TECH FASS MREM 80 AgorGR-TF User manual

MREM 80 AgorGR
APS mini Plus reader modules for A-Bell and IP Bell entry panels
User’s guide
© 2004 – 2014, TECH FASS s.r.o., Věštínská 1611/19, 153 00 Prague, Czech Republic, www.techfass.cz, techfass@techfass.cz
(Date of release: 2014/5/15, valid for FW version 5.11)

All brand or product names are or may be trademarks of, and are used to identify products and services of, their
respective owners.
1 Content
1 Content ....................................................................................................................... 2
2 Product Description .................................................................................................... 3
3 Technical parameters ................................................................................................. 3
3.1 Product version .................................................................................................... 3
3.2 Technical features ................................................................................................ 4
3.3 Mechanical design ............................................................................................... 4
4 Installation .................................................................................................................. 5
4.1 Reader module description .................................................................................. 5
4.2 C1 and C2 cable wiring description ...................................................................... 5
4.3 Reader module standard connection.................................................................... 6
4.4 Inputs and outputs general connection ................................................................. 7
4.5 D1 LED Indication ................................................................................................ 7
4.6 Installation instructions ......................................................................................... 7
4.7 Mounting and removal the MREM 80 AgorGR module ......................................... 8
5 Setting parameters of the reader module .................................................................... 9
5.1 Configurable parameters ...................................................................................... 9
5.2 Reader module parameters setting ...................................................................... 9
6 Reader module functioning ....................................................................................... 10
6.1 “Door Open” function description ....................................................................... 10
6.2 Function permanent door lock release according to a time schedule ................. 10
6.3 Alarm states ....................................................................................................... 11
6.4 Standard operating modes ................................................................................. 12
6.5 Read ID media format ........................................................................................ 12
6.6 Programming mode ........................................................................................... 12
6.7 ID expiration function ......................................................................................... 16
6.8 ID with Alarm flag function ................................................................................. 16
6.9 Antipassback function ........................................................................................ 16
6.10 Disabling function............................................................................................... 18
6.11 Online authorization ........................................................................................... 18
7 Simplified access rights evaluation ........................................................................... 18
8 Useful links ............................................................................................................... 19
Page 3
2 Product Description
The MREM 80 AgorGR 1) reader modules (125 kHz
readers with an embedded single door controller) are
designed for connection to the RS 485 bus of the APS
mini Plus access control system. It is possible to
connect up to 32 reader modules to a single line of the
APS mini Plus system. In effect the number of lines is
not limited.
The module is designed for installation in A-Bell and IP
Bell entry panels of ALPHATECH TECHNOLOGIES
s.r.o. audio and video systems (design as Agora entry
panels of ACI Farfisa company), where it occupies
space of a single push button. The module comes in
GR (anthracite grey) color version of the plug.
1) Commercial designation of available versions is described in table 1.
3 Technical parameters
3.1 Product version
Product version
Product designation Catalogue number
Module features
2)
TF
EM
HID
MREM 80 AgorGR – TF 53480A00
MREM 80 AgorGR – EM 53480A01
Table 1: Product version
2) TF – TECHFASS factory ID media reading; EM – EM Marin ID media reading; HID –
HID Proximity ID media reading
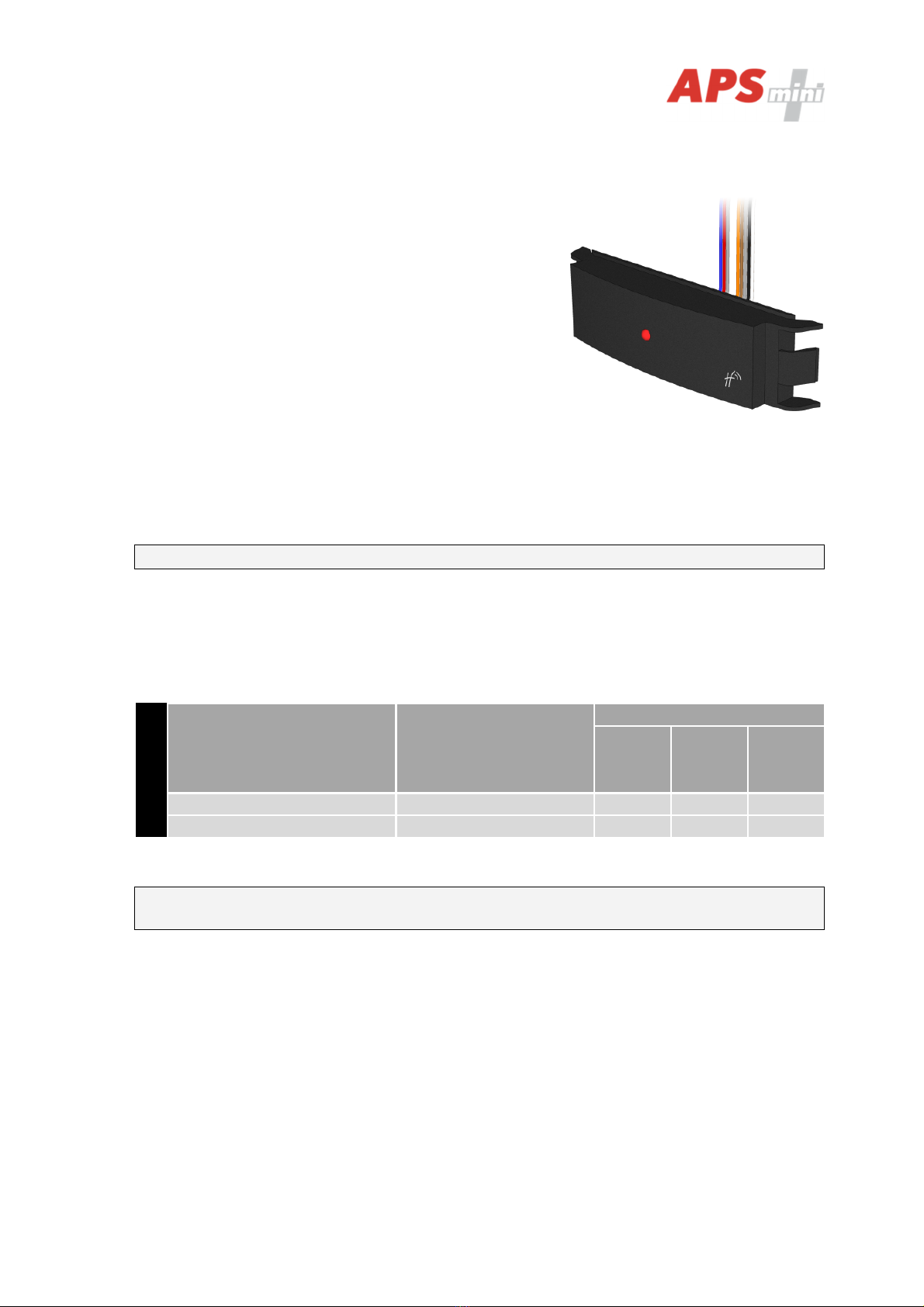
Pic. 1: MREM 80 AgorGR

Page 4
3.2 Technical features
Technical features
Supply voltage 8 ÷ 28 VDC
Current demand Typical 60 mA
Maximal 90 mA (8 V)
Version with keypad N/A
ID technology,
typical reading range
EM Marin 5 cm (with ISO card)
HID Proximity 4 cm (with ISO card)
Real-time clock Yes
Memory
Cards 2,000 ID, 2 programming cards
Events 3,400
Time schedules 64
Inputs 1
st
input Logical potential-free contact
2
nd
input Logical potential-free contact
Output Door lock
3)
1x open collector 0V active, max. 2A, 24V
Alarm N/A
Signalization 1x LED
1x PIEZO
Tamper protection N/A
Communication interface RS 485
Alternative data input / output N/A
Table 2: Technical features
3) The DC type of door lock has to be used only! Suitable anti-parallel diode has to be
connected to its coil as over-voltage protection.
3.3 Mechanical design
Mechanical design
Weight 0.023 kg
Operating temperature -25 ÷ 60 °C
Humidity Max. 95%, non-condensing
Housing IP 54 (built in the entry panel)
Pigtail 2x 0.4 m
Color Anthracite grey
Dimensions (Height x Width x Depth) 21x84x15 mm
Table 3: Mechanical design

Page 5
4 Installation
4.1 Reader module description
Pic. 2: MREM 80 AgorGR reader module, front (left) and rear (right) view
Description
Designation
Purpose
C1 Connector for C1 cable (5-wires) connection
C2 Connector for C2 cable (3-wires) connection
D1 Red-green LED indicator
Table 4: Connectors, jumpers and LED indicators description
4.2 C1 and C2 cable wiring description
Wiring description
C1 cable
C2 cable
Color Function Color Function
White B wire - RS485 line Grey 0 V (GND)
Black A wire - RS485 line Red Power supply +8 ÷ +28VDC
Grey 0 V (GND) Blue Output 1 - OC
Brown Input 1 (IN1)
Orange Input 2 (IN2)
Table 5: C1 cable wiring description
All unused wires must be mutually isolated!
D1
C1
C2

Page 6
4.3 Reader module standard connection
Standard connection
Signal Connection
+ 8 ÷ + 28 VDC + contact (power supplier unit), red wire of C2 cable
(reader module), + contact (door lock)
0 V (GND) - contact (power supplier unit), grey wire of C2 cable
(reader module), COM contact of relay 1 (entry panel)
Release lock from panel NO contact of relay 1 (entry panel), orange wire of C1
cable (reader module)
Release lock from reader Blue wire of C2 cable (reader module), - contact (door
lock)
Table 6: Reader module connection using entry panel relay as a signal for door lock release
This connection requires configuring the function of
the second input of the reader module as Request
to exit button (default module setting, see pic. 4).
Used entry panel relay must be configured for door
lock release function; the relay activation is a signal
for the reader module (orange wire) to release the
door lock then. The door lock release is controlled
by the output of the reader module (open collector,
0 V (GND) active – blue wire).
The reader module is powered by a DC power supplier. When using suitable power
supplier and door lock type, you can power all components (entry panel, reader module
and door lock) from a single power supplier. If an AC powered door lock must be used, it is
necessary to use an individual external relay controlled by the OC signal from the reader
module to control the door lock.
Pic. 3: Standard reader module connection with use DC power
supply and the relay contact of the A-Bell / IP Bell entry panel
Pic. 4: Reader module setting

Page 7
4.4 Inputs and outputs general connection
IO ports
Input 1 Door contact, active when door closed; REX button
Input 2 Request to exit button or handle contact, active when button or
handle pressed; Tamper; Disabling function
Output 1 Door lock control open collector, 0V active (also configurable for
reverse locks)
Table 7: Inputs and outputs general connection
The door monitoring contact (IN1) is operational after its first change of status since
switching on the module. Full door lock timing acc. to tab. 9 is used when the door status
contact is not installed and no Forced Door and Door Ajar alarms are triggered.
4.5 D1 LED Indication
LED indicators
Red Continuously lit Online operating mode via RS 485
Flashing with 4 s period Offline operating mode
Green ID media reading
Red/Green switching Address setting mode, RS 485 bus testing
Yellow Continuously lit / flashing Programming mode
Short flashing with 1s per. Indicating door lock release
Table 8: LED indication
4.6 Installation instructions
The reader module uses passive RF/ID technology, which is sensitive to RF noise sources.
Noise sources are generally of two types: radiating or conducting.
Conducted noise enters the reader via wires from the power supply or the host.
Sometimes, switching power supplies generate enough noise to cause reader malfunction,
it is recommended to use linear system power supplies.
Radiated noise is transmitted through the air. It can be caused by computer monitors or
other electrical equipment generating electromagnetic fields.
Consequently, a short distance between the reader modules themselves can cause
reading malfunctions – for correct operation it is necessary to keep a minimum distance of
50 cm. Various metallic constructions may have a negative influence on this distance; if
there are any doubts, it is recommended to perform a practical test before final mounting.
Nearby metal surfaces may cause a decrease in reading distance and speed. This is
caused by the combined effects of parasitic capacitance and conductance.
Page 8
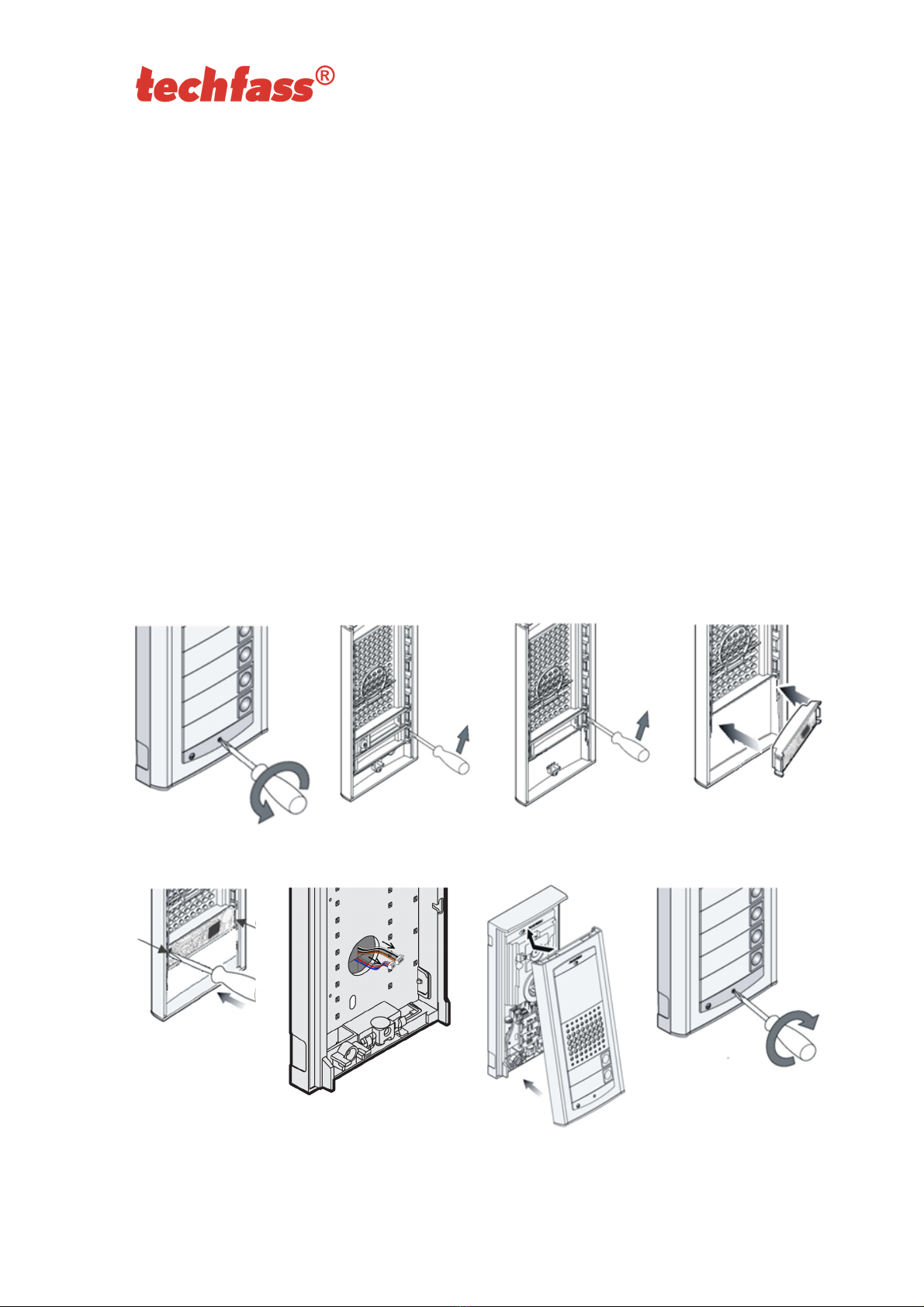
4.7 Mounting and removal the MREM 80 AgorGR module
4.7.1 Module mounting
When mounting the module in the entry panel it is necessary to unscrew the screw located
in the front part of the panel (pic. 5a) and open the front cover. The reader module can be
placed instead of the last but one button in the front part of the panel from top. First it is
necessary to remove the lowest button (pic. 5b). Continue by removing the second button
(pic. 5c). Insert the reader module in the prepared slot (pic. 5d) and press the module until
you hear the click of the latch holding the reader in position (pic. 5e). Insert the button back
to the lowest position with the same procedure as the one used for inserting the reader
module. Lead the C1 and C2 cables from behind into the back part of the panel through the
perforated membrane (pic. 5f). Connect the C1 and C2 cables in the reader module. The
last step is completing the entire panel again. Slide the front part into the back part (pic. 5g)
and screw the securing screw (pic. 5h).
4.7.2 Module removal
When disassembling the module use a similar procedure as described in the previous
chapter, just remember to unplug the panel and the reader module from the power supply
first!
Pic. 5b
Pic. 5a Pic. 5c Pic. 5d
Pic. 5e Pic. 5f Pic. 5g Pic. 5h
Page 9
5 Setting parameters of the reader module
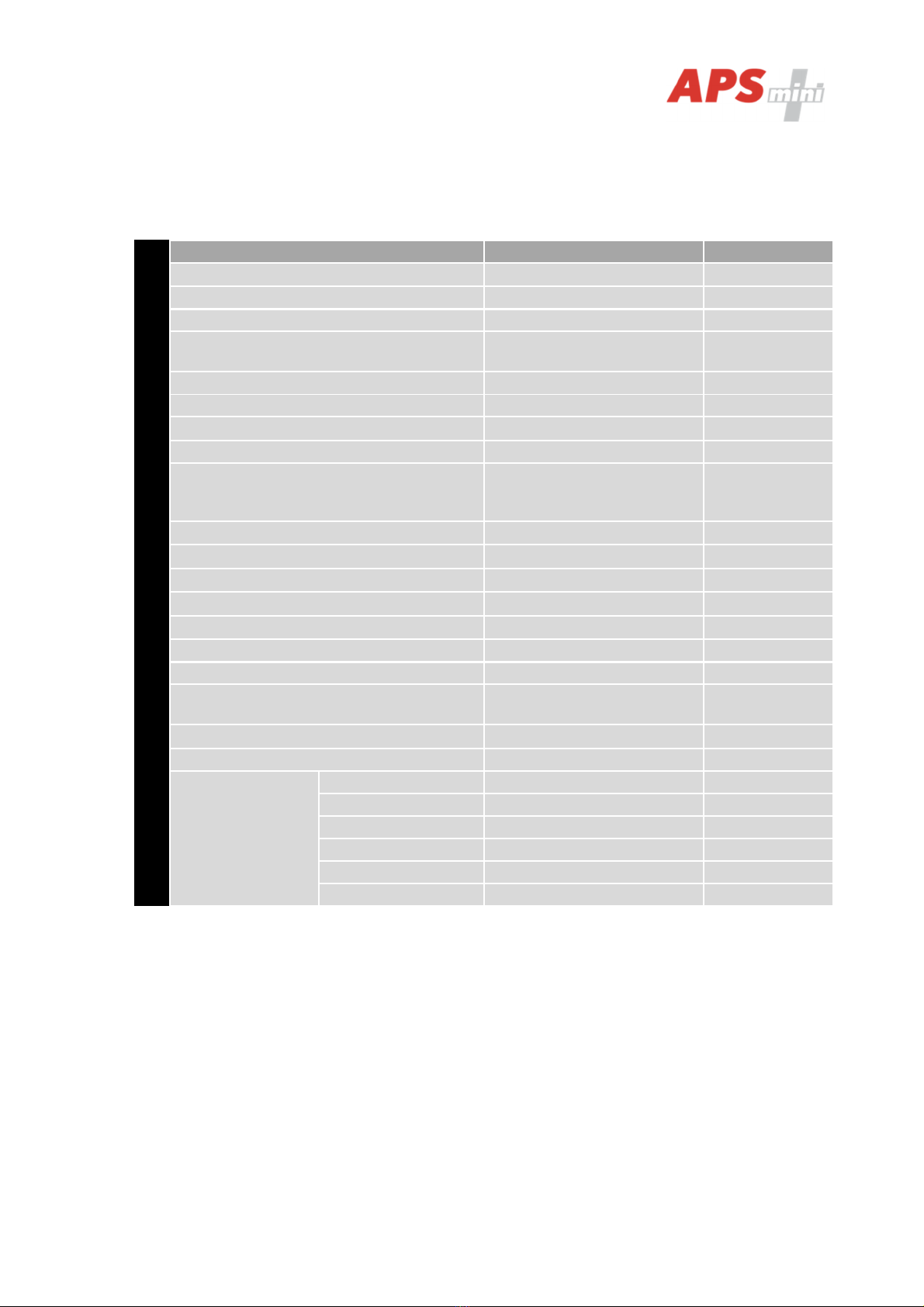
5.1 Configurable parameters
Configurable parameters
Parameter Possible range Default setting
Door lock release time 0 255 s 7 s
Door lock control setting Direct / reverse Direct
Door lock relay function setting Standard / toggle / pulse Standard
Permanent door lock release according to
a time schedule Never / Schedule index Never
Door lock status indication YES / NO NO
Acoustic signal of door lock release YES / NO YES
Door ajar time 0 255 s 20 s
First input configuration Door contact / REX button Door contact
Second input configuration
REX button / handle contact
/ external tamper / disabling
function
REX button
Acoustic signalization time - Tamper 0 255 s 30 s
Acoustic signalization time - Forced door 0 255 s 30 s
Acoustic signalization time – Door ajar 0 255 s 0 s
Acoustic signalization time – APB alarm 0 255 s 0 s
Signalization time – Card alarm 0 255 s 30 s
Antipassback function setting See chapter 6.9 Disabled
Automatic summer time adjustment
YES / NO YES
Release lock with REX button when
tamper alarm active YES / NO YES
Online authorization timeout 0 25500 ms 800 ms
Standalone authorization after timeout YES / NO YES
Saving events in
the module’s
archive
Door opened Enabled / Disabled Enabled
Door closed Enabled / Disabled Enabled
Input 2 On Enabled / Disabled Enabled
Input 2 Off Enabled / Disabled Enabled
Strike released Enabled / Disabled Enabled
Strike closed Enabled / Disabled Enabled
Table 9: Configurable parameters
5.2 Reader module parameters setting
Detailed instructions for setting reader module parameters are described in the APS mini
Plus.Reader configuration program user’s guide available at the address
http://www.techfass.cz/files/m_aps_miniplus_reader_en.pdf.

Page 10
6 Reader module functioning
The reader module supports the following functions:
Standard “Door Open” function.
Door status monitoring.
Exit-devices contact monitoring.
The “Door Open” function can be activated in 3 different ways:
Reading a valid ID (card, key fob…).
Pressing the exit button (according to configuration) – cannot be used in alarm
condition.
Via communication line (program request).
6.1 “Door Open” function description
In case the standard function of the door lock relay is set, the door lock is released and the
beeper activated (when not disabled) when the “Door Open“ function is activated. Both
outputs stay active until the door is opened or the preset door lock release time has
elapsed - see configuration table.
In case the toggle function of the door lock relay is set, the door lock relay status is
switched and the beeper is activated (when not disabled) when the “Door Open” function is
activated. The beeper stays active until the door is opened or the preset door lock release
time has elapsed - see configuration table. The door lock relay status remains unchanged
until another “Door Open” function is activated.
In case the pulse function of the door lock relay is set, the door lock relay status is switched
for the time defined by the Pulse width parameter (ms) after the Door Open function is
activated.
In case the standard function of the door lock relay is set, reading a valid card during
door lock release resets the door lock release time.
6.2 Function permanent door lock release according to a time schedule
When the function is set, the door lock is permanently released when relevant time
schedule is valid. Reading a valid ID is standardly announced via the communication line
(in online operating mode). The forced door alarm cannot be raised when the door lock is
permanently released.
The permanent door lock release function and the toggle function of the door lock relay
are mutually exclusive.

Page 11
6.3 Alarm states
The reader module can get in following alarm states:
1) Tamper alarm
2) Forced door alarm
3) Door ajar alarm
4) Antipassback alarm (Time APB alarm, Zone APB alarm)
5) ID with Alarm flag alarm
Alarm state reporting is performed as follows:
Via communication line (statuses 1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
By acoustic signal (beeper) (statuses 1, 2, 3, 4).
Alarm signaling via communication line requires online running PC with relevant software
suitable for online operation (APS Administrator).
Two ways of acoustic signaling is carried out:
Steady signal (tamper).
Intermittent signal (forced door and/or door ajar, APB alarm).
Acoustic alarm signaling is stopped after a valid ID is presented or pre-set time interval is
elapsed, see the configuration table.
6.3.1 Tamper alarm
In case of tampering the module (by changing the status of input 2 or input 3 in proper
configuration) the “Tamper” state is activated 3).
3) The Tamper alarm handling is operational after their first change of status since
switching on the module. There is no need to configure the module when the tamper
protection is not used.
6.3.2 Forced Door alarm
The “Forced Door” alarm state is activated when the door is opened without activating the
“Door Open” function. The only exception is opening the door with the second module input
IN2 active and configured as a handle contact.
6.3.3 Door Ajar alarm
If the door stays open until the pre-defined Door ajar timeout expires – see Tab. 12, the
“Door Ajar“ alarm is activated.
6.3.4 Antipassback alarm
The Antipassback alarm is raised when an ID is read during the Time APB counter is
running or when the ID is blocked by a Zone APB.
6.3.5 ID with Alarm flag alarm
ID with Alarm flag alarm occurs when an ID with the Alarm flag is read.

Page 12
6.3.6 Reading ID during alarm state
Reading an ID doesn’t affect the alarm state, reading a valid ID only terminates the
acoustic alarm announcement followed by “Door Open” function. Reading an invalid ID only
interrupts the acoustic announcement of the alarm state while signalizing “Invalid ID”.
6.4 Standard operating modes
The reader module can be in either online or offline operating mode. The module’s
functionality is identical in both operating modes; the events archive is read from the reader
module’s memory when the module goes online..When a programming card is read (while
in either online or offline mode), the module goes into programming mode.
6.5 Read ID media format
6.5.1 EM Marin ID media format
The EM Marin ID media format can be changed into selected 24, 32 or 40 bits length of ID
code. The default length is 40 bits. This setting is only used when unifying of the ID media
codes length is required – in combined systems with WIEGAND output readers with a fixed
WIEGAND data format IDs (more information in APS Reader user’s guide available at
http://www.techfass.cz/files/m_aps_miniplus_reader_en.pdf).
6.5.2 HID Proximity ID media format
When working with HID Proximity technology ID media, the module operates with a code in
a recognized 26 or 32 bit format, in other cases it uses all 45 bits of a media (45bit raw
format). If a specific format of the HID Proximity IDs is required, it can be performed by
setting up the user’s configuration of read IDs (more information in APS Reader user’s
guide available at http://www.techfass.cz/files/m_aps_miniplus_reader_en.pdf).
6.6 Programming mode
The module enters programming mode by reading one of the two programming cards
(cards “+” and “-“). The programming mode cannot be entered while the module is in
hardware address setting mode (for modules with HW address setting via the
communication line). The module’s functionality in programming mode can be seen in
pictures 6 a-d.
It is not possible to use time schedules when inserting cards in programming mode,
therefore cards are always valid.

Page 13
6.6.1 Inserting cards into the reader’s memory
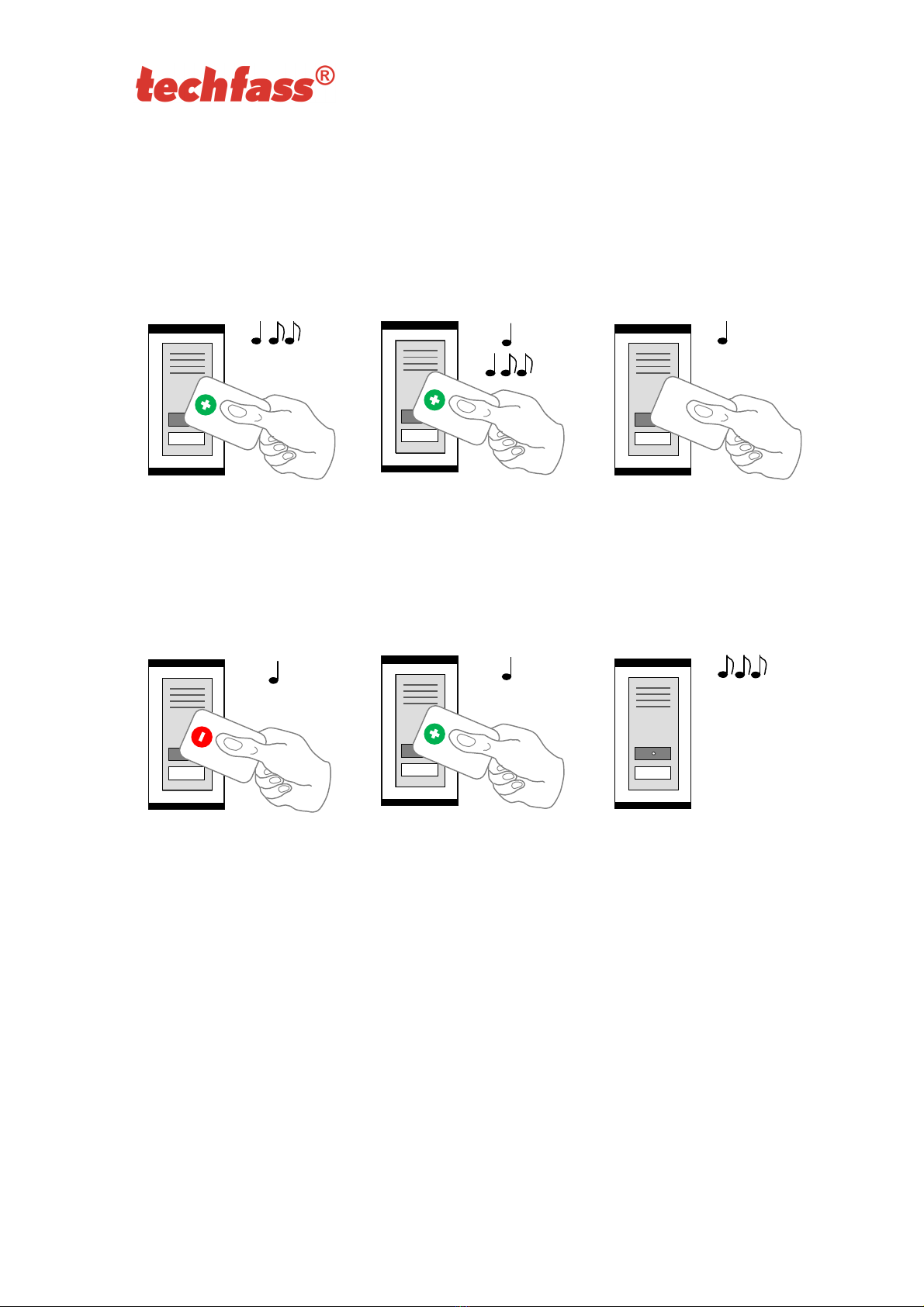
Follow these steps for inserting cards into the reader module’s memory:
Step 1 Step 2 Step 3
Read the programming card
for inserting: the reader goes
into programming mode.
One by one, read the cards
which are to be granted
access.
About 15 seconds after
inserting the last card the
reader module goes back
into standard operating
mode.
Pic.6 a): Inserting cards
6.6.2 Deleting cards from the reader’s memory
For deleting the cards from the reader module’s memory use following steps:
Step 1 Step 2 Step 3
Read the programming card
for deleting: the reader goes
into programming mode.
One by one, read the cards
which are to have their
access revoked.
About 15 seconds after
deleting the last card the
reader module goes back
into standard operating
mode.
Pic.6 b): Deleting cards
Page 14
6.6.3 Deleting cards „above or below“
If a user loses his ID medium, it is usually impossible to delete the ID from the memory with
the procedure described in the previous chapter, since the medium is no longer available
(with an exception of entering the code at the keypad). Following procedure can be used
for deleting such ID. The procedure requires using an ID medium, which was inserted right
before or right after the ID medium, which should be deleted.
Step 1 Step 2 Step 3
Read the programming card
for inserting: the reader goes
into programming mode,
which is indicated by slow
flashing of yellow LED.
Read the programming card
for inserting 5 times in a row;
the reader will go into
Deleting cards “above or
below” mode indicated by
fast flashing of yellow LED.
Read a card, which is
located in the module’s
memory right before or right
after the card you wish to
delete. After this step the
module quickly flashes with
yellow LED.
Step 4 - A Step 4 - B Step 5
For deleting an ID located
right before the ID used in
precious step, read the
programming card for
deleting.
For deleting an ID located
right after the ID used in
precious step, read the
programming card for
inserting.
The reader module goes
back into standard operating
mode.
Pic.6 c): Deleting cards “above or below”

Page 15
6.6.4 Deleting all cards from the reader’s memory
Follow these steps for deleting all cards from the reader module’s memory:
Step 1 Step 2 Step 3
Read the programming card
for deleting: the reader goes
into programming mode.
Read the programming card
for deleting 5 times in a row;
the reader will erase all cards
from its memory.
The reader module goes
back into standard
operating mode.
Pic.6 d): Deleting all cards
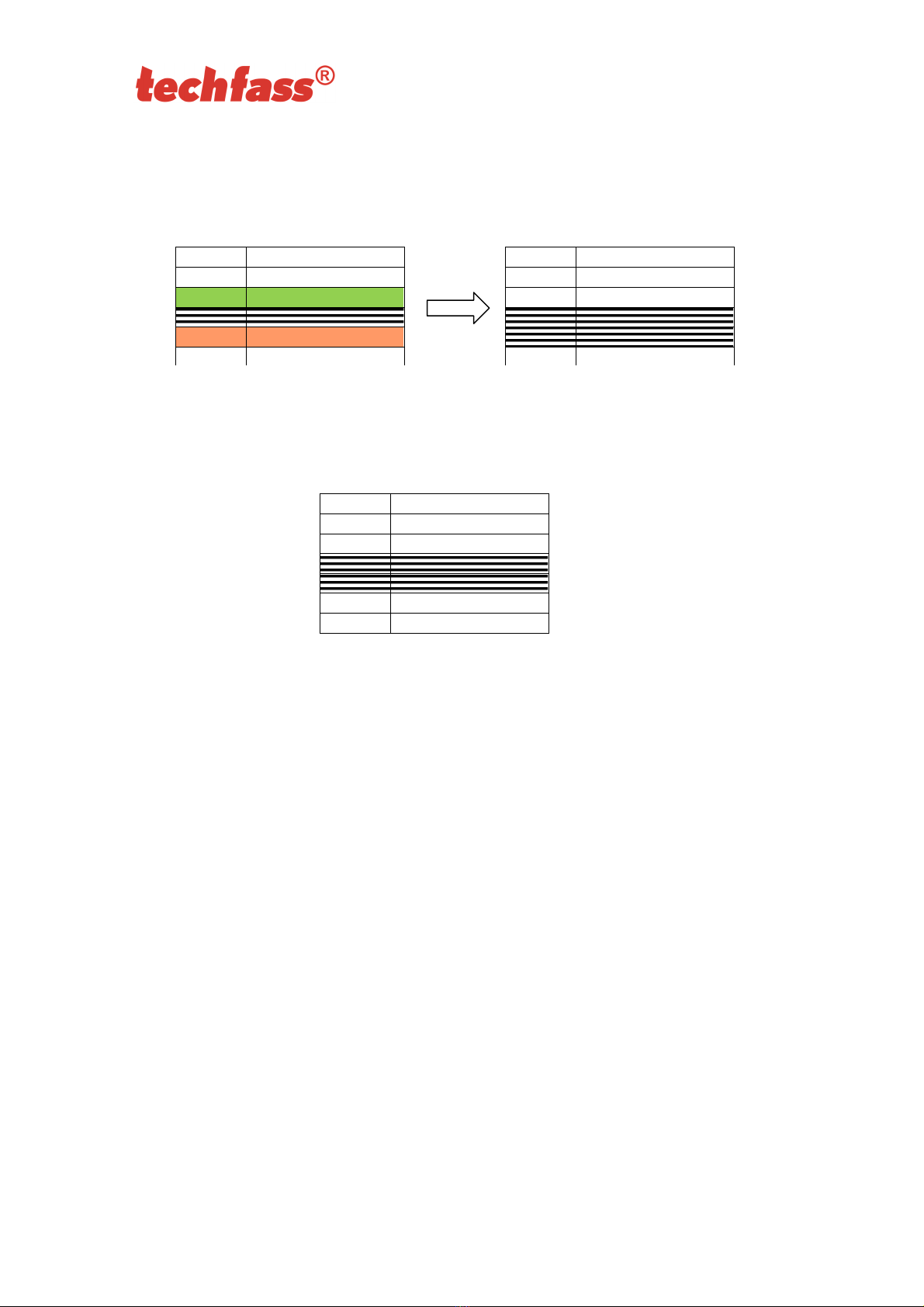
6.6.5 Recommended method for access rights management (using prog. cards)
In case of managing access rights of plenty of users (using programming cards only), it is
appropriate to establish a table, which summarizes operation with the reader module
memory. All operations (adding and deleting cards) should be stored in the table. Following
example shows correct usage of the programming cards and proper filing of the actions:
Inserting 5 new cards using the procedure from chapter 6.7.1 – Read + (inserting)
programming card, read cards 1-5, after 15 s the programming mode is exited,
create a table.
Pic.6 e): Table after inserting 5 cards
Card 3 gets lost – Delete it using the card 4, which is available, and using the
procedure from chapter 6.6.3 – Read + (inserting) programming card, then 5x +
(inserting) programming card again, then card 4, and finally – (deleting)
programming card. Register the change in your table.
Pic.6 f): Deleting card 3 using the card 4, table after deleting card 3
position card
1 card 1
2 card 2
3 card 3 (lost)
4 card 4 (available)
5 card 5
position card
1 card 1
2 card 2
3 card 3
4 card 4
5 card 5
position card
1 card 1
2 card 2
3 card 3
4 card 4
5 card 5
5x
Page 16
Card 4 gets lost – Delete it using the card 2, which is available, and using the
procedure from chapter 6.6.3 – Read + (inserting) programming card, then 5x +
(inserting) programming card again, then card 2, and finally + (inserting)
programming card again. Register the change in your table.
Pic.6 g): Deleting card 4 using the card 2, table after deleting card 4
It is necessary to add another card (card 6). We proceed with the procedure from
chapter 6.7.1 again. 1 – Read + (inserting) programming card, read cards 1-5, after
15 s the programming mode is exited. Register the change in your table.
Pic.6 h): Table after inserting card 6
A new card is always inserted at the position after the last inserted card. In case of deleting
all cards using the procedure described in chapter 6.6.4, it is necessary to create a new
filing table.
6.7 ID expiration function
This function is implemented since the FW version 5.0.
It is possible to set an Expiration date for every ID stored in the module. When the date
occurs, the ID becomes invalid (expired). The expiration evaluation is performed on every
date change in the module’s RTC and when the access rights are downloaded.
6.8 ID with Alarm flag function
This function is implemented since the FW version 5.0.
It is possible so set an Alarm – ID flag for every ID stored in the module. When the ID is
read, relevant alarm is raised (and the alarm output is switched for preset time).
6.9 Antipassback function
This function is implemented since the FW version 5.0.
The Antipassback function is defined in two ways:
position card
1 card 1
2 card 2
3 card 3
4 card 4
5 card 5
6 card 6
position card
1 card 1
2 card 2 (available)
3 card 3
4 card 4 (lost)
5 card 5
position card
1 card 1
2 card 2
3 card 3
4 card 4
5 card 5

Page 17
Time APB – user cannot repeatedly use his ID for defined time
Zone APB – user cannot repeatedly enter an area, where he is already present
The Antipassback function is used only for the users, whose access is driven by a time
schedule. The users with access always granted are not affected by the Antipassback
function.
The Antipassback flags for an ID can be reset by inserting the ID again with use of the
programming cards (offline solution). All Antipassback flags are also reset whenever new
access rights data are downloaded from the program.
Both Zone and Time Antipassback flags are written either immediately after an ID is read,
or after relevant door is opened (relevant input is disconnected).
6.9.1 Time Antipassback
The Time Antipassback is defined by the ABP timer initial value (in minutes), which is set to
the ID after passing at the reader module. If the users uses the ID at the address during the
timer for the ID is running, the Time APB alarm is raised. Following parameters affect the
Time APB function:
APB timer initial value – defines the Time APB flag (timer) value set to the ID after
passing at the reader module. If a user uses the ID again before the timer elapses,
Time APB alarm is raised.
Open door after APB time alarm – if the option is enabled, the Door open function is
performed after the Time APB alarm is raised.
6.9.2 Zone Antipassback
The Zone Antipassback is defined by enabling the option for the relevant address. The
Zone APB flag is set for the ID when passing at the reader module. If a user uses the ID
again when the Zone APB flag is set, the Zone APB alarm is raised. Following parameters
affect the Zone APB function:
Enabled – enable/disable general Zone APB flag setting.
Enable in offline mode – if the option is not set, the module operates in offline mode
like if the APB function was not implemented.
Open door after APB Zone alarm – if the option is enabled, the Door open function is
performed after the Zone APB alarm is raised.

Page 18
6.10 Disabling function
This function is implemented since the FW version 5.08.
The module disabling function can be set as the second input function. The logic of the
function is configurable.
The module behaves as described below when the disabling function is active:
User with access driven by a time schedule cannot run the door open function
User with access always granted is not affected by the disabling function
Remote door open function cannot be performed
Remote identification with ID is disabled for users with access driven by a time
schedule
The disabling status changes and disabled actions are logged in the events archive.
6.11 Online authorization
Since the FW version 5.11 the Online authorization of ID can be used in APS mini Plus
system. When the feature is used, the ID validity is resolved in connected PC. To be able
to use this authorization mode, the reader module has to be equipped with a MLO license.
7 Simplified access rights evaluation
The model of access rights contains time schedules and a table of holidays. A block
diagram for access right evaluation can be seen in Pic.7.
Pic. 7: Simplified access rights evaluation
VALID
UNKNOWN
ID FOUND
ACCESS DRIVEN
BY TIME SCHED.
ACCESS ALWAYS
GRANTED
HOLIDAY?
ACCESS GRANTED
FOR HOLIDAY
AND ACTUAL TIME
ACCESS GRANTED
FOR ACTUAL
DAY & TIME
READING ID
YES
N
O
YES
N
O
N
O
YES
INVALID
YES
N
O
N
O
YES
N
O
YES

Page 19
8 Useful links
Wiring diagrams: http://techfass.cz/diagrams-aps-mini-plus-en.html
Program equipment: http://techfass.cz/software-and-documentation-en.html
This manual suits for next models
3
Table of contents
Other TECH FASS RFID System manuals