SwitchDoc Labs WeatherSense Aftershock Reference guide
Other SwitchDoc Labs Weather Station manuals

SwitchDoc Labs
SwitchDoc Labs WeatherRack2 Operating instructions

SwitchDoc Labs
SwitchDoc Labs SolarMAX2 User manual

SwitchDoc Labs
SwitchDoc Labs SkyWeather2 User manual
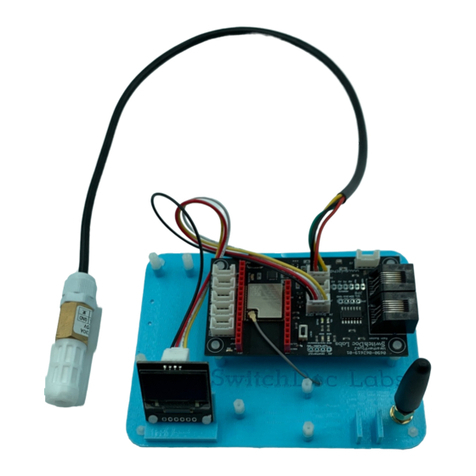
SwitchDoc Labs
SwitchDoc Labs Our Weather User manual

SwitchDoc Labs
SwitchDoc Labs WeatherRack2 User manual

SwitchDoc Labs
SwitchDoc Labs SkyWeather WXLink User manual
Popular Weather Station manuals by other brands

ADE
ADE WS 1711 operating instructions

WAREMA
WAREMA EWFS Weather station eco Operating and installation instructions

Auriol
Auriol z29592 Operation and safety notes

Auriol
Auriol 296289 Operation and safety notes

Hyundai
Hyundai WS 2266 instruction manual
La Crosse Technology
La Crosse Technology WS-2210 Operation manual

La Crosse Technology
La Crosse Technology WS-811561 manual

Ventus
Ventus W177 owner's manual

National Geographic
National Geographic VA Colour RC instruction manual

Instant Transmission
Instant Transmission MA 10410 instruction manual

Lutron Electronics
Lutron Electronics PHB-318 Operation manual

Oregon Scientific
Oregon Scientific Alizé BAR266 user manual















