SICK TR10 Lock User manual

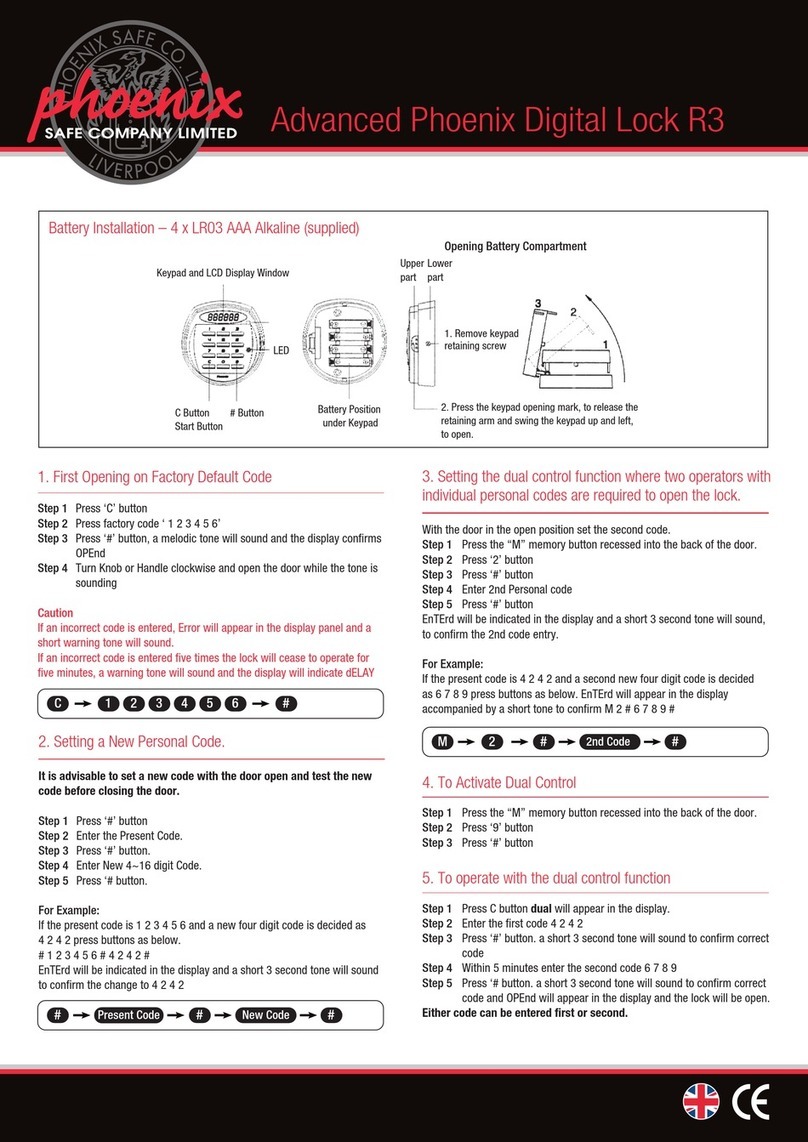
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
TR10 Lock
Safety locking device

Described product
TR10 Lock
Manufacturer
SICK AG
Erwin-Sick-Str. 1
79183 Waldkirch
Germany
Legal information
This work is protected by copyright. Any rights derived from the copyright shall be
reserved for SICK AG. Reproduction of this document or parts of this document is
only permissible within the limits of the legal determination of Copyright Law. Any modi‐
fication, abridgment or translation of this document is prohibited without the express
written permission of SICK AG.
The trademarks stated in this document are the property of their respective owner.
© SICK AG. All rights reserved.
Original document
This document is an original document of SICK AG.
2O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | TR10 Lock 8019972/1CS1/2022-07-20 | SICK
Subject to change without notice

Contents
1 About this document........................................................................ 5
1.1 Function of this document....................................................................... 5
1.2 Scope......................................................................................................... 5
1.3 Additional information.............................................................................. 5
1.4 Symbols and document conventions...................................................... 5
2 Safety information............................................................................ 7
2.1 General safety notes................................................................................ 7
2.2 Intended use............................................................................................. 7
2.3 Improper use............................................................................................. 7
2.4 Requirements for the qualification of personnel.................................... 8
3 Product description........................................................................... 9
3.1 Setup and function................................................................................... 9
3.2 Product characteristics............................................................................ 9
3.3 Manual deactivation................................................................................. 10
4 Project planning................................................................................ 12
4.1 Manufacturer of the machine.................................................................. 12
4.2 Operating entity of the machine.............................................................. 12
4.3 Assembly................................................................................................... 12
4.4 Integrating into the electrical control....................................................... 16
4.5 Testing plan............................................................................................... 18
5 Mounting............................................................................................. 20
5.1 Installation................................................................................................ 20
6 Electrical installation........................................................................ 23
6.1 Notes on cULus......................................................................................... 23
6.2 Device connection (M12, 8-pin).............................................................. 23
6.3 Device connection (flying lead)................................................................ 24
6.4 Connecting a cascade.............................................................................. 25
7 Commissioning.................................................................................. 28
7.1 Switching on.............................................................................................. 28
7.2 Teach-in..................................................................................................... 28
7.3 Testing....................................................................................................... 29
8 Troubleshooting................................................................................. 31
8.1 Diagnostic LEDs........................................................................................ 31
9 Technical data.................................................................................... 34
9.1 Technical data........................................................................................... 34
9.2 Response time.......................................................................................... 36
9.3 Course of the output signal switching device test over time................. 36
CONTENTS
8019972/1CS1/2022-07-20 | SICK O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | TR10 Lock 3
Subject to change without notice

9.4 Dimensional drawings.............................................................................. 37
10 Ordering information........................................................................ 39
10.1 Scope of delivery....................................................................................... 39
10.2 Ordering information for TR10 Lock........................................................ 39
11 Accessories........................................................................................ 40
11.1 Actuator..................................................................................................... 40
11.2 Connectivity............................................................................................... 40
11.3 Mounting bracket...................................................................................... 42
11.4 Mounting accessories.............................................................................. 42
12 Annex.................................................................................................. 43
12.1 Conformities and certificates................................................................... 43
CONTENTS
4O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | TR10 Lock 8019972/1CS1/2022-07-20 | SICK
Subject to change without notice

1 About this document
1.1 Function of this document
These operating instructions contain the information needed during the life cycle of the
safety locking device.
These operating instructions must be made available to all people who work with the
safety locking device.
1.2 Scope
Product
This document applies to the following products:
•Product code: TR10 Lock
•“Operating instructions” type label entry: 8019930
Document identification
Document part number:
•This document: 8019972
•Available language versions of this document: 8019930
You can find the current version of all documents at www.sick.com.
1.3 Additional information
www.sick.com
The following information is available on the Internet:
•Data sheets and application examples
•CAD data and dimensional drawings
•Certificates (e.g. EU declaration of conformity)
•Guide for Safe Machinery Six steps to a safe machine
1.4 Symbols and document conventions
The following symbols and conventions are used in this document:
Safety notes and other notes
DANGER
Indicates a situation presenting imminent danger, which will lead to death or serious
injuries if not prevented.
WARNING
Indicates a situation presenting possible danger, which may lead to death or serious
injuries if not prevented.
CAUTION
Indicates a situation presenting possible danger, which may lead to moderate or minor
injuries if not prevented.
ABOUT THIS DOCUMENT 1
8019972/1CS1/2022-07-20 | SICK O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | TR10 Lock 5
Subject to change without notice

NOTICE
Indicates a situation presenting possible danger, which may lead to property damage if
not prevented.
NOTE
Indicates useful tips and recommendations.
Instructions to action
bThe arrow denotes instructions to action.
1. The sequence of instructions for action is numbered.
2. Follow the order in which the numbered instructions are given.
✓The check mark denotes the result of an instruction.
LED symbols
These symbols indicate the status of an LED:
oThe LED is off.
ÖThe LED is flashing.
OThe LED is illuminated continuously.
1 ABOUT THIS DOCUMENT
6O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | TR10 Lock 8019972/1CS1/2022-07-20 | SICK
Subject to change without notice

2 Safety information
2.1 General safety notes
Product integration
DANGER
The product can not offer the expected protection if it is integrated incorrectly.
bPlan the integration of the product in accordance with the machine requirements
(project planning).
bImplement the integration of the product in accordance with the project planning.
Mounting and electrical installation
DANGER
Death or severe injury due to electrical voltage and/or an unexpected startup of the
machine
bMake sure that the machine is (and remains) disconnected from the voltage
supply during mounting and electrical installation.
bMake sure that the dangerous state of the machine is and remains switched off.
Repairs and modifications
DANGER
Improper work on the product
A modified product may not offer the expected protection if it is integrated incorrectly.
bApart from the procedures described in this document, do not repair, open, manip‐
ulate or otherwise modify the product.
2.2 Intended use
When used in conjunction with a movable physical guard and the machine controller,
the safety locking device prevents the protective device from being opened while a
dangerous machine function is being executed.
The safety locking device may only be used on the machine on which it was configured,
mounted, installed, and commissioned by qualified safety personnel in accordance with
these operating instructions.
Incorrect use, improper modification of or tampering with the safety locking device will
invalidate any warranty from SICK AG; in addition, any responsibility and liability of SICK
AG for damage and secondary damage caused by this is excluded.
NOTE
The safety locking device is also suitable for process protection.
2.3 Improper use
Among others, the safety locking device is not suitable for the following applications:
•Radioactivity (exception: natural radioactivity)
•Vacuum or high pressure
•High UV load
•In the vicinity of low-frequency RFID devices
SAFETY INFORMATION 2
8019972/1CS1/2022-07-20 | SICK O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | TR10 Lock 7
Subject to change without notice

•In the vicinity of magnetic fields
•Ferromagnetic background
Among others, the safety locking device is only suitable for the following applications
with restrictions:
•In the vicinity of flying metal particles (see "Mounting near metal particles",
page 15).
2.4 Requirements for the qualification of personnel
The safety locking device must be planned in, installed, connected, commissioned, and
serviced only by qualified safety personnel.
Project planning
You need safety expertise to implement safety functions and select suitable products
for that purpose. You need expert knowledge of the applicable standards and regula‐
tions.
Mounting, electrical installation and commissioning
You need suitable expertise and experience. You must be able to assess if the machine
is operating safely.
Operation and maintenance
You need suitable expertise and experience. You must be instructed in machine oper‐
ation by the machine operator. For maintenance, you must be able to assess if the
machine is operating safely.
2 SAFETY INFORMATION
8O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | TR10 Lock 8019972/1CS1/2022-07-20 | SICK
Subject to change without notice

3 Product description
3.1 Setup and function
The safety locking device is an interlocking device with a lock consisting of a non-con‐
tact safety switch and a coded actuator. Depending on the product variant, the actuator
either has a low (universally coded) or high (unique coded) coding level.
If the protective device is closed, the actuator is led to the safety switch. If the actuation
field is reached, the actuator code is read out and evaluated by RFID. If the code
is valid, the application diagnostic output switches to the OFF state. When a locking
command is active, the locking pin in extended. Not until the locking pin is detected
in the correct position in the actuator by the integrated proximity sensor is the locking
successful and the safe output signal switching device (OSSD) are switched in the ON
state.
The safety locking device can only be locked when the protective device is closed.
The locking pin is actuated by a bistable magnetic solenoid. As a result, the safety
locking device has a low power consumption and does not give off any heat. The safety
locking device function is nevertheless implemented according to the power to release
or power to lock principle via the electronics.
3.2 Product characteristics
3.2.1 Product variants
The safety locking device is delivered in different variants. An overview of important
distinguishing features between the variants is provided below.
•Designed according to “power to release” or “power to lock” principle
•Versions for universally coded or unique coded actuators
•Cable with M12 plug connector (0.2m) or flying leads (3 or 10m)
Complete overview of all variants: see "Ordering information for TR10 Lock", page 39
Variant according to “power to release” principle
•Activate lock: no voltage at lock input
•Deactivate lock: voltage at lock input
If voltage is interrupted, the locking device remains locked and the protective device
cannot be opened immediately.
Variant according to “power to lock” principle
•Activate lock: voltage at lock input
•Deactivate lock: no voltage at lock input
When the voltage is interrupted, the lock is deactivated and the protective device can
be opened immediately.
DANGER
Hazard due to lack of effectiveness of the protective device
If the voltage drops, the safety locking device deactivates regardless of whether the
dangerous state of the machine has ended
bAssess the accident risk. The device must be configured correctly in order to be
used for protection of personnel.
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION 3
8019972/1CS1/2022-07-20 | SICK O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | TR10 Lock 9
Subject to change without notice

Variant for universally coded actuators
All universally coded actuators are accepted. No teach-in is required.
Variant for unique coded actuators
A unique coded actuator must be taught in during commissioning. Up to 8 actuators
can be taught in one after another. Only the most recently taught-in actuator is valid.
When teaching in an actuator, the safety locking device can be permanently coded
(optional). If the safety locking device is permanently coded, no further actuators can
be taught in. This cannot be undone.
3.2.2 OSSD
Output signal switching device: signal output for the protective device, which is used for
stopping the dangerous movement.
An OSSD is a safety switching output. The functionality of each OSSD is tested periodi‐
cally. OSSDs are always connected in pairs and must undergo dual-channel analysis for
safety reasons. An OSSD pair is formed from 2 OSSDs that are connected and analyzed
together.
3.3 Manual deactivation
In some situations, it may be necessary to deactivate the lock manually (e.g., in the
event of faults). A functional test must be carried out after the lock has been deacti‐
vated.
Mechanical unlocking mechanism
In the event of functional faults, the safety locking device can be deactivated with
the mechanical unlocking mechanism regardless of the state of the electromagnet.
The mechanical unlocking mechanism is not suitable for emergency release or escape
release.
When the mechanical unlocking mechanism is actuated, the lock is deactivated and
the OSSDs switch off. This must generate a stop command.
Actuating the mechanical unlocking mechanism
bGuide a screwdriver with a max. diameter of 2.5mm through the actuator and
push the guard locking pin into the safety locking device.
✓The lock is deactivated. The safety locking device switches to the fault state (DIAG
light emitting diodes flash red).
After using the mechanical unlocking mechanism, disconnect the voltage supply from
the safety locking device and then reconnect. The safety locking device restarts.
3 PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
10 O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | TR10 Lock 8019972/1CS1/2022-07-20 | SICK
Subject to change without notice

< 2,5
Figure 1: Mechanical unlocking mechanism
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION 3
8019972/1CS1/2022-07-20 | SICK O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | TR10 Lock 11
Subject to change without notice

4 Project planning
4.1 Manufacturer of the machine
The manufacturer of the machinery must carry out a risk assessment and apply appro‐
priate protective measures. Further protective measures may be required in addition to
the product.
The product must not be tampered with or changed, except for the procedures descri‐
bed in this document.
The product must only be repaired by the manufacturer of the product or by someone
authorized by the manufacturer. Improper repair can result in the product not providing
the expected protection.
Observe EN ISO 14119 for using interlocking devices associated with physical guards.
4.2 Operating entity of the machine
Changes to the electrical integration of the product in the machine controller and
changes to the mechanical mounting of the product necessitate a new risk assess‐
ment. The results of this risk assessment may require the entity operating the machine
to meet the obligations of a manufacturer.
After each change to the configuration, it is necessary to check whether the protective
measure provides the necessary protection. The person making the change is responsi‐
ble for ensuring that the protection measure provides the necessary protection.
The product must not be tampered with or changed, except for the procedures descri‐
bed in this document.
The product must not be repaired. Defective products must be replaced.
Restrict access to replacement actuators, so they cannot be used for bypassing.
4.3 Assembly
DANGER
Bypassing the protective device
Hazard due to lack of effectiveness of the protective device
bPrevent any incentives to tamper with the safety locking device; for example, with
the following measures:
Variant for universally coded actuators only:
°Cover the safety switch and the actuator with additional equipment or protect
them against access.
Actuation direction
The safety locking device can be actuated from all 4 horizontal directions.
4 PROJECT PLANNING
12 O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | TR10 Lock 8019972/1CS1/2022-07-20 | SICK
Subject to change without notice

421 3
Figure 2: Possible actuation directions
1From front
2From left
3From rear
4From right
The safety locking device is not suitable for vertical actuation. The lock does not
prevent the actuator being moved upward out of the response range.
Figure 3: No vertical lock
Distance
When several safety locking devices are mounted to the machine, they must be
mounted at a distance of at least 200mm to one another.
PROJECT PLANNING 4
8019972/1CS1/2022-07-20 | SICK O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | TR10 Lock 13
Subject to change without notice
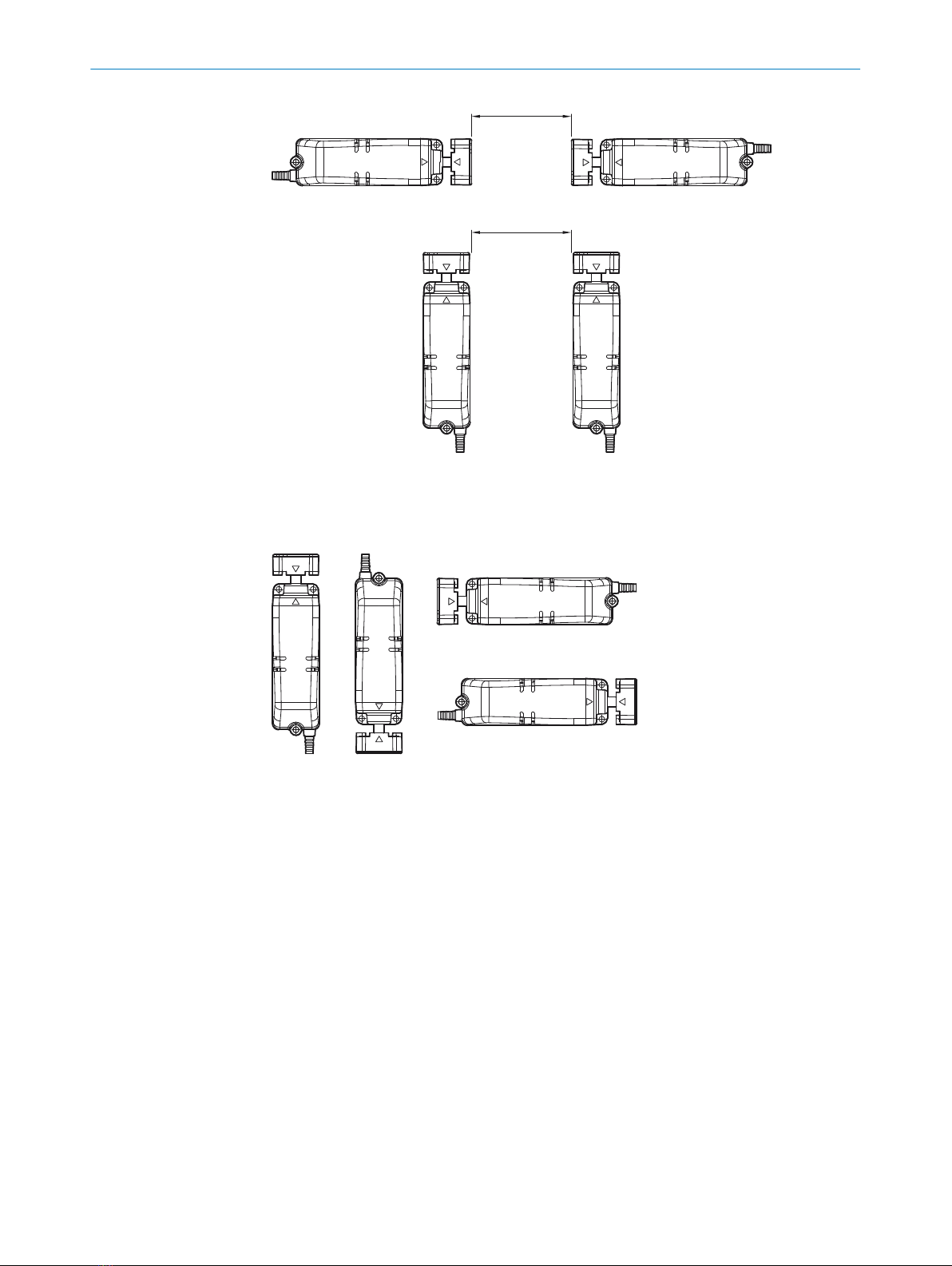
200
200
Figure 4: Min. distance for multiple safety switches
Alignment
The safety locking device can be mounted in any alignment.
Figure 5: Possible alignment of the safety locking device
Mounting bracket for actuator
When mounting the device, the mounting bracket included with delivery must be used.
If other mounting brackets are used or the supplied mounting bracket manipulated,
safe functioning cannot be ensured.
Mounting of switch and actuator on the same level
If the switch and actuator are mounted on the same level, it must ensured that there is
6mm of deviation between the mounting levels of the safety switch and the mounting
bracket of the actuator.
4 PROJECT PLANNING
14 O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | TR10 Lock 8019972/1CS1/2022-07-20 | SICK
Subject to change without notice

6
Figure 6: Deviation between mounting levels of the safety switch and the actuator
Mounting at CIP (Clean-In-Place)
The enclosure rating of the safety locking device is classified with IP69 in accordance
with IEC 60529. The standard stipulates a short thorough check with 80°C water
under high pressure. The IP69 enclosure rating guarantees neither protection from
liquids other than water nor durability at regular and ongoing exposure.
However, this safety locking device is designed for CIP applications, e.g. through the use
of materials resistant to common alkaline cleaning agents.
For maximum service life, the safety locking device must be mounted upside down and
the plug must be removed from the actuator. This ensures the best possible discharge
of liquids and protects the locking pin mechanics.
Figure 7: Ideal mounting direction for CIP applications
Mounting near metal particles
Metal particles (chips or dust) can impair the safety locking device. When metal parti‐
cles collect on the locking pin, it can lead to locking pin blockage and to failure of
the safety locking device in the long term. Ferromagnetic particles from permanent
magnets in particular are drawn to the locking pin. Observe the following when using
the safety locking device near metal particles:
•Protect the safety locking device from metal particles with constructive measures,
e.g.:
°Shielding with protective plates
°Select the mounting site so that the safety locking device is not exposed to
metal particles, e.g. at some distance to the source of metal particles or
outside the room.
•If constructive measures cannot prevent the safety locking device from coming
into contact with metal particles, the safety locking device must be checked and
cleaned regularly before metal particles can collect on the locking pin.
PROJECT PLANNING 4
8019972/1CS1/2022-07-20 | SICK O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | TR10 Lock 15
Subject to change without notice

4.3.1 Measures against accidental damage
You can use the following measures to avoid unintentional damage to the safety switch:
•Select the mounting location so that the safety switch is protected from impacts
and mechanical pressure.
•Fit an additional stop for the door. The safety switch must not be used as a stop.
4.3.2 Measures against manipulation
The safety switch must not be defeated (contacts jumpered), rotated away, removed, or
rendered ineffective in any other way. You must put measures in place, if necessary, to
reduce the possibilities for circumventing the device.
4.4 Integrating into the electrical control
Switch-on commands which bring about a dangerous state of the machine must not be
enabled until the protective device is closed and the lock is activated. The lock must not
be deactivated until the dangerous state has ended. Depending on the safety concept,
the signal is analyzed by, e.g., safety relays or a safety controller.
The connected controller and all devices responsible for safety must comply with
the required performance level and the required category (for example according to
ISO13849-1).
4.4.1 Lock
The logic to generate a locking command with the control changes depending on the
product variant selected.
Variant according to “power to release” principle
To lock, make sure there is no voltage at the “lock input” contact (locking command
active).
To unlock, apply 24VDC voltage at the “lock input” contact (locking command inac‐
tive).
For variants based on the power to lock principle
To lock, apply 24VDC voltage at the “lock input” contact (locking command active).
To unlock, make sure there is no voltage at the “lock input” contact (locking command
inactive).
4.4.2 OSSDs
Safety locking devices with local inputs and outputs can be directly integrated into the
machine controller.
DANGER
Hazard due to lack of effectiveness of the protective device
In the case of non-compliance, it is possible that the dangerous state of the machine
may not be stopped or not stopped in a timely manner.
bMake sure that the following control and electrical requirements are met so the
protective function can be fulfilled.
•The output signals from an OSSD pair must not be connected to each other.
•In the machine controller, both signals from an OSSD pair must be processed
separately.
4 PROJECT PLANNING
16 O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | TR10 Lock 8019972/1CS1/2022-07-20 | SICK
Subject to change without notice

Figure 8: Dual-channel and isolated connection of OSSD 1 and OSSD 2
•The machine must switch to the safe state at any time if at least one OSSD in an
OSSD pair switches to the OFF state.
•Prevent the formation of a potential difference between the load and the protec‐
tive device. If you connect loads to the OSSDs (safety outputs) that also switch if
controlled with negative voltage (e.g., electro-mechanical contactor without reverse
polarity protection diode), you must connect the 0V connections of these loads
and those of the corresponding protective device individually and directly to the
same 0V terminal strip. In the event of a fault, this is the only way to ensure that
there can be no potential difference between the 0V connections of the loads and
those of the corresponding protective device.
Figure 9: No potential difference between load and protective device
DANGER
Hazard due to lack of effectiveness of the protective device
In the case of non-compliance, it is possible that the dangerous state of the machine
may not be stopped or not stopped in a timely manner.
Downstream contactors must be positively guided and monitored depending on appli‐
cable national regulations or required reliability of the safety function.
bMake sure that downstream contactors are monitored (external device monitoring,
EDM).
Requirements for the electrical control of the machine
The OSSDs are short-circuit protected to 24VDC and 0V. When the safety locking
device is locked, the OSSDs signal the ON state with the HIGH signal level (non-iso‐
lated). If the safety locking device is unlocked or there is a device fault, the OSSDs
signal the OFF state with the LOW signal level.
PROJECT PLANNING 4
8019972/1CS1/2022-07-20 | SICK O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | TR10 Lock 17
Subject to change without notice

4.4.3 Application diagnostic output
The application diagnostic output signal changes as soon as the actuator is moved into
or leaves the response range of the safety switch. In other words, it does so when the
moving protective device is opened and closed. This is not a safety output.
Table 1: Application diagnostic output switching behavior
Actuator Application diagnostic output
Actuator not in response area or safety locking
device in a faulty state
ON
Actuator in response area OFF
4.4.4 Cascading
Cascading can be used to connect multiple safety locking devices. The connected
devices will provide the combined safety outputs and therefore act outwardly like one
device.
2
8
4
7
3
5
6
1
OSSD1
OSSD2
OSSD1
OSSD2
OSSD1
OSSD2
OSSD1
OSSD2
OSSD1
OSSD2
2
8
4
7
3
5
6
1
2
8
4
7
3
5
6
1
2
8
4
7
3
5
6
1
2
8
4
7
3
5
6
1
24 V DC
0 V DC
1// /// 111 1 2
1TR10 Lock
2Safe evaluation unit
The maximum number of safety locking devices depends on the following factors:
•Supply voltage applied
•Length of cables used
•Cross-section of cables used
•Load current
The voltage drop in the cascade must be checked to ensure that the defined minimum
voltage is still present at the last safety locking device.
The number of safety locking devices in a cascade influences the response time (see
"Response time", page 36).
The cascade can be implemented using special T-connectors and an end connector
(see "Connecting a cascade", page 25).
NOTE
In the case of safety switches cascaded using T-connectors, it is not possible to evalu‐
ate the application diagnostic output.
4.5 Testing plan
Overview
The manufacturer of the machine and the operating entity must define all required
thorough checks. The definition must be based on the application conditions and the
risk assessment and must be documented in a traceable manner.
4 PROJECT PLANNING
18 O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | TR10 Lock 8019972/1CS1/2022-07-20 | SICK
Subject to change without notice

Important information
DANGER
Insufficient checks or incorrect repair
Hazard due to lack of effectiveness of the protective device
bIn the event of wear or damage, replace the entire safety locking device with
actuator. Never replace individual parts or assemblies.
bCheck the safety locking device following the inspection intervals specified in the
national rules and regulations.
Defining the thorough check
bWhen defining the thorough check, please note the following:
°Define the type and execution of the thorough check.
°Define the frequency of the thorough check.
°Notify the machine operators of the thorough check and instruct them
accordingly.
The following thorough checks are often defined in connection with a protective
device:
•Thorough check during commissioning and modifications
•Regular thorough check
Minimum requirements for the thorough check
The following checks must be done to ensure permanent and proper function:
•Proper switching function
•Manual unlock function (e.g., mechanical unlocking mechanism)
•Safe mounting of all components
•No damage, contamination, deposits or wear
•No loose plug connectors
•No signs of manipulation of the safety locking device
•No alignment error between the fixed and moving part of the physical guard that
impairs the protection, e.g., gap through which operating personnel can reach.
•For variants with unique coding: The actuator used is the taught in actuator.
PROJECT PLANNING 4
8019972/1CS1/2022-07-20 | SICK O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | TR10 Lock 19
Subject to change without notice

5 Mounting
5.1 Installation
Important information
NOTICE
•Arrange the safety switch and actuator so that damage due to unintentional out‐
side influences is prevented.
•If any metal drilling occurs during the mounting work, protect the safety switch
from metal particles.
Prerequisites
•Project planning is completed.
•Assembly is carried out according to the project planning.
•Dangerous condition of the machine is and remains switched off during mounting.
•Do not use a safety switch and actuator as a stop.
•The set-up and mounting of the safety switch and actuator must be stable enough
to maintain proper operation.
•Use only reliable mounting elements that can only be removed with tools.
•The supplied mounting bracket is used for the actuator.
•If possible, use non-detachable mounting methods for actuators (such as welding,
gluing, safety screws, or rivets).
Mounting the actuator
1. Mount the actuator to the mounting bracket with 2 TX10 Torx wrench screws.
When doing so, note the following:
°Max. torque: 2Nm
°The guard locking pin must first pass through the mounting bracket.
Figure 10: The guard locking pin must first pass through the mounting bracket
°The alignment triangles on the actuator and safety switch must point to one
another.
Figure 11: Correct alignment between safety switch and actuator
5 MOUNTING
20 O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | TR10 Lock 8019972/1CS1/2022-07-20 | SICK
Subject to change without notice
Other manuals for TR10 Lock
1
Table of contents
Other SICK Lock manuals
Popular Lock manuals by other brands

Simons Voss Technologies
Simons Voss Technologies SmartHandle Handbok

Siemens
Siemens 3VA9980-0LF20 operating instructions

ZKTeco
ZKTeco AL10B user manual

U-tec
U-tec Ultraloq UL300 user guide

Kaiser+Kraft
Kaiser+Kraft 474243 49 Installation and operation manual

SECO-LARM
SECO-LARM E-941SA-80Q installation manual