6EASY-MIG | Version 1.04
Safety
- Before replacing wearing parts of the torch, the wel-
ding device must be switched off and disconnected
from the mains supply.
- The electrical installation must be carried out in ac-
cordance with the relevant regulations and accident
prevention regulations.
- The welding unit may only be connected to a supply
network with earthed neutral conductor.
- Make sure that the current socket is correctly
connected to the protective earth.
- The welding device must not be used in a damp or
wet environment or in rain.
- Do not use cables with worn insulation or loose
connections - If a liquid cooling unit is available, it
must only be filled when the welding unit is switched
off and disconnected from the mains.
- Do not weld on containers, vessels or pipes that con-
tain or have contained flammable liquids or gases.
- Do not work on materials that have been cleaned
with chlorinated solvents. Do not work near these
solvents.
- Do not weld on pressurized containers.
- Remove all flammable substances (e.g. wood, pa-
per, scraps of fabric, etc.).
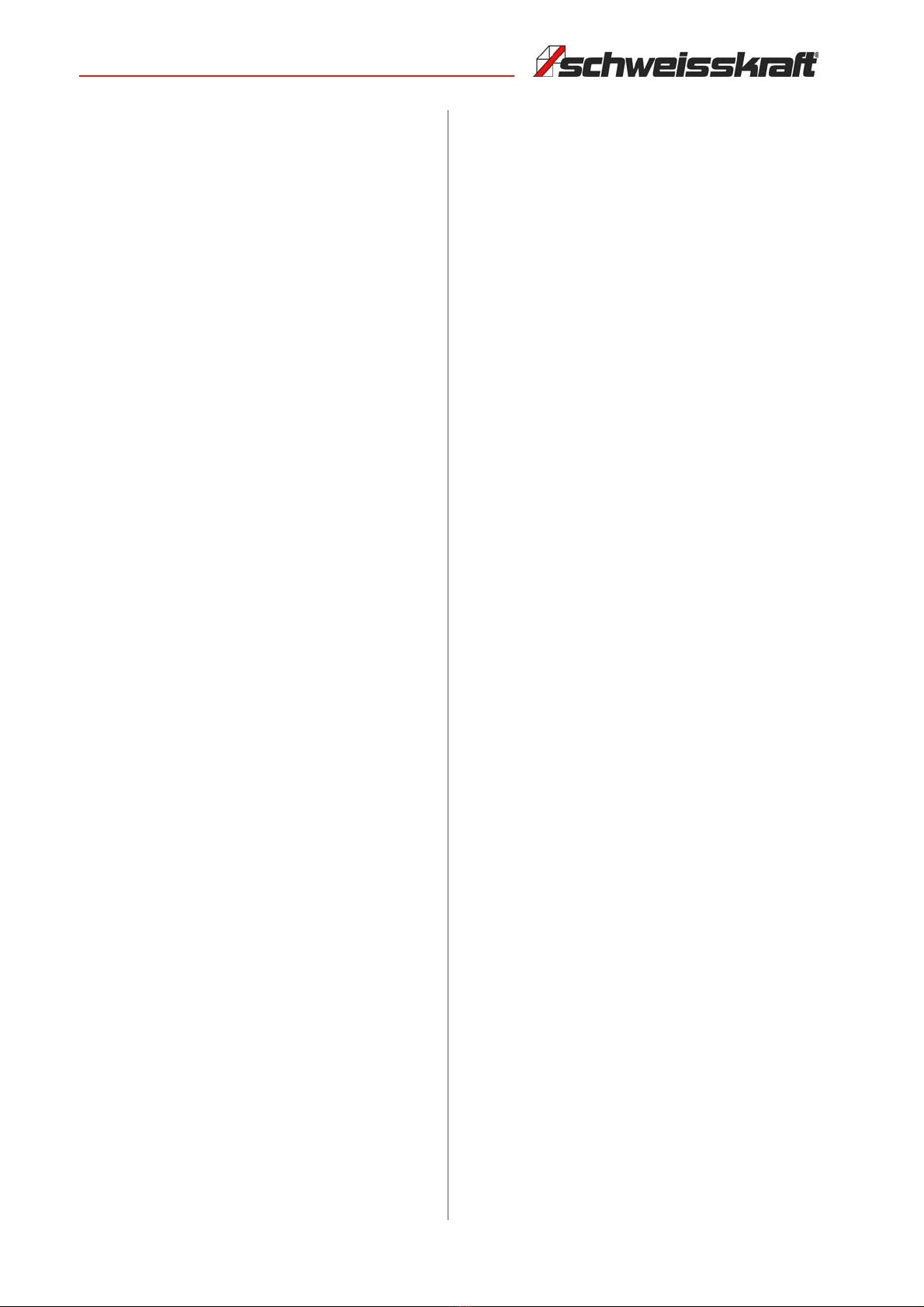
- Ensure that there is sufficient air exchange or
suitable aids to dissipate the flue gases released du-
ring welding near the arc. It must be systematically
examined which limit values apply to the respective
composition, concentration and exposure time of the
welding exhaust gases.
- The gas cylinder must be protected from heat sour-
ces including solar radiation.
- Ensure proper electrical insulation of the electrode,
the workpiece and nearby (accessible) earthed me-
tal parts. It is normally sufficient to wear appropriate
gloves, footwear, headgear and clothing, as well as
footboards and insulating carpets.
- Always protect your eyes with glare glass attached
to masks or helmets. Use appropriate fire-retardant
protective clothing and avoid exposing the skin to
UV and infrared radiation from the arc, and use um-
brellas or non-reflecting curtains to protect third par-
ties near the arc.
- Noise: If a daily level of 85 db(A) or more (LEPd) is rea-
ched during particularly intensive welding work, appro-
priate individual protective equipment must be used.
- When the welding current passes, electromagnetic
fields (EMF) are generated in the vicinity of the wel-
ding current circuit. The electromagnetic fields can
impair medical aids (e.g. pacemakers, breathing
aids or metal prostheses). Appropriate protective
measures must be taken for the wearers of these
aids, for example by prohibiting them from entering
the operating area of the welding device.
- This welding equipment complies with the technical
product standards for exclusive use in commercial
and professional environments. Compliance with the
basic limits applicable to the exposure of humans to
electromagnetic fields in the domestic environment
is not ensured.
The operator must take the following steps to re-
duce the effects of electromechanical fields:
- The two welding cables must be fixed as close as
possible to each other.
- The head and body shall be kept as far away from
the welding circuit as possible.
- Under no circumstances should the welding cables
be wrapped around the body.
- When welding, the body must not be in the middle of
the welding circuit. Hold both cables on the same
side of the body.
- Connect the power return cable to the workpiece as
close to the weld as possible.
- Never weld close to the welding machine, sitting on
the welding machine or leaning against the welding
machine (minimum distance: 50 cm).
- Do not leave any ferromagnetic objects near the wel-
ding circuit. - Minimum distance d=20cm.
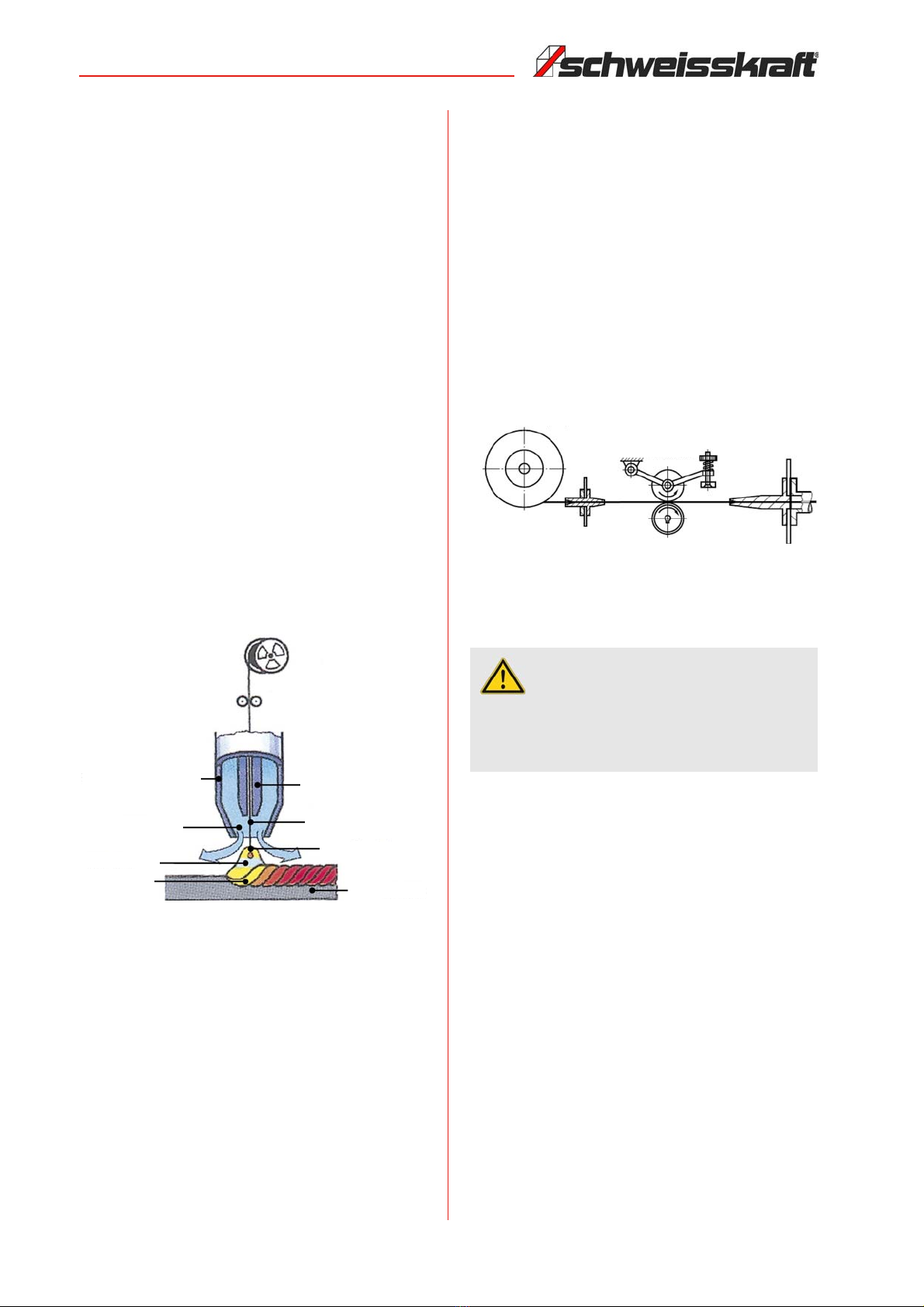
- Use the guards and secure them securely. Never
work without guards and get them working.
- Always keep the welding machine and its working
environment clean. Ensure adequate lighting.
- Always secure your workpiece when working with
suitable clamping devices. Ensure a sufficient con-
tact surface.
- The design of the welding machine must not be
changed and it must not be used for purposes other
than those foreseen by the manufacturer.
- Never work under the influence of concentration-di-
sturbing diseases, fatigue, drugs, alcohol or medica-
tion.
- Keep children and persons not familiar with the wel-
ding machine away from their working environment.
- Do not pull the power cord to unplug the plug from
the outlet. Protect the cable from heat, oil and sharp
edges.
- Immediately remove any malfunctions that may af-
fect safety.
- Protect the welding device from moisture (danger of
short circuits).
- Before each use of the welding machine, make sure
that no parts are damaged. Damaged parts must be
replaced immediately to avoid sources of danger.
- Do not overload the welding machine! You will work
better and safer in the specified power range.
- Use only original spare parts and accessories to
avoid possible dangers and accident risks.