4
B5: Thermal Shock
Taco GT pumps are not designed to withstand rapid changes in
temperature. Where a pump is handling hot liquids, the liquid
should be introduced slowly allowing the pump to gradually
increase in temperature.
B6: Thermal Hazards
Pumps handling hot liquid in excess of 154°F present a hazard to
personnel if the hot surface of the pump casing or associated
pipework is touched. The installer is responsible for warnings and
means of protection.
B7: Materials Compatibility
The materials of construction of this pump have been selected by
agreement between the manufacturer and the buyer, to be com-
patible with the pumped liquid as specified. The installer is
responsible for ensuring that the liquid actually handled on site is
as specified. Should there be any doubt, the installer is to seek
advice before proceeding.
B8: Controlling Solids
Where solids may be present, a strainer may be fitted to the
pump suction line to prevent entry into the pump impeller, pre-
venting possible damage to the impeller. A regular schedule
should be established to check and clean the strainer. A blocked
strainer will cause the pump to cavitate resulting in damage to the
impeller.
B9: Dry Running
The pump must never be allowed to run dry. Possible seizure of
the internal close clearances, and failure of the mechanical seal
may result. The operator should regularly check that the pump
suction source is adequate. In some installations, it may be pru-
dent to fit a level device or other means of automatic protection
to prevent the pump from dry running.
B10: Automatic Operation
Pumps operating on an automatic control system must not be
allowed to run at zero flow or flow below 30% of the peak effi-
ciency flowrate. Interlocks should be fitted appropriate to the
system. The pump should not be started more than 10 times per
hour, as damage to the shaft coupling and driver may result.
Installation of a pressure tank or timers on the electrical control
should be considered as required to reduce the frequency of
starts.
B11: Protection from Freezing
Where the pumpset may be exposed to cold weather, ensure that
the pump and associated pipework is lagged or trace heated to
prevent frost damage.
C: MAINTENANCE
C1: Electrical Supply Isolation
For pumps driven by electric motor, always isolate the electrical
power supply before working on the pump. Affix a notice on the
electrical isolator to inform others that work is being carried out
on the installation. If possible lock closed the supply isolator.
C2: Lubrication
The pump bearings are provided with grease fittings. Apply a high
quality bearing grease (Shell Alvania or equal) every 2000 hours,
or every six months, whichever comes first. Grease containing
dust and particles will quickly destroy the bearings. Only use
fresh grease from a sealed grease gun.
C3: Mechanical Seal
The mechanical seal is a wearing item. Life of a seal depends on
the erosive properties of the pumped liquid, and the temperature
and pressure of operation. The seal is self-adjusting, and requires
no periodic maintenance.
C4: Strainer
If a strainer is fitted to the suction pipe before the pump, period-
ically check and clean the strainer element. A blocked or leaking
strainer will cause cavitation damage to the impeller.
C5: Free Rotation
The pump should rotate freely by hand. Having isolated the
power supply, remove one of the guards and rotate the shaft by
hand to check freedom of rotation. Replace all guards prior to
operating the pump.
C6: Flooding
If the pump is accidentally subjected to flooding, on no account
operate the pump until it is thoroughly dry and checked. If water
has entered the pump’s bearing housing, it is likely that the bear-
ings will need to be cleaned or replaced. For pumps driven by an
electric motor, check that the motor fan is cleared of debris and
is free to rotate.
Inspect the pump shaft for debris.
D: DISASSEMBLY
D1: Special Tools
No special tools are required for disassembly of the pump set. In
preparation for disassembly, the pump should be allowed to cool
to ambient temperature before commencing any work. Close the
suction and discharge valves and drain the pump of liquid by
releasing the casing drain plug. If the pump is driven by an elec-
tric motor, ensure the power supply is isolated.
D2: Removing the Casing Top Half
Access to the pump internals is provided by a removable casing
top half. Before proceeding with removal, ensure that gasket
material of the correct thickness is available, as the gasket should
be replaced.
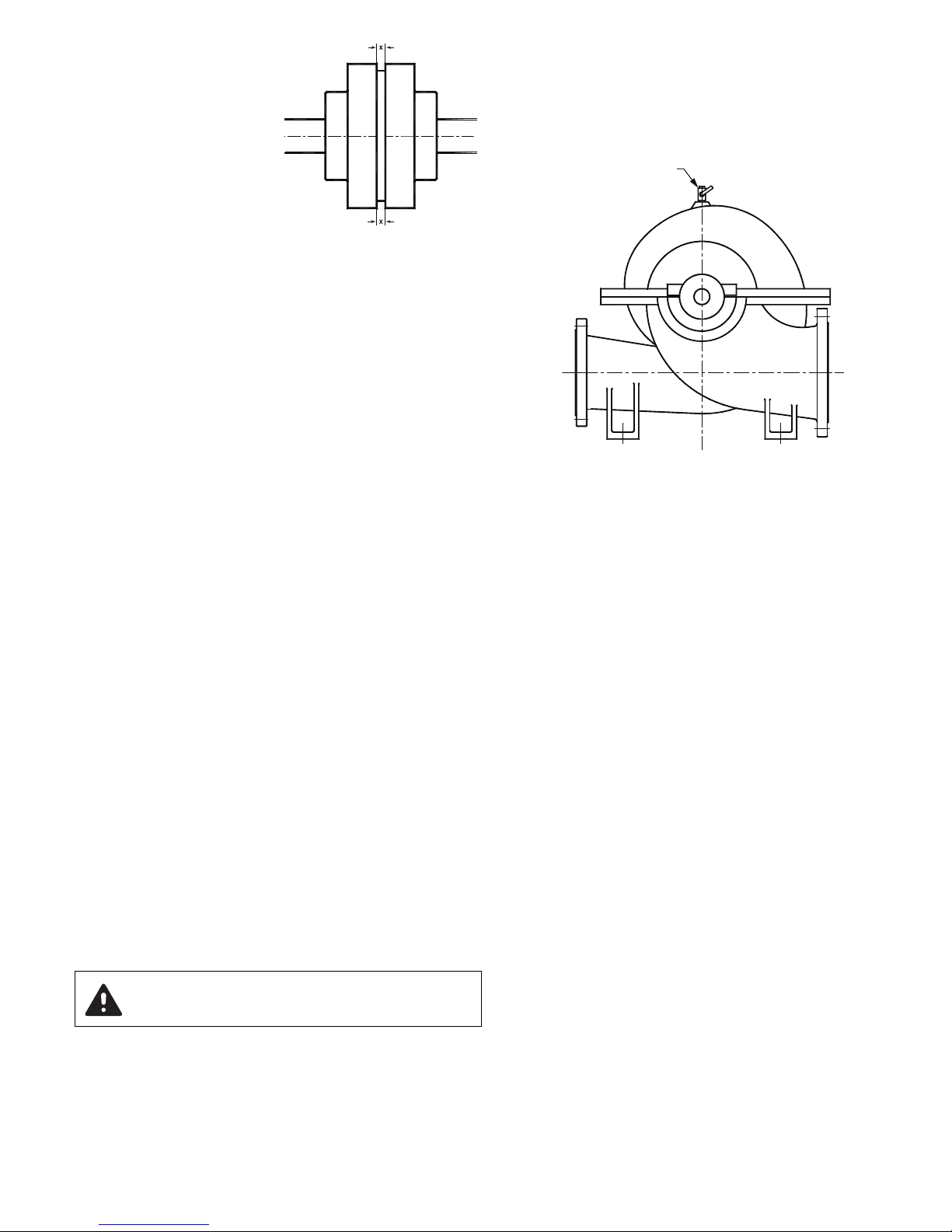
1) With the coupling guard removed, disconnect the drive cou-
pling between pump and driver.
2) Withdraw the two glands (for packed gland pumps) or
mechanical seal glandplates, if fitted, by removal of their
retaining nuts. Slide the glands or glandplates along the shaft
toward each bearing. (See Figure 7.)
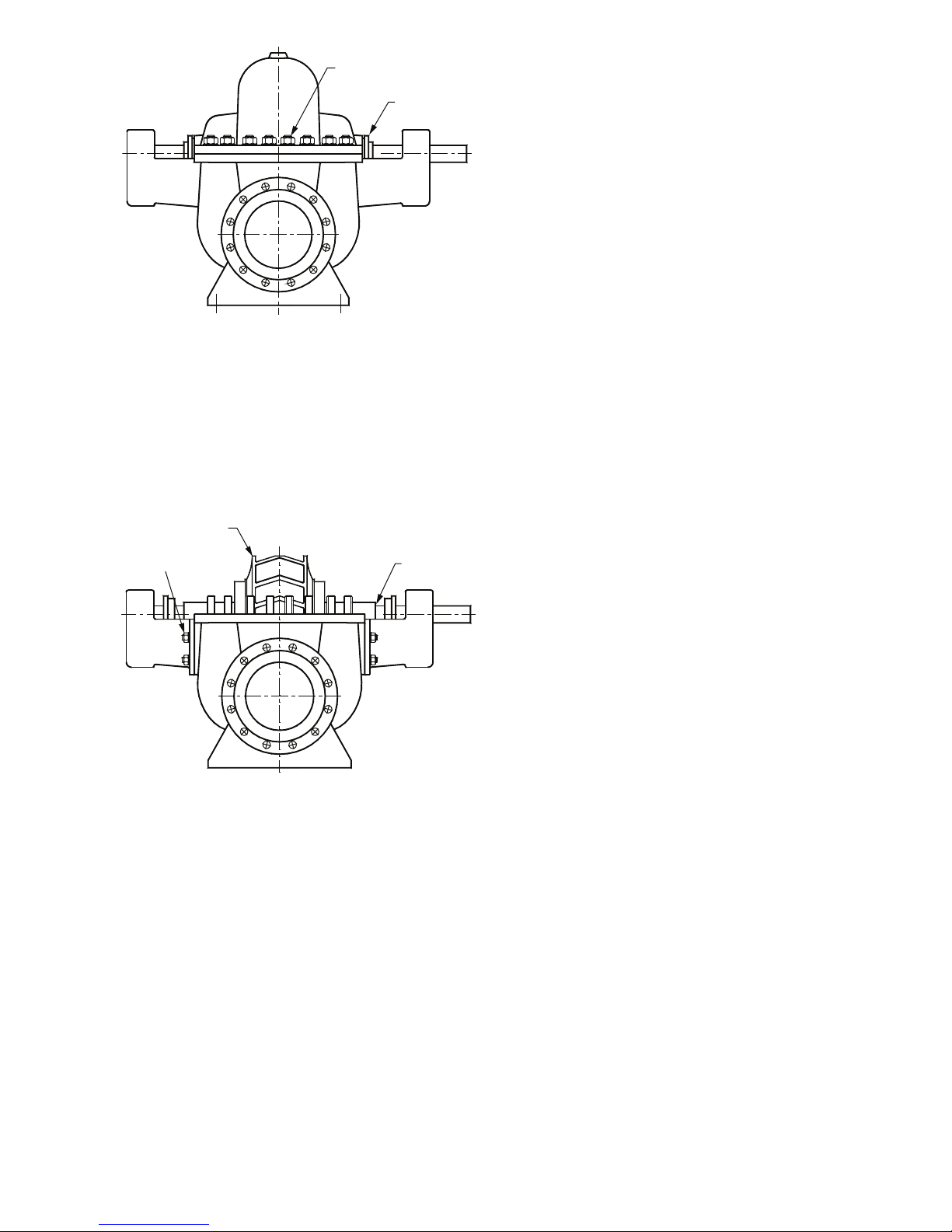
3) Remove all the nuts on the casing split flange.
4) Using the jacking bolts provided, the casing top half may now
be separated and raised by 1-2 mm.
5) Using suitable lifting tackle, the top half casing may now be
lifted away. The pump internals may now be inspected.