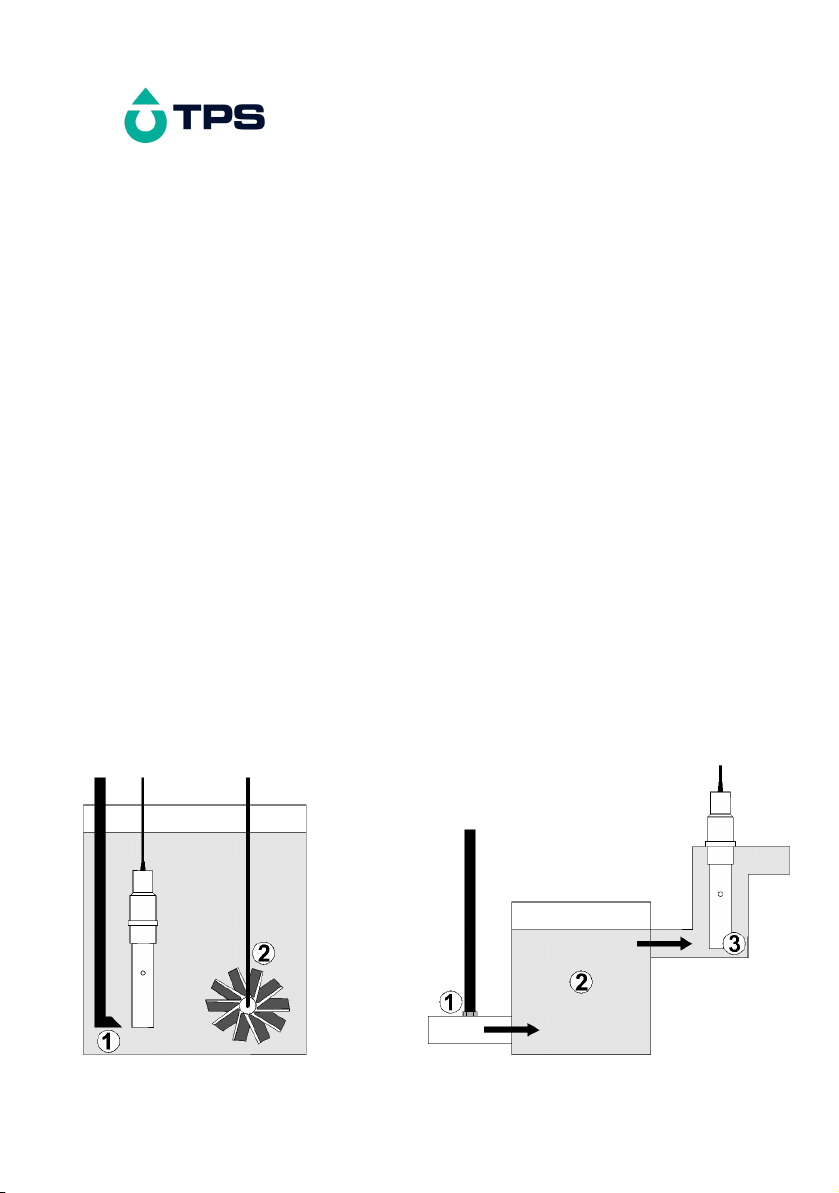
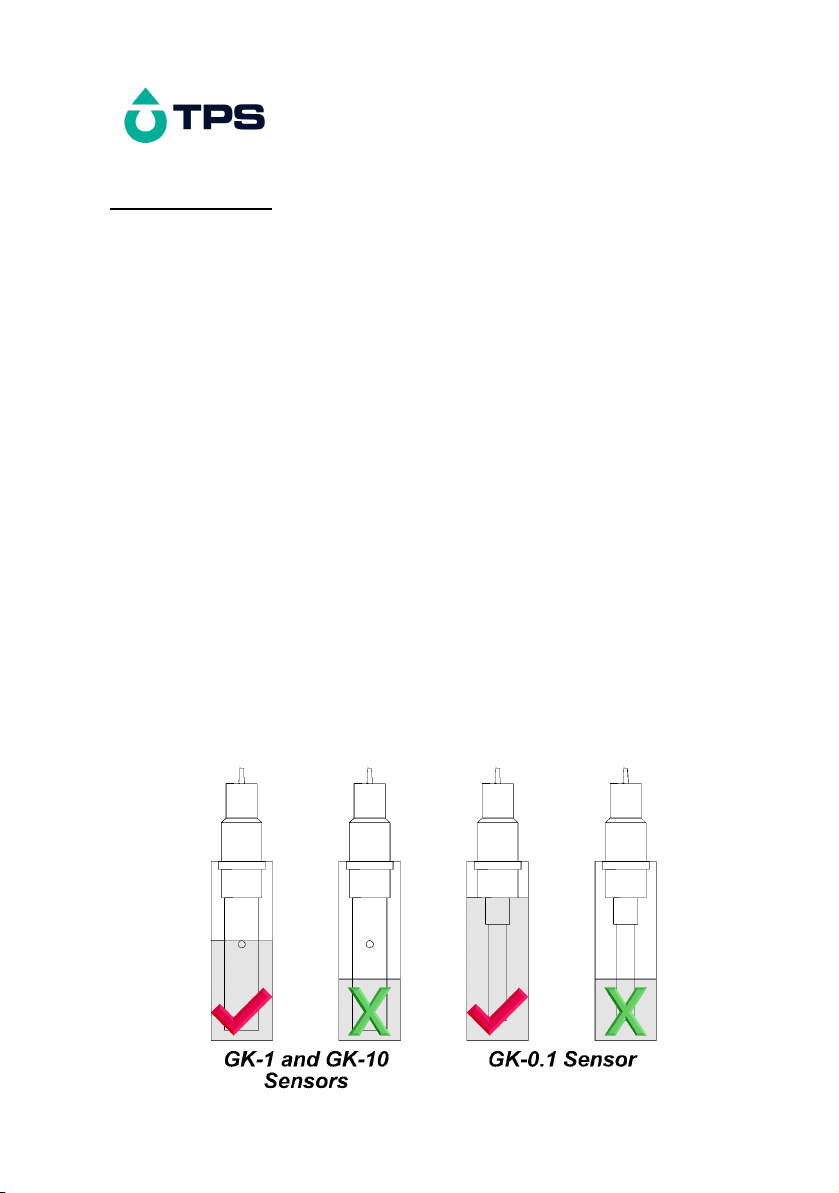
Congratulations !
Your new microCHEM-Sal transmitter module is a simple, lower power device
for interfacing a Salinity/TDS sensor with datalogging and process control
equipment. The industry standard 0 to 1 V DC and 0 to 5 V DC outputs ensure
that the microCHEM-Sal is compatible with most such devices.
The microCHEM-Sal is a breeze to operate. This manual has been designed to
help you get started, and also contains some handy application tips. If at any
stage you require assistance, please contact either your local TPS representative
or the TPS factory in Brisbane.
The manual is divided into the following sections:
1. Table of Contents
Each major section of the handbook is clearly listed. Sub-sections have also
been included to enable you to find the information you need at a glance.
1. Introduction
The introduction has a diagram and explanation of the display and controls
of the microCHEM-Sal. It also contains a full listing of all of the items that
you should have received with the unit. Please take the time to read this
section, as it explains some of items that are mentioned in subsequent
sections.
1. Main Section
The main section of the handbook provides complete details of the
microCHEM-Sal, including operating modes, calibration, troubleshooting,
specifications, and warranty terms.
1. Appendices
Appendices containing background information and application notes are
provided at the back of this manual.