Texas Instruments LOG200EVM User manual
Other Texas Instruments Motherboard manuals
Texas Instruments
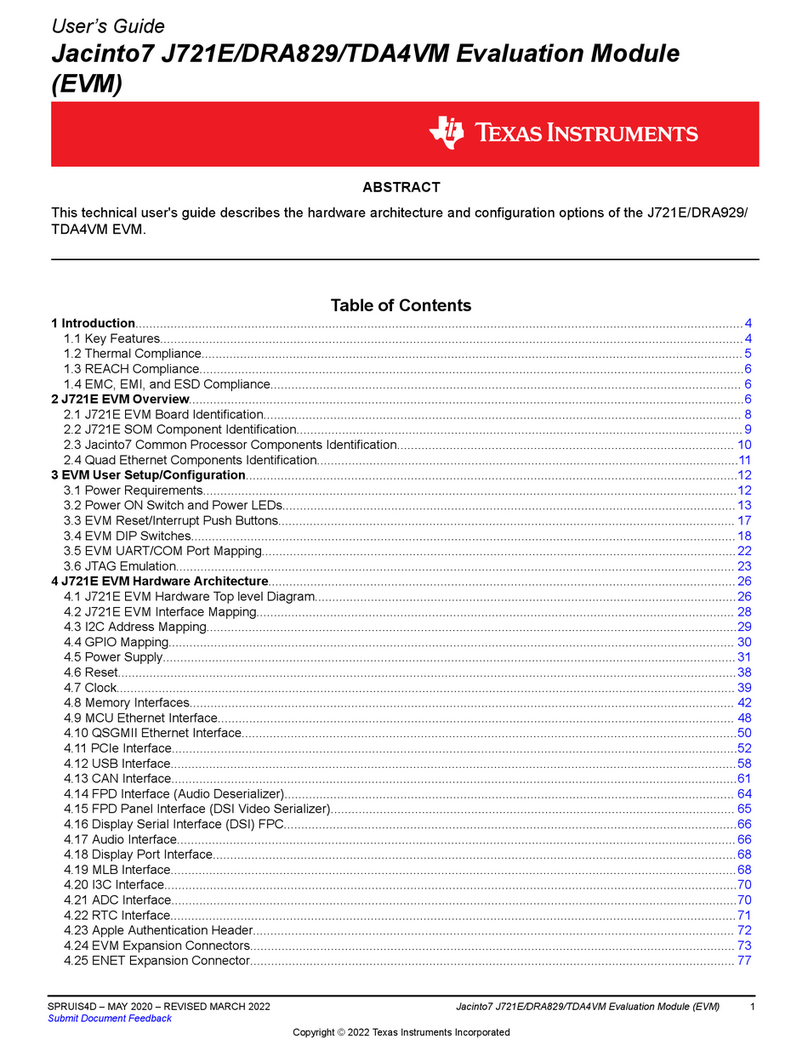
Texas Instruments LM10507 User manual
Texas Instruments
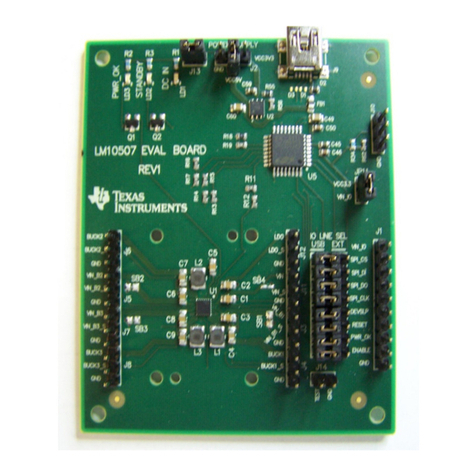
Texas Instruments DACx760EMC-EVM User manual

Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments PCMx140Q1EVM-PDK User manual

Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments AN-1502 LP5526 User manual

Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments PGA411-Q1 EVM User manual

Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments SCAU020 User manual
Texas Instruments
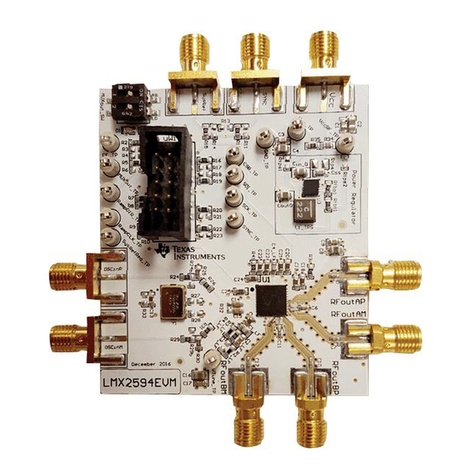
Texas Instruments LMX2594 User manual

Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments AM62-SIP SK Series User manual

Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments bq24725 User manual
Texas Instruments
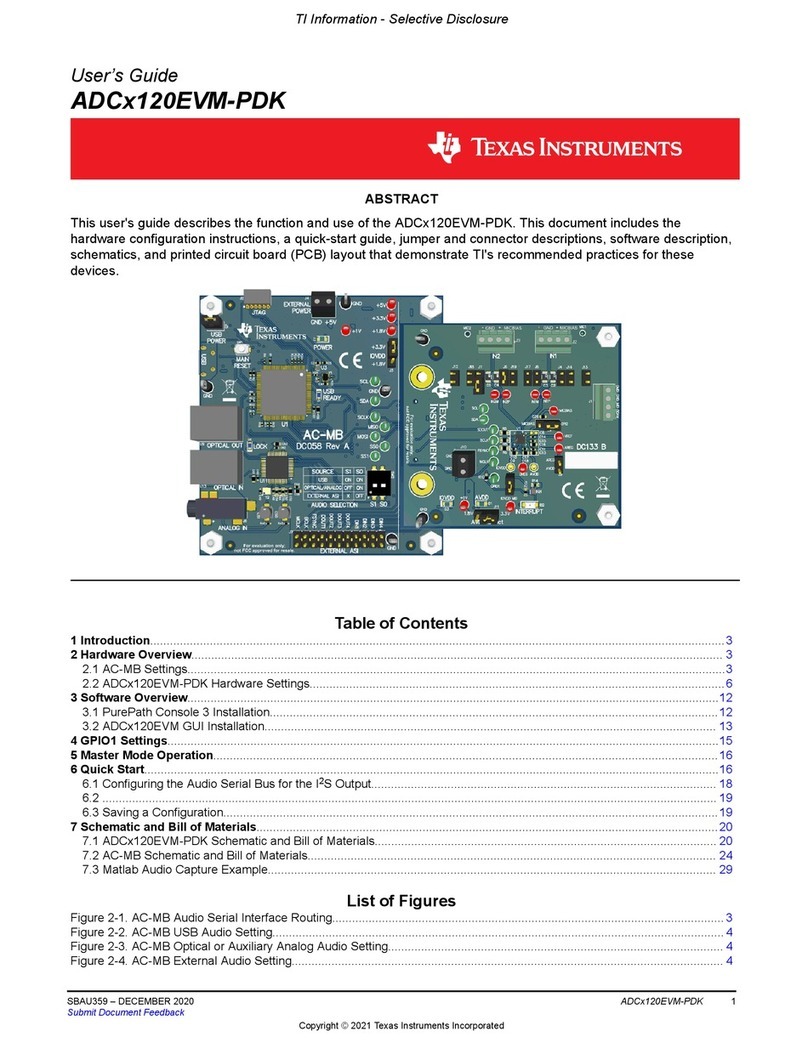
Texas Instruments ADC 120EVM-PDK Series User manual

Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments TPS543B22EVM User manual

Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments Tiva C Series User manual

Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments LP2951EVM User manual

Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments TUSB1064RNQ User manual

Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments TPS62065EVM User manual

Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments INA296EVM User manual
Texas Instruments
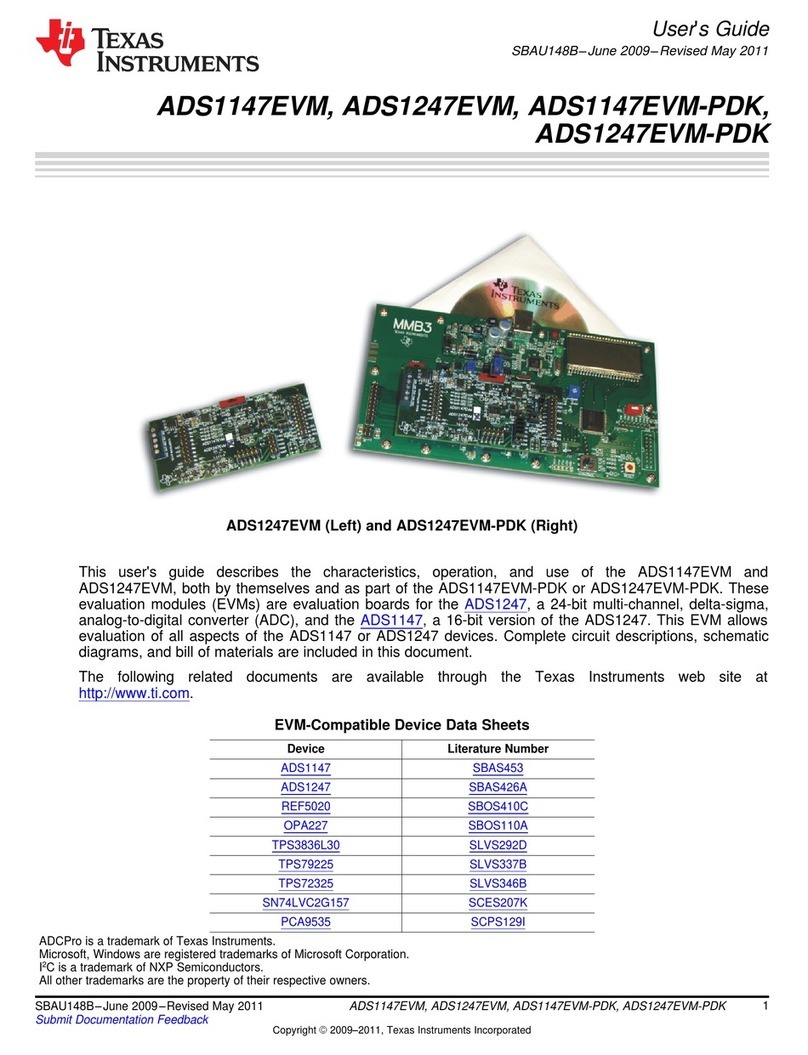
Texas Instruments ADS1147EVM User manual
Texas Instruments
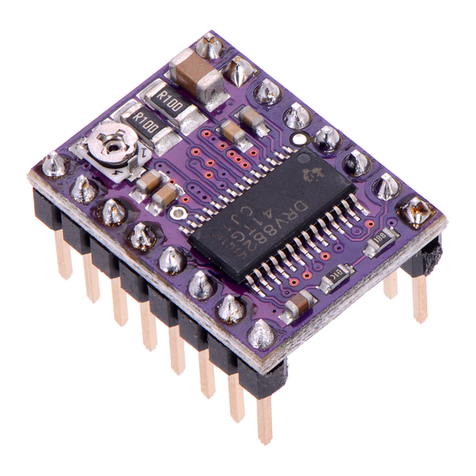
Texas Instruments DRV88 Series User manual

Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments ADS62PXXEVM User manual

Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments TPA6020A2 User manual