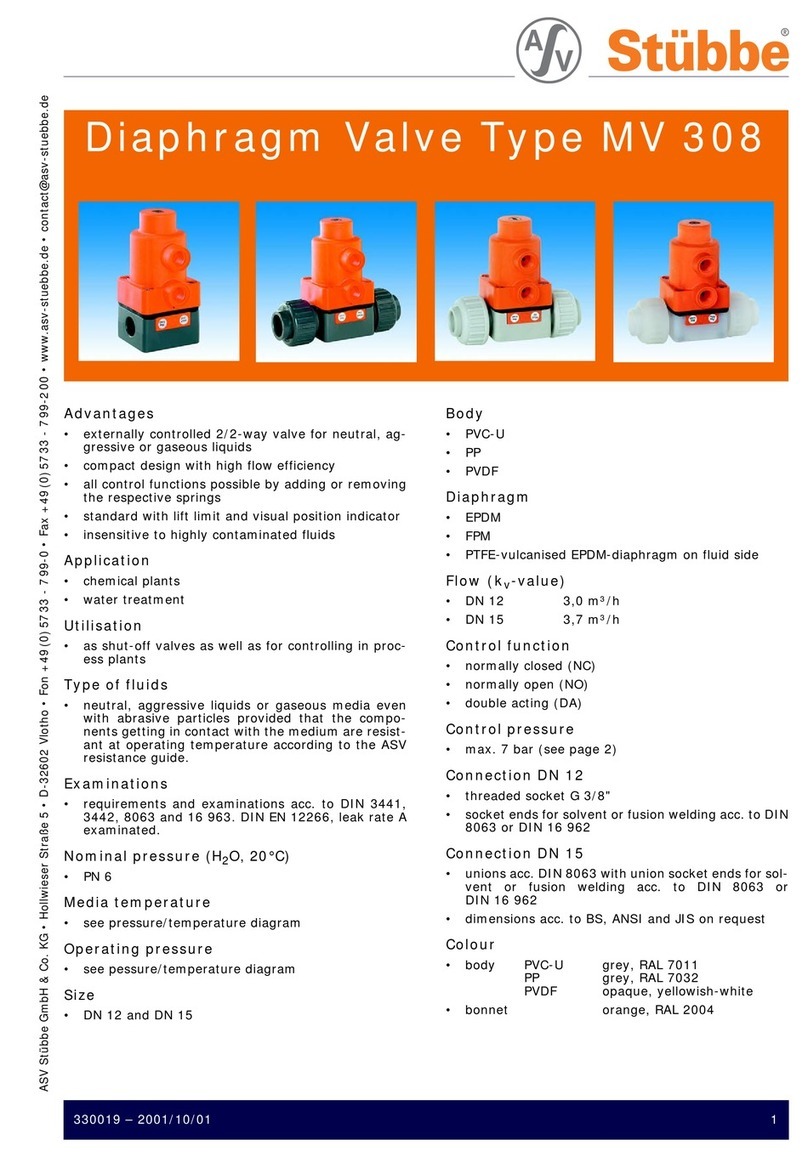
Stübbe MV 309 Series User manual

Diaphragm valve
Operating manual Series MV 309
Version BA-2016.08.04 EN
Print-No. 300 156
TR MA DE Rev001
ASV Stübbe GmbH & Co. KG
Hollwieser Straße 5
32602 Vlotho
Germany
Phone: +49 (0) 5733-799-0
Fax: +49 (0) 5733-799-5000
E-mail: [email protected]
Internet: www.asv-stuebbe.com
We reserve the right to make technical changes.
Read carefully before use.
Save for future use.

Table of contents
Table of contents
1 About this document ............................... 3
1.1 Target groups ................................. 3
1.2 Other applicable documents ................ 3
1.3 Warnings and symbols ....................... 3
2 Safety instructions ................................. 4
2.1 Intended use .................................. 4
2.2 General safety instructions .................. 4
2.2.1 Obligations of the operating company . .... . 4
2.2.2 Obligations of personnel ..................... 4
2.3 Specific hazards .............................. 4
2.3.1 Hazardous media ............................ 4
3 Layout and Function ............................... 5
3.1 Marking ....................................... 5
3.1.1 Name plate ................................... 5
3.2 Layout ......................................... 5
4 Transport, Storage and Disposal ................. 6
4.1 Unpacking and inspection on delivery . . . . . . 6
4.2 Transportation ................................ 6
4.3 Storage ....................................... 6
4.4 Disposal ....................................... 6
5 Installation and connection ....................... 7
5.1 Preparing for installation ..................... 7
5.1.1 Check operating conditions ................. 7
5.2 Planning pipelines ............................ 7
5.2.1 Designing pipelines .......................... 7
5.3 Installing fitting in pipe ....................... 7
5.3.1 Connection with solvent welding/butt-weld
spigot ends ................................... 7
5.3.2 Connection with flange ...................... 7
5.3.3 Connection with union nut and insert . . . . . . . 7
5.4 Connecting the drive ......................... 8
5.4.1 Installing limit switch ......................... 9
5.4.2 Pneumatic connection ....................... 9
5.4.3 Checking the function of the drive .......... 9
5.5 Performing the hydrostatic test .............. 9
6Operation ............................................ 9
6.1 Commissioning ............................... 9
7 Maintenance ......................................... 10
7.1 Servicing ...................................... 10
7.2 Maintenance .................................. 10
7.2.1 Removing fitting .............................. 11
7.2.2 Fixing leaks in the port ....................... 11
7.3 Replacement parts and return .............. 11
8 Troubleshooting .................................... 12
9 Appendix ............................................. 13
9.1 Technicalspecifications ...................... 13
9.1.1 Mechanical specifications ................... 13
9.1.2 Control air connections ...................... 13
9.2 Tightening torques ........................... 13
9.3 Accessories ................................... 13
9.4 Parts .......................................... 13
List of figures
Fig. 1 Nameplate (example) ........................ 5
Fig. 2 Layout ......................................... 5
Fig. 3 Limit switch, type VCSP ..................... 8
Fig. 4 Limit switch, type Nj2–V3–N ................ 8
Fig. 5 Limit switch, type NBB2–V3–E2 ............ 8
Fig. 6 compressed air ............................... 8
Fig. 7 Replacement parts ........................... 13
List of tables
Tab. 1 Other application documents, purpose and
where found .................................. 3
Tab. 2 Warnings and symbols ....................... 3
Tab. 3 Compressed air connection ................. 9
Tab. 4 Diaphragm maintenance interval .. .. .. . . . . . 10
Tab. 5 Troubleshooting .............................. 12
Tab. 6 Mechanical specifications ................... 13
Tab. 7 Tightening torques ........................... 13
Tab. 8 Accessories ................................... 13
Tab. 9 Part numbers and designations ............. 13
2 MV 309 BA-2016.08.04 EN 300 156

About this document
1 About this document
This manual
• ispartofthefitting
• applies to all series referred to
• describes safe and proper operation during all operating
phases
1.1 Target groups
Operating company
• Responsibilities:
– Keep this manual available at the place of operation,
also for future use.
– Ensure that employees read and observe this manual
and other applicable documents, especially the safety
instructions and warnings.
– Observe any additional country-specific rules and reg-
ulations that relate to the system.
Qualified personnel, fitter
• Mechanics qualification:
– Qualified employees with additional training for fitting
the respective pipework.
• Electrical qualification:
– Qualified electrician
• Responsibility:
– Read, observe and follow this manual and the other
applicable documents, especially all safety instructions
and warnings.
1.2 Other applicable documents
Resistance Guide
Chemical resistance of the materials used
http://www.asv-stuebbe.de/pdf_resistance/300051.pdf
Data sheet
technical specifications, operating
conditions
http://www.asv-stuebbe.de/pdf_datasheets/300163.pdf
CE declaration of conformity
Conformity with standards
http://www.asv-stuebbe.de/pdf_DOC/300168.pdf
Tab. 1 Other application documents, purpose
and where found
1.3 Warnings and symbols
Symbol Meaning
• Immediate acute risk
• Death, serious bodily harm
• Potentially acute risk
• Death, serious bodily harm
• Potentially hazardous situation
• Minor injury
• Potentially hazardous situation
• Material damage
Safety warning sign
Take note of all information
highlighted by the safety warning
sign and follow the instructions to
avoid injury or death.
Instruction
1. , 2. , … Multiple-step instructions
Precondition
→Cross reference
Information, notes
Tab. 2 Warnings and symbols
300 156 BA-2016.08.04 EN MV 309 3

Safety instructions
2 Safety instructions
The manufacturer accepts no liability for damages caused
by disregarding any of the documentation.
2.1 Intended use
•Onlyusethefitting to shut off pipes for appropriate media
(→Resistance list).
• Adhere to the operating limits (→data sheet).
2.2 General safety instructions
Read and observe the following regulations before carrying
out any work.
2.2.1 Obligations of the operating company
Safety-conscious operation
• Only operate the fitting if it is in perfect technical condition
and only use it as intended, staying aware of safety and
risks, and in adherence to the instructions in this manual.
• Ensure that the following safety aspects are observed and
monitored:
– Intended use
– Statutory or other safety and accident-prevention reg-
ulations
– Safety regulations governing the handling of haz-
ardous substances
– Applicable standards and guidelines in the country
where the pump is operated
• Make personal protective equipment available.
Qualified personnel
• Make sure all personnel tasked with work on the fitting have
read and understood this manual and all other applicable
documents, especially the safety, maintenance and repair
information, before they start any work.
• Organize responsibilities, areas of competence and the
supervision of personnel.
• The following work should be carried out by specialist tech-
nicians only:
– Installation, repair and maintenance work
– Work on the electrical system
• Make sure that trainee personnel only work on the fitting
under supervision of specialist technicians.
2.2.2 Obligations of personnel
• Observe the instructions on the fitting and keep them legi-
ble, e.g. nameplate, identification marking for fluid connec-
tions.
• Only carry out work on the fitting if the following require-
ments are met:
– System is empty
– System has been flushed
– System is depressurized
– System has cooled down
– System is secured against being switched back on
again
• Do not make any modifications to the device.
2.3 Specific hazards
2.3.1 Hazardous media
• When handling hazardous media (e.g. hot, flammable,
explosive, toxic, hazardous to health or the environment),
observe the safety regulations for the handling of haz-
ardous substances.
• Use personal protective equipment when carrying out any
work on the fitting.
• Collect leaking pumped liquid and residues in a safe man-
ner and dispose of in accordance with environmental reg-
ulations.
4 MV 309 BA-2016.08.04 EN 300 156

Layout and Function
3 Layout and Function
3.1 Marking
3.1.1 Name plate
PP • PTFE • FPM
1
2
3
4
MV309
PN/DN 6 / 15
Id No 145039
1407-87345 5
Fig. 1 Nameplate (example)
1Type
2 ID number
3 Nominal pressure [bar] / Nominal diameter [mm]
4 Materials (valve body, diaphragm, other gaskets)
5 Date of manufacture - Series number
3.2 Layout
Compressed air operated diaphragm valve for shutting off
pipelines or regulating systems.
•Optionalflow direction
• Valve lift OPEN/CLOSE
• Optional installation position
• Valve functions
– Normally closed (NC)
– Normally open (NO)
– Double acting (DA)
1
2
3
4
5
6
Fig. 2 Layout
1 Indicator pin
2 Upper part
3 Compressed air connection A (G 1/4")
4 Compressed air connection B (G 1/4")
5 Membrane
6 Valve body
300 156 BA-2016.08.04 EN MV 309 5

Transport, Storage and Disposal
4 Transport, Storage and Disposal
4.1 Unpacking and inspection on delivery
1. Unpack the fitting when received and inspect it for transport
damage.
2. Report any transport damage to the manufacturer immedi-
ately.
3. Ensure that the information on the type plate agrees with
the order/design data.
4. For immediate installation, dispose of packaging material
according to local regulations.
– For later installation, leave the fitting in the original
packaging.
4.2 Transportation
1. If possible, transport fitting (including drive) in original pack-
aging.
2. To transport, lift the fitting by hand, weight specifications
(→Data sheet)
4.3 Storage
NOTE
Material damage due to inappropriate storage!
Store the fitting properly.
Make sure the storage room meets the following condi-
tions:
–Dry
– Frost-free
– Vibration-free
– Not in direct sunlight
– Storage temperature +10 °C to +60 °C
4.4 Disposal
Plastic parts can be contaminated by poisonous or radioac-
tive media to such an extent that cleaning will not be suffi-
cient.
WARNING
Risk of poisoning and environmental damage from
medium.
Use personal protective equipment when carrying out any
work on the fitting.
Before disposing of the fitting:
– Collect escaping medium and dispose separately
according to local regulations.
– Neutralize residues of medium in the fitting.
Remove plastic parts and dispose of them in accordance
with local regulations.
Dispose of fitting in accordance with local regulations.
6 MV 309 BA-2016.08.04 EN 300 156

Installation and connection
5 Installation and connection
5.1 Preparing for installation
5.1.1 Check operating conditions
1. Ensurethedesignofthefitting is consistent with the pur-
pose intended:
– Materials used (→nameplate).
–Medium(→order and design data).
2. Ensure the required operating conditions are met:
– Resistance of body and seal material to the medium
(→resistance lists).
– Media temperature (→data sheet).
– Operating pressure (→data sheet).
3. Consult with the manufacturer regarding any other use of
the device.
5.2 Planning pipelines
5.2.1 Designing pipelines
WARNING
Risk of poisoning and environmental damage from
medium.
Leaks due to impermissible pipework forces.
Ensure that the fitting is not subject to any pulling or thrust-
ing forces or bending moments.
1. Plan pipes safely:
– No pulling or thrusting forces
– No bending moments
– Adjust for changes in length due to temperature
changes (compensators, expansion shanks)
–Optionalflow direction
– Optional installation position
2. Dimensions (→data sheet).
5.3 Installing fittinginpipe
WARNING
Risk of poisoning and environmental damage from
medium.
Leak due to faulty installation.
Installation work on the pipes should only be performed
by technicians who have been specially trained for the
pipework in question.
NOTE
Material damage due to contamination of the fitting!
Make sure no contamination reaches the fitting.
Flush the pipe with a neutral medium.
The fitting is installed according to the connection type of
the pipes.
5.3.1 Connection with solvent welding/butt-weld
spigot ends
Do not connect the ASV valve body in the version “fixed
connector” by means of butt-welding.
This applies to the heating element as well as infrared butt-
welding procedures.
1. Prepare pipe ends according to connection type.
2. Adhesively apply or weld fitting with solvent welding/butt-
weld socket ends (→manufacturer specifications).
5.3.2 Connection with flange
1. Prepare pipe ends according to connection type.
2. Radially push the fitting and flat seal between the flange
ends.
3. Bolt fitting and flange with flange screws, nuts and wash-
ers.
While doing so, observe tightening torques:
(→9.2 Tightening torques, Page 13).
5.3.3 Connection with union nut and insert
1. Prepare pipe ends according to connection type.
2. Unscrew union nuts and slide over free pipe ends.
– Check mounting direction.
3. Connect inserts with pipe ends.
4. Position fitting between the pipe ends.
5. Hand-tighten the union nut.
300 156 BA-2016.08.04 EN MV 309 7

Installation and connection
5.4 Connecting the drive
Fig. 3 Limit switch, type VCSP
Aclosed
B open
Fig. 4 Limit switch, type Nj2–V3–N
Aclosed
B open
RR
Fig. 5 Limit switch, type NBB2–V3–E2
R Load
Aclosed
B open
A
X
X1
X2
B
Fig. 6 compressed air
A Close valve
BOpenvalve
X1 Valve open
X2 Valve closed
8 MV 309 BA-2016.08.04 EN 300 156

Operation
5.4.1 Installing limit switch
Only necessary for fittings with limit switches.
DANGER
Risk of electrocution!
All electrical work must be carried out by qualified electri-
cians only.
1. Mount limit switch unit onto fitting.
2. Connect limit switch:
–(→Figure Limit switch, type VCSP, Page 8).
–(→Figure Limit switch, type Nj2–V3–N, Page 8).
–(→Figure Limit switch, type NBB2–V3–E2, Page 8).
5.4.2 Pneumatic connection
Solenoid pilot valves are available for control of the com-
pressed air drive:
– 3/2-way valve for single-acting drives
– 5/2-way valve for double-acting drives
CAUTION
Risk of injury from compressed air!
All work on the compressed air system must be carried out
by qualified technicians.
Connect compressed air lines to the compressed air drive.
(→Figure compressed air, Page 8).
Control
pressure on
Function ab
Normally closed (NC) – open
Normally open (NO) close –
Double acting (DA) close open
Tab. 3 Compressed air connection
5.4.3 Checking the function of the drive
Open and close fitting using the pneumatic connection, the
indicator pin signals the corresponding position
– lowered: Fitting is closed
– protruding: Fitting is open
5.5 Performing the hydrostatic test
Pressure test using neutral medium, e.g. water.
1. Pressurize the fitting, ensuring
– Test pressure < permissible system pressure
– Test pressure < 1.5 PN
– Test pressure < PN + 5 bar
2. Check the fitting for leaks.
6 Operation
6.1 Commissioning
Fitting correctly installed and connected
WARNING
Risk of injury and poisoning due to medium spraying out.
Use personal protective equipment when carrying out any
work on the fitting.
1. Open and close fitting, the indicator pin signals the corre-
sponding position
– lowered: Fitting is closed
– protruding: Fitting is open
2. After the initial stresses due to pressure and operating tem-
perature, check if the fitting is sealed.
300 156 BA-2016.08.04 EN MV 309 9

Maintenance
7 Maintenance
WARNING
Risk of injury and poisoning due to hazardous media liq-
uids!
Use personal protective equipment when carrying out any
work on the fitting.
7.1 Servicing
1. Visual and function check (every three months):
– Normal operating conditions unchanged
–Noleaks
– No unusual operating noises or vibrations
2. Ensure that fitting functions properly (opening, closing)
3. Clean fitting with a moist cloth if necessary.
4. Retighten housing screws (→9.2 Tightening torques,
Page 13).
5. Check diaphragm for wear and replace if necessary:
Diaphragm material
Max. number of
actuations1)
EPDM 150,000
FPM: 100,000
PTFE (EPDM) 100,000
Tab. 4 Diaphragm maintenance interval
1) Applies for water at 20 °C. Under different conditions
(chemicals, media that contains solids/abrasives),
shorten the maintenance intervals.
7.2 Maintenance
DANGER
Risk of electrocution!
All electrical work must be carried out by qualified electri-
cians only.
WARNING
Risk of injury and poisoning due to hazardous or hot
media.
Use personal protective equipment when carrying out any
work on the fitting.
Safely collect the media and dispose of it in accordance
with environmental regulations.
WARNING
Risk of injury during disassembly!
Wear protective gloves, components can be very sharp-
edged due to wear or damage.
Remove components with springs (e.g. pneumatic drive)
carefully, since spring tension can cause components to
be ejected.
10 MV 309 BA-2016.08.04 EN 300 156

Maintenance
7.2.1 Removing fitting
1. Ensure that:
– System is empty
– System has been flushed
– System is depressurized
– System has cooled down
– System is secured against being switched back on
again
2. Remove fitting from the pipe.
3. Decontaminate fitting if required.
–Deadspaceinthefitting may still contain medium.
7.2.2 Fixing leaks in the port
(→9.4 Parts, Page 13).
1. Removing fitting (→7.2.1 Removing fitting, Page 11).
Before removing housing screws (5), note:
– For NC drives, apply compressed air pressure to
connection B to bring the drive into the open posi-
tion (→Figure compressed air, Page 8).
– For NO and DA drives, this is not necessary.
2. Unscrew housing screws (5).
3. Remove lift drive (3).
4. For NC drives on connection B, release compressed air.
5. Unscrew diaphragm (2) and dispose of properly.
6. Ensure that pressure piece (3.3) is exposed in the guides.
7. Check state of sealing surfaces of the valve body (1) for
damage.
8. Lightly lubricate new diaphragm with special grease on top
of curvature and on thread (recommended special grease:
Syntheso ProAA2).
9. Screw diaphragm into spindle clockwise until resistance is
felt.
10. Unscrew diaphragm until the diaphragm hole pattern
matches the valve body (1) (max. 180°).
11. Screw in housing screws (5) and tighten crosswise.
Ensure uniform contact pressure.
12. Tighten housing screws (5) with tightening torque.
(→9.2 Tightening torques, Page 13).
7.3 Replacement parts and return
1. Have the following information ready to hand when order-
ing spare parts (→nameplate).
– Fitting type
– ID number
– Nominal pressure and diameter
– Body and seal material
2. Please complete and enclose the document of compliance
for returns
(→http://www.asv-stuebbe.com/service/downloads).
3. Only use spare parts from ASV Stübbe.
300 156 BA-2016.08.04 EN MV 309 11

Troubleshooting
8 Troubleshooting
WARNING
Risk of injury and poisoning due to hazardous or hot
media.
Use personal protective equipment when carrying out any
work on the fitting.
Safely collect the media and dispose of it in accordance
with environmental regulations.
Consult with the manufacturer regarding faults which are not
identified in the following table, or which cannot be traced to
the indicated causes.
Error Possible cause Corrective action
Control connections mixed up Connect control connections
correctly.
Compressed air connection mixed up at
solenoid pilot valve
Check compressed air connection
and correct if necessary
(→supplementary instructions
for drives).
Control function is not right
Electrical connection faulty Check electric connect and correct
if necessary (→supplementary
instructions for limit switch).
Medium escapes between housing and
diaphragm
Housing screws too loose Tighten housing screws
(→9.2 Tightening torques, Page 13).
Medium escapes at the drive Diaphragm leaky (→7.2.2 Fixing leaks in the port,
Page 11).
Control pressure too low Check compressed air supply.
Ensure sufficient air pressure
(→9.1.2 Control air connections,
Page 13).
Diaphragm leaky (→7.2.2 Fixing leaks in the port,
Page 11).
Fitting does not close completely
Drive defective Replace drive.
Tab. 5 Troubleshooting
12 MV 309 BA-2016.08.04 EN 300 156

Appendix
9 Appendix
9.1 Technical specifications
Technical data (→Data sheet).
9.1.1 Mechanical specifications
Size Value
Process conditions (medium)
Pressure and temperature →Data sheet
Materials in contact with medium
Diaphragm EPDM, FPM, PTFE (EPDM
diaphragm, PTFE-coated on
medium-side)
sealing FPM, EPDM
Housing PVC-U, PP, PVDF
Materials not in contact with medium
Upper part PP, glass fiber reinforced
Tab. 6 Mechanical specifications
9.1.2 Control air connections
• Maximum control pressure
– NC, NO – 6 bar
–DA–4bar
• Compressed air classes according to ISO 8573-1
– 2or3atT<0°C
– 3or4atT>0°C
• Control pressure diagram (→data sheet).
9.2 Tightening torques
Description Size Tightening
torque [Nm]
Housing screws
d20 (DN15)
d25 (DN20)
d32 (DN25)
d40 (DN32)
5
5
8
8
Union nut hand-tight
Tab. 7 Tightening torques
9.3 Accessories
Description
limit switch unit
Tab. 8 Accessories
9.4 Parts
1
2
3
4
5
987
3.3
10
Fig. 7 Replacement parts
Pos. Quantity Designation
11Valvebody
21Membrane
31Lift drive
3.3 1 Pressure piece
44Washer
54 Hexagon screw
(housing screw)
72 Union nut
82Unionend
92O-ring
10 1 Indicator pin
Tab. 9 Part numbers and designations
300 156 BA-2016.08.04 EN MV 309 13

Appendix
14 MV 309 BA-2016.08.04 EN 300 156
This manual suits for next models
1
Table of contents
Other Stübbe Control Unit manuals
Popular Control Unit manuals by other brands

Governors America
Governors America SYC6714 manual

TLV
TLV RT3A instruction manual

Buderus
Buderus RC35 Installation and servicing instructions

SIMCom Wireless Solutions
SIMCom Wireless Solutions SIM7600A-H user manual

WAGO
WAGO 751-5701 manual

HEIDENHAIN
HEIDENHAIN ND 1200 QUADRA-CHEK installation instructions