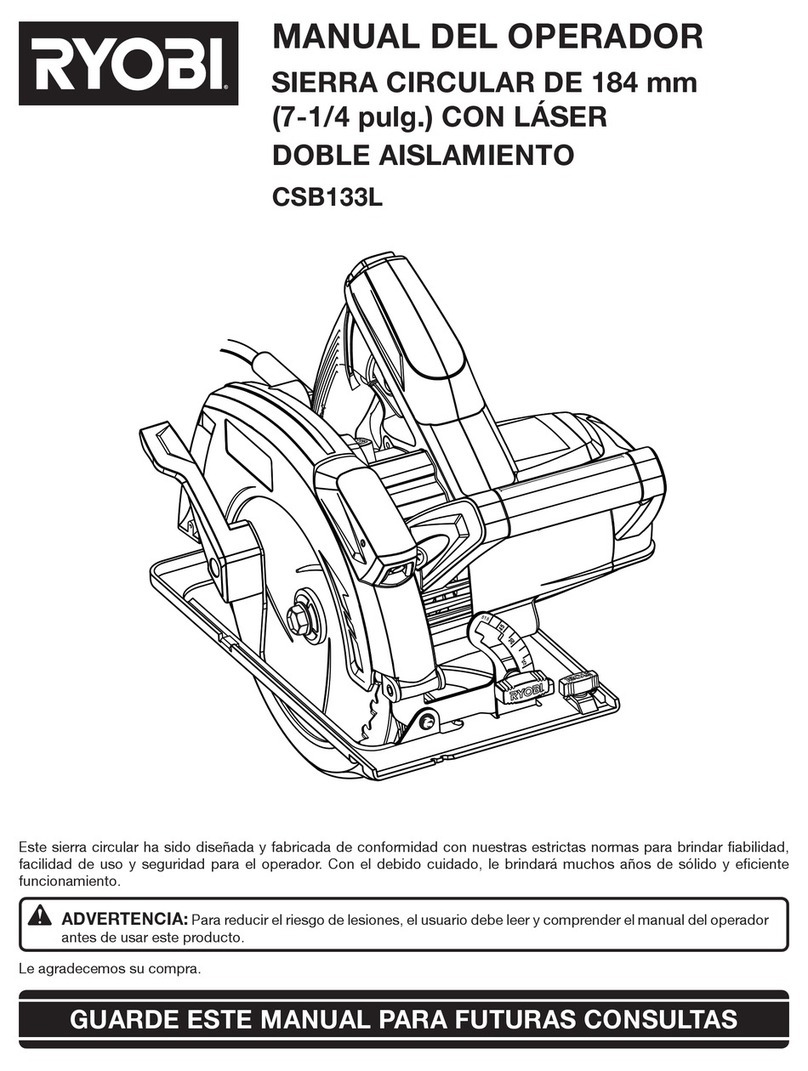
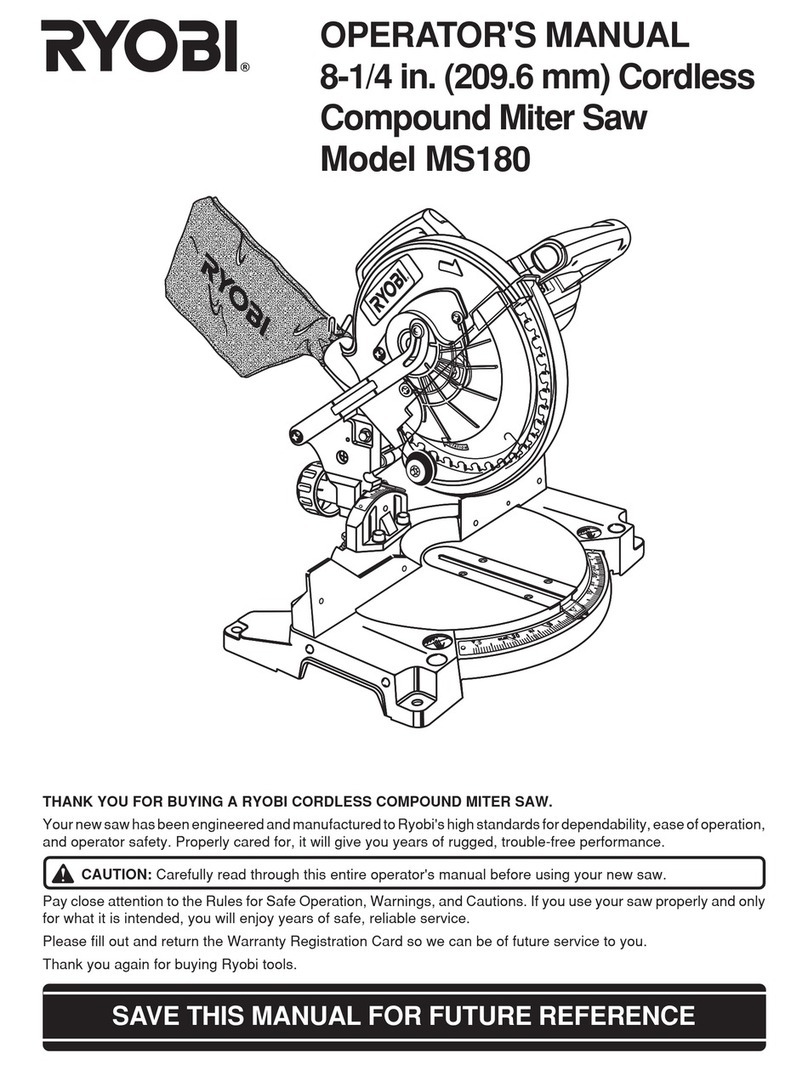
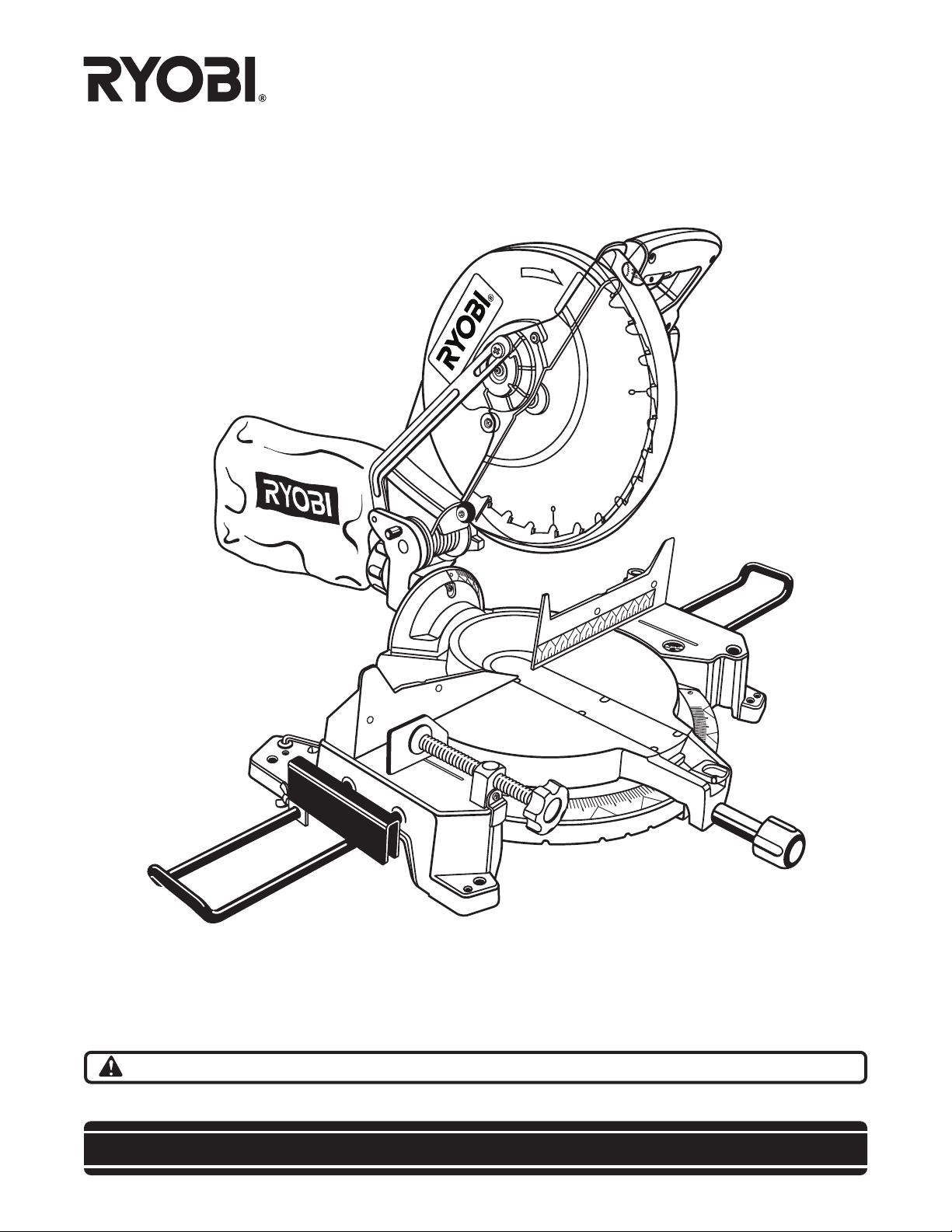
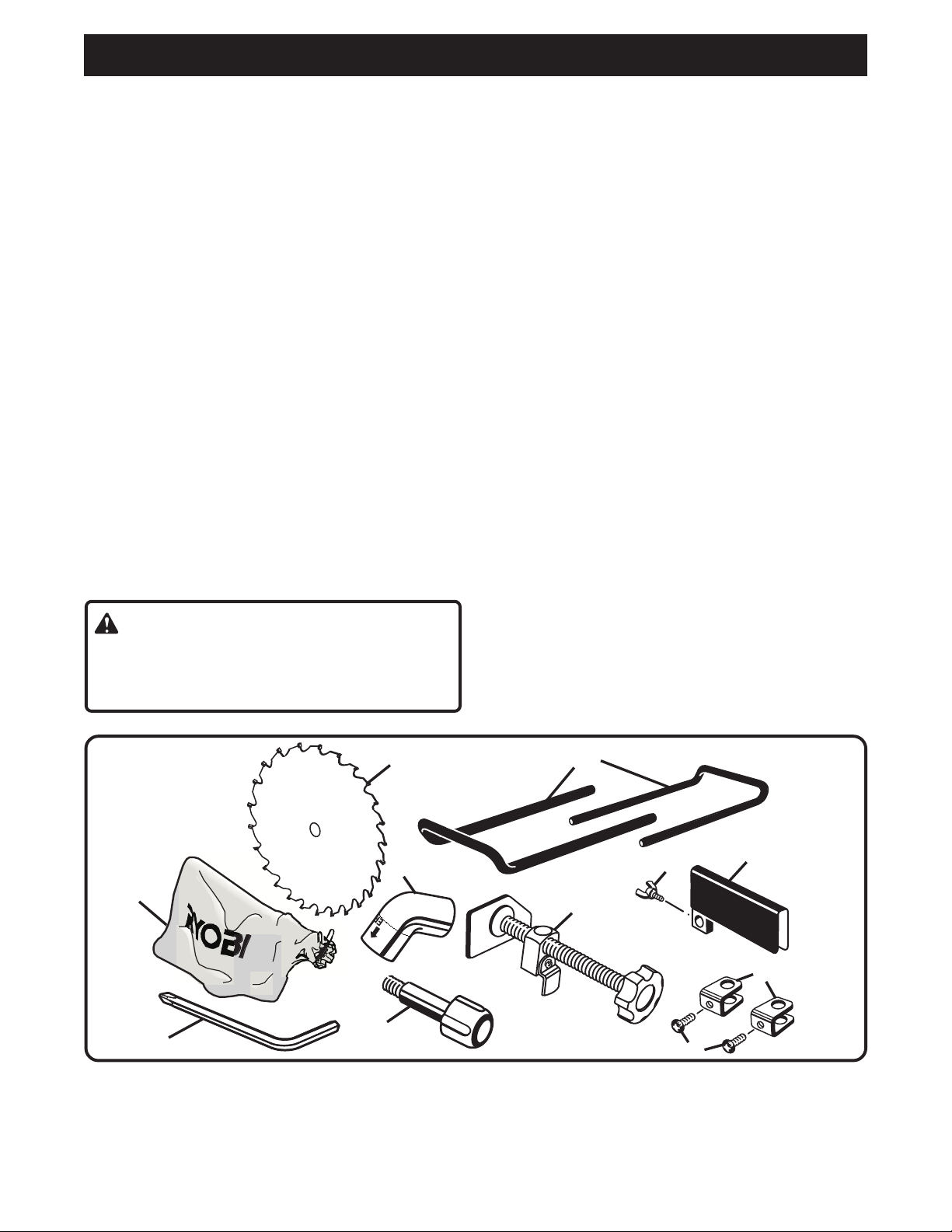
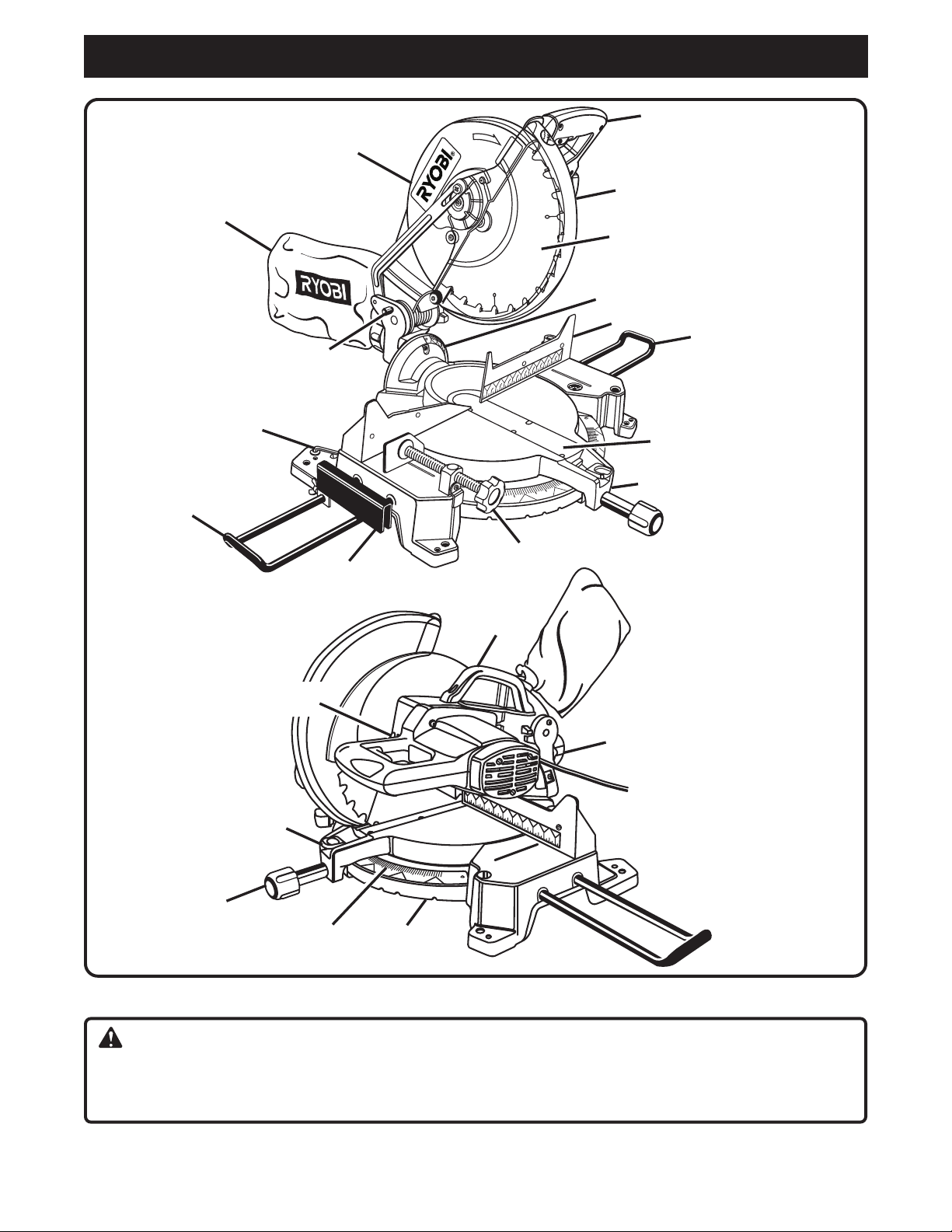
3
RULES FOR SAFE OPERATION
Safe operation of this power tool requires that you read
and understand this operator's manual and all labels
affixed to the tool. Safety is a combination of common
sense, staying alert, and knowing how your tool works.
READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS
■KNOW YOUR POWER TOOL. Read the operator's
manual carefully. Learn the saw's applications and
limitations as well as the specific potential hazards
related to this tool.
■GUARD AGAINST ELECTRICAL SHOCK by pre-
venting body contact with grounded surfaces such as
pipes, radiators, ranges, refrigerator enclosures.
■KEEP GUARDS IN PLACE and in good working
order.
■REMOVE WRENCHES AND ADJUSTING KEYS.
Get in the habit of checking - before turning on tool -
that hex keys and adjusting wrenches are removed
from tool.
■KEEP THE WORK AREA CLEAN. Cluttered work
areas and work benches invite accidents. DO NOT
leave tools or pieces of wood on the saw while it is in
operation.
■DO NOT USE IN DANGEROUS ENVIRONMENTS.
Do not use power tools near gasoline or other flam-
mable liquids, in damp or wet locations, or expose
them to rain. Keep the work area well lit.
■KEEP CHILDREN AND VISITORS AWAY. All visi-
tors should wear safety glasses and be kept a safe
distance from work area. Do not let visitors contact
tool or extension cord while operating.
■MAKE WORKSHOP CHILDPROOF with padlocks
and master switches or by removing starter keys.
■DO NOT FORCE THE TOOL it will do the job better
and more safely at the rate for which it was designed.
■USE THE RIGHT TOOL FOR THE JOB. Do not force
the tool or attachment to do a job it was not designed
for. Use it only the way it was intended.
■USE THE PROPER EXTENSION CORD. Make sure
your extension cord is in good condition. Use only a
cord heavy enough to carry the current your product
will draw. An undersized cord will cause a drop in line
voltage resulting in loss of power and overheating. A
wire gage size (A.W.G.) of at least 14 is recom-
mended for an extension cord 25 feet or less in
length. If in doubt, use the next heavier gage. The
smaller the gage number, the heavier the cord.
■INSPECT TOOL CORDS AND EXTENSION CORDS
PERIODICALLY and, if damaged, have repaired by
a qualified service technician at an authorized ser-
vice center. Stay constantly aware of cord location
and keep it well away from the moving blade.
■DRESS PROPERLY. Do not wear loose clothing,
gloves, neckties, rings, bracelets, or other jewelry
that can get caught and draw you into moving parts.
Nonslip footwear is recommended. Also wear protec-
tive hair covering to contain long hair.
■ALWAYS WEAR SAFETY GLASSES WITH SIDE
SHIELDS. Everyday eyeglasses have only impact-
resistant lenses, they are NOT safety glasses.
■WEAR A DUST MASK to keep from inhaling fine
particles.
■PROTECT YOUR HEARING. Wear hearing protec-
tion during extended periods of operation.
■SECURE WORK. Use clamps or a vise to hold work
when practical. It's safer than using your hand and
frees both hands to operate tool.
■DO NOT OVERREACH. Keep proper footing and
balance at all times.
■MAINTAIN TOOLS WITH CARE. Keep tools sharp
and clean for better and safer performance. Follow
instructions for lubricating and changing accesso-
ries.
■DISCONNECT ALL TOOLS. When not in use, be-
fore servicing, or when changing attachments, all
tools should be disconnected.
■AVOID ACCIDENTAL STARTING. Be sure switch is
off when plugging in any tool.
■USE RECOMMENDED ACCESSORIES. Using im-
proper accessories may risk injury.
■NEVER STAND ON TOOL. Serious injury could
occur if the tool is tipped or if the blade is unintentionally
contacted.
■CHECK DAMAGED PARTS. Before using the tool
again, check any damaged parts, including guards,
for proper operation and performance. Check align-
ment of moving parts, binding of moving parts, break-
age of parts, saw stability, mounting and any other
conditions that may affect its operation. A damaged
part must be properly repaired or replaced by a
qualified service technician at an authorized service
center to avoid risk of personal injury.
■NEVER LEAVE TOOL RUNNING UNATTENDED.
TURN THE POWER OFF. Do not leave tool until it
comes to a complete stop.
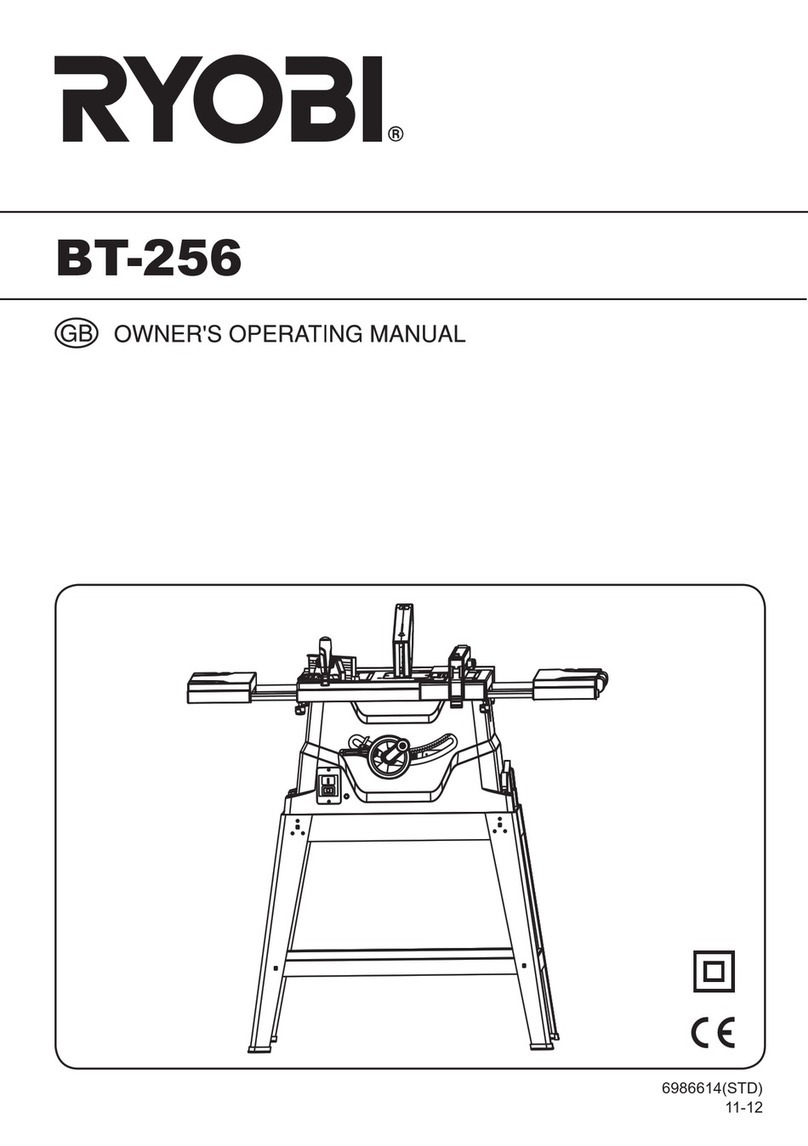
■FIRMLY CLAMP OR BOLT your miter saw to a
workbench or table at approximately hip height.
■USE ONLY CORRECT BLADES. Use the right
blade size, style and cutting speed for the material
and the type of cut. Do not use blades with incor-
rect size holes. Never use blade washers or blade
bolts that are defective or incorrect. The maximum
blade capacity of your saw is 12 in. (305 mm).
■KEEP BLADES CLEAN, SHARP, AND WITH
SUFFICIENT SET. Sharp blades minimize stalling
and kickback.
■DO NOT REMOVE THE SAW'S BLADE
GUARDS. Never operate the saw with any guard or
cover removed. Make sure all guards are operating
properly before each use.