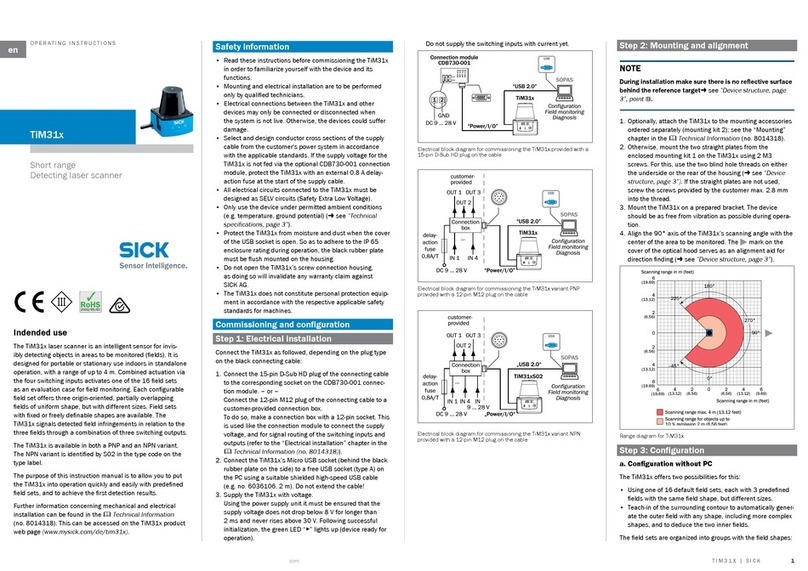
Chapter 2Technical Information
TiM51x ranging laser scanner
5©SICK AG · Germany · All rights reserved · Subject to change without notice 8016425/YZK8/2016-07-07
Operating principle of the TiM51x
2Operating principle of the TiM51x
The TiM51x is an opto-electronic laser scanner that electro-sensitively scans the perimeter
of its surroundings at a single plane with the aid of laser beams. The TiM51x measures its
surroundings using two-dimensional polar coordinates based on its measurement origin.
This is marked on the hood in the centre using a circular indentation. If a laser beam hits
an object, its position in terms of distance and direction is determined.
Scanning is performed across a 270° sector. The maximum range of the TiM51x is 4 m on
light, natural surfaces with an object reflectivity > 50 % (e.g. a white house wall).
2.1 Distance measurement
The TiM51x emits pulsed laser beams using a laser diode. If one of these laser pulses hits
an object or a person, this is reflected at its surface. The reflection is detected in the
TiM51x's receiver by a photodiode. The TiM51x uses HDDM technology (High Definition
Distance Measurement), a SICK own-development. Using this measurement method, a
measured value is formed by the average value for several individual pulses. The TiM51x
calculates the distance to the object from the transit time required by the light from emis-
sion of the beam to receipt of the reflection. This principle of "time-of-flight measurement"
is used by radar systems in a similar manner.
2.2 Direction measurement
The emitted laser beams are deflected by the TiM51x using a rotating mirror and its sur-
roundings scanned in a circular form. The measurements are triggered internally at regular
angle increments using an angular encoder. One complete rotation represents one measur-
ing process (scan).
The TiM51x works at a scanning frequency of 15 Hz, i.e. it performs 15 measuring process-
es per second and makes the measurement results continuously available in real time via
an RS-232 interface.
The measurement method forms an average value from several pulses to determine indi-
vidual measured values. A measuring point is the average value of 84 measurements com-
bined.