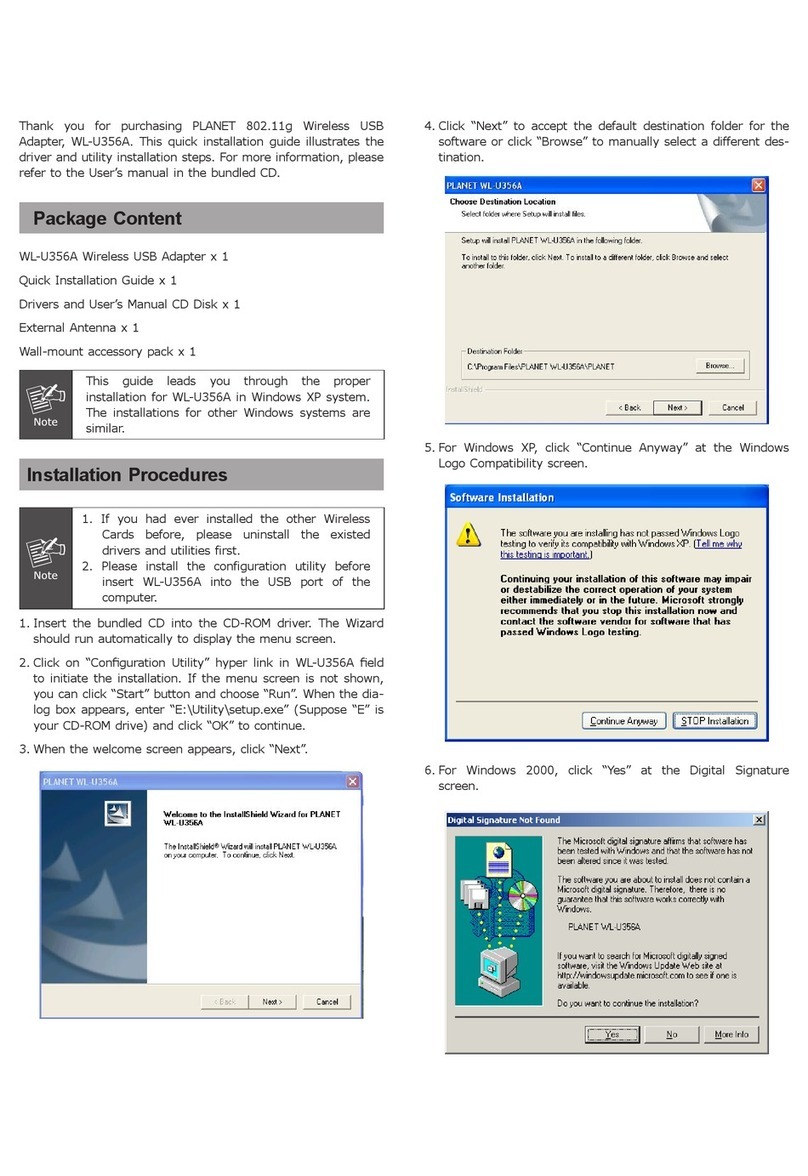
Copyright
Copyrightã2003 by PLANETTechnology Corp.All rightsreserved.No partof this publication may
be reproduced, transmitted, transcribed, stored in aretrieval system, or translated into any language or
computerlanguage,in any formorby any means, electronic, mechanical,magnetic, optical, chemical,
manual orotherwise, without the prior written permission of PLANET.
PLANETmakes no representations or warranties,either expressed orimplied,with respectto the
contentshereofand specifically disclaims any warranties,merchantability orfitness forany particular
purpose.Any software described in this manual is sold orlicensed "as is".Should the programs
prove defective following theirpurchase, the buyer (and not this company,itsdistributor,or itsdealer)
assumes the entirecost of all necessary servicing, repair,and any incidental or consequential
damages resulting from anydefectin the software. Further,this company reserves the right torevise
this publication and tomake changes from time to time in the contentshereof without obligation to
notify any person ofsuch revision orchanges..
All brand and product names mentioned in this manual aretrademarks and/or registered trademarks of
their respective holders.
Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found tocomply with the limitsfor aClass Bdigital device,
pursuant toPart 15 ofFCC Rules. These limitsaredesigned to provide reasonable protection against
harmful interference in aresidential installation.This equipment generates,uses, and can radiate
radio frequency energy and,ifnot installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause
harmful interference to radio communications. However,there is no guarantee that interference will
not occur in aparticular installation. Ifthis equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception,which can be determined by turning the equipmentoffand on,the useris
encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
1. Reorientor relocate the receiving antenna.
2. Increase the separation between the equipmentand receiver.
3. Connect the equipmentinto an outlet on acircuitdifferent from thatto which the receiver is
connected.
4. Consult the dealer or an experienced radio technician forhelp.
FCC Caution:
Toassure continued compliance.(example-use only shielded interface cables when connecting to
computeror peripheral devices). Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party
responsible for compliance could void the user s authority to operate the equipment.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the Following two
conditions:(1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2 )this Device must accept any
interference received, including interference thatmay cause undesired operation.