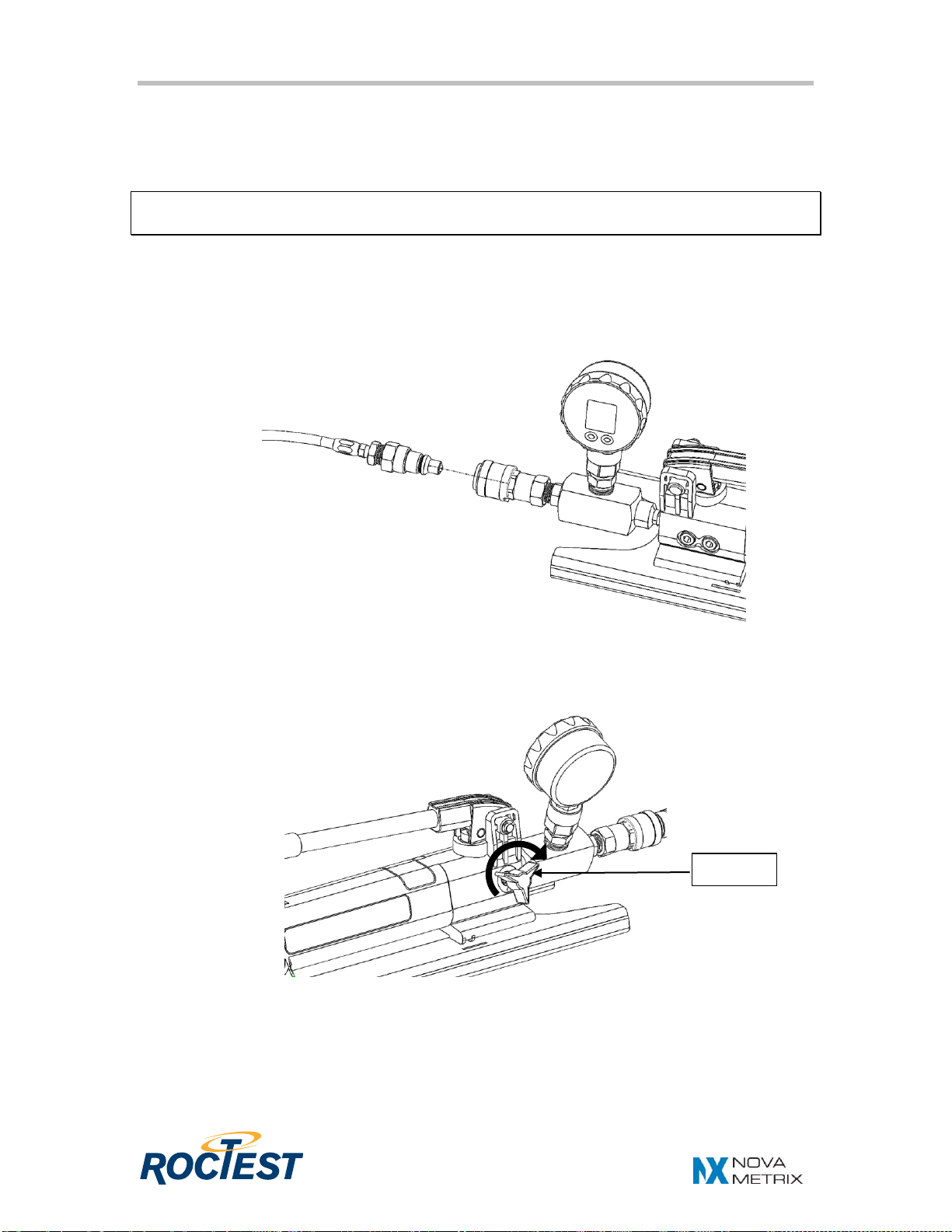
3. If the Keller pressure gauge is used, set the pressure gauge using the guide
provided in appendix C. Enter into the function menu, then:
- select the unit: 1(kN)*, bar, MPa or psi
- choose the peak on,
- set the zero.
*Note: The pressure gauge is delivered configured to display force in kilonewtons (kN)
based on the conversion factor established from calibration. It is represented by
unit 1which is active when the display alternates between 1 and the real-time
reading. The conversion factor cannot be edited from the pressure gauge menu.
If the APG PG7 pressure gauge is used, set the pressure gauge using the
guide provided in appendix D. Enter into the function menu, then:
- select the unit: kN**, bar, MPa or psi
- choose the peak « P HOLd » to enable the function Peak-Hold,
- set the zero
**Note: The pressure gauge is delivered configured to display force in kilonewtons (kN)
based on the conversion factor established from calibration. It is represented by
unit kN which is active when the screen displays the number 0.
4. Place the rock sample on the lower platen and, using the pump lever, raise the
jack piston until the sample is in contact with the two platens. The contact
location depends on the type of test:
- for a diametral test, the platens must make contact with the core along its
diameter;
- for an axial test, contact with the core is made along a line perpendicular
to its end faces;
- for a lump test, contact is made along the smallest dimension of the lump,
away from edges and corners.
Using a two-speed pump: Under no load, the pump operates at rapid advance. When
the pump reaches 200 psi or 14 bar, you must momentarily stop pumping and raise the
handle to shift to high pressure stage. After the pump shifts, pumping takes less effort.
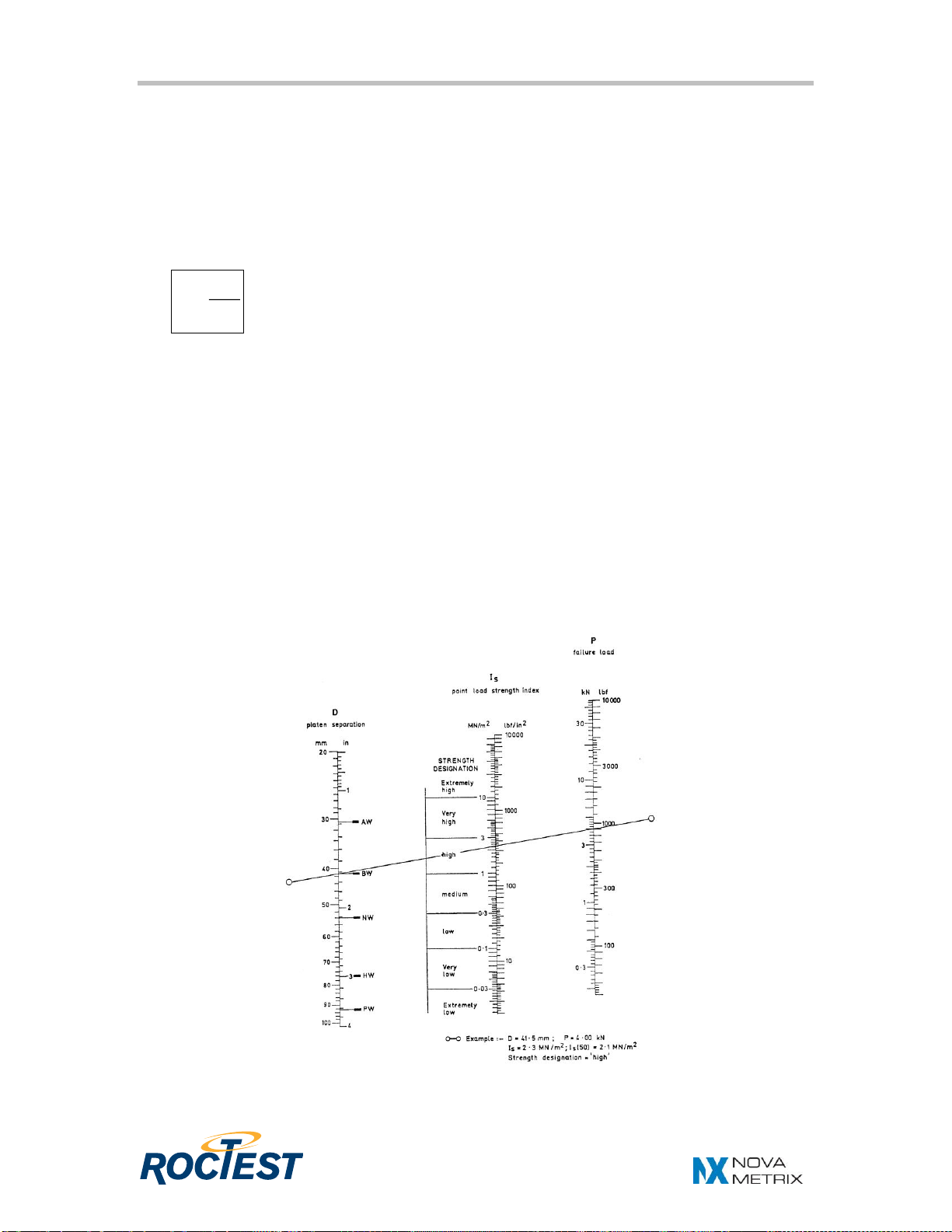
5. Read the distance separating the two contact point on the ruler fixed on the side
of the loading frame.
6. Place the protective enclosure over the top of the tester.
7. Increase load steadily such that failure occurs within 10 to 60 seconds.
NOTE: To reduce handle effort at high pressure, take short strokes. Maximum
leverage is obtained in the last 5° of stroke.