OFF tr nsmitter before touching test le d
or ny un-insul ted conductor.
Do not use where d nger of high volt-
ge cont ct is present. Do not tt ch
le ds to high volt ge conductors. The
equipment is not designed to provide
high volt ge protection nd isol tion.
Loc ting equipment uses electrom g-
netic fields th t c n be distorted nd in-
terfered with. More th n one utility m y
be present in given re . Follow loc l
guidelines nd one c ll/c ll before you dig
service procedures. Exposing utility is
the only w y to verify its existence, loc -
tion nd depth.
Follow set up nd oper ting instructions
to reduce the risk of injury from electric l
shock nd other c uses nd to prevent
tool d m ge
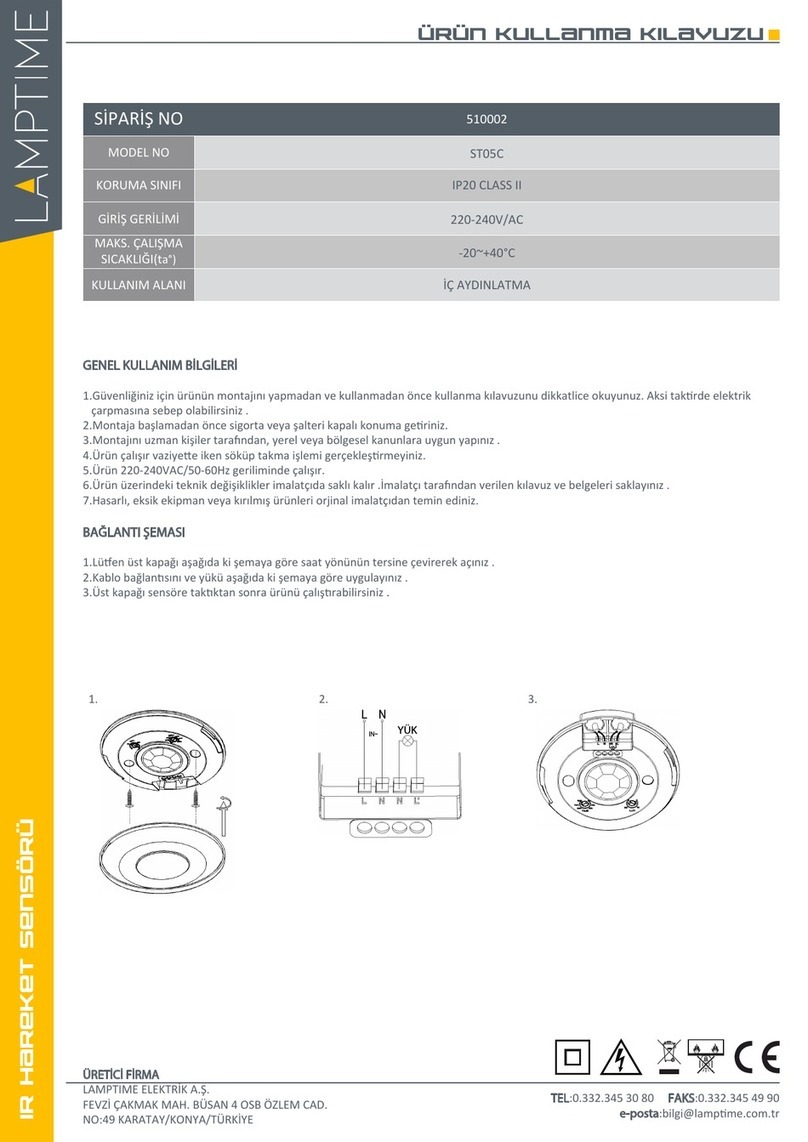
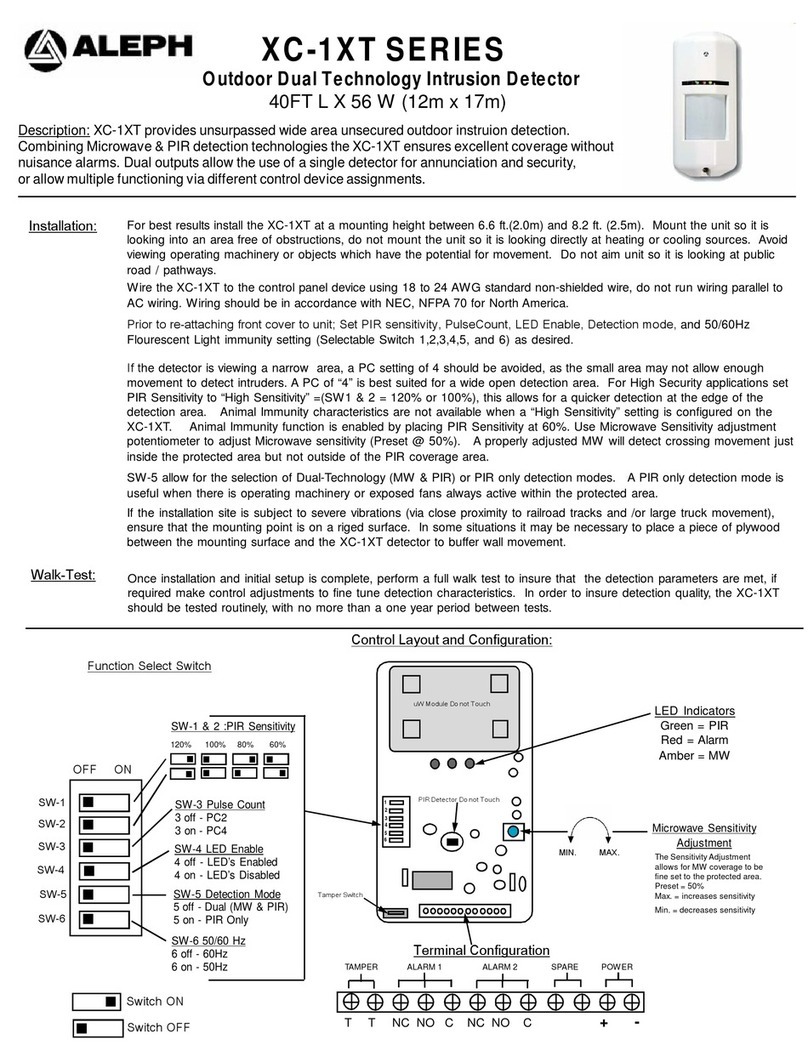
Model FT-103 Transmitter and Model FR-30
Receiver are used for fault locating of con-
ductors through direct connect method.
The Model FT-103 Transmitter only can be
used for path locating with RIDGID SeekTech®
and NaviTrack®Locators. This can be done by
direct connect and inductive methods.
1. Confirm have appropriate work area (See
Ge eral Safety Rules). Operate in clear,
level, stable, dry location.Do not use trans-
mitter while standing in water.
2. Determine the correct equipment for the
application, see Descriptio and Specifi -
catio s sections.
3. Make sure all equipment has been in-
spected and set up as directed in their in-
structions.
F ult Loc ting
It is good practice to locate the conductor path
before attempting to fault locate. This can be
done using a variety of RIDGID locating equip-
ment. If during the location of the conductor
path an unusual amount of signal loss occurs,
this may give some indication of the conductor
insulation fault location. Additionally, use visual
cues and past history to aid in identifying the
conductor path and potential fault locations.
Once the conductor path is determined, the
RIDGID FT-103 Transmitter and FR-30 A-Frame
Receiver can be used to locate ground faults in
the insulated conductor. The Model FT-103
Transmitter connects to the insulated conductor
and establishes a current flow, the current
leaks to ground through the insulation fault
A-Frame Fault Locator
999-995-095.10_REV. A
8
and back to the ground stake. The Model FR-30
Receiver detects the current flow to ground
through the insulation fault. For the A-Frame
fault detector to work, the conductor must be in
contact with the earth – it will not work with con-
ductors in conduit. Generally, the A-Frame Fault
Locator works best in earth. Use with gravel,
asphalt, concrete or other ground covers may
not work as well.
The signal strength at the fault depends on
the amount of current leaking there. The greater
the leakage, the greater the signal strength.
Connecting Tr nsmitter
1. Disconnect all loads and grounds from
the conductor to be tested and all neigh-
boring conductors to prevent damage from
high voltage and false reading. Both ends
should be known and disconnected. Dis -
connecting both ends of the conductor
forces all of the transmitter signal through
the fault, improving the fault locate.
2. Insert supplied ground stake into the earth.
Ideally, the ground stake should be in line
with the conductor, 3' to 6' (1m to 2m)
from the end. If conditions require, the
ground stake can be placed to the side of
the conductor. Do not to place the ground
stake over the conductor. It is not recom-
mended to use other existing grounds,
existing grounds may result in signal being
inadvertently applied to non-target cables.
A good ground results in a stronger tracing
signal. To get a good ground, insert the
ground stake as far as possible into the
earth. Moist earth will give a better ground
than dry earth. Wetting the earth around
the ground stake can improve grounding.
This lowers the resistance of the circuit.
While moist earth around the ground stake
improves the circuit, do not use the trans-
mitter in areas that are wet, this can in-
crease the risk of electrical shock.
3. Make sure that the transmitter is OFF.
4. Connect BLACK test lead to the ground
stake. Always connect to the ground stake
first.
5. Connect the BLACK and RED test leads
to the Transmitter.
6. Connect the RED test lead to the conduc-
tor to be tested (see Figure 9).