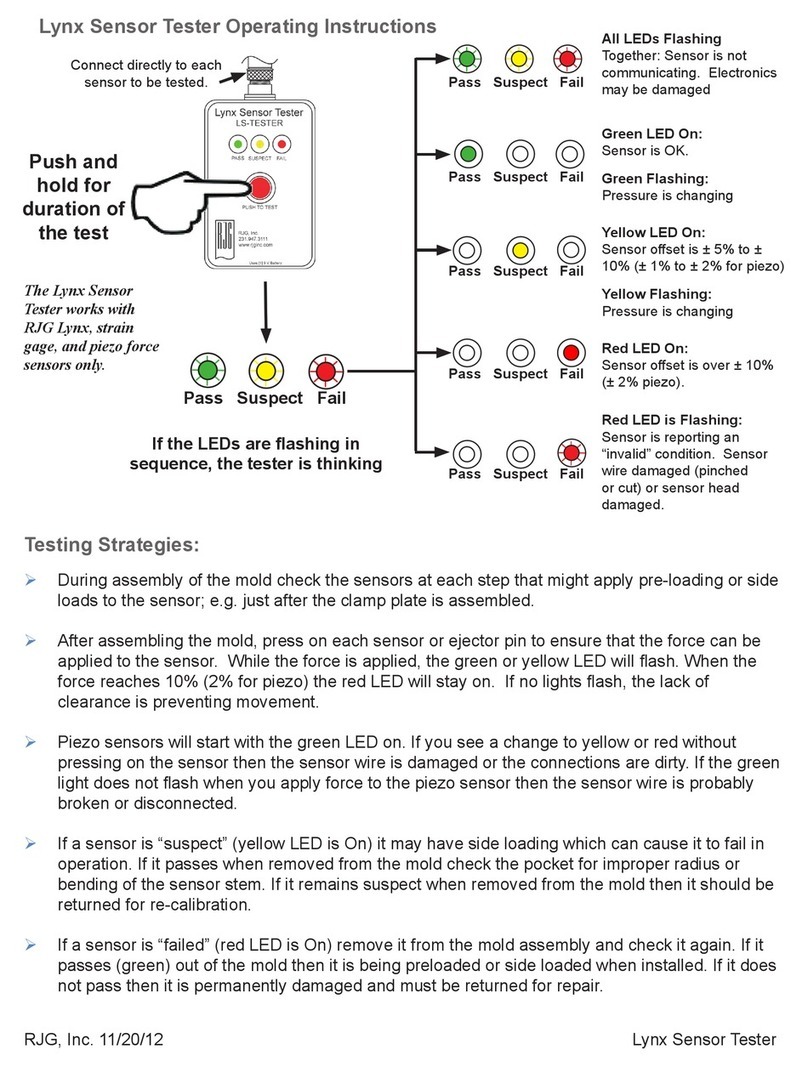
TECHNO-AC Success AG-309.15 N Manual


DEVELOPMENT, MANUFACTURING AND SUPPLY OF INSTRUMENTATION
2
www.technoac.com
Table of Contents
Introduction. ........................................... 3
1. Appearnce of Receiver .......................... 4
2. OPERATING MODES .............................. 5
2.1 “Route” mode ....................................5
2.2 «Graphic» mode .................................6
2.3 «Graphic+» mode ..............................6
2.4 «Minimum maximum» .........................7
2.5 Modes with graphic representation of
“Relative distance to the Utility”(R.dist.) .....7
2.5.1 “R.dis. Graph” mode ........................8
2.5.2 «MIN&R.Dist» mode .........................9
2.6 «2 frequencies» mode window .............9
3. Receiver menu description .................. 11
3.1. Receiver switching on and menu call . 11
3.2. The general view of the menu screen. 11
3.3. Menu parameter selection ...............11
4. Start of work ........................................ 16
5. Search of cables in the mode «Route» . 17
5.1. Cable location in the passive mode ...17
5.2. Search of a communication and
measurement of its burial depth .......18
5.3. Cable route location in the active
mode..............................................20
6. Search of communications in the mode
«Graphic» ............................................ 23
6.1. Setting of the receiver for work in the
«Graphic» mode ..............................23
6.2. «Hot» keys for work in the «Graphic»
mode .............................................25
6.3. Search of communications in the mode
«Graphic» ......................................26
7. Search of the utilities in the mode
« Graphic+» .......................................... 27
7.1. Setting of the receiver for work in
the «Graphic+» mode .......................27
7.2. Search of communications in the
mode «Graphic+» ............................27
8. Perfoming the cable location in the
mode «MIN & MAX» ............................. 29
9. Performing cable route location in the
mode «2 frequencies» ......................... 2 9
10. The work mode «Cable selection from
a bunch» .............................................. 32
10.1. The work with the receiver in the mode
«Selection of the cable from a bunch» ..32
10.2. «Hot» keys for the work in the mode
«Selection of the cable from the bunch» 34
11. Mode «Search of defects» using
external sensors .............................. 35
11.1. The work with the receiver in the mode
«Search for defects» ..................................35
11.2. «Hot» keys for work in the «Graphic»
mode with DODK and DKI ...............39
Appendix 1 ........................................... 40
Appendix 2. .......................................... 41
Appendix 3. .......................................... 45
Appendix 4. .......................................... 47
12. Transmitter AG-105 .......................... 49
12.1. Purpose of use and physical
configuration .................................49
12.2. Control and indication elements ......50
12.3. Ways of external commutation ........53
12.4. Accessories ..................................53
12.5. Design and function .......................54
12.6. Illustrative use information about
«Power supply monitoring»,
«Buttons functionality», «Symbols» ...55
12.7. «Multimeter» of the output
parameters ...................................55
12.8. Sound signals ...............................56
13. Working with the device .................... 56
13.1. Preparatory activities ................... 56
13.2. Settings ....................................... 59
13.3. Clips ........................................... 59
13.4. Internal transmitting inductor «In» . . . 60
13.5. External induction transmitting
antenna .........................................60
13.6. Transmitting induction “clamp” .......60
13.7. External power sources .................60
13.8. Electromagnetic compatibility .........60
13.9. Ingress protection rating ................60
14. Transmitter direct connection
to utility .................................................... 61
Appendix 5 ........................................... 62
Appendix 6 ........................................... 64

3
DEVELOPMENT, MANUFACTURING AND SUPPLY OF INSTRUMENTATION
www.technoac.com
Introduction
This operation manual contains a description of the
cable and pipe locator Success AG-
309.15N
, its working modes and the information necessary for its proper use The basic set
consists of the receiver and a tracing transmitter. The receiver can be used individually or with
the transmitter. The receiver works at the network frequencies 50(60) Hz, 100(120) Hz, and with
route locating transmitters at frequencies of 512Hz, 1024 Hz, 8192 Hz, 32768 Hz (33 kHz) .
AG-309.15N is used for:
- Detection of cables and metal pipelines underground up to 10 m;
- Direct digital measurement of the depth up to 10 m;
- Indication of the deviation from the communication axis in the mode “ROUTE”;
- Measurement of the current in the cable;
- Survey the ground before the excavation works;
- Distance of tracing from the place of transmitter connection is up to 3 km.
Operation with optional equipment:
- Sensor “NR -117”
- Sensors DKI and DODK.
Searching of cable faults at shorting of its armoring to the ground
- Searching of outer insulation defects of metal pipelines (water, gas) at trenchless laying.
- Inductive clamps CI-105/110
- Identification of the cable, the function “selection the cable from a bunch”
- Non-contact connection to the pipelines or to the cable lines
Intended use
- Power
- Public utilities
- Oil and gas industry
- Geodesy
- Communication
- Construction
- Other industries
Operation conditions
- Ambient temperature, °С ..........................................from -20С to +60
- Relative humidity, % .................................................up to 85 at t=35 °С
- Pressure, kPa,..........................................................84 to 106
- Device protection class............................................. IP 54
Receiver working principle
The cable and pipe locator’s Success AG-309.15N
working principle is based on the analysis
of the electromagnetic field, created by the presence of alternating current flowing through
underground services. The electrical signals induced in the receiver sensors are amplified,
filtered, processed by the processor and then displayed on the graphical display in the form of
the utility’s position line, linear scale, digital value of the signal level amplification coefficient,
distance to the communication axis, the value of the current flowing through it, the graphic of the
signal level change and other parameters.
Due to constant improvement of produced instruments, Technoac LLC reserves the right
to change schematics, software and user manuals, without degradation of performance
characteristics for its devices, without preliminary notification. Separate changes in user
manual content may be implemented after its reissue.
Up-to-date information about all produced instruments is published
on www.technoac.com

DEVELOPMENT, MANUFACTURING AND SUPPLY OF INSTRUMENTATION
4
www.technoac.com
1. Appearance, AP-019.1 receiver controls
AP-019.1 receiver is made in the solid cast IP54 body to the battery compartment the body
provides the protection IP68, the device can be splitted in three components: the face panel with
controls and displays, battery compartment and bottom part with the antenna block. There is
external sensor connection port on the back side of receiver.
A slot for connection of the
external sensors
A graphical display with
the lighting
Сonnection of external sensors.
Sensor DODK-117Sensor DKI-117
NR-117
Superimposed
frame
CI-105
Inductive clamps
Face panel, controls
A module for omnidirected
antenna
Battery compartment for
four batteries «type C»
Built-in sound transmitter
Six-button
keyboard
«Power» button (1)
Switching on/off the receiver
«Enter» button (6)
- calls out a menu,
- enters into the editing mode of the
selected menu option,
- exit for the editing mode saving
selected parameters.
Buttons «Up» (3), «Down» (4), «Right»
(5), «Left» (2).
- selection of the menu option (icon),
- selection or changing the parameter
inside the menu,
- operative change in the parameters
1 2
34
56

5
DEVELOPMENT, MANUFACTURING AND SUPPLY OF INSTRUMENTATION
www.technoac.com
2. OPERATING MODES
2.1 “Route” mode
The ball on the screen shows
the direction in which utility
is located.
When turning on the receiver for the first time, the device will begin in route mode and the service
information will appear. Route mode is the primary screen. Below, the indications are shown, which
are dependent on the operator position near the located utility.
The receiver can’t detect the utility. Position of utility axis shows,
where the utility is situated.
Depth and current measurement
enable automatically, If the utility
indicating line is aligned
with the axis of the receiver.
When above the utility, a solid line
will appear which is perpendicular
to the utility’s direction.
Battery charge level
Type of incoming signal
(continuous or pulse)
Frequency of
the enabled filter
Area where utility axis
visibility
Quick switch to
“graph” mode
Centre of receiver axis
Limits of utility position
where current and depth
measurements are available
Route Mode Description
Amplification coefficient
in dB
* The four-digit number “signal level” (0000 - 4100) represents the intensity of the electromagnetic
field, which is dependent on the filter frequency. The numeric value of the “signal level” becomes
greater when an operator approaches the source of electromagnetic signal of the chosen frequency.
The signal gains its maximum level when the receiver is placed strictly above the utility. The first number
of four-digit figure represents the order of the three-digit figure, generated by other figures: 0 –x1, 1- x10,
2 – x100, 3 – x1000, 4 - x10000. Dynamic range of changing signal levels is 1,000,000 times (120 dB).
Signal level
When approaching the utility,
a blurred line indicates its position.
Utility position indication line

DEVELOPMENT, MANUFACTURING AND SUPPLY OF INSTRUMENTATION
6
www.technoac.com
When the operator stands strictly
above the utility and the line indicating
the utility is positioned strictly in the
centre field between the two dotted
lines, an automatic depth and current
measurement is performed.
Route Mode and Depth Measurement
In graphic mode, the receiver screen is split into two segments. The upper segment indicates
utility position in 2D, and the lower segment is a moving graph of signal level change in time
according to a “maximum” method, where a maximum signal is reached when the receiver is
positioned strictly above the utility and signal decreases when the receiver is moved further away
from it. In this mode, current and depth measurement function is not available.
2.2 Graphic Mode
Signal level diagram. Every
time image is refreshed, the
graph moves 1 position left
and right position is filled
with new measurement
value
Digit representing current
(far right) value of the graph in
percentage terms. If there is
an incoming signal overload,
a special symbol will be visible
on the screen instead of the
digit “XX”. Indicated data is
incorrect in this case.
Utility position indication
line
2.3 Graphic+ Mode
This mode is different from the ordinary graphic mode. The main difference is that the utility
axis indication line represents only 50/60Hz utilities (power cables or utilities with induced signal)
which can be accidentally met during the operation on active frequencies.
Amplification
coefficient in dB
Graph scale setting
(buttons “up” and “down”
change scale of the graph)
Type of incoming signal
(continuous or pulse)
Frequency
of the enabled filter
Quick switch to route mode.
Press and hold “down” button
for 1 second in order to hide
the graph.
Indication of the frequency
of located energized cable
(can be 50 or 60 Hz)
Signal level moving
diagram
50/60 Hz Utility position
indication line
Frequency filter
(for diagram)
NOTE: When performing a depth
measurement, the receiver antenna
should be positioned perpendicularly
to the utility.
Buried depth
of the utility
Current
of the utility
Receiver and utility
axis are perfectly
aligned

7
DEVELOPMENT, MANUFACTURING AND SUPPLY OF INSTRUMENTATION
www.technoac.com
2.4 “Minimum maximum”
In “MIN & MAX” mode, the receiver screen is split into two segments. The upper segment is a
moving diagram which represents signal level changes according to the “minimum” method
– it means that the signal will be minimal when the receiver is positioned strictly over the utility. If
the receiver is moved aside, the signal level will increase.
The lower segment represents the “maximum” method diagram – the signal will be maximal
if the receiver is positioned strictly over the utility, and it will decrease if the device is moved further
away.
This mode does not allow depth and current measurements.
Every time image is refreshed,
the graph moves 1 position left
and far right position is filled with
new measurement value
Digit, representing
current (far right) value
of the graph in percentage
terms
Battery charge level
Amplification coefficient in dB
Quick change of diagram scale
Indication of lower
sensor operation (Filter,
Broadband, Radio)
Quick change of lower sensor
operation mode
Type of incoming
signal
(continuous or pulse)
Frequency filter
2.5 Modes with Graphic Representation of “Relative distance to the
Utility” (R.dist.)
In cases given above, both utilities lay beside each other. However, in this case “MIN & MAX” mode
does not allow the user to measure the depth of these cables. For this reason, it is better to use
graphic modes with indication of the “relative distance to the utility”.
While approaching the utility, the value of “relative distance to the utility” changes in the way
described on pictures, shown below:
Parameter value
«R.dist.», indicated
by «∞» symbol
Zones of utility presence
Utilites
Parameter value “R.dist.”
is equal to burial depth
of the utility

DEVELOPMENT, MANUFACTURING AND SUPPLY OF INSTRUMENTATION
8
www.technoac.com
Utility
This parameter can have values from “0.01” to “30.00”, “>30” and “∞”. Value “∞” are indicated
when the receiver is positioned aside from the utility or when the utility is positioned above the receiver
(an example being when there are overhead voltage lines around). The parameter “relative distance
to the utility” will have its minimum value when the receiver is positioned directly above the utility
axis. In this case, this value is equal to the real burial depth of the utility.
Minimum value of the
parameter - 2.40 is equal to
real burial depth of utility.
The receiver has two modes with indication of “relative distance to the utility”: “R.dis. Graph” is
used when the “relative distance to the utility” graph and utility route are indicated simultaneously,
whilst the “MIN&R.Dist mode“ is used when screen of the receiver indicates 2 graphs (minimal
signal and “relative distance to the utility”).
2.5.1 “R.dis. Graph” mode
This mode is the same as “Graph” mode. The screen is split in two parts, an upper display
and a lower display.
• Upper Part: Route axis indication
• Lower Part: “relative distance to the utility” graph
Indication of “R.dis. Graph”:
Hint: “Hide”– return to
“Route” mode by pressing
button “<” for 1 second
Hint: – change of graph
scale in 2\4 and 8 times by
pressing “up” and “down”
arrows
Graph of changing
“Relative distance to the
utility” in real time

9
DEVELOPMENT, MANUFACTURING AND SUPPLY OF INSTRUMENTATION
www.technoac.com
When two utilities are buried close to each other while moving the receiver straight across the
utility axis in “R dist” mode, an operator will be able to see the indication shown below:
Minimal values of “relative distance to the utility” indicate the presence of the utility with some
fault because in the case of multiple utilities laying nearby, minimum signal point may move
due to coinfluence of the signals.
You can enable the “R.dis.Graph” mode from “Route” mode by pressing the “>” button or
by switching it in the “Modes” section of the receiver’s main menu.
2.5.2 “MIN & R.Dist” Mode
In this mode the screen is split in two parts. Upper part: Minimal signal graph, lower part: “relative
distance to the utility” graph in real time.
Digit indicates the minimum
signal level of far right point of the
display
Digit indicates relative distance
value of far right part of the
display
“R.dist” value indicated by
“∞” icon
Hint – change of graph
scale in 2, 4 and 8 times
by pressing “up” and
“down” arrows
You can enable “MIN & R.Dist” mode only from “Modes” section of main menu.
2.6 “2 Frequencies” Mode Window
In the “2 frequencies” mode, the cable condition and pipeline protection diagnostic is performed
using the external generator. When conducting works on cable route location, it is possible
to select the communication located as “my own” and perform a route location on it.
Amplification coefficient in dB
The sum of frequency
components (A8+A1)
Frequency components
amplitude modulation
(A8/A1)
Frequency components change
of phase difference
Signal direction
(straight / reverse)
Signal level on 1024
and 8192 Hz
Quick reset of readings
and “reference” to the
utility
Battery charge level

DEVELOPMENT, MANUFACTURING AND SUPPLY OF INSTRUMENTATION
10
www.technoac.com
IMPORTANT NOTE:
Modes are split in two sets: basic and extended. In basic set, only 3 modes are available:
“Route”,“Graph” and“R.dis.graph”. All modes are available in extended set: “Route”,
“Graph”, “Graph+”, “MIN & MAX”, “2 Frequency”, “R.dis.graph” and “MIN&R.dist.”.
You can switch between two sets in menu: Settings –> Modes select.
Dynamic Overload Protection
There is protection in the receiver which prevents
the influence of dynamic overload. When the receiver is
operated in the area with tense electromagnetic fields,
this function automatically reduces the incoming signal
and prevents the electronics of the receiver from being
damaged and notifies the user with a special message on
the screen.

11
DEVELOPMENT, MANUFACTURING AND SUPPLY OF INSTRUMENTATION
www.technoac.com
To open
the menu
press
«Enter».
Menu option
selection is
performed with
buttons
«Up», «Down»,
«Right», «Left».
The menu will appear on the screen. Active "icon" is flashing and
highlighted by dotted line
to change or
view the menu
item
The changed value
is immediately
applied.
To exit the menu to the
general menu or
transfer to the set mode
with the closing of the
menu, you should press
the button «Enter».
If you wait for several
seconds, menu icons will
disappear.
In the upper part of the
indicator the parameter editing
panel will open.
If you don’t press any buttons for a period of time, the menu will disappear automatically.
The length os this period is set in the corresponding menu option (see Table 1. p.6)
3. Receiver menu description
3.1 Receiver switching on and menu call
To switch on the
receiver press
the button
«Power»
Press «Enter»
button to
open the
Menu
3.2 The general view of the menu screen
menu option name
brief menu option
description
3.3 Menu parameter selection
The selected menu
option is highlighted with
the dotted line, flashes
with light/dark

DEVELOPMENT, MANUFACTURING AND SUPPLY OF INSTRUMENTATION
12
www.technoac.com
Thirteen items of menu contain parameters of setting, which are opened in the panel located in the
upper part of the indicator.
№
Item
of the
menu Display image Parameter description
1
Filter The working frequency of the receiver
It is selected from the set: 50(60) Hz,
100(120) Hz, 512 Hz, 1024 Hz, 8192 Hz
32768 Hz.
2
Gain
The amplification coefficient of the scaling
amplifier can be changed from 0 dB to 80 dB
with 2 dB step.
The optimum coefficient of amplification can
be selected:
- manually,
-semiautomatically (by a command),
-automatically depending on the regime of
the analysis and signal representation.
Table 1
3
Signal The type of signal received can be
«Continuous» or «Impulse».
4
Advanced
bottom
sensor
setting
This option has several settings affecting
the efficiency og bottom sensor.
- «Filter» (narrow-band filter)
- «WB» (wide band, sensor receives all
frequencies below 8kHz).
- «Radio» (sensor receives all frequencies
over 8kHz).
‘Filter’ setting is used only in ‘Route mode’,
other settings are used in ‘Graphic’ mode.

13
DEVELOPMENT, MANUFACTURING AND SUPPLY OF INSTRUMENTATION
www.technoac.com
5
Base
Mode Set of modes:
- «Route» (2D display of the location of the
route cable;
6
Base
Mode
- «Graph» (visually represents the changes
of signal level of surveyed cable);
7
Аdvanced
Mode
Advanced mode:
- «Graph+» (this mode combines two previous
modes and allows to locate two cables
simultaneously: one on 50Hz, and the other on
freqency set by transmitter.z);

DEVELOPMENT, MANUFACTURING AND SUPPLY OF INSTRUMENTATION
14
www.technoac.com
8
Advanced
Modes
Advanced mode:
- «MIN&MAX» (graph representation of
minimum and maximum signals)
9
Advanced
Modes
Advanced mode:
«2 frequency» (simultaneous operation in two
frequencies, also know as frend-or-foe mode).
10
Sound
Switching on / switching off of sound
notifications the created by the built-in speaker.
11
Settings
This menu is opened in the main field of an
indicator
Language <Russian/English>
Locale of the device
System of units <Meter/Foot>
Measurement system: metrical or imperial
Network
frequency <Europe/USA>
The network frequency for passive search:
«Europe» (50 и 100 Hz) / «USA» (60 and 120 Hz).

15
DEVELOPMENT, MANUFACTURING AND SUPPLY OF INSTRUMENTATION
www.technoac.com
12
Settings
Sound of keys <ON/OFF>
Disables keys sound
Delay of menu <1 sec/2 sec/ 3 sec/ 4 sec/5
sec>
Time-out before closing the menu when no
buttons are pressed.
• Popup hints <ON/OFF>
Disables pop-ups with useful hints.
• Reset
osettings <Reset>
Resets the receiver to factory settings

DEVELOPMENT, MANUFACTURING AND SUPPLY OF INSTRUMENTATION
16
www.technoac.com
With factory settings enabled, you can perform the cable location with network
frequency 50 Hz without the transmitter.
4. Start of work
If alkaline batteries are used - Before start of work, you should install the batteries into the
corresponding compartment of the receiver in the following sequence:
Note
To switch on the receiver, press the “Power” button
Receiver switching
A description of factory settings can be found in the
“settings” menu. You can go back to factory settings by
selecting the “reset settings” option.
Install the batteries,
observing the polarity
Unsnap Battery
compartment. Pull out the
ring on the receiver handle.
Install four new elements into
the battery compartment of the
device, minding polarity.
Install the battery compartment
into the body until it snaps.
The indication of the Firmware version, manufacturer logo and
device name will appear on the screen.
Then, the receiver will automatically enter into “Route” mode
in 5 seconds. When first switching, the factory settings are set by
default . The filter frequency is 50 Hz.
External Power
With the help of the mini-USB cable (included), the operator can connect to external power
sources with 4-7V voltage. For example, a power bank (supplied separately).
The external power source can be placed under overclothes of the operator. It will allow an
extension of the battery life in low temperature conditions. External power can be used with
inserted batteries or without them.
NOTE: Power Bank should be placed as far as possible from the antenna block of the receiver
in order to evade interference.

17
DEVELOPMENT, MANUFACTURING AND SUPPLY OF INSTRUMENTATION
www.technoac.com
5. Search of Utilities in “Route” mode
Route mode is the main mode for route location of various utilities (cables & pipelines) at all
supported frequencies, both in “passive” cable route location and at the “active” (with the use of
the route locating generator). In passive mode, the cable location is carried out at frequencies
of 50(60) and 100Hz, while cable location in active mode is performed at frequencies of -512, 1024,
8192 and 33Hz.
5.1 Cable Location in Passive Mode
This mode is used to search and locate the route of power cables under voltage with a frequency
of 50(60) Hz and other communications with the induced signal in frequency 50(60) Hz. The
external generator is not used.
Basic Receiver Functions
• Location and tracing of underground utilities with depth measurement in “Route” mode.
• Location and tracing of utilities in “Graph”, “Graph+”, and “MIN & MAX” modes.
• Tracing of non-metal utilities in “Sonde” mode.
• Saving of coordinates and parameters of located points.
• Operation in “2 Frequency” mode (fault location and detection of signal direction).
• Selection of the cable from a bunch with inductive clamp.
Receiver Setting for Operation in “Route” Mode
To enable “Route” mode, please, do the following:
Turn
on the
receiver
Press
“enter”
button
in order
to open
main
menu
Press
“enter”
to enter
the mode
change
menu
Choose
“Modes”
icon
buttons
Choose “Route”
buttons
Press
“enter”
button in
order to
open main
menu
Press “enter”
to enter the
mode change
menu
Then go to
“Filter” menu
buttons
Select 50(60)
Hz frequency
buttons
When filter 50(60)Hz is chosen, the type of incoming signal is automatically set to
continuous.

DEVELOPMENT, MANUFACTURING AND SUPPLY OF INSTRUMENTATION
18
www.technoac.com
5.2 Search of a Communication and Measurement of its Burial Depth
1. Come to the supposed place of the utility under the voltage or induced voltage in frequency
50(60)Hz.
2. If the utility is far from the operator, you will see on the screen:
3. When moving towards the supposed place of the utility location, the “ball” will appear
on the screen. It shows the presence of a utility and that it is a significant distance from the
operator.
4. The “ball” position shows the direction of the utility relative to the operator.
communication
communication
utility
utility
utility
5. When the operator moves closer to the utility, the axis will move to the centre of the
circle. This means that the operator is standing directly over the utility
utility

19
DEVELOPMENT, MANUFACTURING AND SUPPLY OF INSTRUMENTATION
www.technoac.com
Power cables most frequently lay at a depth of 60-80 cm, allowing to differ them from
pipelines. It is possible that a cable lays in one channel with a pipeline, when the burial
depth can significantly exceed 1 metre.
If the communication axis cannot be located exactly in the limited area, and the periodical
jumps are happening from one border to the other, it indicates the presence of several
cables under voltage with the 50 Hz frequency. You can specify number and position
of the cables in “Graphic” mode.
Note
In a case when the signal is significantly distorted, the receiver automatically shows
the corresponding notification, offering the option of switching to “Graph” mode.
The receiver switches the
“Graphic” mode
The dialogue box appears “Should
a message about the field
distorted be further displayed?
Attention:
Before measuring the depth of the utility, make sure that your device is positioned perpendicularly to the
utility. Even a slight deviation from vertical position can influence the precision of the depth measurement.
7. Further you should rotate
the device, until the utility axis
is aligned along the receiver
axis. In this position, given
‘f’ (the current in the cable)
is sufficient, the window will
appear displaying its burial
depth and current Now, the
operator stands alongside the
utility.
In this position, it is possible
to move forward and trace
a whole cable).
The measurement of the burial depth of utility
indications of the burial
depth
indications of the
current
Cable

DEVELOPMENT, MANUFACTURING AND SUPPLY OF INSTRUMENTATION
20
www.technoac.com
The filter on the receiver is set manually in accordance with the selected generator frequency.
When locating the cable route in the conditions of the large number of surrounding utilities,
you should set the frequency to 512 Hz.
When it is impossible to ground the connection, you should select higher frequencies. To
perform the cable location with damage detection, you should select a higher frequency.
5.3 Cable Route Location in the Active Mode
This mode is used for the location and tracing of electro-conducting underground utilities (power
cables, optic fibre cables with metal armouring and pipelines) by using the signal transmitter.
Tracing is possible at the following frequencies: 512, 1024, 8192 and 32768 Hz.
Note
Transmitter Connection
Contact mode
The generator output is connected
directly to the communication
Contactless method
using the transmitting antenna
Note
transmitter
communication
Contactless method
using the induction clamps
communication
transmitting antenna
Inductive clamps
communication
transmitter
transmitter
Contactless method
Connection with internal inductive
antenna of the transmitter
Other manuals for Success AG-309.15 N
1
Table of contents
Other TECHNO-AC Test Equipment manuals
Popular Test Equipment manuals by other brands

Redtech
Redtech TRAILERteck T05 user manual

Venmar
Venmar AVS Constructo 1.0 HRV user guide

Test Instrument Solutions
Test Instrument Solutions SafetyPAT operating manual

Hanna Instruments
Hanna Instruments HI 38078 instruction manual

Kistler
Kistler 5495C Series instruction manual

Waygate Technologies
Waygate Technologies DM5E Basic quick start guide

StoneL
StoneL DeviceNet CK464002A manual

Seica
Seica RAPID 220 Site preparation guide

Kingfisher
Kingfisher KI7400 Series Training manual
Kurth Electronic
Kurth Electronic CCTS-03 operating manual

SMART
SMART KANAAD SBT XTREME 3G Series user manual

Agilent Technologies
Agilent Technologies BERT Serial Getting started