sorin Paradym VR 8250 User manual

Implant manual
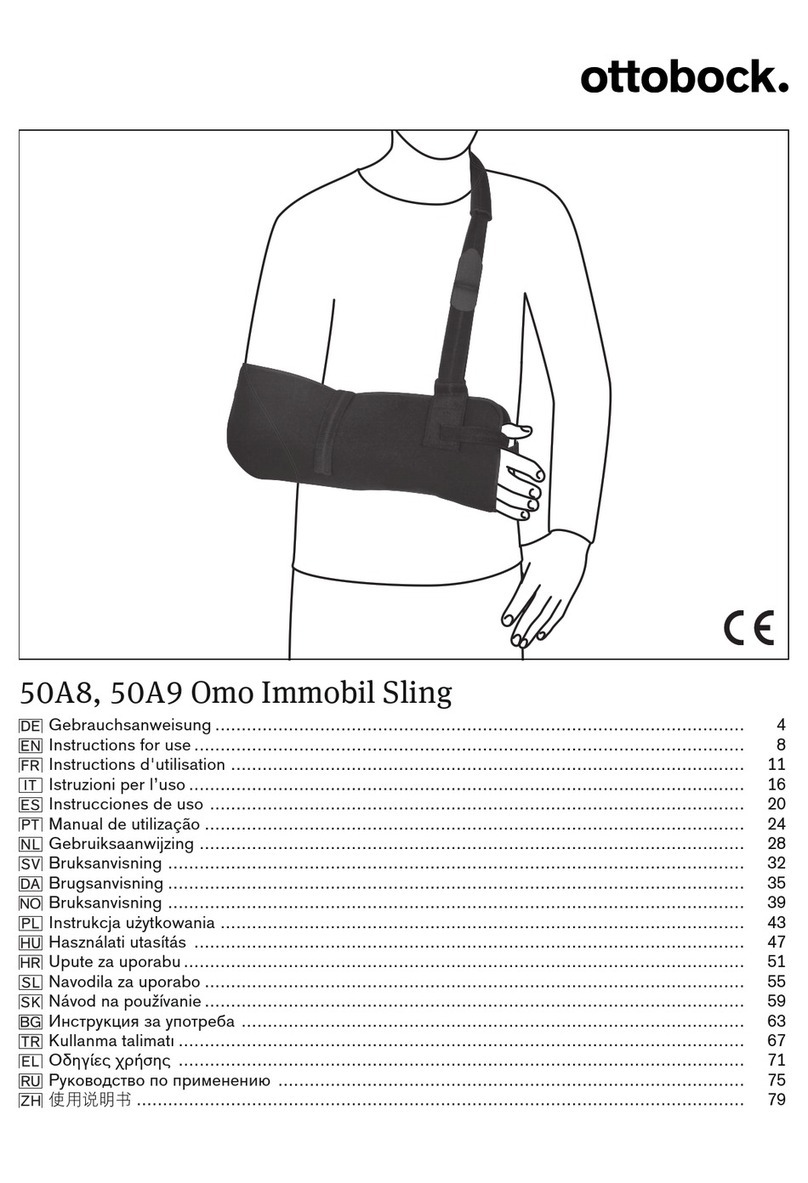
8250 model
Implantable cardioverter defibrillator

TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. General description .....................................................................3
2. Indications ....................................................................................3
3. Contraindications.........................................................................3
3.1. Potential complications ......................................................4
4. Warnings to patient......................................................................5
4.1. Risks related to medical environment...............................6
4.2. Storage .................................................................................7
4.3. Characteristics of the sterile packaging ...........................8
5. Implant procedure........................................................................8
5.1. Necessary equipment .........................................................8
5.2. Optional equipment.............................................................9
5.3. Before opening the package ..............................................9
5.4. Prior to implantation ...........................................................9
5.5. Device placement ..............................................................10
5.6. Choosing the type of lead.................................................10
5.7. Measurement of thresholds at implant ...........................10
5.8. Lead connection ................................................................11
5.9. Device implantation...........................................................11
5.10. Tests and programming....................................................12
5.11. Device registration ............................................................12
6. Special modes ............................................................................12
6.1. Safety mode (nominal values)..........................................12
6.2. Magnet mode .....................................................................13
6.3. Response in the presence of interference......................14
6.4. Detection characteristics in the presence of
electromagnetic fields.......................................................14
6.5. Protection against short-circuits .....................................14
7. Main functions............................................................................15
7.1. Automatic lead measurements ........................................15
7.2. Ventricular tachyarrhythmia management .....................15
7.3. Pacing.................................................................................15
7.4. Sensing...............................................................................16
7.5. Follow-up functions ..........................................................16
8. Patient follow-up ........................................................................17
8.1. Follow-up recommendations ...........................................17
8.2. Elective Replacement Indicator (ERI)..............................17
8.3. Explantation .......................................................................18
8.4. Defibrillator identification.................................................19
9. Physical characteristics ............................................................20
9.1. Materials used....................................................................20
10. Electrical characteristics.........................................................21
10.1. Table of delivered shock energy and voltage ................21
10.2. Battery ................................................................................22
10.3. Longevity............................................................................23
11. Programmable parameters .....................................................24
11.1. Antibradycardia pacing ....................................................24
11.2. Ventricular arrhythmia detection .....................................27
11.3. Ventricular arrhythmia therapies.....................................28
Therapy parameters in slow VT zone..................................29
Therapy parameters in VT zone..........................................30
Therapy parameters in fast VT / VF zone ...........................32
12. Non programmable parameters..............................................33
13. Limited warranty ......................................................................33
13.1. Article 1 : Terms of limited warranty ...............................34
13.2. Article 2 : Terms of replacement......................................35
14. Explanation of symbols...........................................................36
ENGLISH – 3
1. GENERAL DESCRIPTION
PARADYM VR 8250 is an implantable single-chamber cardioverter
defibrillator. It is equipped with an accelerometer to allow adaptation
of pacing to suit the patient’s activity.
PARADYM VR 8250 provides a range of therapeutic and diagnostic
functions:
―high energy shocks
―audible alarms
2. INDICATIONS
Pacing and defibrillation indications are provided by the American
College of Cardiology and the American Heart Association:
"ACC/AHA/ESC 2006 guidelines for management of patients with
ventricular arrhythmias and the prevention of sudden cardiac death”,
European Heart Journal 2006; 27:2099-2140, a report of the
American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task
Force on Practice Guidelines (ACC/AHA/NASPE Committee to
Update the 1998 Pacemaker Guidelines). J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002
Nov 6;40(9):1703-19.
3. CONTRAINDICATIONS
Implantation of PARADYM VR 8250 is contraindicated in patients:
―whose tachyarrhythmias are induced by drug treatment,
electrolyte imbalance, or any other reversible cause,
―whose tachyarrhythmias are due to acute myocardial infarction or
unstable ischemic episodes,
―who present incessant tachyarrhythmia,
―whose tachyarrhythmia was due to electrocution.
4– ENGLISH
The benefits of pacing to pediatric subjects have not been evaluated.
Adverse interactions may occur between the patient's spontaneous
rate and device functions.
3.1. POTENTIAL COMPLICATIONS
Complications may arise with any implanted pacing or defibrillation
system. They may be related to the device itself:
―early battery depletion,
―component failure,
―sensing circuit inhibition, reversion to standby mode, or other
failures due to electromagnetic interference,
―pectoral stimulation,
―any complication related to failure to detect arrhythmias and
terminate detected arrhythmias, to inappropriate delivery of therapy
in the absence of arrhythmia, to acceleration of an arrhythmia by
therapy, and to pain experienced during or after delivery of therapy.
These complications may be life-threatening for the patient.
Complications may be related to the pacing and defibrillation leads:
―improper lead connection,
―lead displacement, cardiac wall perforation, or tissue reaction at
the myocardium-electrode interface,
―insulation fracture,
―conductor fracture,
―lead fracture.
Medical complications may also arise:
―infection,
―fluid accumulation at the implant site,
―casing migration,
―skin erosion by the defibrillator with possible protrusion of the
casing,
―haematoma.

ENGLISH – 5
4. WARNINGS TO PATIENT
The patient should be warned of the potential risks of defibrillator
malfunction if he is exposed to external magnetic, electrical, or
electromagnetic signals.
These potential interference sources may cause conversion to
inhibited mode (because of noise detection), erratic delivery of VT or
VF therapies, nominal programming, or much more rarely,
irreversible damage to the device’s circuits.
The main sources of high magnitude electromagnetic interference
are: powerful radiofrequency equipment (radar), industrial motors
and transformers, arc-welding equipment, high power loudspeakers.
Electrical equipment: Household electrical appliances do not affect
the functioning of the defibrillator, providing they are insulated to
current standards. However, patients should avoid using induction
ovens and cookers.
Antitheft gates: Since antitheft devices at the entrance to stores are
not subject to any safety standards, it is advisable to spend as little
time as possible in their vicinity.
Airport detection systems: Since airport detection systems are not
subject to any safety standards, it is advisable to spend as little time
as possible in their vicinity.
Work environment: The patient's work environment may be an
important source of interference. In that case, specific
recommendations may be required.
Cellular phones: Radiofrequency signals can interfere with the
functioning of PARADYM VR 8250 if the handset is placed too close
to the defibrillator. It is advisable to maintain a minimum distance of
15 cm (6 inches) between the cellular telephone and the implanted
device, when the telephone is turned on.
Sun exposure: Avoid prolonged sun exposure, since it may
overheat the defibrillator casing and its electronic components.
6– ENGLISH
Audible alarms: The patient should be warned about possible
audible alarms emitted by the device.
CAUTION: Do not tap sharply on the ICD can after implant, because
the ICD's sensing circuits can detect this as R-waves, and such
oversensing could result in inappropriate pacing, inhibition, or
therapy. Normal activities after implant do not result in such
oversensing.
4.1. RISKS RELATED TO MEDICAL ENVIRONMENT
It is advisable to carefully monitor defibrillator operation prior to and
after any medical treatment during which an electrical current from an
external source passes through the patient's body.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging: MRI is strictly contraindicated in
cardiac defibrillator patients.
Electrocautery or diathermy device: Diathermy and electrocautery
equipment should not be used. If such devices must be used:
1. Before procedure, deactivate ATP and shock therapies. 2. During
the procedure, keep the electrocautery device as far as possible from
the cardiac defibrillator. Set it at minimum intensity. Use it briefly.
3. After the procedure, check for proper implant function. The device
should never be exposed directly to the diathermy source.
External defibrillation: PARADYM VR 8250 is protected from
external defibrillation shocks. Before external defibrillation, deactivate
ATP and shock therapies. During external defibrillation, it is advisable
to avoid placing the defibrillating paddles directly over the casing or
over the lead. The defibrillating paddles should preferably be placed
in an anteroposterior position. Avoid any direct contact between the
defibrillation paddles and the conductive parts of the implanted leads
or casing of the implanted device. After external defibrillation, check
for proper device function.
Internal pacemaker: Use of the defibrillator is contraindicated in
implantable pacemaker patients.
ENGLISH – 7
Radiation therapy: Avoid exposure to ionizing radiation. Betatrons
are contraindicated. If high doses of radiation therapy cannot be
avoided, the defibrillator should be protected from direct exposure
with a screen. ATP and shock therapies should be disabled during
exposure and proper device function should be checked regularly
afterwards. Resulting damage may not be immediately detectable. If
irradiation of tissues close to the implantation site is necessary, it is
recommended that the cardiac defibrillator be moved. As a safety
measure, an external defibrillator should be immediately available.
Ultrasound therapy (lithotripsy): It is advisable not to administer
ultrasound therapy (or lithotripsy) to a patient with a defibrillator
implanted in the abdominal position. Concentrating the ultrasonic
field over the device could harm the patient and cause damage to the
defibrillator.
Diagnostic ultrasound (echography): The defibrillator is not
affected by ultrasound imaging devices.
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS): TENS may
interfere with defibrillator function. If necessary, the following
measures may reduce interference: 1. Place the TENS electrodes as
close together as possible and as far as possible from the pulse
generator and leads. 2. Monitor cardiac activity during TENS use.
Scales with body fat monitors and electronic muscle
stimulators: A patient with an implanted PARADYM VR 8250 should
not use these devices.
Surgical procedure: For safety reasons, it is preferable to not
program the Rate Response function before any surgical procedure
on the defibrillator patient.
4.2. STORAGE
The defibrillator is packaged in sterile packaging inside a cardboard
storage box. It is recommended that the device be stored at a
temperature ranging from 0 °C to 50 °C.
8– ENGLISH
Devices subjected to excessive impact, such as those that have
been dropped on a hard floor, should not be implanted. Any device
subjected to such an impact should be returned to your Sorin Group
representative for examination.
Devices MUST NOT be interrogated and programmed within the
vicinity of other devices.
4.3. CHARACTERISTICS OF THE STERILE PACKAGING
The sterile packaging contains:
―the defibrillator
―a ratcheting screwdriver
―a DF-1 defibrillating connector insulating plug
All of this equipment is ethylene oxide sterilized and hermetically
sealed in two-ply clear packaging compliant international standards.
5. IMPLANT PROCEDURE
5.1. NECESSARY EQUIPMENT
Implantation of PARADYM VR 8250 requires the following
equipment:
―Sorin Group dedicated programmer, equipped with the smartView
software interfaced with the programming head,
―pacing system analyser, as well as its sterile connecting cables,
to evaluate the pacing and sensing thresholds,
―a complete set of leads with corresponding introducers,
―physiological signal monitor capable of displaying simultaneously
the surface ECG and arterial pressure,
―an external defibrillator with sterile external paddles,
―sterile cover for the telemetry head.

ENGLISH – 9
5.2. OPTIONAL EQUIPMENT
The following equipment may be required during implantation
of PARADYM VR 8250:
―sterile water to clean and lubricate the lead terminal pins
―a lead cap to isolate a lead which is not used
5.3. BEFORE OPENING THE PACKAGE
Before opening the package, check the "Use Before" date printed on
the labels on the box and on the sterile package. Defibrillators that
have not been implanted before that date should be returned to your
Sorin Group representative.
Devices MUST NOT be interrogated and programmed within the
vicinity of other devices.
Also check the integrity of the sterile package. The sterility of the
contents is no longer guaranteed if the package has been pierced or
altered. If the defibrillator is no longer sterile, it should be returned in
its packaging to your Sorin Group representative. Any re-sterilization
of the unit is at the discretion of Sorin Group.
5.4. PRIOR TO IMPLANTATION
The minimum acceptable magnet rate and battery voltage of the
device before implantation are:
―magnet rate greater than or equal to 94 min-1 and
―battery voltage greater than or equal to 3.0 V.
Use the programmer to verify the defibrillator can be interrogated
before implantation.
Verify all shock therapies are disabled in order to avoid accidental
discharge during implantation.
10 – ENGLISH
It is not advisable to program the Smoothing function before
implantation, since the defibrillator may detect noise and pace at a
rate higher than the programmed basic rate.
CAUTION: Do not shake or tap sharply on the ICD package with the
ICD inside, because the ICD's sensing circuits can interpret this as
R-waves and record these as an arrhythmia episode. If unusual
shaking or tapping of the package results in a stored arrhythmia
episode, erase the recording before using the ICD.
5.5. DEVICE PLACEMENT
The pocket should be prepared in the left pectoral position, either
subcutaneously or submuscularly.
Implantation in an abdominal position is not advisable.
In its final position, the defibrillator should be no more than 3.5 cm
below the skin surface.
5.6. CHOOSING THE TYPE OF LEAD
The defibrillator should be connected to:
―one ventricular defibrillation lead with sensing/pacing bipolar
electrodes, and one or two defibrillation electrodes.
The choice of leads and their configuration is left to the implanting
physician’s judgment.
Connectors: The bipolar pacing/sensing connector is compliant with
the IS-1 standard and the defibrillation connectors are compliant with
the DF-1 standard.
5.7. MEASUREMENT OF THRESHOLDS AT IMPLANT
Pacing and sensing thresholds should be measured at implant.
ENGLISH – 11
Pacing thresholds: Acute thresholds should be lower than 1 V (or
2 mA) for a 0.35 ms pulse width.
Sensing thresholds: For proper ventricular sensing, the amplitude
of the R-wave should be greater than 5 mV.
Impedance measurements: Ventricular pacing impedance should
range from 200 to 3000 ohms (refer to the lead characteristics,
especially if high impedance lead is used).
5.8. LEAD CONNECTION
Each lead must be connected to the corresponding connector port.
The position of each connector is indicated on the casing.
Caution: Tighten only the distal inserts.
To connect each lead, proceed as follows:
1. Insert the screwdriver into the pre-inserted screw socket of the
appropriate port (in order to allow excess air to bleed out and to
make the insertion of the lead pin easier).
2. Insert the lead pin all the way into the port (check that the pin
protrudes beyond the distal insert).
3. Tighten and check the tightness.
Caution: 1. Do not tighten the pre-inserted screws when there is no
lead (this could damage the connector). 2. Do not loosen the screws
before inserting the connector (subsequent risk of being unable to
reinsert the screw). 3. Removing the screwdriver: to avoid all risk of
loosening screws during removal, hold the screwdriver by its metal
part and not by the handle.
5.9. DEVICE IMPLANTATION
Place the device in the pocket.
Carefully wind excess lead and place in a separate pocket to the side
of the defibrillator.
12 – ENGLISH
Suture the casing connector to the muscle using the hole provided
for this purpose, in order to avoid potential migration of the device
into the pectoral muscle.
5.10. TESTS AND PROGRAMMING
During the implant testing procedure, it is recommended that a
security margin of at least 10 J be demonstrated between the
effective shock energy and maximum programmable energy.
Enable shock therapies, then program the defibrillator.
Verify that the defibrillation lead impedance for each shock delivered
ranges from 30 to 150 ohms. Check the lead connection if the values
are outside these bounderies.
Save the programming data on the programmer’s hard disk and on a
floppy disk (if desired).
5.11. DEVICE REGISTRATION
Complete the registration form (EURID/IAPM for Europe). One of the
sheets should be given to the patient on discharge from the hospital,
to use as an identification and follow-up card. One copy should be
returned to Sorin Group within 30 days after implantation to activate
the warranty. The two other copies are for the hospital and for the
national registration centre (for Europe).
6. SPECIAL MODES
6.1. SAFETY MODE (NOMINAL VALUES)
Nominal values may be rapidly restored by pressing the following
button on the programming head or programmer keyboard:

ENGLISH – 13
In safety mode, the defibrillator operates with the parameters
underlined in the table of programmable parameters.
6.2. MAGNET MODE
When the magnet is applied:
―antiarrhythmia functions are inhibited (detection of rhythm
disturbances, charging, and therapy),
―pacing amplitude is set to 6 V,
―pulse width is set to maximum,
―pacing rate is set to the magnet rate,
―the following functions are disabled: Smoothing, Rate Response.
When the magnet is removed:
―the sensor rate is forced to the basic rate,
―arrhythmia detection algorithms and sequential therapies are
reinitialized,
―therapies start with the least aggressive program for each area.
The other parameters remain at their programmed value.
NOTE: The magnet is inactive during telemetry.
The magnet rate values are as follow:
Magnet rate (min-1) 96 94 91 89 87 85
Magnet period (ms) 625 641 656 672 688 703
Magnet rate (min-1) 83 82 80 78 77
Magnet period (ms) 719 734 750 766 781
14 – ENGLISH
6.3. RESPONSE IN THE PRESENCE OF
INTERFERENCE
If the defibrillator senses electrical noise at a frequency above 16 Hz,
it switches to an asynchronous mode at the basic rate. The
programmed mode is restored as soon as the noise is no longer
detected.
Ventricular pacing is also inhibited by ventricular noise. It can be
restored by setting the parameter V pacing on noise to Yes.
6.4. DETECTION CHARACTERISTICS IN THE
PRESENCE OF ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS
Per Clause 27.4 of Standard EN 45502-2-2, detection in the
presence of electromagnetic fields is characterized as follows:
―In differential mode: measurements in progress
―In common mode: measurements in progress
6.5. PROTECTION AGAINST SHORT-CIRCUITS
The defibrillator can undergo a short-circuit if the anode and cathode
are not adequately separated. In this case, the shock is aborted to
prevent damaging the defibrillator.
ENGLISH – 15
7. MAIN FUNCTIONS
7.1. AUTOMATIC LEAD MEASUREMENTS
Automatic lead impedance measurement: A lead impedance
measurement is automatically performed on atrial and ventricular
leads every 6 hours. The daily mean impedance is stored for each
chamber.
Shock circuit continuity test: A shock circuit continuity test is
automatically performed once a week on RV and SVC coils. The
result is stored in the device memory.
7.2. VENTRICULAR TACHYARRHYTHMIA
MANAGEMENT
Fast VT treatment: Applies detection criteria on fast ventricular
tachycardia, that are different from those of the VT zone, as well as
different therapies. The fast VT zone is included in the VF zone: its
lower limit is determined by the programmed value for the VF zone
and its upper limit by the programmed value for the fast VT zone.
Polarity alternation on shock Max: Reverses the programmed
polarity of every second shock set at maximum energy. The number,
type, and energy of shocks is independently programmable by
detection zone.
7.3. PACING
BTO (Brady Tachy Overlap): Allows pacing in the slow VT zone,
without affecting detection specificity.
Post-shock mode: After any shock therapy (other than T-wave
shock), the post-shock mode make it possible to apply different
pacing parameters.
16 – ENGLISH
7.4. SENSING
Automatic Refractory Periods: Optimize sensing and make the
implant progamming easier. These periods are composed of a
minimal Refractory Period and a triggerable Refractory Period. The
duration of the refractory periods lengthens automatically as needed.
Protection against noise: Allows the distinction between ventricular
noise and ventricular fibrillation. If the device senses ventricular
noise, the ventricular sensitivity is decreased until noise is no longer
detected. Ventricular pacing can be inhibited to avoid a potential
paced T-wave.
Automatic sensitivity control: Optimizes arrhythmia detection and
avoids late detection of T-waves and over-detection of wide QRS
waves. The device automatically adjusts the sensitivities based on
the ventricular sensing amplitude. The minimum ventricular
sensitivity threshold is 0.4 mV. In case of arrhythmia suspicion or
after a paced event, the programmed ventricular sensitivity will be
applied.
7.5. FOLLOW-UP FUNCTIONS
Storage of memory data: AIDA+ (Automatic Interpretation for
Diagnosis Assistance) software provides access up to 6 months of
patient follow-up with day by day data collection, or up to 24 hours
with hourly data collection. Episodes of ventricular tachyarrhythmia
are recorded with the programmable EGM channels.
Follow-up assistant: The series of tests recommended during the
patient follow-up can be performed in an automated sequence to
minimize navigation within screens and facilitate device testing
procedure.

ENGLISH – 17
8. PATIENT FOLLOW-UP
8.1. FOLLOW-UP RECOMMENDATIONS
Before the patient is discharged and at each subsequent follow-up
visit, it is advisable to:
―check the occurence of system warnings
―check the battery status,
―check the integrity of the pacing and defibrillation leads,
―check for proper sensing (sensitivity) and pacing ; set the pacing
amplitude to twice the pacing threshold,
―interrogate the implant memories (AIDA+),
―check the efficacy of the therapies delivered,
―keep a printout of programmed parameters, test results, and
memory data,
―reset the memory data and statistics.
These operations should be performed by medical personnel in an
appropriate care unit, with resuscitation equipment present.
It is recommended that a routine follow-up examination be done one
month after discharge, and then every three months until the device
nears the replacement date.
Contact your Sorin Group representative should any "charging
aborted", "reset" or “overload” be identified in the specific warning
window.
8.2. ELECTIVE REPLACEMENT INDICATOR (ERI)
Elective Replacement Indicators (ERI) are:
―magnet rate equal to 80 ± 1 min-1 or
―battery voltage equal to 2.66 V ± 0.01 V
Caution: The defibrillator should be replaced as soon as the battery
voltage reaches the ERI voltage.
18 – ENGLISH
Between the ERI voltage and the EOL voltage, PARADYM VR 8250
can still function for:
―6 months (100% atrial and pacing in DDD mode, 500 ohms, with
as-shipped settings), and deliver 7 shocks at 34 J or
―6.8 months (0% pacing, sensor OFF, one 42 J shock every
2 weeks).
Once the Elective Replacement Indicator (ERI) point has been
reached, the device operates normally, except that the charge time
increases. Under normal conditions (and without programmer use)
the charge times are as follows:
Shock energy Charge time (sec)
BOL 42 J 10 (± 2)
ERI 42 J 13 (± 3)
8.3. EXPLANTATION
The defibrillator should be explanted in the following cases:
―The Elective Replacement Indicator (ERI) point is reached
―Confirmed malfunction
―Burial of the patient (for environmental reasons, the local
regulation may require the explantation of the devices containing
a battery supply)
―Cremation of the patient (the defibrillator may explode if placed in
an incinerator)
The explanted defibrillator should not be reused in another patient.
All explanted defibrillators should be returned to Sorin Group,
carefully cleaned of all traces of contamination, with the card
explantation form (EURID/IAPM for Europe). This may be done by
immersing them in an aqueous sodium hypochlorite containing at
least 1% chlorine, followed by rinsing copiously with water.
ENGLISH – 19
The defibrillator should be protected against mechanical impact and
the temperature variations that may occur during shipping.
Before explantation, it is advisable to:
―Print out all programmed parameters, statistics and AIDA+
function report,
―disable shock therapies (VT and VF) to avoid any risk of untimely
shock.
8.4. DEFIBRILLATOR IDENTIFICATION
The defibrillator can be interrogated and programmed via telemetry,
using the programming head interfaced with the Sorin Group
dedicated programmer.
Position the programming head over the telemetry antenna located in
the upper part of the device, in order to communicate effectively via
telemetry (see diagram below).
The device can be non-invasively identified as follows:
1. Take an x-ray to identify the name of the manufacturer printed on
the device (S = Sorin ; D = Defibrillator ; A = PARADYM).
20 – ENGLISH
2. Interrogate the device using the Sorin Group dedicated
programmer. The model and serial number of the device are
automatically displayed. The first figure in the serial number
corresponds to the last figure in the year of manufacture.
9. PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Dimensions 58.7 x ?? x 11 mm
Weight ??
Active surface area of casing 69 cm2
Connector IS-1, DF-1
9.1. MATERIALS USED
Active surface area of casing 99% pure titanium
Connectors polyurethane*
Distal terminal pin of DF-1 insulating plug 99% pure titanium
*Medical-grade materials that have undergone "in vitro" and "in vivo"
qualifications.

ENGLISH – 21
10. ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Ventricular input impedance 80 kilohms ± 30 %
D.C. capacitance 180 µF ± 8 %
Reformation No reformation required
Rate limit 192 min-1 ± 10 min-1
Pacing waveform
Defibrillation waveform
10.1. TABLE OF DELIVERED SHOCK ENERGY AND
VOLTAGE
The relationship between stored energies, maximum voltages for
each phase (V1 and V2) and delivered energy during each phase (at
37 °C, 50 ohm load) for the minimum, low, mean and maximum
programmed energy values:
22 – ENGLISH
Stored energy (J) 0.5 10 20 34 42
V1 (Volt) 67 311 441 575 640
V2 (Volt) 34 156 222 287 321
Delivered E: Phase 1 (J) 0.29 6.9 13.9 23.8 29.3
Delivered E: Phase 2 (J) 0.09 1.8 3.5 5.9 7.4
Tolerances are 12% for voltage (25% at 0.5 J) and 30% for energy.
10.2. BATTERY
Manufacturer Greatbatch
Type Quasar High Rate (QHR)
Model GB 2593
Number of batteries 1
Total capacity 1964 mAh
Usable capacity Between BOL and ERI: 1278 mAh.
Between BOL and EOL: 1675 mAh.
Voltage BOL: 3.25 V. ERI: 2.66 V. EOL: 2.5 V.
ENGLISH – 23
10.3. LONGEVITY
The longevities mentioned below are calculated by taking into
account 6 months storage.
7.8 years Pacing in VVI mode, 100%, 500 ohm, 3.5 V, 0.35 ms,
60 min-1, one 42 J shock per quarter, sensor OFF
7.5 years Pacing in VVI mode, 100%, 500 ohm, 3.5 V, 0.35 ms,
60 min-1, one 42 J shock per quarter, G sensor ON
10.1 years Pacing in VVI mode, 1%, 500 ohm, 3.5 V, 0.35 ms,
60 min-1, one 42 J shock per quarter, sensor OFF
8.9 years Pacing in VVI mode, 15%, 500 ohm, 4.5 V, 0.50 ms,
60 min-1, one 42 J shock per quarter, sensor OFF
10.1 years 0% pacing, one 42 J shock per quarter, sensor OFF
The mean longevity as a function of shocks delivered at maximum
energy, with and without pacing, is as follows:
24 – ENGLISH
11. PROGRAMMABLE PARAMETERS
measured at 37 °C under a 500 ohm load
Legend:
Value in bold: "as shipped" value
Underlined value: nominal value
11.1. ANTIBRADYCARDIA PACING
Basic parameters Values
Mode VVI-VVIR
Basic rate (min-1) (1) From 30 to 90 by steps of 5 ; 60
(± 4 %)
Maximum rate (min-1) From 100 to 145 by steps of 5 ; 120
(± 6 %)
Hysteresis (%) 0-5-10-20-35 (± 18 ms)
Special features Values
Smoothing OFF-Very slow-Slow-Medium-Fast
Physical activity Very low-Low-Medium-High-Very
high
(1) The corresponding periods are (in ms): 2000-1714-1500-1333-1200-
1091-1000-923-857-800-750-706-667 ms.

ENGLISH – 25
Pacing/Sensing Values
Ventricular sensitivity (mV) (1) From 0.4 to 4 by steps of 0.2 ; 0.4
(± 50 %)
Ventricular amplitude (V) (2) 1-1.5-2-2.5-3-3.5-4-4.5-5-6
(± 20 %)
Ventricular pulse width (ms) 0.12-0.25-0.35-0.5-0.6-0.75-0.85-1
(± 10 %)
(1) Values are measured using a positive and negative triangular signal of
2/13 ms.
(2) The correlation between the programmed amplitudes, the stored
amplitudes and the mid-pulse delivered amplitudes under a 500 ohm
load are given in the following table:
Programmed ampl. (V) 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5
Mid-pulse delivered ampl. (V) 0.97 1.39 1.79 2.35 2.84 3.25
Stored amplitude (V) 1.14 1.63 2.1 2.76 3.33 3.82
Programmed ampl. (V) 4 4.5 5 6
Mid-pulse delivered ampl. (V) 3.58 4.23 4.47 5.37
Stored amplitude (V) 4.2 4.96 5.25 6.3
26 – ENGLISH
Audible alarms Values
Battery depletion ON-OFF
High battery drain ON-OFF
Abnormal lead impedance ON-OFF
Abnormal RV/SVC continuity ON-OFF
Abnormal shock delivery ON-OFF
Excessive charge time ON-OFF
Inefficient shock max ON-OFF
Duration (min) 1-2-3-4-5-10-15
Time of day 01:00 am-02:00 am-03:00 am-
04:00 am-05:00 am-06:00 am-
07:00 am-08:00 am-09:00 am-
10:00 am-11:00 am-12:00 am-
01:00 pm-02:00 pm-03:00 pm-
04:00 pm-05:00 pm-06:00 pm-
07:00 pm-08:00 pm-09:00 pm-
10:00 pm-11:00 pm-12:00 pm
Repetition (Days) 1-2-3-4-5-6-7
Post-shock mode Values
Mode OFF-VVI
Duration 10s-20s-30s-1min-2min-3min-
4min-5min
Basic rate (min-1) From 50 to 90 by steps of 5 ; 60
(± 4 %)
V amplitude (V) 1-1.5-2-2.5-3-3.5-4-4.5-5-6
(± 20 %)
V pulse width (ms) 0.12-0.25-0.35-0.5-0.6-0.75-0.85-1
(± 10 %)
ENGLISH – 27
Sensitivity margins Values
Ventricular post pacing margin (mV) From 0 to 2 by steps of 0.2 ; 0.8
Response to noise Values
Automatic sensitivity on noise Yes-No
V pacing on noise Yes-No
11.2. VENTRICULAR ARRHYTHMIA DETECTION
Therapy zones Values
Slow VT detection zone Slow VT ON-Slow VT OFF
VT detection zone VT ON-VT OFF
Fast VT / VF detection zone Fast VT+VF ON-VF ON
Slow VT rate (lower limit) (min-1) From 100 to 200 by steps of 5 ; 190
VT rate (lower limit) (min-1) 130-135-140-145-150-155-160-
165-170-175-180-185-190-195-
200-210-220-230-240
VF rate (lower limit) (min-1) 150-155-160-165-170-175-180-
185-190-195-200-210-220-230-240
Fast VT rate (upper limit) (min-1) 150-155-160-165-170-175-180-185-
190-195-200-210-220-230-240-255
Slow VT persistence (cycles) 4-6-8-12-16-20-30-50-100-200
VT persistence (cycles) 4-6-8-12-16-20-30-50-100-200
VF persistence (cycles) From 4 to 20 by steps of 1 ; 6
Slow VT and VT sorting criteria Rate Only-Stability-Stability+-
Stability/Acc-Stability+/Acc
Fast VT sorting criteria Rate+Stability-Rate Only
28 – ENGLISH
Sorting criteria Values
Majority: (X/Y), Y (cycles) 8-12-16
Majority: (X/Y), X (%) 65-70-75-80-90-95-100
Window of RR stability for Slow VT
and VT (ms)
30-45-65-80-95-110-125
Window of RR stability for fast VT
(ms)
30-45-65
Prematurity acceleration (%) 6-13-19-25-31-38-44-50
Long cycle persistence extension
(cycles)
From 0 to 16 by steps of 1 ; 10
Long cycle gap (ms) 15-30-45-65-80-95-110-125-140-
155-170-190-205
11.3. VENTRICULAR ARRHYTHMIA THERAPIES
Common parameters Values
Enable ATP therapy Yes-No
Enable shock therapy Yes-No
Polarity alternation (42 J) Yes-No
Atrial coil (SVC) present Yes-No
Active case Yes-No
Shock configuration Case to RV-SVC to RV-Case +
SVC to RV-RV to Case-RV to
SVC-RV to Case + SVC
SVC exclusion (shock < 15J) Yes-No

ENGLISH – 29
♦11.3.1. Therapy parameters in slow VT zone
ATP 1 program Values
ATP program OFF-Burst-Burst+Scan-Ramp-
Ramp+Scan
Number of sequences 1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15
Cycles in first sequence 1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15
Cycles added per sequence 0-1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15
Coupling interval (%) 50-55-60-65-70-75-80-85-90-95
Ramp decrement (per cycle) (ms) 0-4-8-12-16-20-30-40-50-60
Scan decrement (per sequence)
(ms)
0-4-8-12-16-20-30-40-50-60
Time limit (min) 0.5-1-1.5-2-2.5-3-3.5-4
Minimum cycle length (ms) 95-110-125-140-155-170-190-205-
220-235-250-265-280-295-310
ATP 2 program Values
ATP program OFF-Burst-Burst+Scan-Ramp-
Ramp+Scan
Number of sequences 1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15
Cycles in first sequence 1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15
Cycles added per sequence 0-1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15
Coupling interval (%) 50-55-60-65-70-75-80-85-90-95
Ramp decrement (per cycle) (ms) 0-4-8-12-16-20-30-40-50-60
Scan decrement (per sequence) (ms) 0-4-8-12-16-20-30-40-50-60
Time limit (min) 0.5-1-1.5-2-2.5-3-3.5-4
Minimum cycle length (ms) 95-110-125-140-155-170-190-205-
220-235-250-265-280-295-310
30 – ENGLISH
Shock program Values
Shock 1 (J) OFF-0.5-0.8-1-1.3-1.5-2-2.5-3-3.5-
4-5-6-7-8-9-10-12-14-16-18-20-22-
24-26-28-30-32-34-42 (± 30 %)
Shock 2 (J) OFF-0.5-0.8-1-1.3-1.5-2-2.5-3-3.5-
4-5-6-7-8-9-10-12-14-16-18-20-22-
24-26-28-30-32-34-42 (± 30 %)
Number of Shock Max (42 J) OFF-1-2-3-4
♦11.3.2. Therapy parameters in VT zone
ATP 1 program Values
ATP program OFF-Burst-Burst+Scan-Ramp-
Ramp+Scan
Number of sequences 1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15
Cycles in first sequence 1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15
Cycles added per sequence 0-1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15
Coupling interval (%) 50-55-60-65-70-75-80-85-90-95
Ramp decrement (per cycle) (ms) 0-4-8-12-16-20-30-40-50-60
Scan decrement (per sequence)
(ms)
0-4-8-12-16-20-30-40-50-60
Time limit (min) 0.5-1-1.5-2-2.5-3-3.5-4
Minimum cycle length (ms) 95-110-125-140-155-170-190-205-
220-235-250-265-280-295-310
ENGLISH – 31
ATP 2 program Values
ATP program OFF-Burst-Burst+Scan-Ramp-
Ramp+Scan
Number of sequences 1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15
Cycles in first sequence 1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15
Cycles added per sequence 0-1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15
Coupling interval (%) 50-55-60-65-70-75-80-85-90-95
Ramp decrement (per cycle) (ms) 0-4-8-12-16-20-30-40-50-60
Scan decrement (per sequence)
(ms)
0-4-8-12-16-20-30-40-50-60
Time limit (min) 0.5-1-1.5-2-2.5-3-3.5-4
Minimum cycle length (ms) 95-110-125-140-155-170-190-205-
220-235-250-265-280-295-310
Shock program Values
Shock 1 (J) OFF-0.5-0.8-1-1.3-1.5-2-2.5-3-3.5-
4-5-6-7-8-9-10-12-14-16-18-20-22-
24-26-28-30-32-34-42 (± 30 %)
Shock 2 (J) OFF-0.5-0.8-1-1.3-1.5-2-2.5-3-3.5-
4-5-6-7-8-9-10-12-14-16-18-20-22-
24-26-28-30-32-34-42 (± 30 %)
Number of Shock Max (42 J) OFF-1-2-3-4
32 – ENGLISH
♦11.3.3. Therapy parameters in fast VT / VF zone
ATP 1 program Values
ATP program OFF-Burst-Burst+Scan-Ramp-
Ramp+Scan
Number of sequences 1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15
Cycles in first sequence 1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15
Cycles added per sequence 0-1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15
Coupling interval (%) 50-55-60-65-70-75-80-85-90-95
Ramp decrement (per cycle) (ms) 0-4-8-12-16-20-30-40-50-60
Scan decrement (per sequence)
(ms)
0-4-8-12-16-20-30-40-50-60
Time limit 10s-20s-30s-1min-1.5min-2min
Minimum cycle length (ms) 95-110-125-140-155-170-190-205-
220-235-250-265-280-295-310
Shock program Values
Shock 1 (J) OFF-0.5-0.8-1-1.3-1.5-2-2.5-3-3.5-
4-5-6-7-8-9-10-12-14-16-18-20-22-
24-26-28-30-32-34-42 (± 30 %)
Shock 2 (J) OFF-0.5-0.8-1-1.3-1.5-2-2.5-3-3.5-
4-5-6-7-8-9-10-12-14-16-18-20-22-
24-26-28-30-32-34-42 (± 30 %)
Number of Shock Max (42 J) 1-2-3-4

ENGLISH – 33
12. NON PROGRAMMABLE PARAMETERS
Ventricular refractory periods Values
Post ventricular sensing 95 ms (± 16 ms)
Post ventricular pacing 220 ms (± 4 ms)
Therapies Values
Waveform Constant tilt (50% - 50%)
Stored energy for the shock MAX 42 J (± 16 %)
Pacing amplitude during ATP
therapies
7 V (Actual value at 300 ms: 5.3 V )
13. LIMITED WARRANTY
The PARADYM implantable cardioverter defibrillator is the result of
highly advanced research and all components have been selected
after exhaustive testing.
Sorin Biomedica S.r.l. (identified as “SORIN” hereafter) guarantees
the product PARADYM against any damage caused by component
failure or production defects during a period of four years after the
implantation date, and SORIN commits itself to replace all
PARADYM devices according to the terms described in article 1 and
described in article 2 of this section.
SORIN makes no claim that the human body will not react unsuitably
to the implantation of the PARADYM device, or that failure will never
occur.
SORIN does not guarantee the suitability of PARADYM in defined
types of patients; selection of the device is a medical decision.
34 – ENGLISH
SORIN shall not be held liable for any damage indirectly associated
with the PARADYM, whether as part of normal or abnormal
operation, nor damage from its explantation or replacement.
SORIN does not authorise anyone to modify these limited warranty
conditions.
13.1. ARTICLE 1 : TERMS OF LIMITED WARRANTY
1. The PARADYM implantable cardioverter defibrillator is only
guaranteed for one implantation.
2. The EURID/IAPM implant form must be sent to SORIN within 30
days after implantation.
3. The PARADYM cardioverter defibrillator must be implanted prior
to the use-before date indicated on the packaging.
4. The limited guarantee only applies to suspect devices returned
to the manufacturer, carefully packed and accompanied by an
explantation report duly completed by the hospital or the doctor
and considered defective after analysis by SORIN.
The device must be returned within the 30 days following
explantation to SORIN.
Any device returned and replaced under the terms of this limited
warranty will become the exclusive property of SORIN.
Any rights under the terms of this limited warranty will be
forfeited if the PARADYM device has been opened by anyone
other than SORIN.
These rights will also be forfeited if the device has been
damaged by carelessness or accident.
This is the case especially if the device has been exposed to
temperatures above 50°C, to electrical abuse or to mechanical
shock, particularly as a result of being dropped. Consequently,
any expert opinion offered by a third party after the device has
been removed also nullifies the guarantee.
ENGLISH – 35
5. The limited warranty will be forfeited if it is proven that the device
has been misused or inadequately implanted, against the
physicians’manual recommendations of PARADYM.
6. The limited warranty does not include leads and other
accessories used for the implantation.
7. The replacement terms or conditions described in article 2
include all devices that shall be replaced within the limited
warranty period because of battery depletion, without any link to
a component failure or a production hazard. The device battery
longevity varies with the type and number of delivered therapies.
8. Legal requirements of jurisdictions where the PARADYM device
is distributed will supersede any warranty conditions indicated in
this manual that conflict with such laws.
13.2. ARTICLE 2 : TERMS OF REPLACEMENT
1. In case of PARADYM failure because of a component failure, a
production defect, or a conception error, occurring within two-
year period starting from the implantation date, SORIN is
committed to:
―replacing free of charge the explanted device by a SORIN
device with equivalent features,
―or issuing a replacement credit equal to the purchase price for
the purchase of any other SORIN replacement device.
2. After a two-year period and up to 4 years after the implantation,
SORIN, because of limited warranty terms, will issue a
replacement credit to the buyer of an amount equivalent to half
of the initial purchase price minus prorata temporis during this
two-year period.
3. In any case the credit issued by the limited warranty terms
cannot exceed the purchase price of a SORIN replacement
device.
36 – ENGLISH
14. EXPLANATION OF SYMBOLS
The symbols on product labeling have the following meaning:
Use before
Date of manufacture
Serial number
Batch number
For single use only.
Sterilised with ethylene oxide
High voltage
Attention: Consult accompanying documentation.

???A - October 2007
0459 – 2007
Via Crescentino s.n. – 13040 Saluggia (VC) – Italy
Tel. : +39 161 487323 – 487095 / Fax +39 161 487524
www.sorin-crm.com

Table of contents
Other sorin Medical Equipment manuals

sorin
sorin PARADYM RF SonR CRT-D 9770 User manual

sorin
sorin ORCHESTRA PLUS LINK KA 351 User manual
sorin
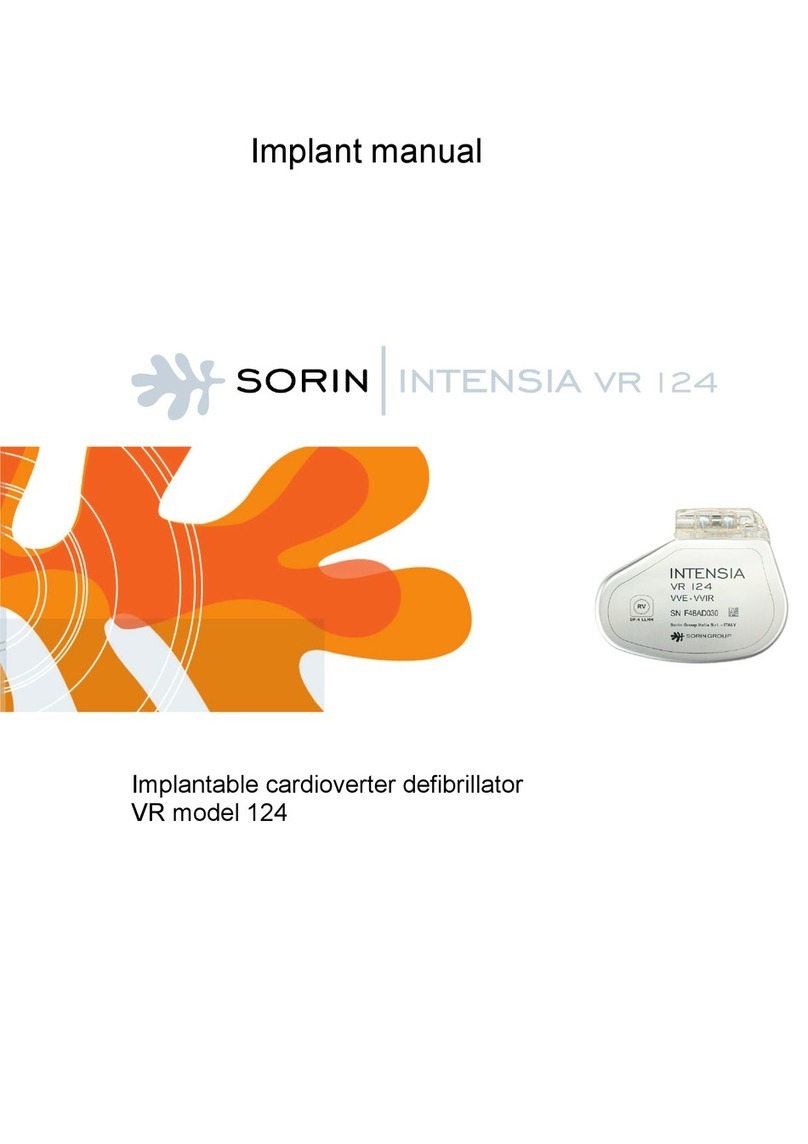
sorin Intensia VR 124 User manual

sorin
sorin TILDA T 53 User manual

sorin
sorin SMARTVIEW KA960 User manual

sorin
sorin Platinum VR 1210 User manual

sorin
sorin SMARTVIEW KA961 User manual
sorin
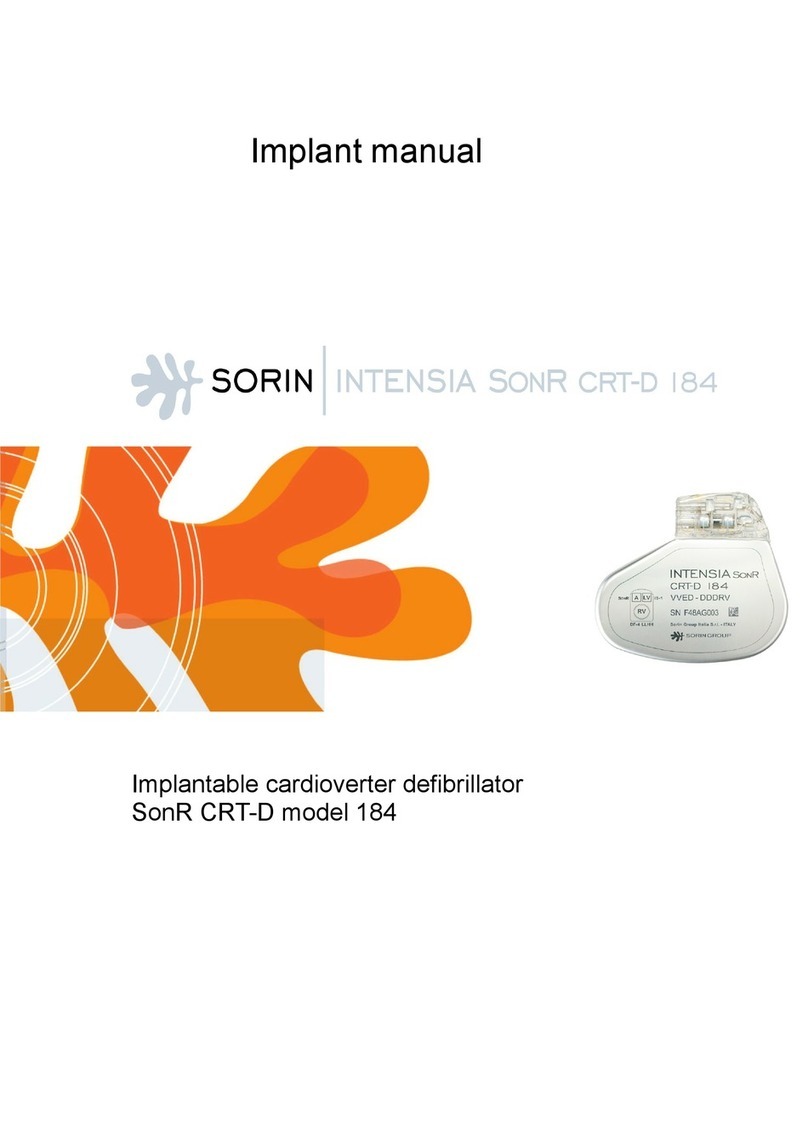
sorin Intensia SonR CRT-D 184 User manual
sorin
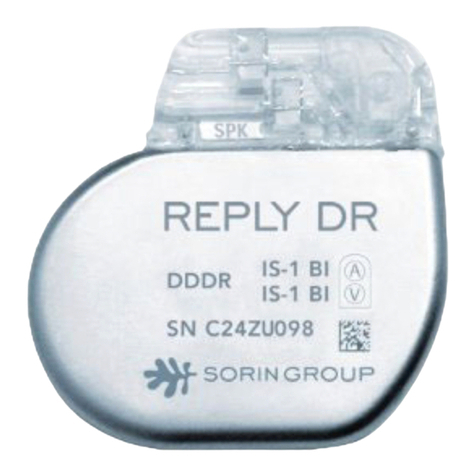
sorin REPLY DR User manual

sorin
sorin PARADYM RF DR 9550 User manual