Sua ionTig 200 AC/DC User manual

ionTig 200 AC/DC
Copyright © Mundaka Welding & Gases, Inc.
ionTig 200 AC/DC
INVERTER - AC/DC PULSED TIG WELDER
OPERATION MANUAL
IMPORTANT: Read this Owner’s Manual Completely before attempting to use this
equipment. Save this manual and keep it handy for quick reference. Pay particular
attention to the safety instructions we have provided for your protection. Contact your
distributor if you do not fully understand this manual.
ionTig 200 AC/DC
Copyright © Mundaka Welding & Gases, Inc.
2
CONTENT
1. SAFETY .................................................................................................................................................... 3
1.1 Signal Explanation....................................................................................................................................... 3
1.2 The Knowledge of Electricand Magnetic Fields........................................................................................... 6
2. Overview................................................................................................................................................... 7
2.1 Brief Introduction ........................................................................................................................................ 7
2.3 Volt-Ampere Characteristic........................................................................................................................ 10
3. Installation andAdjustment..................................................................................................................... 11
3.1 Parameters................................................................................................................................................ 11
3.2 Duty cycle and Over-heat........................................................................................................................... 12
3.3 Movement and Placement.......................................................................................................................... 12
3.4 Power supply input connection ................................................................................................................. 13
3.5 Polarity Connection (MMA)........................................................................................................................ 13
3.6Assembling the equipment (TIG)................................................................................................................ 13
4. Operation................................................................................................................................................ 14
4.1 Layout for the panel................................................................................................................................... 14
4.2 Control panel............................................................................................................................................. 15
4.3 Remote control.......................................................................................................................................... 20
4.3.1 Pedal switch control ............................................................................................................................... 20
4.3.2 Remote box control................................................................................................................................. 21
4.3.3 Gun switch control current ..................................................................................................................... 22
4.4ArgonArc Welding Operation .................................................................................................................... 22
4.4.1 TIG welding (4T operation)............................................................................................................... 22
4.4.2 TIG welding (2T operation)...................................................................................................................... 24
4.5 Welding Parameters................................................................................................................................... 26
4.5.1 Joint forms in TIG/MMA......................................................................................................................... 26
4.5.2 The explanation of welding quality.......................................................................................................... 26
4.5.3 TIG Parameters Matching........................................................................................................................ 27
4.6 Operation Environment.............................................................................................................................. 30
4.7 Operation Notices...................................................................................................................................... 31
5. Maintenance & Troubleshooting.............................................................................................................. 31
5.1 Maintenance.............................................................................................................................................. 31
5.2 Troubleshooting ........................................................................................................................................ 33
5.3 Electrical principle drawing: ...................................................................................................................... 36

ionTig 200 AC/DC
Copyright © Mundaka Welding & Gases, Inc.
3
1. SAFETY
1.1 Signal Explanation
Welding may damage your body or others, so please take protection
measure in operation.
Only ones who are trained professionally can install, debug, operate,
maintain and repair the equipment.
Do not maintain and repair the machine when the machine is
connected with power.
THE ROTATING PARTS MAY BE DANGEROUS
Keep all equipment safety guards, covers and devices in position and
in good repair. Keep hands, hair, clothing and tools away from V-belts,
gears, fans and all other moving parts when starting, operating or
repairing equipment.
Do not put your hands near the engine fan. Do not attempt to override
the governor or idler by pushing on the throttle control rods while the
engine is running.
Use only compressed gas cylinders containing the correct shielding
gas for the process used and properly operating regulators designed
for the gas and pressure used. All hoses, fittings, etc. should be
suitable for the application and maintained in good condition.
Always keep cylinders in an upright position securely chained to an
undercarriage or fixed support.
Cylinders should be located:
oAway from areas where they may be struck or subjected to
physical damage.
oA safe distance from arc welding or cutting operations and any
other source of heat, sparks, or flame.
Never allow the electrode, electrode holder or any other electrically
“hot” parts to touch a cylinder.
Keep your head and face away from the cylinder valve outlet when
opening the cylinder valve.
Valve protection caps should always be in place and hand tight except
when the cylinder is in use or connected for use.

ionTig 200 AC/DC
Copyright © Mundaka Welding & Gases, Inc.
4
FUMESAND GASES CAN BE DANGEROUS
Welding may produce fumes and gases hazardous to health. Avoid
breathing these fumes and gases. When welding, keep your head out
of the fume. Use enough ventilation and/or exhaust at the arc to keep
fumes and gases away from the breathing zone. When welding with
electrodes which require special ventilation such as stainless or hard
facing or on lead or cadmium plated steel and other metals or coatings
which produce highly toxic fumes, keep exposure as low as possible
and below Threshold Limit Values using local exhaust or mechanical
ventilation. In confined spaces or in some circumstances, outdoors, a
respirator may be required. Additional precautions are also required
when welding on galvanized steel.
Do not weld in locations near chlorinated hydrocarbon vapors coming
from degreasing, cleaning or spraying operations. The heat and rays of
the arc can react with solvent vapors to form phosgene, a highly toxic
gas, and other irritating products.
Shielded gases used for arc welding can displace air and cause injury
or death. Always use enough ventilation, especially in confined areas,
to insure breathing air is safe.
Read and understand the manufacturer’s instructions for this
equipment and the consumables to be used, including the material
safety data sheet and follow your employer’s safety practices.
ARC RAYS CAN BURN.
Use a shield with the proper filter and cover plates to protect your eyes
from sparks and the rays of the arc when welding or observing open
arc welding.
Use suitable clothing made from durable flame-resistant material to
protect your skin and that of your helpers from the arc rays.
Protect other nearby personnel with suitable, non-flammable screening
and /or warn them not to watch the arc nor expose themselves to the
arc rays or to hot spatter or metal.

ionTig 200 AC/DC
Copyright © Mundaka Welding & Gases, Inc.
5
ELECTRIC SHOCK CAN KILL.
Never touch electrical parts.
Wear dry, hole-free gloves and clothes to insulate yourself.
Insulate yourself from work and ground using dry insulation. Make
certain the insulation is large enough to cover your full area of physical
contact with work and ground.
Take carefully when using the equipment in small place, falling-off and
wet circumstance.
Never close the machine power before installation and adjustment.
Ensure to install the equipment correctly and ground the work or metal
to be welded to a good electrical (earth) ground according the
operation manual.
The electrode and work (or ground) circuits are electrically “hot” when
the welder is on. Do not touch these “hot” parts with your bare skin or
wet clothing. Wear dry, hole-free gloves to insulate hands.
In semiautomatic or automatic wire welding, the electrode, electrode
reel, welding head, nozzle or semiautomatic welding gun are also
electrically “hot”.
Always be sure the work cable makes a good electrical connection with
the metal being welded. The connection should be as close as possible
to the area being welded.
Maintain the electrode holder, work clamp, welding cable and welding
machine in good, safe operating condition. Replace damaged
insulation.
Never dip the electrode in water for cooling.
Never simultaneously touch electrically “hot” parts of electrode holders
connected to two welders because voltage between the two can be the
total of the open circuit voltage of both welders.
When working above the floor level, use a safety belt to protect yourself
from a fall should you get a shock.
FIREAND EXPLOSION
Remove fire hazards from the welding area. If this is not possible,
cover them to prevent the welding sparks from starting a fire.
Remember that welding sparks and hot materials from welding can
easily go through small cracks and openings to adjacent areas. Avoid
welding near hydraulic lines. Have a fire extinguisher readily available.

ionTig 200 AC/DC
Copyright © Mundaka Welding & Gases, Inc.
6
1.2 The Knowledge of Electric and Magnetic Fields
Electric current flowing through any conductor causes localized Electric and Magnetic Fields (EMF). The
discussion on the effect of EMF is ongoing all the world. Up to now, no material evidences show that
EMF may have effects on health. However, the research on damage of EMF is still ongoing. Before any
Where compressed gases are to be used at the job site, special
precautions should be used to prevent hazardous situation.
When not welding, make certain no part of the electrode circuit is
touching the work or ground. Accidental contact can cause overheating
and create a fire hazard.
Do not heat, cut or weld tanks, drums or containers until the proper
steps have been taken to insure that such procedures will not cause
flammable or toxic vapors from substances inside. They can cause an
explosion even though they have been “cleaned”.
Vent hollow castings or containers before heating, cutting or welding.
They may explode.
Sparks and spatter are thrown from the welding arc. Wear oil free
protective garments such as leather gloves, heavy shirt, cuff less
trousers, high shoes and a cap over your hair. Wear ear plugs when
welding out of position or in confined places. Always wear safety
glasses with side shields when in a welding area.
Connect the work cable to the work as close to the welding area as
practical. Work cables connected to the building framework or other
locations away from the welding area increase the possibility of the
welding current passing through lifting chains, crane cables or other
alternate circuits. This can create fire hazards or overheat lifting chains
or cables until they fail.
Hot parts can lead to burn.
Do not touch the hot parts.
Please use the torch after cooling or use the welding blow lamp.

ionTig 200 AC/DC
Copyright © Mundaka Welding & Gases, Inc.
7
conclusion, we should minimize exposure toEMF as few as possible.
In order to minimize EMF, we should use the following procedures:
Route the electrode and work cables together – Secure them with tape when possible.
All cables should be put away and far from the operator.
Never coil the power cable around your body.
Make sure welding machine and power cable to be far away from the operator as far as possible
according to the actual circumstance.
Connect the work cable to the work piece as close as possible to the area being welded.
The people with heart-pacemaker should be away fromthe welding area.
2. Overview
2.1 Brief Introduction
ionTig 200 AC/DC arc welding machine adopts the latest pulse width modulation (PWM) technology and
insulated gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) power module, which can change work frequency to medium
frequency so as to replace the traditional hulking work frequency transformer with the cabinet medium
frequency transformer. Thus, it is characterized with portable, small size, light weight, low consumption
and etc.
The parameters of ionTig200 AC/DC on the front panel all can be adjusted continuously and sleeplessly,
such as start current, crater arc current, welding current, base current, duty ratio, upslope time,
downslope time, pre-gas, post-gas, pulse frequency, AC frequency, balance, hot start, arc force and arc
length etc. When welding, it takes high frequency and high voltage for arc igniting to ensure the success
ratio of igniting arc.
WSME Characteristics:

ionTig 200 AC/DC
Copyright © Mundaka Welding & Gases, Inc.
8
MCU control system, responds immediately to any changes.
High frequency and high voltage for arc igniting to ensure the success ratio of igniting arc, the
reverse polarity ignition ensures good ignition behavior inTIG-AC welding.
AvoidAC arc-break with special means, even if arc-break occurs the HF will keep the arc stable.
Pedal control the welding current.
TIG/DC operation, if the tungsten electrode touches the work piece when welding, the current will
drop to short-circuit current to protect tungsten.
Intelligent protection: over-voltage, over-current, over-heat, when the problems listed before
occurred, the alarm lamp on the front panel will be on and the output current will be cut off. It can
self-protect and prolong the using life.
Double purpose: AC inverter TIG/MMA and DC inverter TIG/MMA, Excellent performance on
Al-alloy、carbon steel、stainless steel、titanium.
According to choosing the front panel functions, the following six welding ways can be realized:
I. DC – MMA
II. DC – TIG
III. DC - Pulse TIG
IV. AC – MMA
V. AC – TIG
VI. AC - Pulse TIG
I. For DC MMA, polarity connection can be chosen according to different electrodes,please refer to
3.5
II. For DC TIG, DCEP is used normally (work piece connected to positive polarity, while torch
connected to negative polarity). This connection has many characters, such as stable welding
arc, low tungsten pole loss, more welding current, narrow and deep weld.

ionTig 200 AC/DC
Copyright © Mundaka Welding & Gases, Inc.
9
III. DC Pulsed TIG has the following characters: 1) Pulse heating. Metal in Molten pool has short time
on high temperature status and freezes quickly, which can reduce the possibility to produce hot
crack of the materials with thermal sensitivity. 2) The work piece gets little heat. Arc energy is
focused. Be suitable for thin sheet and super thin sheet welding. 3) Exactly control heat input
and the size of the molten pool. The depth of penetration is even. Be suitable for welding by one
side and forming by two sides and all position welding for pipe. 4) High frequency arc can make
metal for microlite fabric, eliminate blowhole and improve the mechanical performance of the
joint. 5) High frequency arc is suitable for high welding speed to improve the productivity.
IV. ForAC MMA, magnetic flow caused by invariable DC polarity can be avoided.
V. For AC TIG (rectangle wave), arc is more stable than Sine AC TIG. At the same time, you can not
only obtain the max penetration and the min tungsten pole loss, but also obtain better clearance
effect.
ionTig 200 AC/DC welding machine is suitable for all positions welding for various plates made of
stainless steel, carbon steel, alloyed steel, titanium, aluminum, magnesium, cuprum, etc., which is also
applied to pipe installment, mold mend, petrochemical, architecture decoration, car repair, bicycle,
handicraft and common manufacture.
MMA- Manual MetalArc welding;
PWM - Pulse-Width Modulation;
IGBT - Insulation Gate Bipolar Transistor
TIG - Tungsten Insert Gas welding
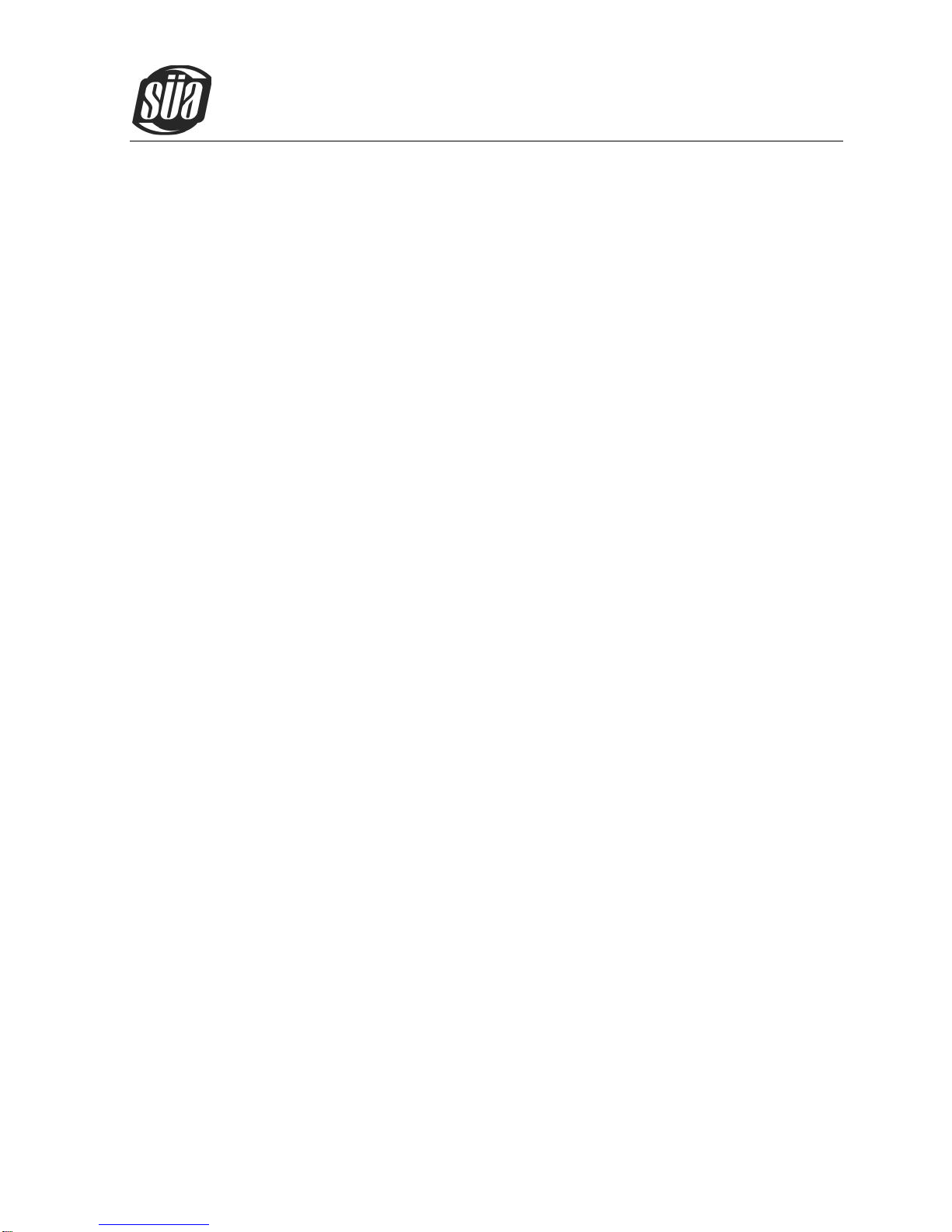
2.2 Working Principle
The working principle of ionTig 200 AC/DC welding machines is shown as the following figure.
ionTig 200 AC/DC
Copyright © Mundaka Welding & Gases, Inc.
10
Single-phase 220V work frequency AC is rectified into DC (about 312V), then is converted to medium
frequency AC (about 20KHz) by inverter device (IGBT module), after reducing voltage by medium
transformer (the main transformer) and rectifying by medium frequency rectifier (fast recovery diodes),
then is outputted DC or AC by selecting IGBT module. The circuit adopts current feedback control
technology to insure current output stably. Meanwhile, the welding current parameter can be adjusted
continuously and steplessly to meet with the requirements of welding craft.
Rectif
ier Invert
er
Trans
forme
r
Rectif
ier
Hall
devic
e
Current feedback
control
Single-phase, AC DC AC DC
220V,50Hz
AC Invert
er
AC or DC
Control signal
AC or DC
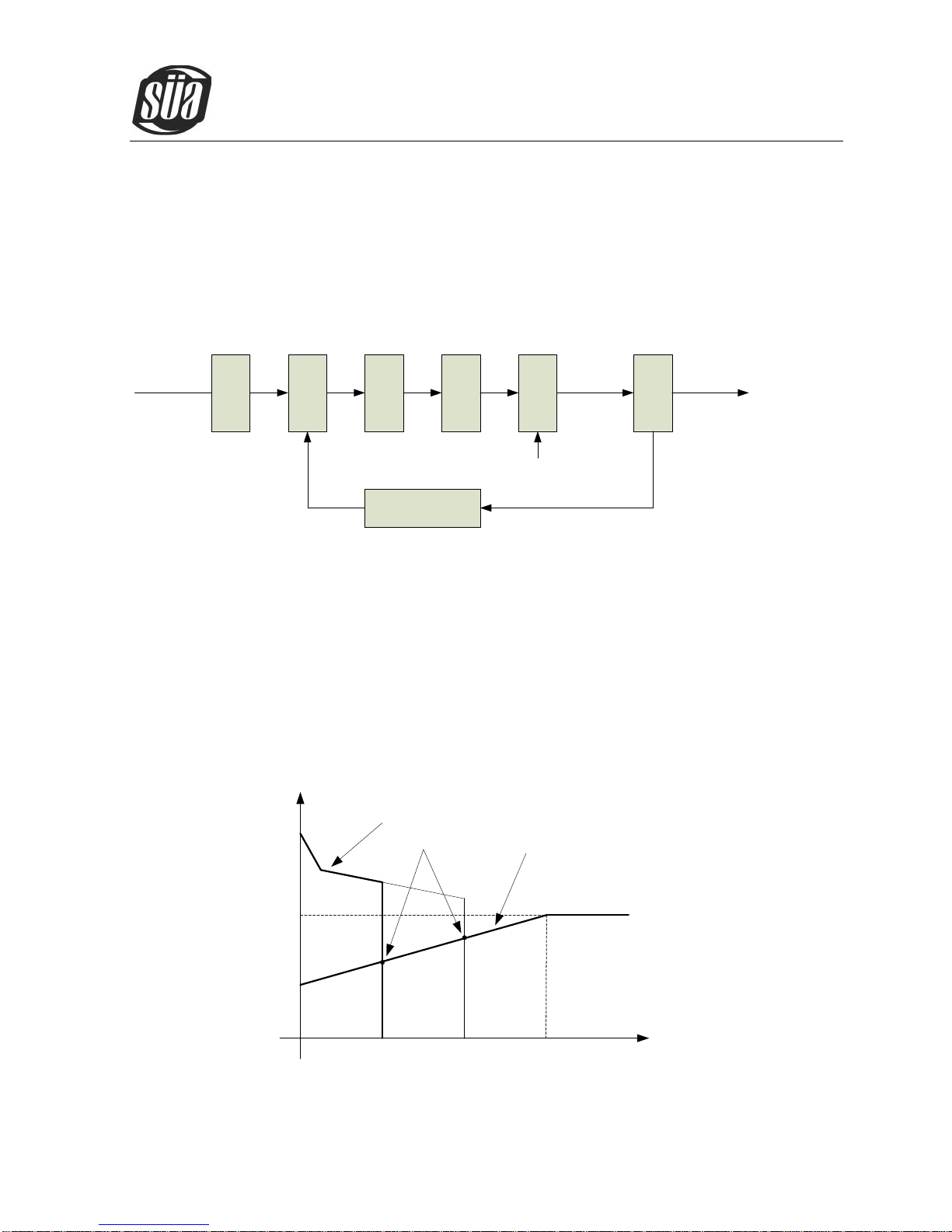
2.3 Volt-Ampere Characteristic
ionTig 200AC/DC welding machine has an excellent volt-ampere characteristic, whose graph is shown
as the following figure. The relation between the conventional rated loading voltage U2 and the
conventional welding current I2 is as follows:
When I2≤600A,U2=10+0.04I2(V); When I2¬>600A,U2=34(V).
67
34
10
0 600 I2(A)
U2(V)
Working
point
Volt-ampere characteristic The relation between the
conventional loading
voltage and welding current

ionTig 200 AC/DC
Copyright © Mundaka Welding & Gases, Inc.
11
3. Installation and Adjustment
3.1 Parameters
Models
Parameters
ionTig 200AC/DC
Input power
1~220±10%,50Hz
Rated input current(A)
35.4(TIG)
39.5(MMA)
Rated input power(KW)
5.2(TIG)
6.4(MMA)
Power factor
0.68
Max no-load voltage(V)
66
Adjustment range of start
current(A)
TIG
MMA
AC
D
C
AC
DC
HF
LIFT
5~
weldi
ng
curre
nt
—
—
10~
welding
current
30~
welding
current
Adjustment range of
welding current(A)
10~
200
30~
200
5~
200
10~
170
5~170
Adjustment range of Crater
arc current(A)
10~
200
30~
200
5~
200
10~
170
5~170
Adjustment range of
downslope time(S)
0~10
Pre-gas time(S)
0.1~1
Adjustment range of
post-gas time(S)
0.1~10
Clearance effect(%)
15~50
Efficiency
Duty cycle (40℃,10
minutes)
AC
DC
25% 200A
25% 200A
60% 90A
60% 110A
100% 70A
100% 80A
Protection class
IP23S

ionTig 200 AC/DC
Copyright © Mundaka Welding & Gases, Inc.
12
Insulation class
F
Dimensions of Machine
(L×W×H)(mm)
470×240×380
Weight(Kg)
20
Note: The above parameters are subject to change with the improvement of machines.
3.2 Duty cycle and Over-heat
The letter “X” stands for duty cycle, which is defined as the proportion of the time that a machine
can work continuously within a certain time (10 minutes). The rated duty cycle means the proportion of
the time that a machine can work
continuously within 10 minutes when it
outputs the rated welding current.
The relation between the duty cycle “X”
and the output welding current “I” is shown as
the right figure.
If the welder is over-heat, the IGBT
over-heat protection unit inside it will output an
instruction to cut output welding current, and brighten the over-heat pilot lamp on the front panel. At this
time, the machine should be relaxed for 15 minutes to cool the fan. When operating the machine again,
the welding output current or the duty cycle should be reduced.
3.3 Movement and Placement
Please take care for the welder when moving it, and do not make it sloped.
I(A)
0
100%
25%
100 200
XThe relation of the welding current and
duty cycle for WSME -200

ionTig 200 AC/DC
Copyright © Mundaka Welding & Gases, Inc.
13
It also can be moved by the handle on the top of the welder. Place the welder well when moving it to
the right position. When the machine gets to thedestination, it needs to be fixed upto avoid gliding.
When using forklift, its arm length must be long enough to reach the outside so as to ensure lifting
safely.
The movement may result in the potential danger or substantive hazard, so please make sure
that the machine is on the safe position before using it.
3.4 Power supply input connection
ionTig 200AC/DC welding machines’ power supply connects to 220V.
When the power supply voltage is over the safe work voltage, there are over voltage and under
voltage protection inside the welder, the alarm light will on, at the same time, the current output will
be cut off.
If the power supply voltage continually goes beyond the safe work voltage range, it will shorten the
welder life-span. The below measures can be used:
Change the power supply input net. Such as, connect the welder with the stable power supply
voltage of distributor;
Induce the machines using power supply in the same time;
Set the voltage stabilization device in thefront of power cable input.
3.5 Polarity Connection (MMA)
MMA (DC): Choosing the connection of DCEN or DCEP according to the different electrodes.
Please refer to the electrode manual.
MMA(AC): No requirements for polarity connection.
3.6 Assembling the equipment (TIG)
Work piece is connected to the positive electrode of welding machine, and welding torch is
connected to the negative electrode, which is called DC POSITIVE CONNECTION; otherwise,
that is called DC NEGATIVE CONNECTION. Generally, it is usually operated in DC POSITIVE
CONNECTION in TIG welding mode.
The control cable of torch switch consists of 2 wires, pedal control of 3 wires and the aero
socket has 14 leads.
Consumable parts for TIG torch, such as tungsten electrode、tip、gas nozzle、electrode shield
(short/long), please enquire us by mail or phone according to the accessory codes.

ionTig 200 AC/DC
Copyright © Mundaka Welding & Gases, Inc.
14
When WSME welding machines are operated in HF ignition method, the ignition spark can
cause interferences in equipment near the welding machine. Be sure to take specially safety
precautions or shielding measures.
4. Operation
4.1 Layout for the panel
WSME-200 DIGITAL CONTROL
AC frequency Balance
AC
~
DC
DC
AC
~
Hz
%
S
V
A
AC/DC PULSED TIG WELDER
1~220V
ON
OFF
1234
56
7
8
(1) Positive output: The welder’s positive polarity output.
(2) Aero socket: Is connected to torch switch control wire. (It has 14 leads and lead 8 - lead 9
are connected to torch switch control wire).
(3) Negative output: The welder’s negative polarity output.
(4) Shield gas connector: Is connected to the gas input pipe of torch.
(5) Power source switch: Switch to “ON”, the welder is turned on, while switch to “OFF”, the
welder is turned off.
(6) Power source input: To connect power source.

ionTig 200 AC/DC
Copyright © Mundaka Welding & Gases, Inc.
15
(7) Shield gas input joint: To connect one head of the gas hose while the other head of which is
connected to argon gas cylinder.
(8) Fan: It is used for cooling the components and parts inside the welder.
4.2 Control panel
(1) AC/DC selecting key
(2) Mode selecting key
(3) Gas-test key
(4) HF (high-frequency) ignition key
(5) Pulse key
(6) Parameter selection key
(7) Parameter selection key
(8) Adjusting dial
(9) Rod electrode welding key
(10)Power/Alarm indicator
(11)Welding voltage/other parameter display

ionTig 200 AC/DC
Copyright © Mundaka Welding & Gases, Inc.
16
(12)Welding current display
Overview
The key feature of the control panel is the logical way in which the controls are arranged. All the main
parameters needed for day-to-day working can easily be
-selected with the keys
-altered with the adjusting dial
-shown on the display during welding.
The illustration below shows an overview of the main settings needed for day-to-day working, using the
WSME-200 control panel as an example. You will find a detailed description of these settings in the
following section.
(1) AC/DC selecting key
AC welding
DC welding
(2) Mode selecting key
2-step mode
4-step mode
(3) Gas-test key
Lights up when Gas-test key is pressed, after that gas will flow out for 15s. Press the key again to stop
the gas flow before the 15s are up.
(4) HF (high-frequency) ignition key
Lights up when High frequency key is pressed, HF (high-frequency) ignition has been selected.
(5) Pulse key
Lights up when Pulse key is pressed, Pulse has been selected.
(6) and (7) Parameter selection keys
If “2T/4T mode” has been selected, it is possible to change parameter indicator by means of the
parameter selection keys (6) and (7) while the welding operation in progress.
(8) Adjusting dial
If the parameter indicator lights up, then the selected parameter can be altered on adjusting dial.

ionTig 200 AC/DC
Copyright © Mundaka Welding & Gases, Inc.
17
Available parameters where 2T and 4T mode have been selected:
Tpr Gas pre-flow time
Unit S
Setting range 0.1—1
Factory setting 0.3
Is Starting current (only with 4T)
Unit A
Setting range 5—100%of main current Iw (DC);10—100%of main current Iw (AC-HF)
30—100%of main current Iw (AC-LIFT)
Factory setting 5
Tup Upslope time
Unit S
Setting range 0—10
Factory setting 0
Iw Welding current
Unit A
WSME-160 5—160 (TIG-DC);10—160 (TIG-AC-HF);30—160 (TIG-AC-LIFT);
WSME-200 5—200 (TIG-DC);10—200 (TIG-AC-HF);30—200 (TIG-AC-LIFT);
5—170 (MMA-DC);10—170 (MMA-AC)
Tpr
Is
Tup
Iw
Ic
Tpo
Tdown
Fp
Dcy
Ib
Iw

ionTig 200 AC/DC
Copyright © Mundaka Welding & Gases, Inc.
18
Ib Base current
Unit A
WSME-160 5—160 (DC);10—160 (AC-HF);10—160 (AC-LIFT)
WSME-200 5—200 (DC);10—200 (AC-HF);10—200 (AC-LIFT)
Important! Only selectable when “pulse key” has been pressed.
Suggestion! Ib and Iw cannot differ greatly.
Dcy Ratio of pulse duration to base current duration
Unit %
Setting range 5—100
Factory setting 5
Important! Only selectable when “pulse key” has been pressed.
Fp Pulse frequency
Unit Hz
Setting range 0.5—200
Factory setting 0.5
Important! Only selectable when “pulse key” has been pressed.
Tdown Downslope time
Unit S
Setting range 0—10
Factory setting 0
Ic Crater arc current (only with 4T)
Unit S
Setting range 5—100% of main current Iw (DC);10—100% of main current Iw (AC-HF)
30—100% of main current Iw (AC-LIFT)
Factory setting 5
Tpo Gas post-flow time
Unit S
Setting range 0.1—10
Factory setting 3
AC frequency (only with TIG-AC)

ionTig 200 AC/DC
Copyright © Mundaka Welding & Gases, Inc.
19
Unit Hz
Setting range 50—250 (Iw<50A)
50—200 (50A≤Iw<100A)
50—150 (100A≤Iw<150A)
50—100 (150A≤Iw<200A)
Balance (only with TIG-AC)
Balance adjustment is mainly used to set the adjustment of eliminating metal-oxide (such as Aluminum,
Magnesium and its alloy) whileAC output.
Unit %
Setting range 15—50
Factory setting 15
(9) Rod electrode (MMA) welding key
Parameter Setting range
Arc force 0-10
Hot start 0-10
Arc length 0-10
(10) Power/Alarm indicator
Light up if the power switch on
Light up if the welder overheat, over-voltage or over-current. At the same time,
display Err 001.
(11) Welding voltage/other parameter display
Indicate the welding voltage or other parameter.
Before the start of welding, the right-hand display shows the pre-set value of Tpr, Tup, Dcy, Fp, Tdown
andTpo. There is a 3s time-lag, open-circuit voltage is displayed after adjusting those parameters.
After the start of welding, the right-hand display shows the presentactual value of the welding voltage.
(12) Welding current display
Display the pre-set or the actual welding current value.
Before the start of welding, the left-hand display shows the pre-set current value of Is, Iw, Ib and Ic.

ionTig 200 AC/DC
Copyright © Mundaka Welding & Gases, Inc.
20
After the start of welding, the left-hand display shows the present actual value of the welding current.
The control panel indicates which position has been reached in the welding process by brightening the
light.
NOTE:
Only “Parameter selection keys” and “Adjusting dial” can be used in the welding process.
Only “Rod electrode welding key”, “Adjusting dial” and “AC/DC selecting key” can be used on MMA
mode.
4.3 Remote control
1-3 CURRENT SET :They are factory set, can’t be changed. If they are changed, the welder may
be broken.
4 FACTORY TEST:When it is ON, the welder is on debug state.
5 FOOT_REMOTE BOX SELECT:When it is ON, the pedal control can be used;When it is OFF,
the remote box can be used. Gun switch control currentcan be used both ON and OFF.
4.3.1 Pedal switch control
When plug the fourteen-lead aero-socket of pedal switch in it. Welder will identify the pedal
switch, the welding current knob on the front panel will can’t use,and only 2T can be
selected.
When use the adjustment knob of max-welding current beside the pedal, can set the
max-current you want.
The eighth and ninth of the fourteen-lead aero-socket is gun switch; the first and second of
Table of contents
Other Sua Welding System manuals





















