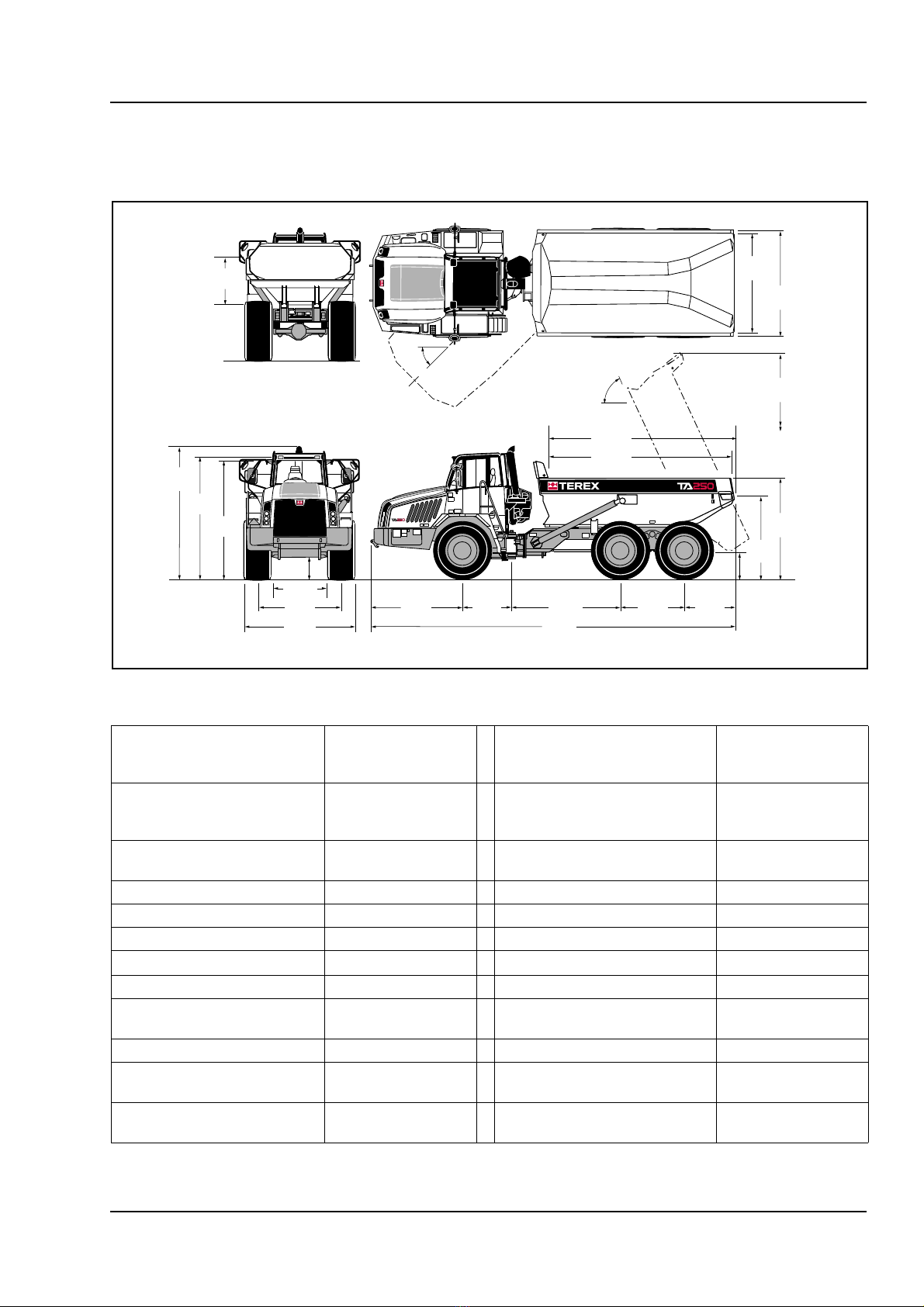
GENERAL INFORMATION - Technical Data TA250
MM 2738 06-12 3
Section 000-0000
Inflation Pressures (Continental):
Front Rear
23.5 R25 5.0 bar (73 lbf/in²) 5.0 bar (73 lbf/in²)
Note: Tyre pressures should be regarded as nominal
only. It is recommended that for tyres both
listed and unlisted, the user should consult the
tyre manufacturer and evaluate all job
conditions in order to make the proper
selection.
HYDRAULIC SYSTEM
The braking, steering and body hoist hydraulic
systems are controlled by a manifold block mounted
on the frame. Systems are supplied with oil from a
common tank by the main hydraulic pump, driven
from the power takeoff on transmission. System
components are protected by full flow filtration on the
return line.
Pump:
Type..................................................................Piston
Capacity at 2 100 rev/min...........................4.9 litres/s
(77.4 US gal/min.)
Brakes
The machine has a full hydraulic braking system with
enclosed, oil-immersed multiple discs on each wheel.
Independent circuits serve the front and rear brake
systems. Warning lights and audible alarm indicate
low brake system pressure. The brake system
conforms to ISO 3450, SAE J1473.
Actuating Pressure........................60 bar (870 lbf/in²)
Braking surface........................22 000 mm² (34.1 in²)
Parking: Spring-applied, hydraulic-released disc on
the rear driveline.
Emergency: There is automatic application of drive
line brake should pressure fall in the
main brake hydraulic system. Service
brakes may also be applied using the
parking-emergency brake control.
Retardation: Standard exhaust brake and standard
hydraulic retarder integral with
transmission.
Steering
Hydrostatic power steering is provided by two single-
stage, double-acting, cushioned steering cylinders.
Emergency steering pressure is provided by a
ground driven pump mounted on the rear of the
transmission. An audible alarm and warning light
illuminates should the emergency system activate.
Conforms to ISO 5010, SAE J53.
System Pressure......................241 bar (3 500 lbf/in²)
Steering Angle to either side.................................45°
Lock to Lock Turns, steering wheel.........................4
Body Hoist
Two single-stage, double-acting hoist rams,
cushioned at both ends of stroke. Electro servo
assisted hoist control.
SystemPressure.......................220 bar (3 200 lbf/in²)
Control Valve...............Pilot Operated, Closed Centre
Body Raise Time (loaded)................................12 sec
Body Lower Time (power down)......................7.5 sec
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM
Type.....................................24 volt, Negative Ground
Battery.................................Two,12 Volt, 143 Ah each
Accessories.....................................................24 Volt
Alternator......................................................100 Amp
BODY
The body is an all welded construction, fabricated
from high hardness (min. 360 BHN) 1 000 MPa (145
000 lbf/in²) yield strength steel. A 25° tail chute angle
provides good load retention without the tailgate.
Plate Thicknesses:
Floor and Tailchute.............................14 mm (0.55 in)
Sides..................................................12 mm (0.47 in)
Front.....................................................8 mm (0.31 in)
Volume:
Struck (SAE)...................................12.5 m³ (16.4 yd³)
Heaped 2:1 (SAE)..........................15.5 m³ (20.3 yd³)
SERVICE CAPACITIES
Fuel tank....................................370 litres (98 US gal)
Hydraulic System...................256 litres (67.6 US gal)
Engine Crankcase and filters....45 litres (11.9 US gal)
Cooling System.....................48.8 litres (12.9 US gal)
Transmission (including cooler)......................49 litres
(12.9 US gal)
Transmission Cooler..............8.25 litres (2.18 US gal)
Differential - Front, IFS................21 litres (5.5 US gal)
Differentials
Front [not IFS] and Rear (each)..28 litres (7.4 US gal)
Differential - Centre.....................23 litres (6.0 US gal)
Planetaries (Front)......................11 litres (3.0 US gal)
Planetaries - Centre&Rear........7.5 litres (2.0 US gal)
Hand Pump Tank..........................1 litre (0.26 US gal)
Air Conditioning Compressor.....................0.125 litres
(0.033 US gal)
DEF tank capacity...................52 litres (13.74 US gal)
Find manuals at https://best-manuals.com