E10190-000816 FOS
1 PRODUCT
1.1 INTRODUCTION
The SENSOPTIC line of fiber optic sensors are specially developed instruments that can
be used in a variety of applications where their small size, high accuracy, broad
measurement range and complete immunity to EMI / RFI / Lightning are of paramount
importance. In addition, they have an excellent dynamic response, which allows
combined static and dynamic measurements, according to the specific needs of the
investigated structure.
The FOS can be surface-mounted on a variety of materials including steel, concrete and
composite materials using suitable industrial quality adhesives. The gauge is intended for
long-term, precise strain measurements and can be read by all ROCTEST's fiber-optic
readout units which displays readings directly in units of microstrains (see separate
instruction manual for operation of the readout unit).
1.2 DESCRIPTION
The gauge, namely a Fabry-Perot strain gauge, is based on a white-light interferometric
extrinsic principle that uses a common multimode fiber.
The patentedprinciple consists in assessing the length of a Fabry-Perot cavity
contained in the strain gauge by means of a Fizeau interferometer located in the readout
unit, that optically reproduces the length of the Fabry-Perot cavity and allows to digitize
that length on a high density linear photodiode array attached along one side of the
interferometer (Figure 1).
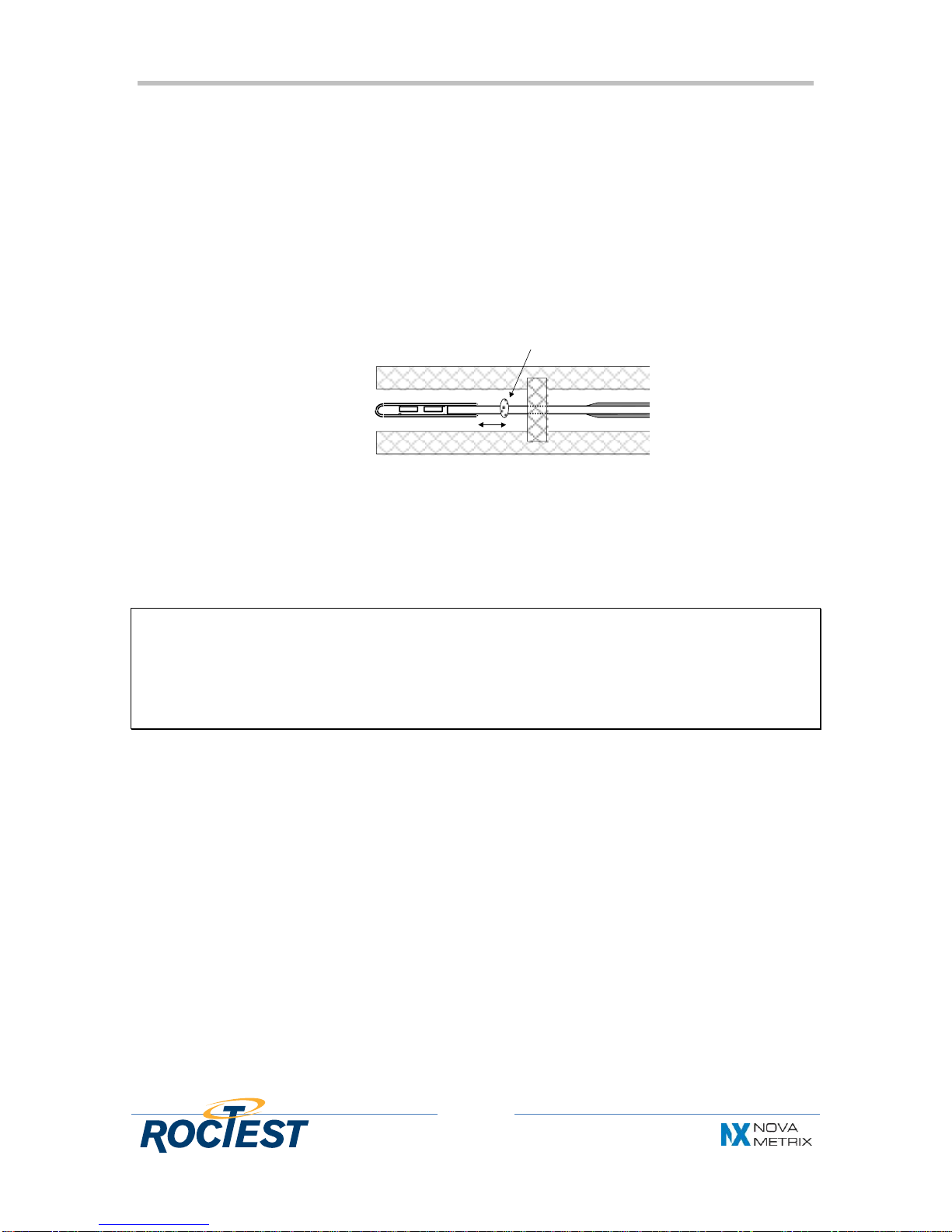
The Fabry-Perot cavity is made of two 125 microns diameter fibers facing each other
and fused in a 200 microns diameter glass micro-capillary, with a semi-reflective mirror
coating on each fiber’s tip. Then, the strain variations transferred to the gauge are
converted into cavity length variations.
The length of the Fabry-Perot cavity, as compared to the distance between the fused
welding spots on the fibers, defines the range of the strain gauge, whereas the
sensitivity of the gauge is defined by the density of the photodiode array used in the
readout unit.
The FOS-B model consists of an FOS sensor embedded in a composite material blade
ready to be bonded to concrete and other surfaces.
U.S. Patent 5,202,939