2
MENU
1. PRECAUTIONS........................................................................ 1
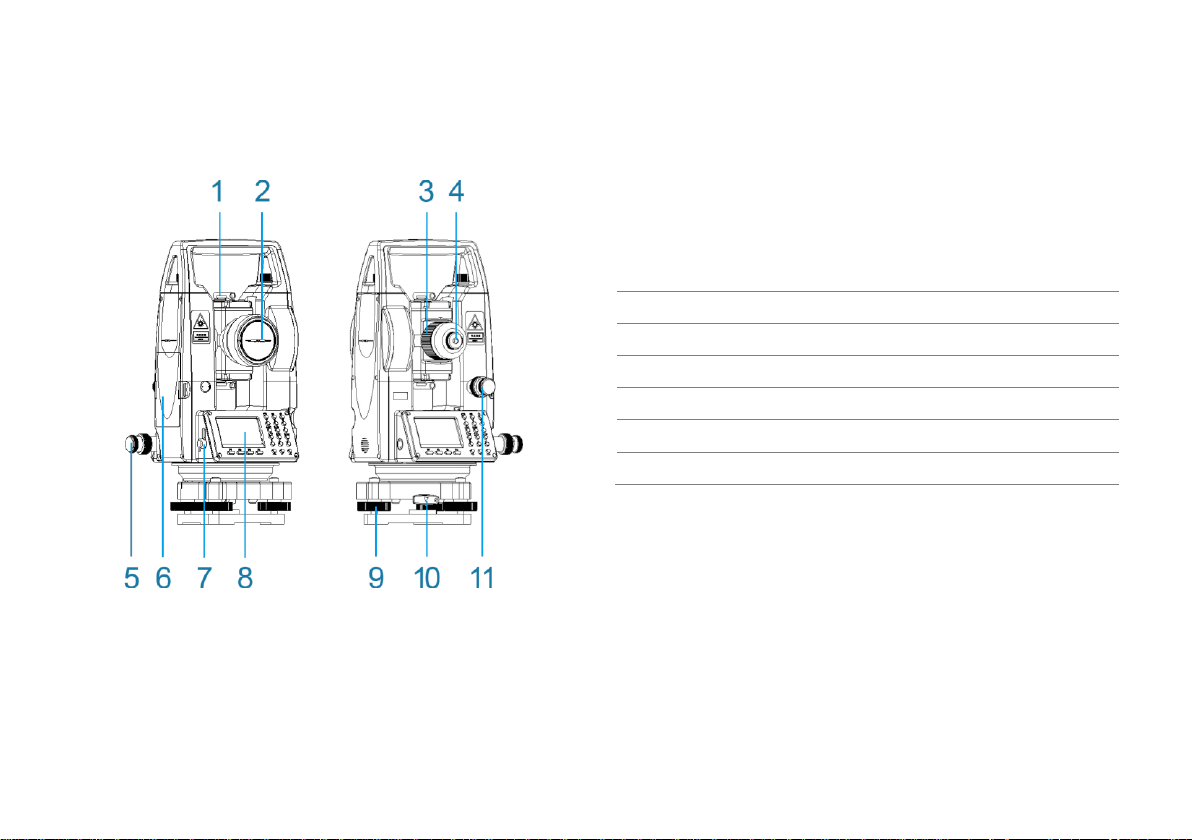
2. PART NAMES........................................................................... 3
3. OPERATION............................................................................. 4
3.1 Keys............................................................................ 4
3.2 Abbreviation................................................................ 5
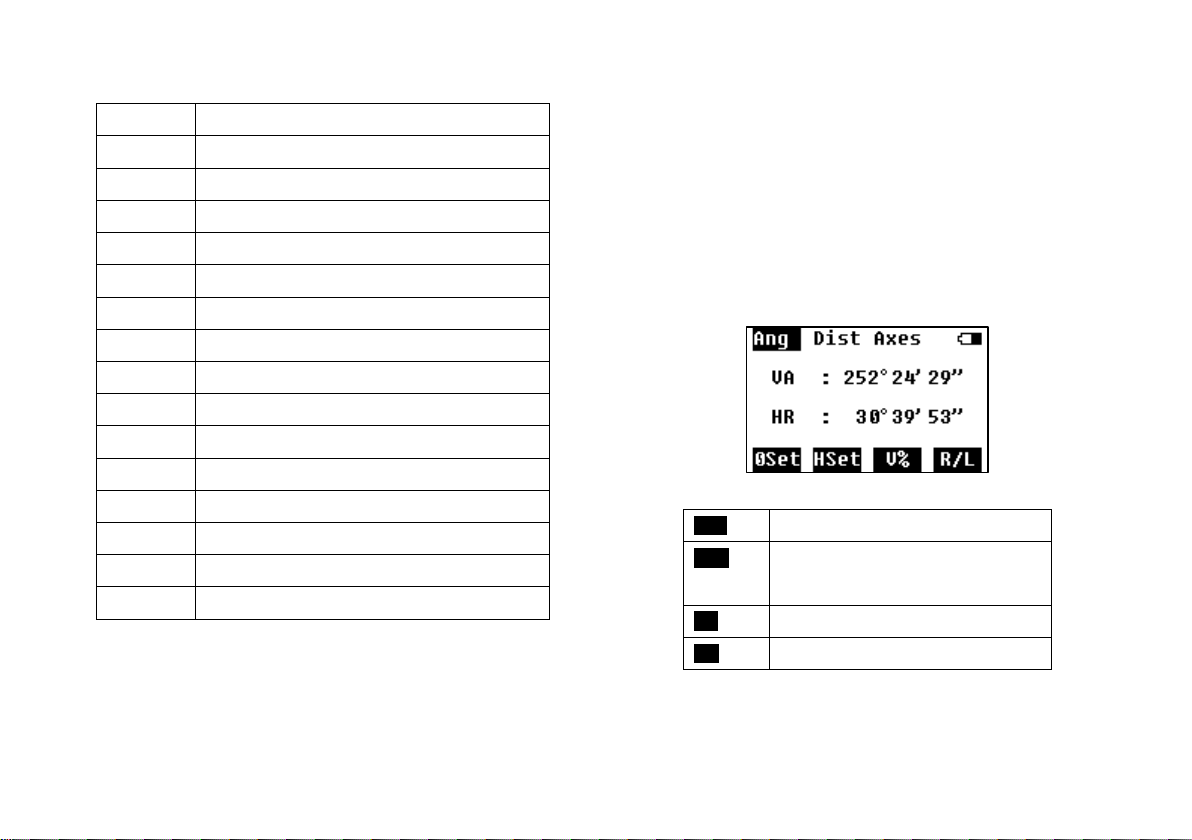
4. ANGLE MEDASUREMENT...................................................... 5
4.1 Angle .......................................................................... 5
4.2 HSet............................................................................ 6
5. DISTANCE MEASUREMENT................................................... 6
5.1 Distance...................................................................... 6
5.2 Stake Out (S.O.) ......................................................... 7
5.3 Mode........................................................................... 7
6. AXES STAKE-OUT................................................................... 8
6.1 Stake Out of One Side on the Axes............................ 8
6.2 Stake Out of Any Point ............................................... 9
7. QUICK SETTING.................................................................... 10
7.1 Laser Plummet ......................................................... 10
7.2 Laser Pointer ............................................................ 11
7.3 Compensation on X .................................................. 11
7.4 Distance Setting ....................................................... 11
7.5 Backlight and Sound .................................................11
8. SETTING.................................................................................12
8.1 Unit............................................................................12
8.2 Angle .........................................................................12
8.3 Distance ....................................................................12
8.4 PPM ..........................................................................12
8.5 Power ........................................................................13
9. CALIBRATION ........................................................................13
9.1 Calibrate i Angle ........................................................13
9.2 Correction of Additive Constant.................................14
10. INFORMATION...................................................................15
10.1 Firmware Upgrade ....................................................15
10.2 Factory Mode ............................................................16
10.3 System Information ...................................................16
11. SPECIFICATION ................................................................17
12. ERROR CODE ...................................................................18