SICK i15-EM0123 User manual

OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
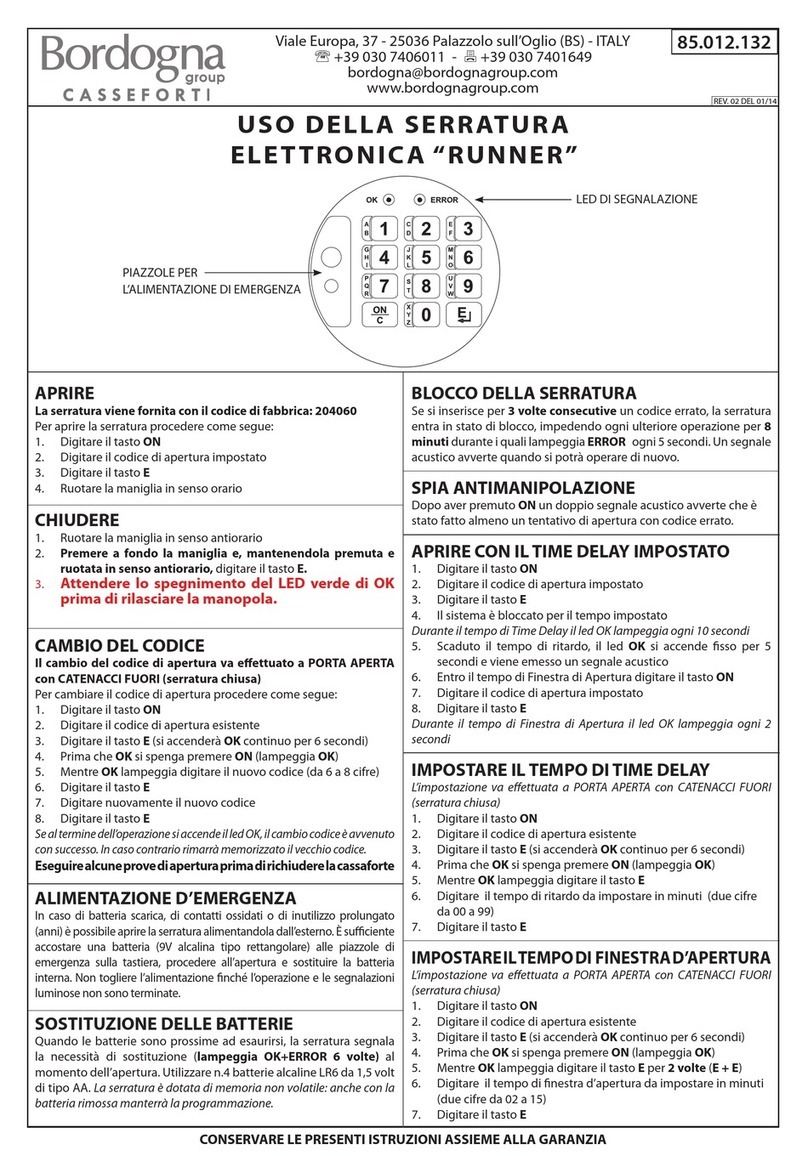
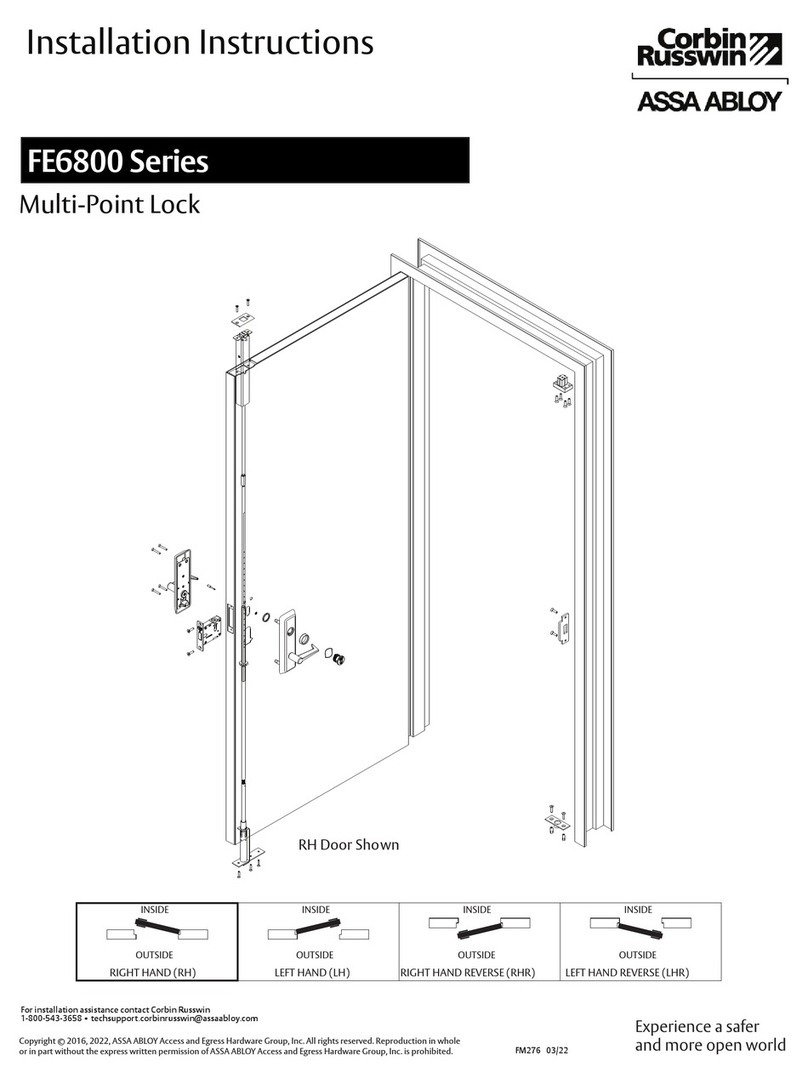
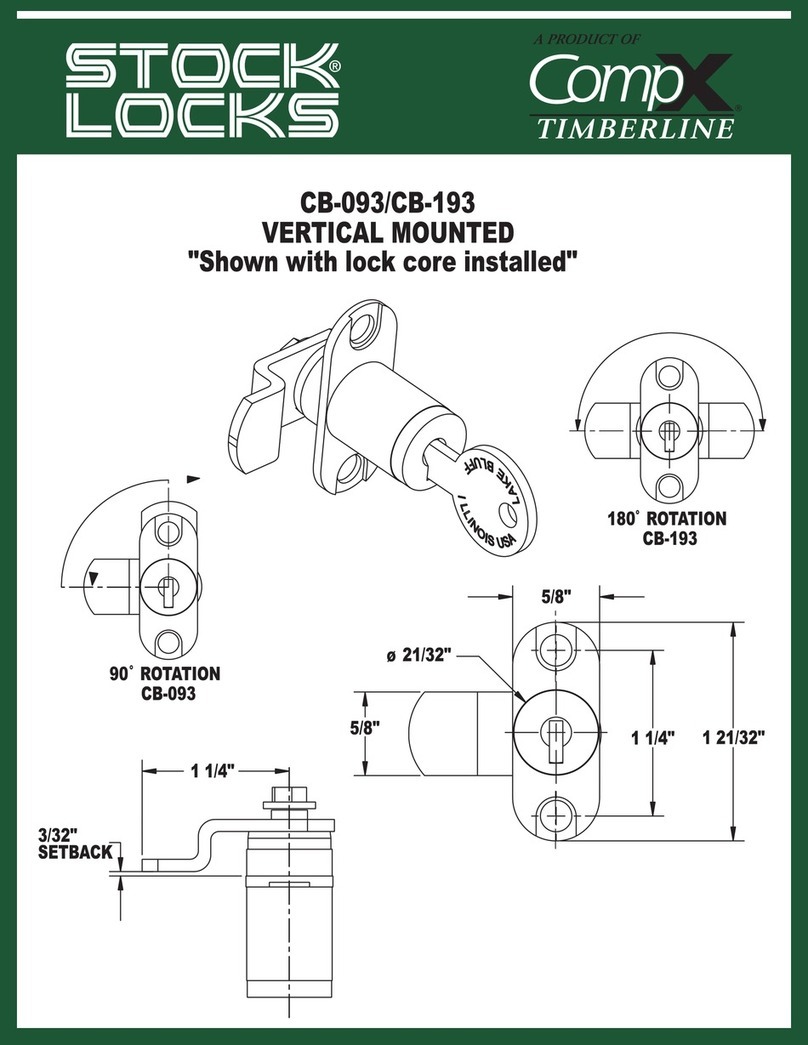
i15 Lock
Safety locking device

Described product
i15 Lock
Manufacturer
SICK AG
Erwin-Sick-Str. 1
79183 Waldkirch
Germany
Legal information
This work is protected by copyright. Any rights derived from the copyright shall be
reserved for SICK AG. Reproduction of this document or parts of this document is
only permissible within the limits of the legal determination of Copyright Law. Any modi‐
fication, abridgment or translation of this document is prohibited without the express
written permission of SICK AG.
The trademarks stated in this document are the property of their respective owner.
© SICK AG. All rights reserved.
Original document
This document is an original document of SICK AG.
2O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | i15 Lock 8020548/1FVF/2022-04-27 | SICK
Subject to change without notice

Contents
1 About this document........................................................................ 5
1.1 Scope......................................................................................................... 5
1.2 Additional information.............................................................................. 5
1.3 Symbols and document conventions...................................................... 5
2 Safety information............................................................................ 7
2.1 General safety notes................................................................................ 7
2.2 Intended use............................................................................................. 7
2.3 Requirements for the qualification of personnel.................................... 7
3 Product description........................................................................... 8
3.1 Setup and function................................................................................... 8
3.2 Product characteristics............................................................................ 8
3.3 Symbols on the product........................................................................... 9
3.4 Manual unlocking..................................................................................... 9
4 Project planning................................................................................ 11
4.1 Manufacturer of the machine.................................................................. 11
4.2 Operator of the machine.......................................................................... 11
4.3 Design........................................................................................................ 12
4.4 Integrating into the electrical control....................................................... 12
4.5 Testing plan............................................................................................... 12
5 Mounting............................................................................................. 13
5.1 Safety......................................................................................................... 13
5.2 Converting the actuating head................................................................. 13
5.3 Mounting................................................................................................... 14
5.4 Protection from environmental influences.............................................. 14
6 Electrical installation........................................................................ 15
6.1 Safety......................................................................................................... 15
6.2 Pin assignment......................................................................................... 15
6.3 System connection (cable entry)............................................................. 15
7 Commissioning.................................................................................. 17
7.1 Check during commissioning and modifications.................................... 17
7.2 Recurring technical checks...................................................................... 17
8 Decommissioning............................................................................. 19
8.1 Disposal..................................................................................................... 19
9 Technical data.................................................................................... 20
9.1 Technical data........................................................................................... 20
9.2 Dimensional drawings.............................................................................. 21
CONTENTS
8020548/1FVF/2022-04-27 | SICK O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | i15 Lock 3
Subject to change without notice

10 Ordering information........................................................................ 23
10.1 Ordering information................................................................................. 23
11 Accessories........................................................................................ 24
11.1 Actuator..................................................................................................... 24
11.2 Additional accessories............................................................................. 24
12 Annex.................................................................................................. 25
12.1 Conformities and certificates................................................................... 25
CONTENTS
4O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | i15 Lock 8020548/1FVF/2022-04-27 | SICK
Subject to change without notice

1 About this document
1.1 Scope
These operating instructions are valid for all i15 Lock safety locking devices.
This document is included with the following SICK part numbers (this document in all
available language versions):
8022220
1.2 Additional information
www.sick.com
The following information is available on the Internet:
•Data sheets and application examples
•CAD data and dimensional drawings
•Certificates (e.g. EU declaration of conformity)
•Guide for Safe Machinery Six steps to a safe machine
1.3 Symbols and document conventions
The following symbols and conventions are used in this document:
Safety notes and other notes
DANGER
Indicates a situation presenting imminent danger, which will lead to death or serious
injuries if not prevented.
WARNING
Indicates a situation presenting possible danger, which may lead to death or serious
injuries if not prevented.
CAUTION
Indicates a situation presenting possible danger, which may lead to moderate or minor
injuries if not prevented.
NOTICE
Indicates a situation presenting possible danger, which may lead to property damage if
not prevented.
NOTE
Indicates useful tips and recommendations.
Instructions to action
bThe arrow denotes instructions to action.
1. The sequence of instructions for action is numbered.
2. Follow the order in which the numbered instructions are given.
✓The check mark denotes the result of an instruction.
Terminology
Dangerous state
ABOUT THIS DOCUMENT 1
8020548/1FVF/2022-04-27 | SICK O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | i15 Lock 5
Subject to change without notice

A dangerous state is a status of the machine or facility, where people may be injured.
Protective devices prevent this risk if the machine is operated within its intended use.
The figures in this document always show the dangerous state of the machine as
movement of a machine part. In practice, there are different dangerous states, such as:
•Machine movements
•Electrical parts
•Visible and invisible beam
•A combination of multiple hazards
1 ABOUT THIS DOCUMENT
6O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | i15 Lock 8020548/1FVF/2022-04-27 | SICK
Subject to change without notice

2 Safety information
2.1 General safety notes
The safety locking device must be configured and operated correctly by qualified safety
personnel according to the machine requirements.
2.2 Intended use
The safety locking device is a locking unit with a safety locking function and is suitable
for the following applications:
•Temporarily preventing access to a hazardous area
•Monitoring of movable physical guards
In conjunction with a movable physical guard and the machine controller, the safety
locking device prevents the protective device from being opened. The locking device
remains locked for as long as the hazardous machine function is performed or until the
production step has finished.
The product is only suitable for use in industrial environments.
Incorrect use, improper modification of or tampering with the safety locking device will
invalidate any warranty from SICK AG; in addition, any responsibility and liability of SICK
AG for damage and secondary damage caused by this is excluded.
2.3 Requirements for the qualification of personnel
The safety locking device must be planned in, installed, connected, commissioned, and
serviced only by qualified safety personnel.
Project planning
For project planning, a person is considered qualified when he/she has expertise and
experience in the selection and use of protective devices on machines and is familiar
with the relevant technical rules and work safety regulations.
Mechanical mounting, electrical installation, and commissioning
For the task, a person is considered qualified when he/she has the expertise and
experience in the relevant field and is sufficiently familiar with the application of the
protective device on the machine to be able to assess whether it is in an operationally
safe state.
Operation and maintenance
For operation and maintenance, a person is considered competent when he/she has
the expertise and experience in the relevant field and is sufficiently familiar with the
application of the protective device on the machine and has been instructed by the
machine operator in its operation.
SAFETY INFORMATION 2
8020548/1FVF/2022-04-27 | SICK O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | i15 Lock 7
Subject to change without notice

3 Product description
3.1 Setup and function
The safety locking device is an interlocking device consisting of a mechanically-actu‐
ated position switch and a coded actuator. The actuator has a lower coding level.
The position switch contains a rotating switching cylinder which the actuator grips
during closing. The switching cylinder is locked or unlocked electromagnetically (variant-
dependent).
When inserting and removing the actuator, switching contacts for door monitoring are
opened and closed. When locking and unlocking the locking device, switching contacts
for locking device monitoring are opened and closed.
If the locking device is locked, the actuator cannot be removed from the actuating head.
The locking device can only be locked when the protective device is closed.
3.2 Product characteristics
3.2.1 Product variants
The safety locking device is delivered in different variants. You will find an overview of
important distinguishing features of the variants in the following.
•Locking principle: operating or standby current
•Type of contacts for door monitoring
•Maximum locking force
Complete overview of all variants: see "Ordering information", page 23
Standby current locking principle
i15-M
•Locking locking device: close protective device, no voltage on the magnet
•Unlocking locking device: apply voltage to magnet
If voltage is interrupted at the magnet, the locking device remains locked and the
protective device cannot be opened immediately.
WARNING
The locking device locks even when voltage is not present
People could get trapped.
bIf people are in the hazardous area, do not close the protective device even
voltage is not present.
Operating current locking principle
i15-E
•Locking locking device: apply voltage to magnet
•Unlocking locking device: disconnect voltage from magnet
If voltage is disconnected at the magnet, the locking device is unlocked and the protec‐
tive device can be opened immediately.
3 PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
8O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | i15 Lock 8020548/1FVF/2022-04-27 | SICK
Subject to change without notice

DANGER
Hazard due to lack of effectiveness of the protective device
In the event of a voltage drop, the safety locking device unlocks regardless of whether
the dangerous state of the machine has ended.
bAssess the risk of accident. Use for protecting people requires correct project
planning.
3.2.2 Locking device monitoring
All variants feature at least 1 positive opening normally closed contact for locking
device monitoring. The output state changes when locking or unlocking the locking
device.
3.2.3 Door monitoring
All versions feature at least 2 contacts for door monitoring. At least 1 contact is a
positive opening normally closed contact. Depending on the product variant, 1 contact
can be a normally open contact. The output state changes when opening or closing the
protective device.
3.3 Symbols on the product
Table 1: Symbols on the product
Symbol Meaning
Positive opening normally closed contact for locking device moni‐
toring
Positive opening normally closed contact for door monitoring
Mechanical unlocking mechanism actuated, safety locking device
unlocked
Mechanical unlocking mechanism not actuated, safety locking
device functions normally
3.4 Manual unlocking
In some situations, it necessary to unlock the locking device manually (e.g. is faults are
present). After unlocking, a function test must be performed.
Mechanical unlocking mechanism
With the mechanical unlocking mechanism, the safety locking device can be unlocked
regardless of the status.
When actuating the mechanical unlocking mechanism, the contacts for locking device
monitoring open. A stop command must be generated.
Actuating the mechanical unlocking mechanism
bEnsure tensile stress is not applied on the actuator.
bLoosen safety screw with the screwdriver.
bUse the screwdriver to rotate the mechanical unlocking mechanism in the direc‐
tion of the arrow to the following symbol:
✓The locking device is unlocked.
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION 3
8020548/1FVF/2022-04-27 | SICK O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | i15 Lock 9
Subject to change without notice

WARNING
Permanent actuation of the mechanical unlocking mechanism
Hazard due to lack of effectiveness of the protective device
bAfter use, put back the mechanical unlocking mechanism, screw in the safety
screw and seal (e.g. with locking varnish).
3 PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
10 O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | i15 Lock 8020548/1FVF/2022-04-27 | SICK
Subject to change without notice

4 Project planning
4.1 Manufacturer of the machine
DANGER
Failure to comply with manufacturer’s obligations
Hazard due to lack of effectiveness of the protective device
bCarry out a risk assessment before using the safety locking device.
bDo not tamper with or modify the components of the safety locking device.
bMake sure that the safety locking device is only repaired by the manufacturer or by
someone authorized by the manufacturer. Improper repair can lead to a loss of the
protective function.
bMake sure that switch-on commands which bring about a dangerous state of the
machine are not enabled until the protective device is closed and the lock is
activated.
bMake sure that the lock is not deactivated until the dangerous state of the
machine has stopped.
bMake sure that closing a protective device and activating the lock does not cause
a dangerous machine function to start by itself. This must be controlled by a
separate start command.
bThe safety locking device must not be bypassed (contacts jumpered), turned
away, removed, or rendered ineffective in any other way. Take measures to reduce
bypassing options as necessary.
If several devices are switched in succession and the simplified process according to
ISO 13849 is used to determine the performance level (PL), the PL may be reduced.
A logical series connection of safe contacts may be possible up to PL d under certain
circumstances. For more detailed information, see ISO TR 24119.
The safety locking device is designed so that internal errors according to ISO 13849-2,
Table A4, can be ruled out.
Observe EN ISO 14119 for using interlocking devices associated with physical guards.
4.1.1 Application of the safety locking device to protect people
At least one safe contact must be used for locking device monitoring (contact assign‐
ment see table 2).
4.1.2 Application of the safety locking device for process protection
At least one safe contact must be used for door monitoring.
Contacts for locking device monitoring can also be used (pin assignment see table 2).
4.2 Operator of the machine
Changes to the electrical integration of the device in the machine controller and
changes to the mechanical mounting of the device necessitate a new risk assessment.
The results of this risk assessment may require the entity operating the machine to
meet the obligations of a manufacturer.
PROJECT PLANNING 4
8020548/1FVF/2022-04-27 | SICK O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | i15 Lock 11
Subject to change without notice

The device must not be tampered with or changed, except for the procedures described
in this document.
The device must not be repaired. Improper repair can result in the device not providing
correct protection.
Restrict access to replacement actuators, so they cannot be used for bypassing.
4.3 Design
DANGER
Bypassing the protective device
Hazard due to lack of effectiveness of the protective device
bEliminate any temptation to tamper with the safety locking device by implementing
measures such as the following:
°Attach safety switches with a cover or with shielding, or ensure they are out of
reach.
°Cover the safety switch and the actuator with additional equipment or protect
them against access. Cover the sensor and the actuator with additional
equipment or protect them against access.
4.3.1 Selection of the actuator
NOTICE
Selecting unsuitable actuators or improper mounting can damage the device.
bSelect the right actuator (see table 7).
bPay attention to the door radius and mounting options.
4.4 Integrating into the electrical control
Switch-on commands which bring about a dangerous state of the machine must not be
enabled until the protective device is closed and the lock is activated. The lock must not
be deactivated until the dangerous state has ended. Depending on the safety concept,
the signal is analyzed by, e.g., safety relays or a safety controller.
The connected controller and all devices responsible for safety must comply with
the required performance level and the required category (for example according to
ISO 13849-1).
4.5 Testing plan
The safety locking device must be tested by appropriately qualified safety personnel
when commissioning, after modifications, and at regular intervals.
The regular thorough checks serve to investigate the effectiveness of the safety locking
device and discover defects because of modifications or external influences (such as
damage or tampering).
The manufacturer and user must define the type and frequency of the thorough checks
on the machine on the basis of the application conditions and the risk assessment.
Determination of the thorough checks must be documented in a traceable manner.
4 PROJECT PLANNING
12 O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | i15 Lock 8020548/1FVF/2022-04-27 | SICK
Subject to change without notice

5 Mounting
5.1 Safety
DANGER
Hazard due to unexpected starting of the machine
Death or severe injury
bMake sure that the dangerous state of the machine is and remains switched off.
DANGER
Bypassing the protective device
Hazard due to lack of effectiveness of the protective device
bEliminate any temptation to tamper with the safety locking device by taking at least
one of the following measures:
°Attach safety switches with a cover or with shielding, or ensure they are out of
reach.
°If possible, use permanent mounting methods for actuators (e.g., welding,
glue, disposable screws, or rivets).
CAUTION
Hot housing
Risk of burns
bAt ambient temperatures > 40 °C, protect the safety locking device from uninten‐
tional touching by people.
NOTICE
If incorrectly installed or the ambient conditions are not suitable, the safety locking
device can get damaged.
bArrange the safety switch and actuator so that damage due to unintentional out‐
side influences is prevented.
bDo not use safety switch and actuator.
bThe set-up and mounting of the safety switch and actuator must be stable enough
to maintain proper operation.
bUse only reliable mounting elements that can only be removed with tools.
bIf an opening is created in the physical guard due to alignment errors, it must not
impair the protective function.
bAt ambient temperatures > 40 °C, protect the safety switch from contact with
flammable materials.
bThe specified IP enclosure rating only applies if the housing screws, cable entries,
and plug connectors have been fastened correctly. Observe the tightening torque.
5.2 Converting the actuating head
1. Insert the actuator into the actuating head.
2. Loosen the screws on the actuating head.
3. Turn the actuating head in the desired direction.
MOUNTING 5
8020548/1FVF/2022-04-27 | SICK O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | i15 Lock 13
Subject to change without notice

4. Tighten the screws to 0.6 Nm.
5. Seal unused actuation slots with the supplied slot covers.
5.3 Mounting
1. Insert the actuator into the actuating head.
2. Connect the safety switch to the fixed part of the protective device with positive
locking with 2 M5 screws. Tightening torque: 1.4 Nm.
3. In addition, insert 2 M5 coiled spring pins to fasten the safety switch.
4. Connect the actuator permanently to the moving part of the protective device so it
cannot be disengaged.
5. Fit an additional stop for the moving part of the protective device.
5.4 Protection from environmental influences
The prerequisite for a proper and permanent safety function is protection of the actuat‐
ing head from foreign bodies such as chips, sand, beams of light, etc.
When doing painting work, cover the actuation slot, the actuator and the type label.
5 MOUNTING
14 O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | i15 Lock 8020548/1FVF/2022-04-27 | SICK
Subject to change without notice

6 Electrical installation
6.1 Safety
DANGER
Hazard due to electrical voltage
Death or severe injury
bMake sure that the machine and the connecting cables of the safety locking
device are and remain disconnected from the power supply during the electrical
installation.
DANGER
Incorrect safety locking device connection
Loss of safety function
bWith insulation material or connection slots, pay attention to the temperature
resistance and mechanical load capability.
bIf different voltages are used between the contact pairs and the magnet coil (e.g.
230 V and 24 V), when wiring in the terminal compartment, make sure safe
separation is always present.
bFor safety functions, use only safe contacts for locking device monitoring and door
monitoring.
bTo ensure a secure contact, strip the individual wires back about 6 mm (± 1 mm).
6.2 Pin assignment
Table 2: Switching elements and switching functions
Actuator inserted Actuator removed
Locked Unlocked
E2
E1
E2
E1
E2
E1
i15-**0123 Lock
21
11
22
12 11 12
21
11
22
12 11 12
21
11
22
12 11 12
i15-**0133 Lock
23
11
24
12 11 12
23
11
24
12 11 12
23
11
24
12 11 12
All variants E1: +24 V DC magnet coil voltage supply (locking device)
E2: +0 V DC magnet coil voltage supply (locking device)
6.3 System connection (cable entry)
1. Open desired insertion opening with a suitable tool.
2. Mount the cable gland with corresponding enclosure rating.
3. Connect contacts (contact assignment see table 2).
°Operate all contact pairs in the same voltage range.
°Protect the magnet coil separately.
°Tighten terminals to 0.5 Nm.
ELECTRICAL INSTALLATION 6
8020548/1FVF/2022-04-27 | SICK O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | i15 Lock 15
Subject to change without notice

4. Pay attention to tightness of the cable entries.
5. Close switch cover and fasten it (tightening torque 0.8 Nm).
6 ELECTRICAL INSTALLATION
16 O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | i15 Lock 8020548/1FVF/2022-04-27 | SICK
Subject to change without notice

7 Commissioning
7.1 Check during commissioning and modifications
DANGER
Hazard due to unexpected starting of the machine
Death or severe injury
bBefore carrying out the functional test, make sure that there are no people in the
hazardous area.
Approach
Check that the device is functioning properly after installation and after every fault. To
do this, proceed as follows:
Mechanical functional test
bOpen the protective device and close it again. The components of the safety
locking device must not collide with other parts. When the protective device is
closed, the actuator must be in a position which enables the lock to be actuated.
Electrical functional test
1. Switch on the supply voltage.
2. Close all protective devices and activate the locks. The machine must not start up
on its own.
3. Check the lock. It must not be possible to open the protective device.
4. Start the machine function.
5. Stop the machine function and deactivate the lock.
6. Check whether the protective device is kept locked until there is no more risk of
injury (e.g., due to run-on movements).
7. Repeat steps 3 to 9 individually for each protective device.
Complementary information
NOTE
You can simulate an active lock command, by applying the referred voltage to the “Lock
input” contact.
7.2 Recurring technical checks
DANGER
Insufficient checks or incorrect repair
Hazard due to lack of effectiveness of the protective device
bIn the event of wear or damage, replace the entire safety locking device with
actuator. Never replace individual parts or assemblies.
bCheck the safety locking device following the inspection intervals specified in the
national rules and regulations.
The following checks must be done to ensure permanent and proper function:
•Proper switching function
•Safe mounting for all components
•No damage, contamination, deposits or wear
•Tightness of cable entries
COMMISSIONING 7
8020548/1FVF/2022-04-27 | SICK O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | i15 Lock 17
Subject to change without notice

•No loose cable connections or plug connectors
•No manipulation by employees
7 COMMISSIONING
18 O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | i15 Lock 8020548/1FVF/2022-04-27 | SICK
Subject to change without notice

8 Decommissioning
8.1 Disposal
Approach
bAlways dispose of unusable devices in accordance with national waste disposal
regulations.
Complementary information
SICK will be glad to help you dispose of these devices on request.
DECOMMISSIONING 8
8020548/1FVF/2022-04-27 | SICK O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | i15 Lock 19
Subject to change without notice

9 Technical data
9.1 Technical data
Table 3: Features
Features
Housing material Fiberglass-reinforced thermoplastic
Enclosure rating (IEC 60529) IP 67
Mechanical service life 2 × 106 Switching operations
B10d (EN ISO 13849) at DC-13 100 mA / 24 V 2 × 106 Switching operation with small load
Type Type 2 (EN ISO 14119)
Coding level of the actuator Low coding level (EN ISO 14119)
Ambient operating temperature –20 °C … +55 °C
Connection type M 20
Max. actuation speed 20 m × min–1
Max. actuation frequency 1,200 × min–1
Pollution degree
(external, according to EN 60947)
3 × (industry)
Max. actuating force at 20 °C 35 N
Max. force against which unlocking is possible 20 N
Max. retaining force, unlocked 30 N
Locking force Fmax
i15-*M (metal actuating head)
i15-*M (metal actuating head) with angled
actuator
i15-*P (metal actuating head)
2,000 N
1,500 N
1,000 N
Locking force FZh according to (EN ISO 14119)
(FZh = Fmax /1.3)
i15-*M (metal actuating head)
i15-*P (metal actuating head)
1,500 N
700 N
Minimum door radii see table 7
Table 4: Electrical data
Electrical data
Thermal current lth 4 A
Switching principle Slow action switching element
Wire cross-section, (rigid/flexible) 0.34 mm²... 1.5 mm²
Rated insulation voltage Ui250 V
Rated impulse withstand voltage Uimp 2.5 kV
Utilization category (IEC 60947-5-1) AC-15: 230 V, 4 A; DC-13: 24 V, 4 A
Min. switching voltage 1) 12 V
Min. switching current at 24 V DC 1 mA
Conditional rated short-circuit current 100 A
Short-circuit protection (control fuse) (IEC
60269)
4 A gG
Solenoid supply voltage (+10% … –15%) AC/DC 24 V
Max. solenoid power 6 W
9 TECHNICAL DATA
20 O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | i15 Lock 8020548/1FVF/2022-04-27 | SICK
Subject to change without notice
This manual suits for next models
15
Table of contents
Other SICK Lock manuals