MD 5850 Installation Manual
Table of Content
1INTRODUCTION ..............................................................................................................4
1.1 Abbreviations..........................................................................................................................4
2MULTIREADER HARDWARE INSTALLATION..........................................................4
2.1 MultiReader Cabinet Installation .........................................................................................4
2.2 Installation site .....................................................................................................................5
2.2.1 Toll plaza superstructure................................................................................................................. 5
2.3 Basic installation ..................................................................................................................5
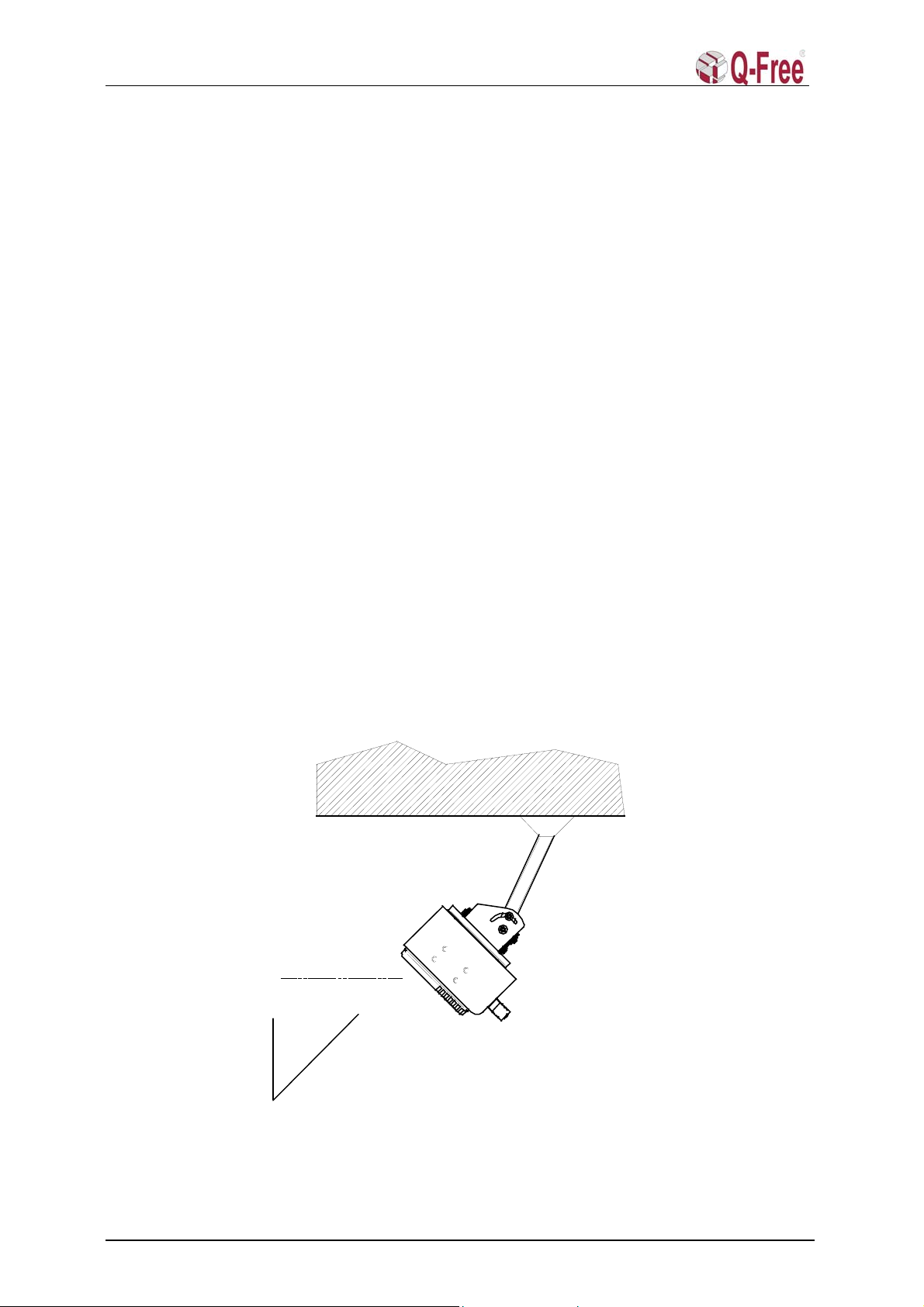
2.3.1 Mounting height and angle ............................................................................................................. 5
2.4 Square tube from customers construction........................................................ 6
2.4.1 Requirements for using the Uni-bracket ......................................................................................... 6
2.4.2 Fixing the square tube..................................................................................................................... 6
2.4.3 Square tube angles .......................................................................................................................... 6
2.5 Square tube sideways angles.................................................................................................. 6
3MULTIREADER CABLE INTERFACE..........................................................................7
3.1 MultiReader Power Supply and Data Interface ..................................................................7
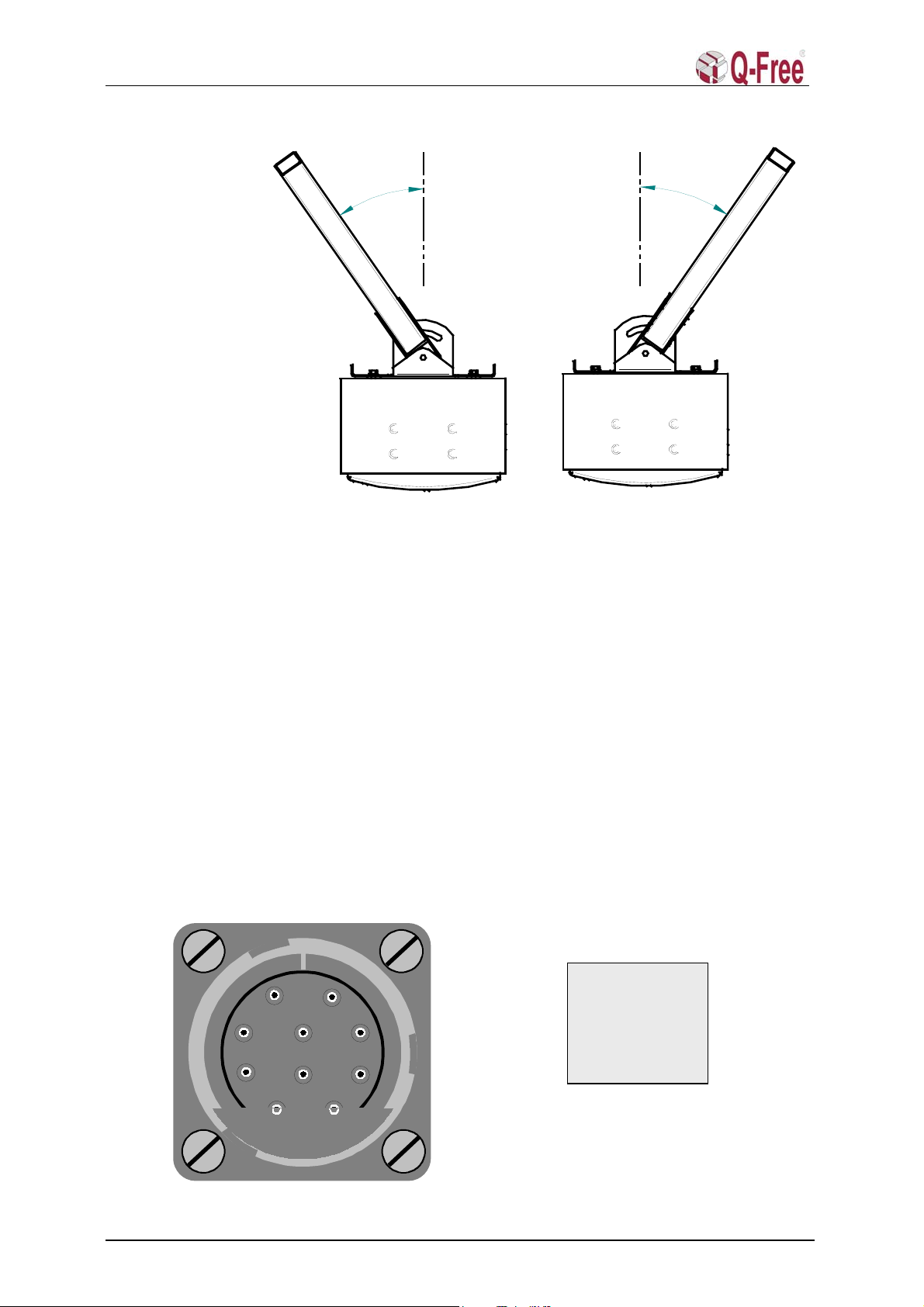
3.2 Circular Chassis Connector................................................................................................... 7
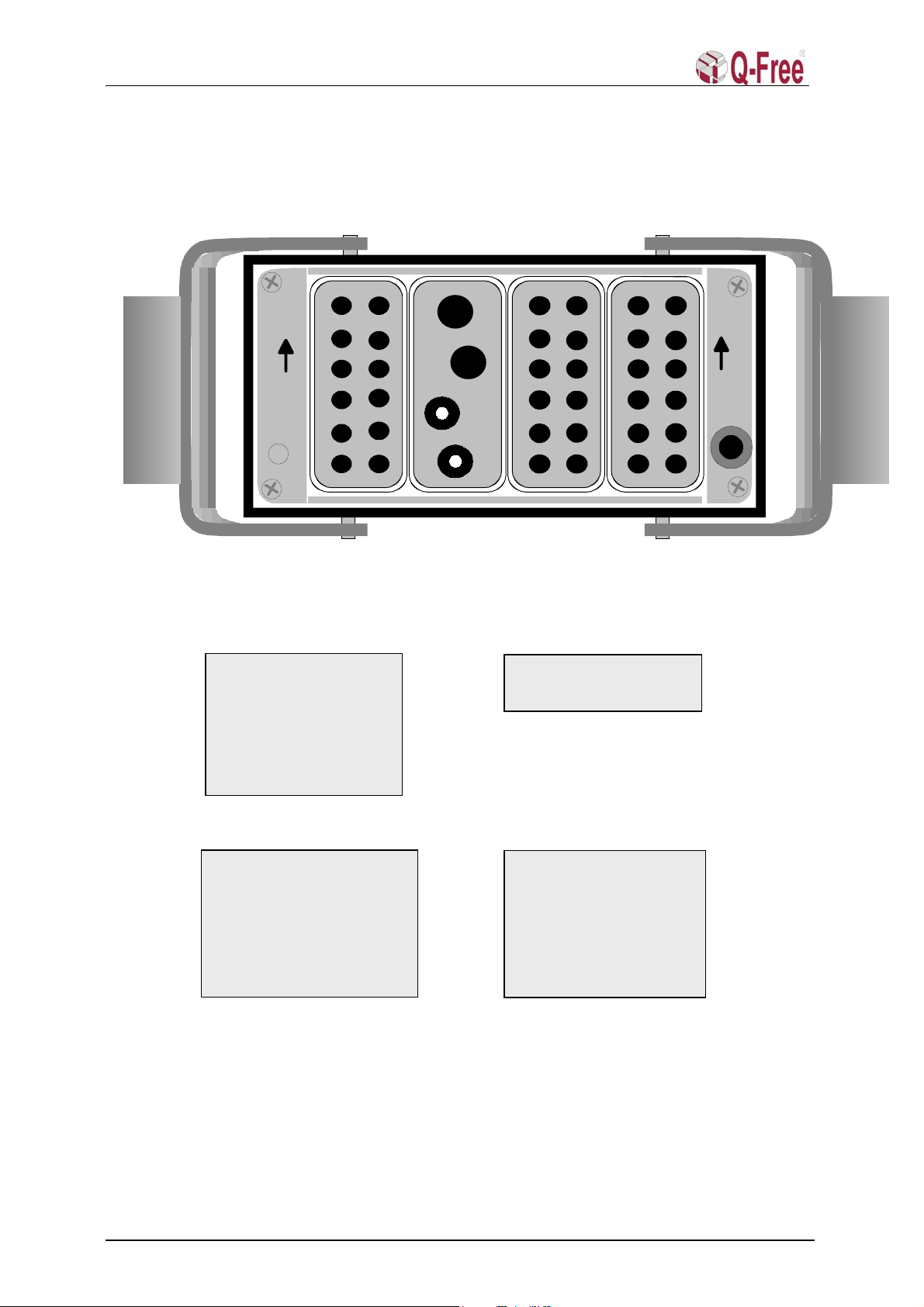
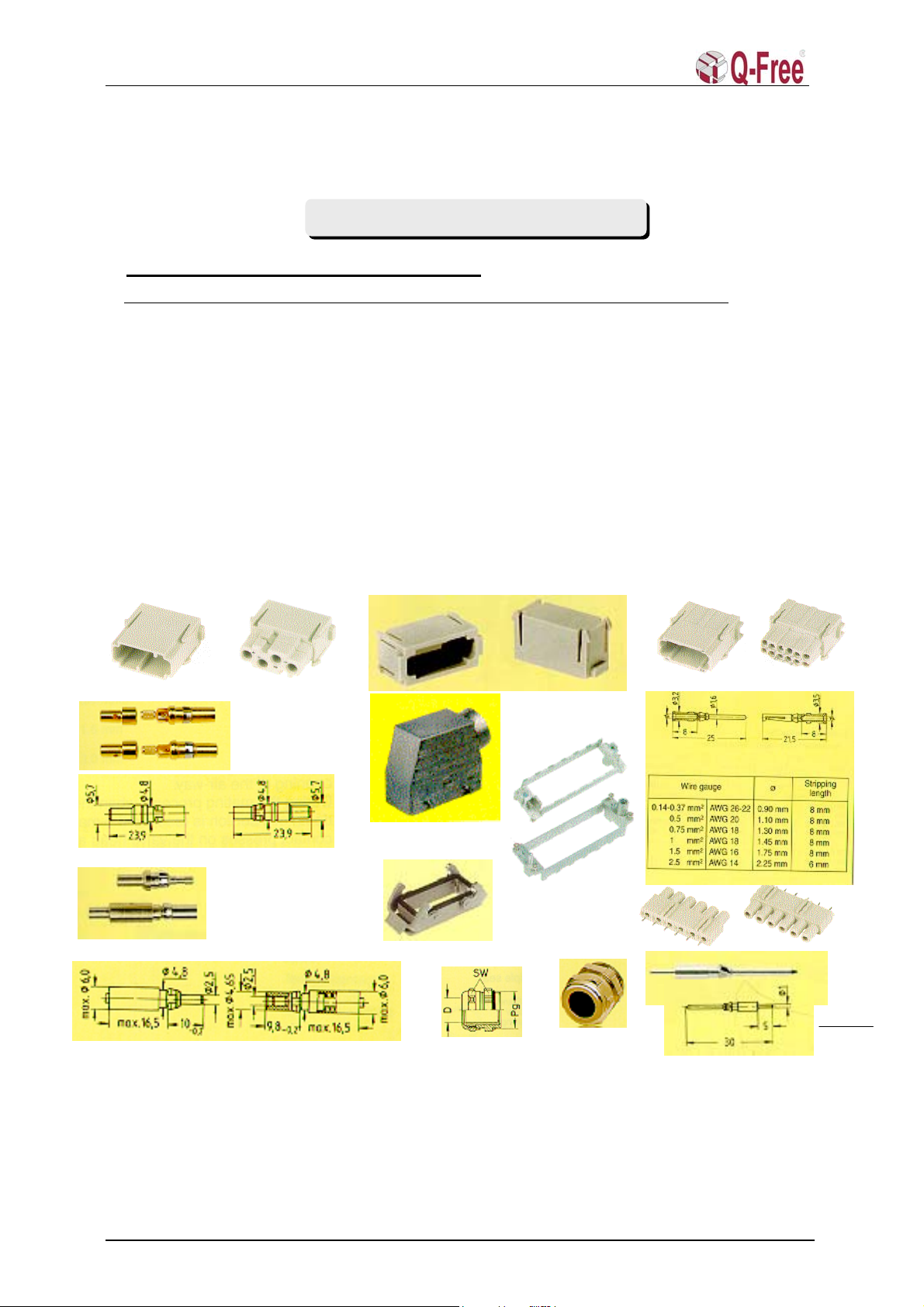
3.3 Han-Modular Connector .......................................................................................................8
3.4 Han-Modular connector assembly parts ..............................................................................9
3.5 Installation tools (preferred) ...............................................................................................10
4EXTERNAL CABLE INTERFACE................................................................................11
4.1 Cable dimensions.................................................................................................................. 11
4.2 Circular connector ...............................................................................................................11
4.3 Han-Modular connector ...................................................................................................... 12
5MULTIREADER SOFTWARE INSTALLATION.........................................................12
5.1 How to flash the MV162-12 and MVME162P CPU-card through the serial port
(console)............................................................................................................................................12
5.1.1 Loading the software and flashing................................................................................................ 13
5.1.2 Closing up..................................................................................................................................... 14
5.1.3 Make new startup file ................................................................................................................... 15
5.1.4 bootChange................................................................................................................................... 15
5.2 How to flash the MultiReader via Ethernet. ......................................................................15
6TEST WITH APPLICATION SW ...................................................................................16
6.1 PC/ Terminal Connection to MultiReader......................................................................... 16
6.2 PC/ Terminal connection to MultiReader through a TPC ............................................... 16
6.3 Testmode ...............................................................................................................................17
6.4 Format ...................................................................................................................................17
7TEST WITH TEST TAGS AND INSTRUMENTS.........................................................18
7.1 Downlink signal test .............................................................................................................18
7.1.1 Test Tag measurements. ............................................................................................................... 18
7.1.2 Measuring the MultiReader footprint with a test tag. ................................................................... 18
7.1.3 Spectrum Analyser measurement. ................................................................................................ 19
Q-Free®ASA 645-054-1999 rev.4 2 of 20