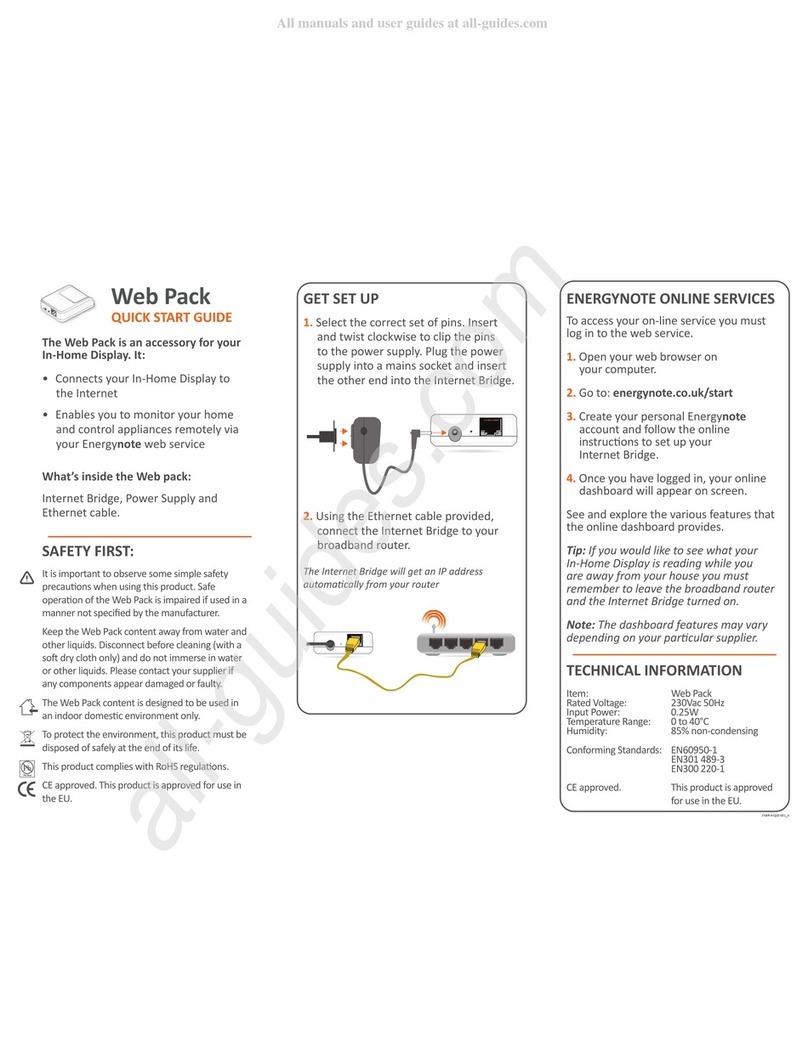
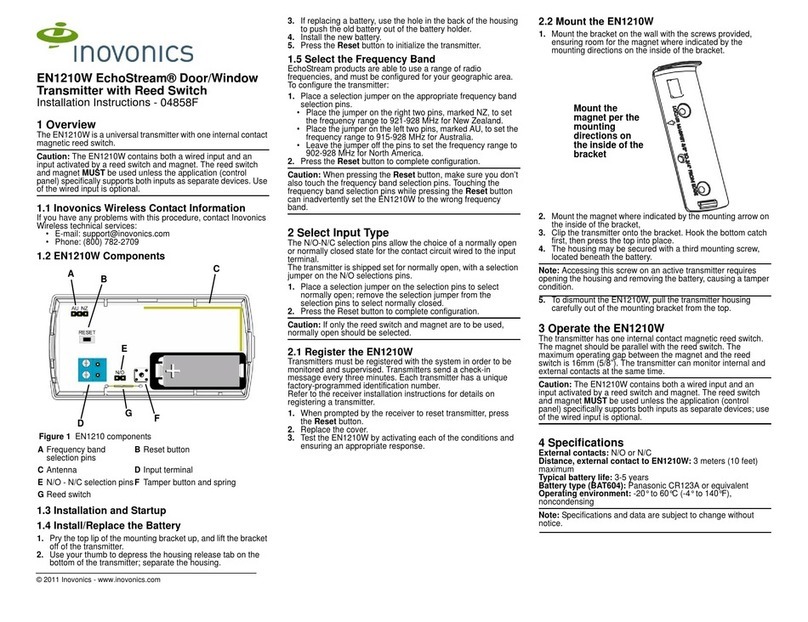
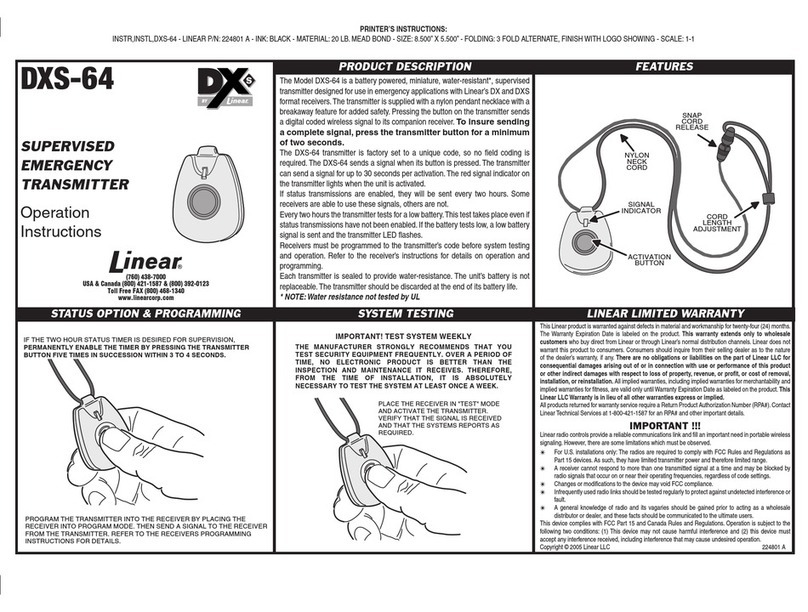
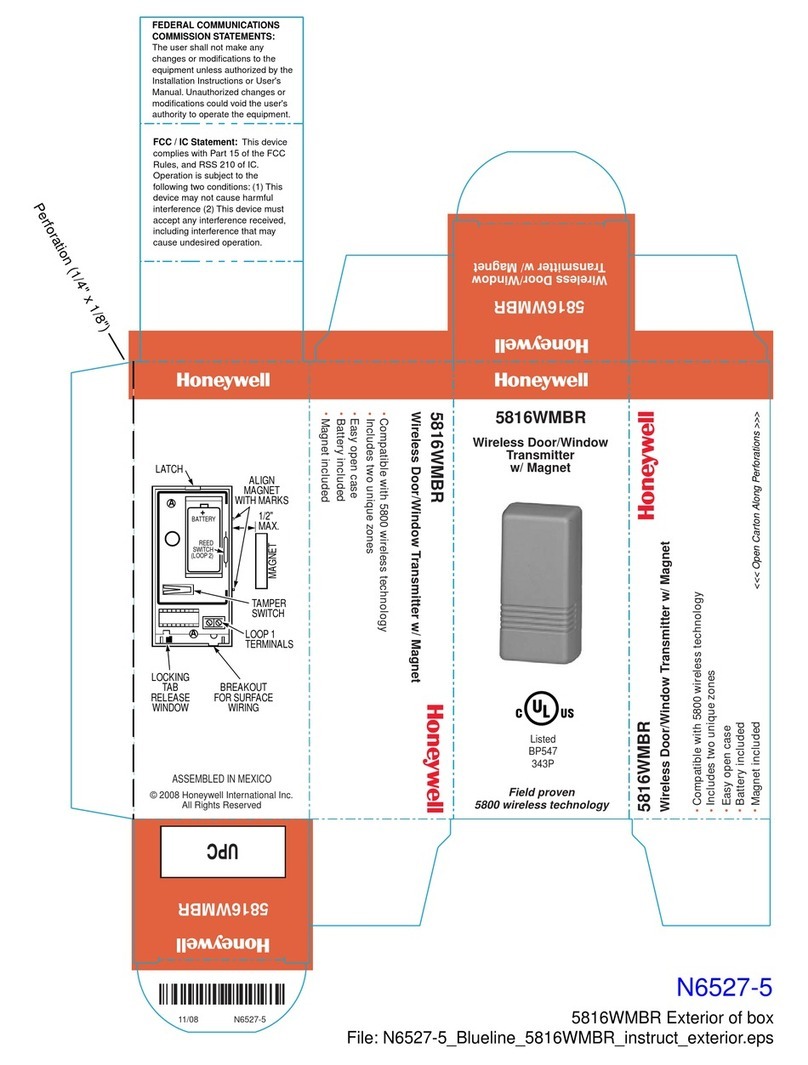
Figure 23: TIMTER™ Welcome Message ..................................................................................................33
Figure 24: PCM/FM (Tier 0) Power Spectral Density with Mask ................................................................83
Figure 25: SOQPSK-TG (Tier I) Power Spectral Density with Mask..........................................................83
Figure 26: MULTI-h CPM (Tier II) Power Spectral Density with Mask .......................................................84
Figure 27: Phase Noise Limit Curve ...........................................................................................................85
Figure 28: Vibration / Shock Testing System..............................................................................................86
Figure 29: TIMTER™ Mounted for Z-axis Testing......................................................................................86
Figure 30: TIMTER™ Mounted for X-axis Testing......................................................................................87
Figure 31: TIMTER™ Mounted for Y-axis Testing......................................................................................87
Figure 32: TIMTER™ Vibration Profile .......................................................................................................87
Figure 33: Z-axis Vibration Spectrum .........................................................................................................88
Figure 34: Y-axis Vibration Spectrum .........................................................................................................89
Figure 35: X-axis Vibration Spectrum .........................................................................................................89
Figure 36: Shock Pulse, Z-axis Positive .....................................................................................................90
Figure 37: Shock Pulse, Z-axis Negative....................................................................................................91
Figure 38: Shock Pulse, Y-axis Positive.....................................................................................................91
Figure 39: Shock Pulse, Y-axis Negative....................................................................................................92
Figure 40: Shock Pulse, X-axis Positive.....................................................................................................92
Figure 41: Shock Pulse, X-axis Negative....................................................................................................93
Figure 42: Transmitter Clock and Data Logic ...........................................................................................101
List of Tables
Table 1: Model Configuration Example.........................................................................................................3
Table 2: Frequency Band Codes ..................................................................................................................4
Table 3: Clock and Data Interface Codes.....................................................................................................6
Table 4: Serial Control Interface Codes........................................................................................................7
Table 5: ARTM Tier 0 Codes ........................................................................................................................8
Table 6: ARTM Tier I Codes .........................................................................................................................8
Table 7: ARTM Tier II Codes ........................................................................................................................8
Table 8: Legacy Codes.................................................................................................................................8
Table 9: RF Output Power Codes.................................................................................................................9
Table 10: Package Codes.............................................................................................................................9
Table 11: Standard Data Bit Rates and Rate Adaptation Compared to Clock Free Data Bit Rates ..........13
Table 12: Standard Bit Rates Compared to Low/High Rate Options..........................................................15