sorin Intensia SonR CRT-D 184 User manual

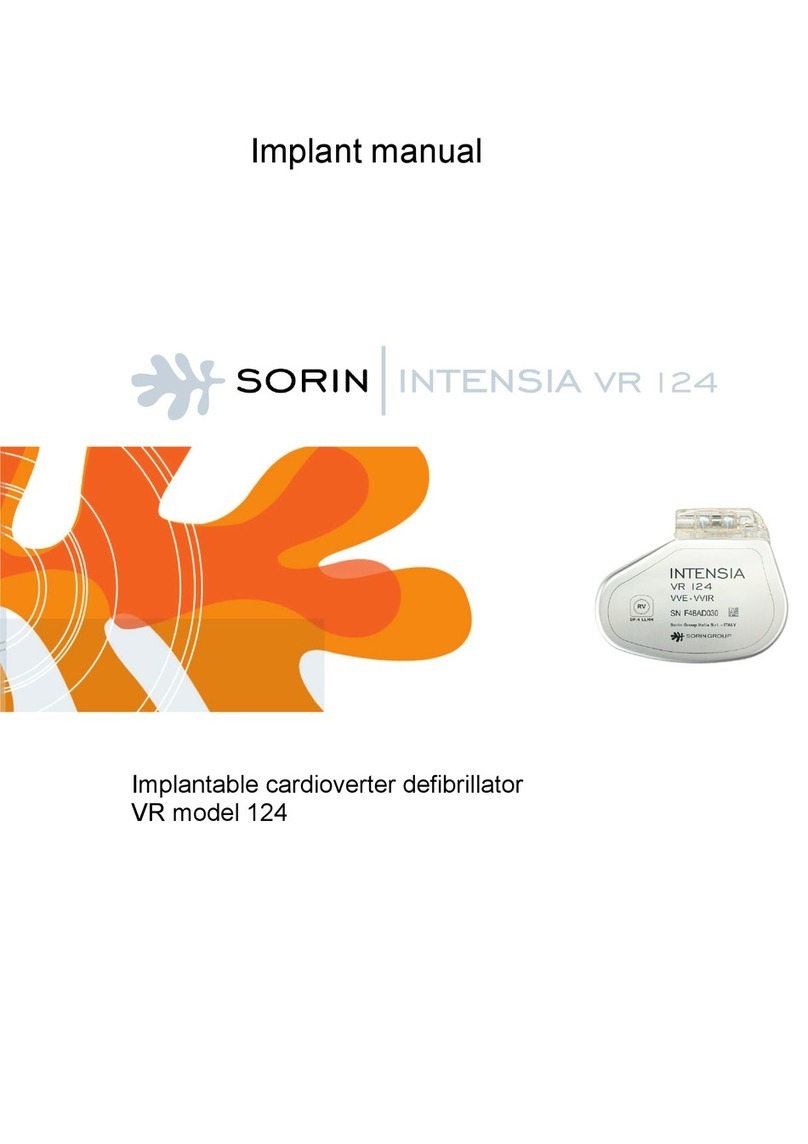
Implant manual
Implantable cardioverter defibrillator
SonR CRT-D model 184

blank


blank

TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. General description................................................................................................................ 5
2. Indications............................................................................................................................... 6
3. Contraindications....................................................................................................................
4. Warnings and precautions.....................................................................................................8
4.1. Risks related to medical environment.......................................................................................9
4. . Sterilization, storage and handling..........................................................................................10
4.3. Implantation and device programming....................................................................................10
4.4. Lead evaluation and lead connection......................................................................................11
4.5. Generator explant and disposal..............................................................................................1
5. Adverse events...................................................................................................................... 13
5.1. MSP study............................................................................................................................... 13
5. . Potential adverse events.........................................................................................................14
6. Clinical studies...................................................................................................................... 16
6.1. MSP clinical study................................................................................................................... 16
. Patient selection and treatment...........................................................................................20
7.1. Individualization of treatment.................................................................................................. 0
7. . Specific patient populations.................................................................................................... 1
8. Patient counselling information..........................................................................................22
9. Conformance to standards..................................................................................................23
10. Physician guidelines.............................................................................................................26
10.1. Physician training.................................................................................................................... 6
10. . Directions for use.................................................................................................................... 6
10.3. Maintaining device quality....................................................................................................... 6
10.4. V-V Programming Recommendation....................................................................................... 7
11. Patient information............................................................................................................... 28
12. How supplied......................................................................................................................... 29
1 .1. Sterility.................................................................................................................................... 9
1 . . Warranty and replacement policy............................................................................................ 9
13. Device description................................................................................................................ 30
14. Implant procedure................................................................................................................. 32
14.1. Necessary equipment............................................................................................................. 3
14. . Packaging............................................................................................................................... 3
14.3. Optional equipment.................................................................................................................3
14.4. Before opening the package...................................................................................................33
14.5. Prior to implantation................................................................................................................33
14.6. Device placement....................................................................................................................33
14.7. Choosing the type of lead....................................................................................................... 33
14.8. Shock configuration (+ -> -).....................................................................................................34
14.9. Measurement of thresholds at implant....................................................................................34
14.10.Leads connection.................................................................................................................... 35
14.11. Device implantation................................................................................................................. 36
14.1 .Tests and programming........................................................................................................... 36
15. Special modes....................................................................................................................... 3
15.1. Safety mode (nominal values).................................................................................................37
SORIN – INTENSIA SonR CRT-D 184 – U150A 3

15. . Magnet mode..........................................................................................................................37
15.3. Response in the presence of interference..............................................................................37
15.4. Detection characteristics in the presence of electromagnetic fields........................................38
15.5. Protection against short-circuits..............................................................................................38
16. Main functions....................................................................................................................... 39
16.1. Automatic lead measurements................................................................................................39
16. . Atrial tachyarrhythmia management.......................................................................................39
16.3. Ventricular tachyarrhythmia management...............................................................................39
16.4. Pacing.....................................................................................................................................39
16.5. Sensing...................................................................................................................................40
16.6. SonR CRT optimization...........................................................................................................40
16.7. Follow-up function...................................................................................................................41
16.8. Remote Monitoring function....................................................................................................41
1 . Patient follow-up................................................................................................................... 43
17.1. Follow-up recommendations...................................................................................................43
17. . Holter Function........................................................................................................................43
17.3. Recommended Replacement Time (RRT)..............................................................................44
17.4. Explantation............................................................................................................................ 44
17.5. Defibrillator identification.........................................................................................................45
18. Supplemental Information....................................................................................................46
18.1. Adverse events in the SafeR (AAI <> DDD) study..................................................................46
18. . SafeR (AAI <> DDD) clinical study..........................................................................................47
19. Physical characteristics.......................................................................................................49
19.1. Materials used.........................................................................................................................49
20. Electrical characteristics......................................................................................................50
0.1. Table of delivered shock energy and voltage..........................................................................50
0. . Battery..................................................................................................................................... 50
0.3. Longevity.................................................................................................................................51
21. Programmable parameters...................................................................................................52
1.1. Antibradycardia pacing............................................................................................................5
1. . Ventricular tachyarrhythmia detection.....................................................................................55
1.3. Ventricular tachyarrhythmia therapies.....................................................................................56
1.4. Remote alerts and warnings................................................................................................... 59
22. Non programmable parameters...........................................................................................61
23. Limited warranty................................................................................................................... 62
3.1. Article 1 : Terms of limited warranty........................................................................................6
3. . Article : Terms of replacement..............................................................................................63
24. Patents................................................................................................................................... 64
25. Explanation of symbols........................................................................................................65
4SORIN – INTENSIA SonR CRT-D 184 – U150A

1. GENERAL DESCRIPTION
1. GENERAL DESCRIPTION
INTENSIA SonR CRT-D 184 is an implantable cardioverter defibrillator for the recognition
and treatment of ventricular tachycardia and fibrillation, with ventricular resynchronization, in
patients with spontaneous or inducible tachyarrhythmias.
INTENSIA SonR CRT-D 184 is equipped with an accelerometer to allow adaptation of
pacing to suit the patient’s activity.
INTENSIA SonR CRT-D 184 is also equipped with the RF wireless technology which
enables to remotely monitor the patients who have the Sorin SMARTVIEW Monitor installed
at home.
INTENSIA SonR CRT-D 184 provides high energy shocks (4 J) for enhanced safety, as
well as automatic lead measurements to monitor system integrity.
INTENSIA SonR CRT-D 184 is protected against high-frequency signals emitted by cellular
telephones.
SORIN – INTENSIA SonR CRT-D 184 – U150A 5

. INDICATIONS
2. INDICATIONS
INTENSIA SonR CRT-D 184 is indicated for ventricular antitachycardia pacing and
ventricular defibrillation for automated treatment of life threatening arrhythmias.
The device is also indicated for the reduction of heart failure symptoms in medically
optimized NYHA Functional Class III and IV patients with left ventricular ejection fraction of
35% or less, and a QRS duration of 150 ms or longer.
6SORIN – INTENSIA SonR CRT-D 184 – U150A

3. CONTRAINDICATIONS
3. CONTRAINDICATIONS
Implantation of INTENSIA SonR CRT-D 184 is contraindicated in patients:
─whose ventricular tachyarrhythmias may have transient or reversible causes such as:
acute myocardial infarction, digitalis intoxication, drowning, electrocution, electrolyte
imbalance, hypoxia, sepsis, or unstable ischemic episodes,
─who present incessant tachyarrhythmia,
─who have an internal pacemaker,
─whose primary disorder is bradyarrhythmias, or atrial tachyarrhythmias.
Dual-chamber and single chamber atrial pacing is contraindicated in patients with chronic
refractory atrial tachyarrhythmias.
SORIN – INTENSIA SonR CRT-D 184 – U150A 7

4. WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
4. WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
The patient should be warned of the potential risks of defibrillator malfunction if he is
exposed to external magnetic, electrical, or electromagnetic signals.
These potential interference sources may cause conversion to inhibited mode (because of
noise detection), erratic delivery of VT or VF therapies, nominal programming, or much more
rarely, irreversible damage to the device’s circuits.
The main sources of high magnitude electromagnetic interference (EMI) are: powerful
radiofrequency equipment (radar), industrial motors and transformers, induction furnaces,
resistance, arc-welding equipment and high power loudspeakers.
Be aware that the changes in the patient’s condition, drug regimen, and other factors may
change the defibrillation threshold (DFT) which may result in non-conversion of the
arrhythmia post-operatively. Successful conversion of ventricular fibrillation or ventricular
tachycardia during arrhythmia conversion testing is no assurance that conversion will occur
post-operatively.
Resuscitation Availability:
Do not perform device testing unless an external defibrillator and medical personnel skilled
in cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) are readily available.
Electrical Isolation:
Do not permit the patient to contact grounded equipment that could produce hazardous
leakage current. Ensuing arrhythmia induction could result in the patient’s death.
Disable the ICD During Handling:
Program Shock Therapy to OFF during surgical implant and explant or post mortem
procedures. The device can deliver a serious high energy shock should accidental contact
be made with the defibrillation electrodes.
Antitheft gates:
Since antitheft devices at the entrance to stores are not subject to any safety standards, it is
advisable to spend as little time as possible in their vicinity.
Airport detection systems:
Since airport detection systems are not subject to any safety standards, it is advisable to
spend as little time as possible in their vicinity.
High voltage power transmission lines:
High voltage power transmission lines may generate enough EMI to interfere with
defibrillator operation if approached too closely.
Communication equipment:
Communication equipment such as microwave transmitters, linear power amplifiers, or high-
power amateur transmitters may generate enough EMI to interfere with defibrillator
operation if approached too closely.
Home appliances:
Home appliances that are in good working order and properly grounded do not usually
produce enough EMI to interfere with defibrillator operation. There are reports of device
8SORIN – INTENSIA SonR CRT-D 184 – U150A

4. WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
disturbances caused by electric hand tools or electric razors used directly over the device
implant site.
4.1. RISKS RELATED TO MEDICAL ENVIRONMENT
It is advisable to carefully monitor defibrillator operation prior to and after any medical
treatment during which an electrical current from an external source passes through the
patient's body.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging:
MRI is strictly contraindicated in cardiac defibrillator patients.
Radiofrequency ablation:
A radiofrequency ablation procedure in a patient with a generator may cause device
malfunction or damage. RF ablation risks may be minimized by:
1. Programming Shock Therapy and ATP to OFF.
. Avoiding direct contact between the ablation catheter and the implanted lead or generator.
3. Positioning the ground, placing it so that the current pathway does not pass through or
near the device, i.e. place the ground plate under the patient’s buttocks or legs.
4. Having external defibrillation equipment available.
Electrocautery or diathermy device:
Diathermy and electrocautery equipment should not be used. If such devices must be used:
1. Keep the current path and ground plate as far away from the device and the leads as
possible (a minimum of 15 cm [six inches]).
. Before procedure, disable ATP and shock therapies.
3. During the procedure, keep the electrocautery device as far as possible from the cardiac
defibrillator. Set it at minimum intensity. Use it briefly.
4. After the procedure, check for proper implant function. The device should never be
exposed directly to the diathermy source.
External defibrillation:
INTENSIA SonR CRT-D 184 is protected from external defibrillation shocks.
1. Before external defibrillation, disable ATP and shock therapies.
. During external defibrillation, it is advisable to avoid placing the defibrillating paddles
directly over the casing or over the leads. The defibrillating paddles should preferably be
placed in an anteroposterior position.
3. Avoid any direct contact between the defibrillation paddles and the conductive parts of the
implanted leads or casing of the implanted device.
4. After external defibrillation, check for proper device function.
Radiation therapy:
Avoid exposure to ionizing radiation. Betatrons are contraindicated. If high doses of radiation
therapy cannot be avoided, the defibrillator should be protected from direct exposure with a
SORIN – INTENSIA SonR CRT-D 184 – U150A 9
CAUTION: Do not tap sharply on the ICD can after implant, because the ICD's sensing
circuits can detect this as P-waves or R-waves, and such oversensing could result in
inappropriate pacing, inhibition, or therapy. Normal activities after implant do not result in
such oversensing.

4. WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
protection shield. ATP and shock therapies should be disabled during exposure and proper
device function should be checked regularly afterwards. Resulting damage may not be
immediately detectable. If irradiation of tissues close to the implantation site is necessary, it
is recommended that the cardiac defibrillator be moved. As a safety measure, an external
defibrillator should be immediately available.
Lithotripsy:
Lithotripsy may permanently damage the device if it is at the focal point of the lithotripsy
beam. If lithotripsy must be used, keep the defibrillator at least .5 to 5 cm (1- inches) away
from the focal point of the lithotripsy beam.
Diagnostic ultrasound (echography):
The defibrillator is not affected by ultrasound imaging devices.
Scales with body fat monitors and electronic muscle stimulators:
A patient with an implanted INTENSIA SonR CRT-D 184 should not use these devices.
4.2. STERILIZATION, STORAGE AND HANDLING
Resterilization:
Do not resterilize and re-implant explanted ICDs.
"Use Before" Date:
A "Use Before" date is printed on the outer storage package and on the sterile package. Do
not implant the device after this date because the battery may have reduced longevity and
sterility may be affected. It should be returned to Sorin.
If Package is damaged:
Do not use the device or accessories if the packaging is wet, punctured, opened or
damaged because the integrity of the sterile packaging may be compromised. Return the
device to the manufacturer.
Device Storage:
Store the device in a clean area, away from magnets, kits containing magnets, and sources
of electromagnetic interference to avoid device damage. Store the device between 0 - 50 °C
(3 - 1 °F). Temperatures outside the specified range may damage the device.
Equilibration:
Allow the device to reach room temperature before programming or implanting the device
because rapid temperature changes may affect initial device function.
4.3. IMPLANTATION AND DEVICE PROGRAMMING
Use only a Sorin programmer to communicate with the device.
Do not inadvertently position any magnet over the ICD; this suspends tachyarrhythmia
detection and treatment.
Replace the device when the RRT (Recommended Replacement Time*) point (defined by a
battery voltage of .66 ± 0.01 V or a magnet rate lower than or equal to 80 bpm) is reached.
Program device parameters such as sensitivity threshold and VT and VF detection intervals
as specified in the device manuals.
10 SORIN – INTENSIA SonR CRT-D 184 – U150A

4. WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Lead System:
Do not use a lead system other than those with demonstrated compatibility because
undersensing cardiac activity and failure to deliver necessary therapy may result.
In situations where an ICD and a pacemaker are implanted in the same patient, interaction
testing should be completed. If the interaction between the ICD and the pacemaker cannot
be resolved through repositioning of the leads or reprogramming of either the pacemaker or
the ICD, the pacemaker should not be implanted (or should be explanted if previously
implanted).
Failure to properly insert the torque screwdriver into the perforation at an angle
perpendicular to the connector receptacle may result in damage to the sealing system and
its self-sealing properties.
It is recommended that a security margin of at least 10 J be demonstrated between the
effective shock energy and maximum programmable energy. Carefully confirm that true
ventricular fibrillation has been induced because the DFT for ventricular tachycardia or flutter
may be lower.
The defibrillator should be implanted with the engraved side facing outwards in order to
facilitate telemetric communication with the programming head and to display the
radiographic identification correctly.
*: corresponds to ERI (Elective Replacement Indicator) previously used.
4.4. LEAD EVALUATION AND LEAD CONNECTION
INTENSIA SonR CRT-D 184 has one DF-4, one IS-1, and one SonR connector ports. The
SonR connector port has been specifically designed by Sorin to accept three connections
(tripolar).
The SonR port accepts either a conventional atrial lead (without SonR capability) or a SonR
atrial lead (bipolar pacing/sensing and SonR capability).
IS-1 refers to the international standard whereby leads and generators from different
manufacturers are assured a basic fit (ISO 5841-3: 013).
DF-4 refers to the international standard for defibrillation lead connectors (ISO 7186: 010).
Do not use the device with leads which have not been positively tested.
Do not tie a ligature directly to the lead body, tie it too tightly, or otherwise create excessive
strain at the insertion site as this may damage the lead. Use the lead stabilizer to secure the
lead lateral to the venous entry site.
Do not grip the lead with surgical instruments.
Do not use excessive force or surgical instruments to insert a stylet into a lead.
Use ventricular transvenous leads with caution in patients with either a mechanical or
bioprosthetic tricuspid valvular prosthesis.
Use the correct suture sleeve (when needed) for each lead, to immobilize the lead and
protect it against damage from ligatures.
Never implant the system with a lead system that has a measured shock impedance of less
than 30 ohms. A protection circuit in the defibrillator prevents shock delivery when
impedance is too low. If the shock impedance is less than 30 ohms, reposition the lead
system to allow a greater distance between the electrodes.
Do not kink leads. Kinking leads may cause additional stress on the leads, possibly resulting
in lead fracture.
Do not insert a lead connector pin into the connector block without first visually verifying that
the setscrews are sufficiently retracted. Do not tighten the setscrews unless a lead
connector pin is inserted because it could damage the connector block.
SORIN – INTENSIA SonR CRT-D 184 – U150A 11

4. WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Lead electrodes in contact during a cardioversion or defibrillation therapy will cause current
to bypass the heart, possibly damaging the ICD and the leads. While the ICD is connected
to the leads, make sure that the metal portions of any electrodes do not touch each other.
If a pacing lead is abandoned rather than removed, it must be capped to ensure that it is not
a pathway for currents to or from the heart.
If a thoracotomy is required to place epicardial patches, it should be done during a separate
procedure to reduce the risk of morbidity and mortality.
Do not place the patch lead over nerve tissue as this may cause nerve damage.
Place the patch lead with the conducting coil side facing the heart to ensure delivery of
energy to the heart.
Place the sutures well outside the coil of the patch lead or in the area between the coils to
avoid possible coil fracture.
If countershock is unsuccessful using external paddles, adjust the external paddle position
(e.g., anterior-lateral to anterior-posterior) and be sure that the external paddle is not
positioned over the patch.
Do not fold, alter, or remove any portion of the patch as it may compromise electrode
function or longevity.
If a header port is unused on the generator, the port must be plugged to protect the
generator.
4.5. GENERATOR EXPLANT AND DISPOSAL
Interrogate the device, and program shock therapy off prior to explanting, cleaning or
shipping the device to prevent unwanted shocks.
Return all explanted generators and leads to the manufacturer.
Never incinerate the device due to the potential for explosion. The device must be explanted
before cremation.
1 SORIN – INTENSIA SonR CRT-D 184 – U150A

5. ADVERSE EVENTS
5. ADVERSE EVENTS
Clinical data presented in this section are from the MSP clinical study.
INTENSIA SonR CRT-D 184 is similar in design and function to the ALTO MSP and
OVATIO CRT-D devices. The data provided are applicable to INTENSIA SonR CRT-D 184.
5.1. MSP STUDY
Sorin conducted an international, multi-center, randomized clinical trial of its cardiac
resynchronization therapy system. Investigators attempted to implant study devices in 190
patients. A total of 18 patients received study devices and had an exposure of over 165
device years. Of those patients, 19 received OVATIO CRT-D, 160 received ALTO MSP,
and 3 received ALTO MSP. The clinical data collected on ALTO MSP, ALTO MSP and
OVATIO CRT-D are applicable to INTENSIA SonR CRT-D 184. The table below summarizes
the adverse events observed for the CRT-D system. No deaths were related to the system.
Event # of Patients % of Patients # of Events Events/100
Device-Years
Deaths not related to the
system
16 8.4 16 0.8
Cardiac arrest 5 .6 5 0.3
Worsening CHF / CHF
decompensation
3 1.6 3 0.
Multi-organ dysfunction 1.1 0.1
Complications related to the
system
28 14. 35 2.1
Dislodgment or migration 9 4.7 11 0.6
Extracardiac stimulation (e.g.,
phrenic stim)
9 4.7 9 0.5
Complications related to the
implant procedure
18 9.5 21 1.3
Dislodgment or migration 4 .1 4 0.
Observations related to the
system
23 12.1 2 1.
Extracardiac stimulation (e.g.,
phrenic stim)
1 7.9 15 0.8
Observations related to the
implant procedure
24 12.6 28 1.
Heart block 6 3. 6 0.3
Extracardiac stimulation (e.g.,
phrenic stim)
3 1.5 5 0.3
SORIN – INTENSIA SonR CRT-D 184 – U150A 13

5. ADVERSE EVENTS
Serious adverse events not
related to the system
85 44. 1 6 10.8
Worsening CHF/CHF
decompensation
4 1 .6 4 .1
Atrial fibrillation/flutter 14 7.4 14 0.7
Not Serious events not
related to the system
58 30.5 121 .4
Pain (in back, arms, chest,
shoulder, groin, head, other)
10 5.3 13 0.7
Worsening CHF/CHF
decompensation
13 6.8 16 0.8
Atrial fibrillation/flutter 7 3.7 8 0.4
Ventricular tachycardia 7 3.7 7 0.4
5.2. POTENTIAL ADVERSE EVENTS
Adverse events (in alphabetical order), including those reported in the previous tables,
associated with ICD systems include:
─Acceleration of arrhythmias (caused by device),
─Air embolism,
─Bleeding,
─Chronic nerve damage,
─Erosion,
─Excessive fibrotic tissue growth,
─Extrusion,
─Fluid accumulation,
─Formation of hematomas or cysts,
─Inappropriate shocks,
─Infection,
─Keloid formation,
─Lead abrasion and fracture,
─Lead migration/dislodgment,
─Myocardial damage,
─Pneumothorax,
─Shunting current or insulating myocardium during defibrillation with internal or external
paddles,
─Potential mortality due to inability to defibrillate or pace,
─Thromboemboli,
─Venous occlusion,
─Venous or cardiac perforation.
Patients susceptible to frequent shocks despite antiarrhythmic medical management may
develop psychological intolerance to an ICD system that may include the following:
─Dependency,
─Depression,
14 SORIN – INTENSIA SonR CRT-D 184 – U150A

5. ADVERSE EVENTS
─Fear of premature battery depletion,
─Fear of shocking while conscious,
─Fear that shocking capability may be lost,
─Imagined shocking (phantom shock).
SORIN – INTENSIA SonR CRT-D 184 – U150A 15

6. CLINICAL STUDIES
6. CLINICAL STUDIES
Clinical data presented in this section are from the MSP clinical study. INTENSIA SonR
CRT-D 184 is similar in design and function to the ALTO MSP and OVATIO CRT-D
devices. The data provided are applicable to INTENSIA SonR CRT-D 184.
6.1. MSP CLINICAL STUDY
OVATIO CRT-D and earlier models were evaluated clinically in an international, multi-center,
randomized clinical trial of Sorin’s cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT-D) system.
Investigators attempted to implant study devices in 190 patients. A total of 18 patients
received study devices and had an exposure of over 165 device years. Of those patients, 19
received OVATIO CRT-D, 160 received ALTO MSP, and 3 received ALTO MSP.
6.1.1 . Objectives
The primary objectives of the study were to demonstrate:
─Greater improvement in a composite endpoint (percent improvement in peak VO
percent improvement in quality of life) for CRT-D patients than for control patients.
─System complication-free rate ≥ 67 % at six months.
6.1. . Methods
Patients were New York Heart Association class III or IV and had one or more indications for
an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD). Patients performed cardiopulmonary exercise
testing at baseline and six-months after randomization. Patients were implanted with a Sorin
ICD with CRT-D, a Situs UW 8D left ventricular lead, and commercially available right atrial
and ventricular leads. Routine follow-ups were at pre-discharge, randomization (3-14 days
post-implant), one month, three months, and six months post randomization.
6.1.3 . Results
Improvement in composite endpoint
Patients were included in the analysis if complete (peak VO and quality of life) baseline and
six-month data were available.
Number of
patients
contributing to
analysis
Mean percent
improvement in
composite
endpoint for
control group
Mean percent
improvement in
composite
endpoint for
CRT-D group
Percent greater
improvement for
CRT-D group
p-value
13 15.5 % 4.9 % 9.4 % 0.046
16 SORIN – INTENSIA SonR CRT-D 184 – U150A

6. CLINICAL STUDIES
Six-month system complication-free rate
Number of patients
contributing to analysis
Kaplan-Meier six-month
complication-free estimate
One-sided lower 95%
confidence bound for six-
month complication-free
estimate
190 89.5 % 84.1 %
6.1.4 . Absolute Differences in Peak VO and QOL
The tables below show the absolute differences between the control and test groups’ peak
VO and QOL over the 6 month follow-up period in the clinical trial.
Absolute difference between test and control groups’ change in peak V0 over 6 months
Baseline
Mean ± SD
(range)
6-month
Mean ± SD
(range)
Difference
within group
Difference
between
groups
Change in
Peak VO
(mL/min/Kg)
Control group
(n=41)
13.39 ± 4.58
(5.0 , 4.10)
13.1 ± 3.99
(3.30, 0.70)
- 0. 8 1.85
Test group
(n=91)
11.84 ± 3.90
(3.50, 6.3)
13.41 ± 4. 8
(6.18, 7.67)
1.57
Absolute difference between test and control groups’ change in QOL score over 6 months
Baseline
Mean ± SD
(range)
6-month
Mean ± SD
(range)
Difference
within group
Difference
between
groups
Change in QOL Control group
(n=41)
47.5 ± 19. 9
(9, 90.3)
31. 1 ± 3.96
(0, 95)
16. 9 1. 8
Test group
(n=91)
5 .81 ± 1.84
(9, 9 )
35. 4 ± 3.73
(0, 93)
17.57
The table below presents the percentage of patients in each group who improved,
worsened, or remained unchanged in each element of the composite score and the
composite score itself.
QOL score VO2 Score Composite Score
Control
GROUP
Test GROUP Control
GROUP
Test GROUP Control
GROUP
Test GROUP
% Improved 75.6 74.7 48.8 67.0 6 . 70.9
% Worsened 4.4 5.3 51. 31.9 37.8 8.6
%
Unchanged
0.0 0.0 0.0 1.1 0.0 0.0
Histograms for Respiratory Exchange Rate (RER) at peak VO at baseline and 6 month
follow-up are provided below:
SORIN – INTENSIA SonR CRT-D 184 – U150A 17

6. CLINICAL STUDIES
6.1.5 . Clinical Results V-V timing
V-V programmable settings were available for the clinical study devices as follows: ALTO
MSP model 617 (not programmable for V-V delay), ALTO MSP model 6 7 values (0, 31,
39, 47, 55 and 63 ms) and OVATIO CRT-D 6750 values (0 to 63 ms in steps of 8 ms).
The graph below shows the programmed V-V settings at randomization by percentage of
patients programmed to each combination of Synchronous BiV pacing and V-V delay.
The optimization protocol in the clinical study specified that each patient randomized should
undergo echo guided V-V optimization. Per the investigational plan for the MSP Clinical
18 SORIN – INTENSIA SonR CRT-D 184 – U150A
Table of contents
Other sorin Medical Equipment manuals
sorin
sorin SYNTHESIS C Ph.I.S.I.O User manual

sorin
sorin dideco KIDS D130 User manual
sorin
sorin Intensia DR 154 User manual
sorin
sorin REPLY DR User manual

sorin
sorin PARADYM RF DR 9550 User manual

sorin
sorin Paradym VR 8250 User manual

sorin
sorin PARADYM RF SonR CRT-D 9770 User manual

sorin
sorin PLATINIUM SonR CRT-D 1811 User manual

sorin
sorin SMARTVIEW KA960 User manual

sorin
sorin SMARTVIEW KA961 User manual