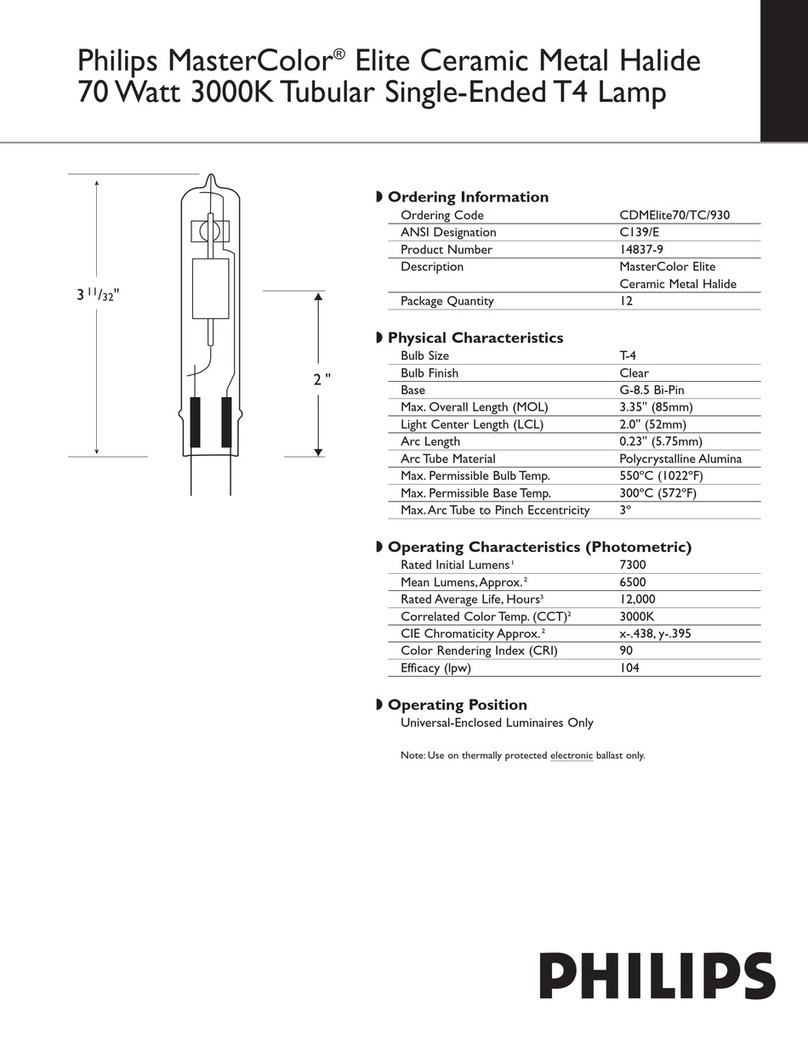
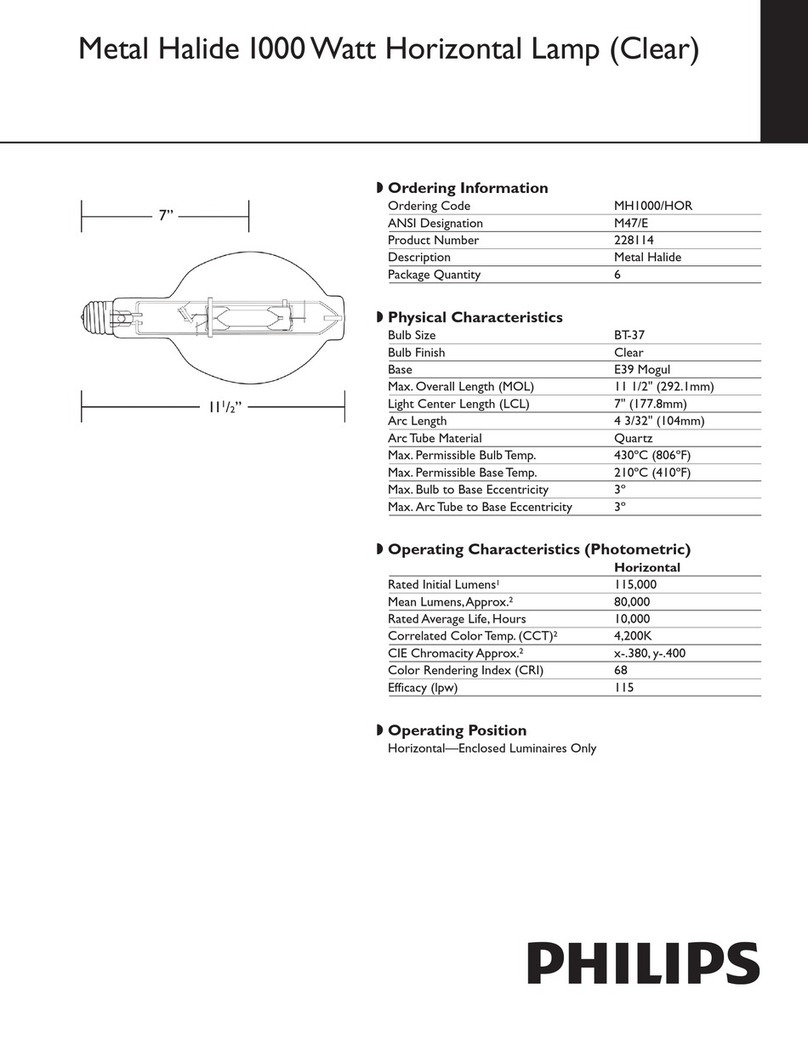
The most important value for stabilisation is the ballast impedance.It
is expressed as voltage/current ratio in ohm (Ω) and defined for a
certain mains voltage,mains frequency and calibration current (normally
the nominal lamp current).
Chokes can be used for virtually all discharge lamps,provided that
one condition is fulfilled:the mains voltage should be about twice the
arc voltage of the lamp.If the mains voltage is too low,another type
of circuit should be used,like the autoleak or constant-wattage circuits.
The advantages of a choke coil are:
- the wattage losses are low in comparison to those of a resistor,
- it is a simple circuit:the ballast is connected in series with the lamp.
Disadvantages of a choke coil are:
- the current in a lamp with choke circuit exhibits a phase shift with
respect to the applied voltage,the current lagging behind the voltage
(see also section 5.3.4:Power factor correction).
- a high starting current:in inductive circuits the starting current is
about 1.5 times the rated current.
- sensitivity to mains voltage fluctuations:variations in the mains
voltage cause variations in the current through the lamp.
Ballast specification and marking
There are two ways of selecting the right ballast for a certain lamp
and/or to compare various ballasts:
1) the ballast marking,
2) the manufacturer’s documentation.
As all ballasts have to comply with the norm IEC 920/921 some data
has to be marked on the ballast and other data can be mentioned in
the documentation.
On the ballast can be found:
- marks of origin,such as the manufacturer’s name or trade mark,
model or reference number,country of origin,production date code,
- rated supply voltage and frequency,nominal ballast current(s),
- type(s) of lamp with rated wattage,
- type(s) of ignitor with wiring diagram and peak voltage if this
exceeds 1500V,
- twand ∆t (see section 5.1.6),
- max.cross-section of mains or lamp cable;e.g.4 means 4 mm2,
- symbols of the officially recognised certification institutes,such as
VDE,SEMKO,SEV,KEMA,if applicable;CE marking for safety,
- in case of an independent ballast:the symbol ;an independent
ballast is a ballast which is intended to be mounted separately outside
a luminaire and without any additional enclosure,
- a symbol like top if there are mounting restrictions,
- F-marking if the ballast fulfils the IEC F-requirements;that means
it is suitable to be mounted directly on normally flammable surfaces,
-TS,P-marking or if the ballast is thermally protected
(* = thermo-switch temperature in degrees Celsius),
- indication of terminals:L for single phase,N for neutral, for
protective earth (PE), for functional earth,
15
5
110
1.4 Types of ballasts